Imaging lens and imaging apparatus
An imaging lens and imaging equipment technology, applied in installation, optics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficult compactness, and achieve the effect of improving mass productivity and low sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
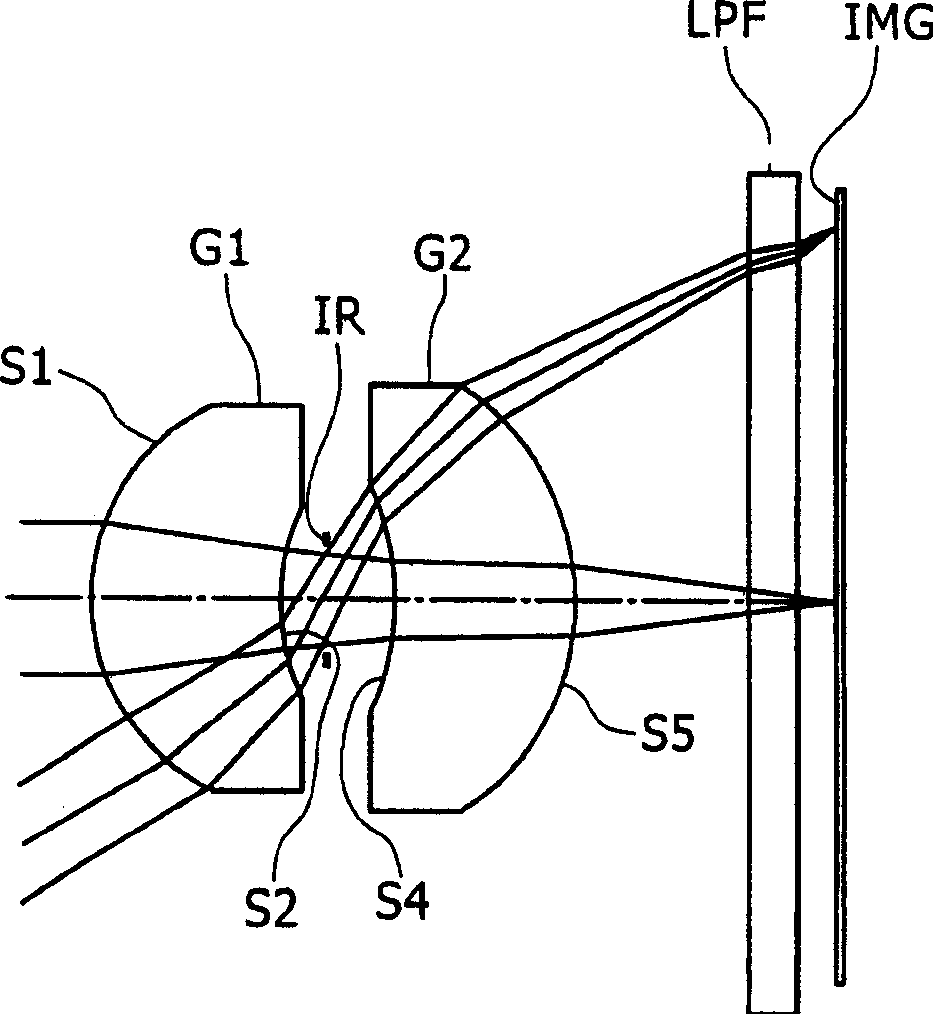
[0093] figure 1 is a view showing the lens structure according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The imaging lens of the first embodiment is configured by a first lens G1, a second lens G2, and an aperture stop IR arranged in this order from the object side. The first lens G1 has a meniscus shape with a convex surface facing the object side and has a positive refractive index, and the second lens G2 has a meniscus shape with a convex surface facing the image side and has a positive refractive index. "LPF" is a low-pass filter inserted between the second lens G2 and the imaging plane IMG.
