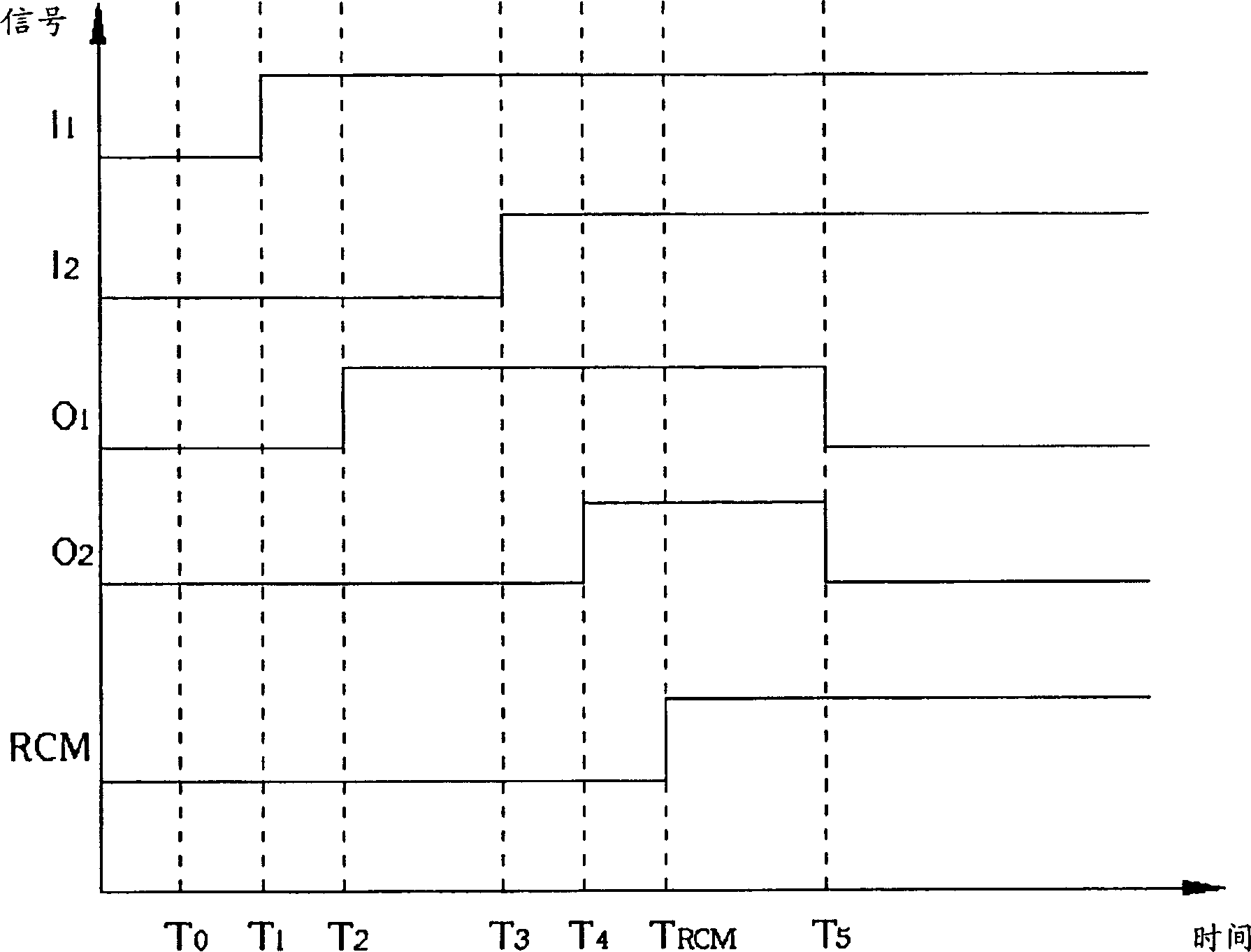Digital phase-frequency identification circuit
A technology of phase frequency and circuit identification, which is applied to circuits and electrical components that oscillate independently of each other, and can solve problems such as excessive jitter.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
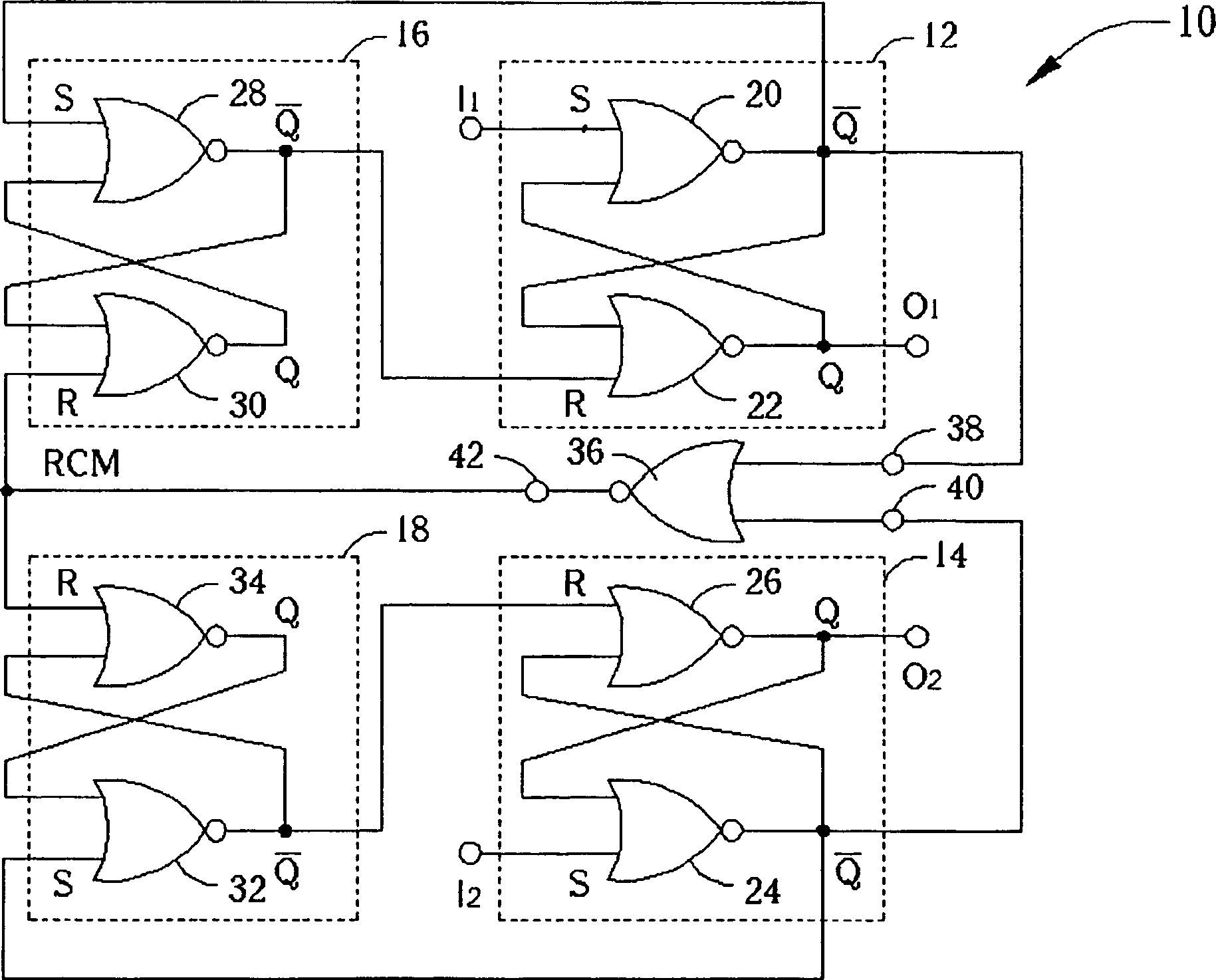
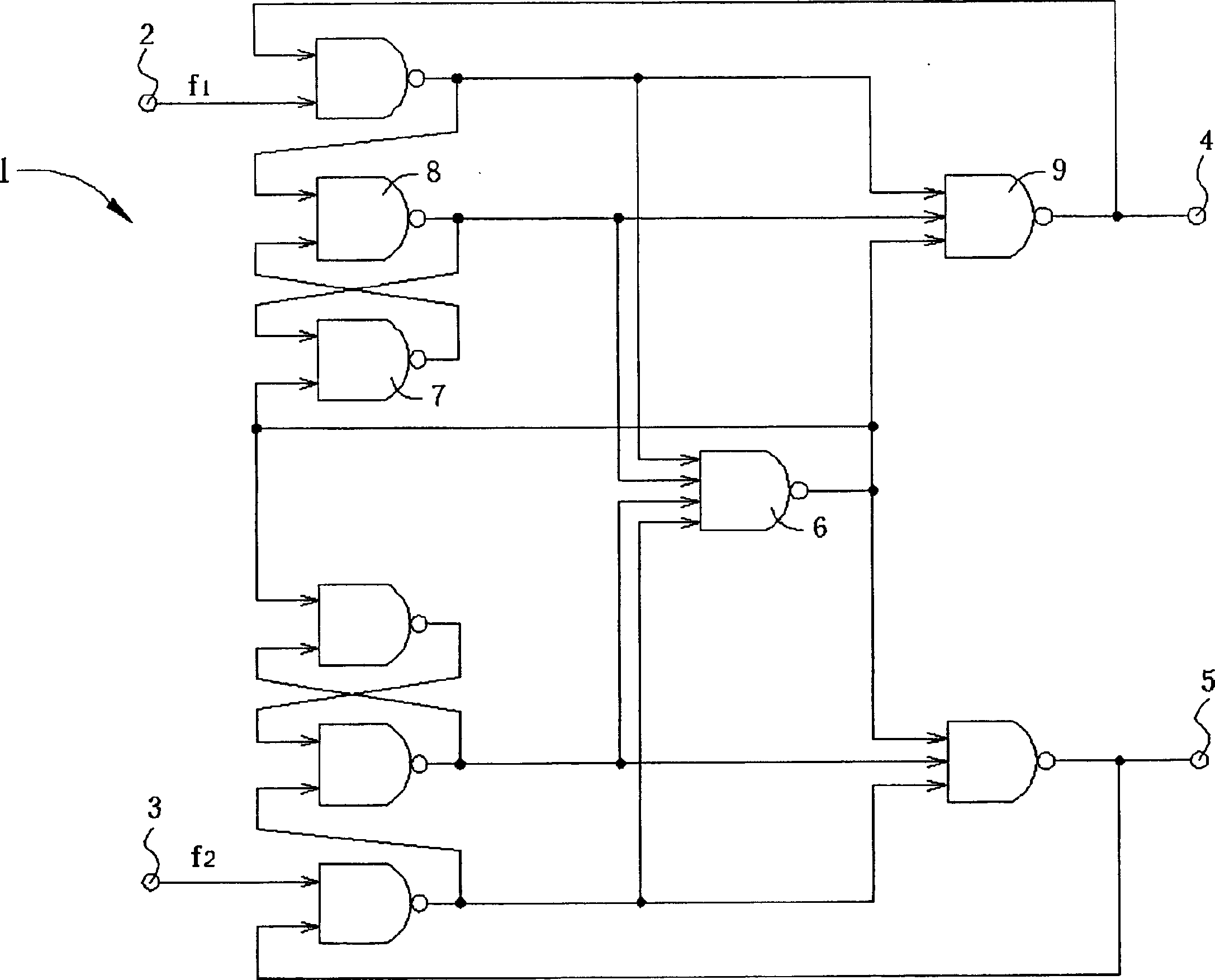
[0053] see Figure 5 , Figure 5 It is a circuit diagram of a DPFD 50 in the preferred embodiment of the present invention. DPFD 50 comprises a first SR latch 52, a second SR latch 54, a third SR latch 56 and a fourth SR latch 58, the first and the SR latches 52 and 54 Each includes a pair of interleaved NOR gates, and the third and third SR latches 56 and 58 respectively include a pair of interleaved NAND gates (NAND gates), and each NOR gate or NAND gate includes Two input terminals.
[0054] The first SR latch 52 comprises a first NOR gate 60 and a second NOR gate 62, an input terminal of the first NOR gate 60 is used as the S input terminal of the first SR latch 52, and the second OR One input end of the NOT gate 62 is used as the R input end of the first SR latch 52, and the other input end of the first NOR gate 60 is connected to the output end of the second NOR gate 62 in an interleaved manner, and the second NOR gate 62 The other input end of the NOR gate is connec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com