Process for producing electrophoresis display device
A manufacturing method and electro-display technology, which can be applied to instruments, nonlinear optics, optics, etc., can solve the problems of uniformly setting sealing materials, narrowing the selection range of sealing film materials, and limiting the specific gravity of sealing materials, and achieve the effect of good adhesion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
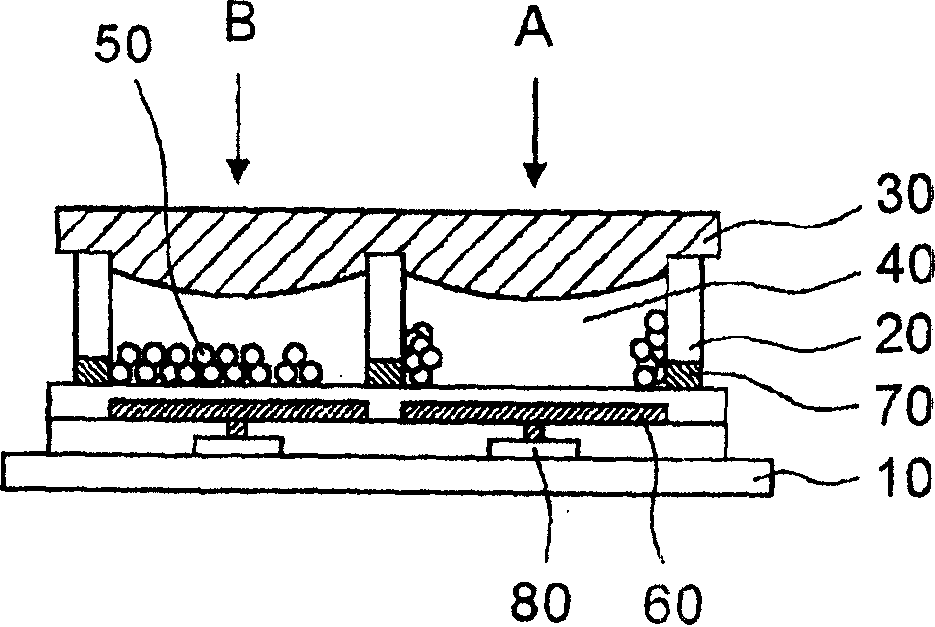
[0165] preparation figure 1 The electric display device shown in.
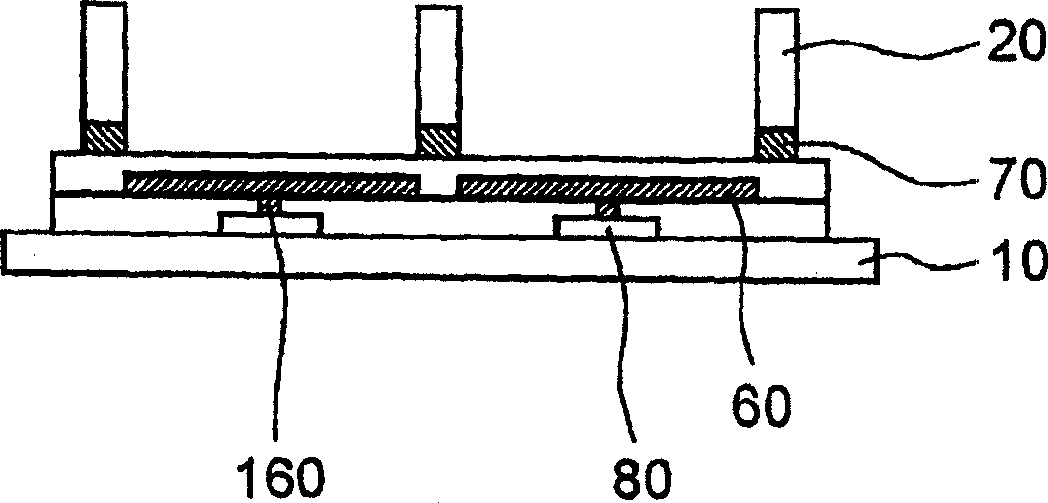
[0166]The resulting display device had 200 x 600 pixels, each pixel having a size of 240 μm x 80 μm. Each pixel is surrounded by a partition wall 20 having a width of 8 μm and a height of 28 μm. The first electrode 60 is disposed between adjacent partition walls 20 and connected to the switching device 80 . The second electrode 70 is provided between the partition wall 20 and the substrate 10 . The second electrode 70 is an electrode common to all pixels.
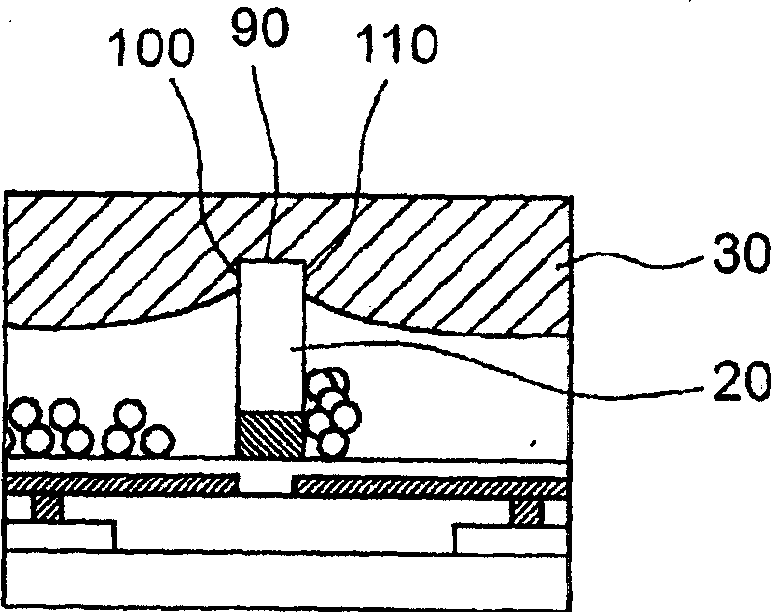
[0167] will refer to image 3 - 5 and 10 describe the specific manufacturing method of the display device in this embodiment.
[0168] The switching device 80 is formed on a stainless steel substrate 10 of 0.1 mm thick. The substrate is then coated with an insulating layer of acrylic resin, and the insulating layer is provided with contact holes. After that, on the insulating layer, a resist pattern for scattering incident light is formed, and an alu...
Embodiment 2
[0178] An electric display device was fabricated in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the supporting member 130 was removed from the sealing film 30 and the sealing film 30 was exposed to ambient air.
[0179] When the display device was driven in the same manner as in Embodiment 1, the display device exhibited the same display state change as in Embodiment 1. When the display device was driven, it was not observed that the electrophoretic particles 50 moved so as to overflow the partition walls 20 . In addition, peeling of the sealing film 30 from the partition wall 20 side and volatilization of the dispersion medium 40 were not observed, proving that the sealing film 30 and the partition wall 20 were adhered to each other.
[0180] Thus, although the display device was bent backward and forward, the phenomenon that the electrophoretic particles 50 moved so as to overflow the partition walls was not observed. In addition, the driving of the display device was evalu...
Embodiment 3
[0182] An electric display device was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the sealing film matrix was changed to polyethylene glycol methacrylate (trade name: "PE200"; specific gravity: not less than 1; manufactured by Nippon Yushi K.K.). Methacrylate is insoluble in Isoper H and has a specific gravity greater than that of Isoper H.
[0183] When the resulting display device was driven in the same manner as in Example 1, the same display state change as in Example 1 was observed. Even if the display device was driven continuously, it was not observed that the electrophoretic particles 50 moved so as to overflow the partition walls 20 . In addition, the sealing film 30 was not peeled off from the partition wall side.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com