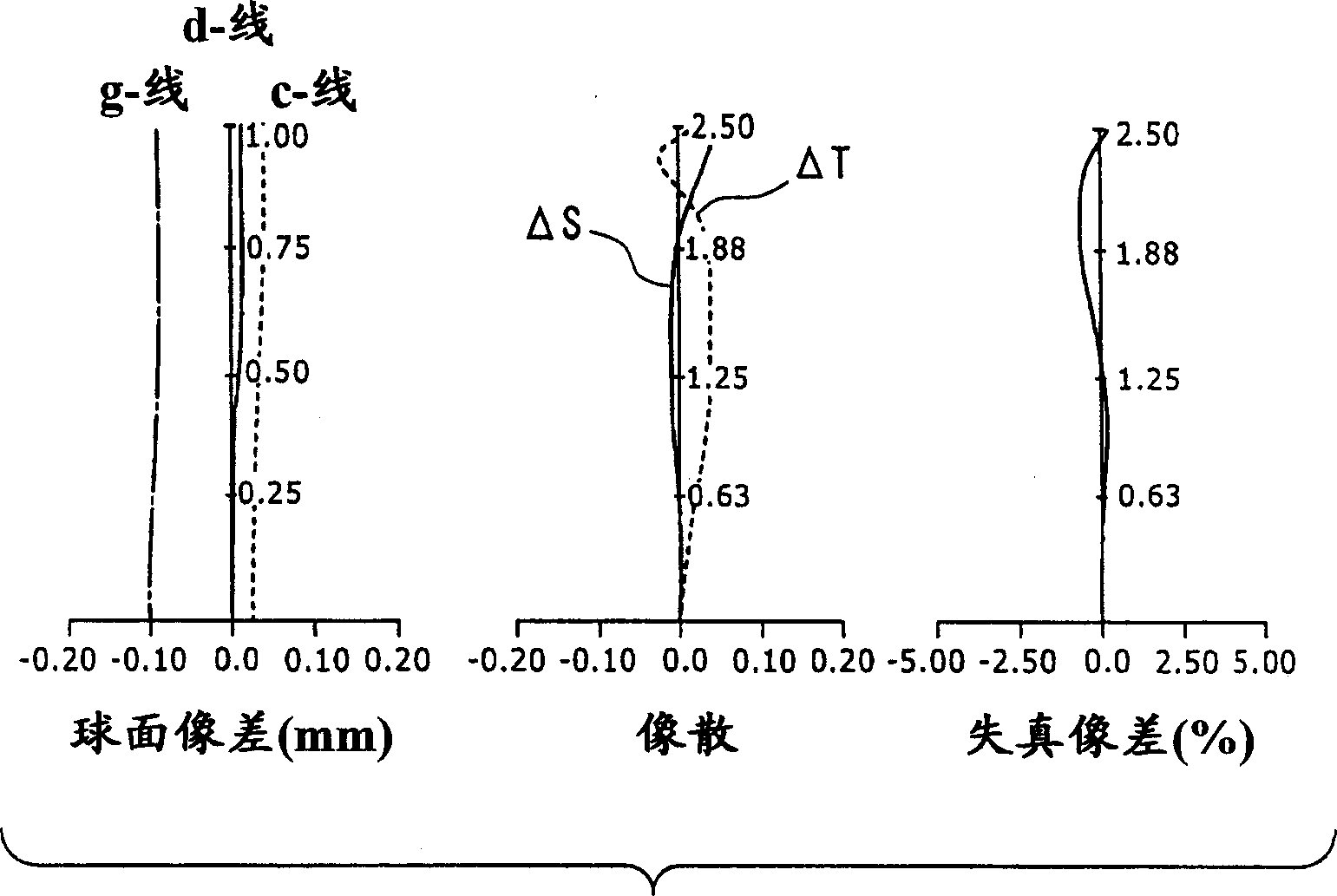
[0094] Table 1 shows the data of the optical system according to Numerical Example 1 in the case of applying actual numerical values to the first Example.
[0095] Table 1
[0096] FNo = 4.0
[0097] f=4.09
[0098] Si
Ri
di
ni
vi
1
1.529 (ASP)
1.25
1.7680
49.2
2
1.648 (ASP)
0.30
3 ...
no. 2 example
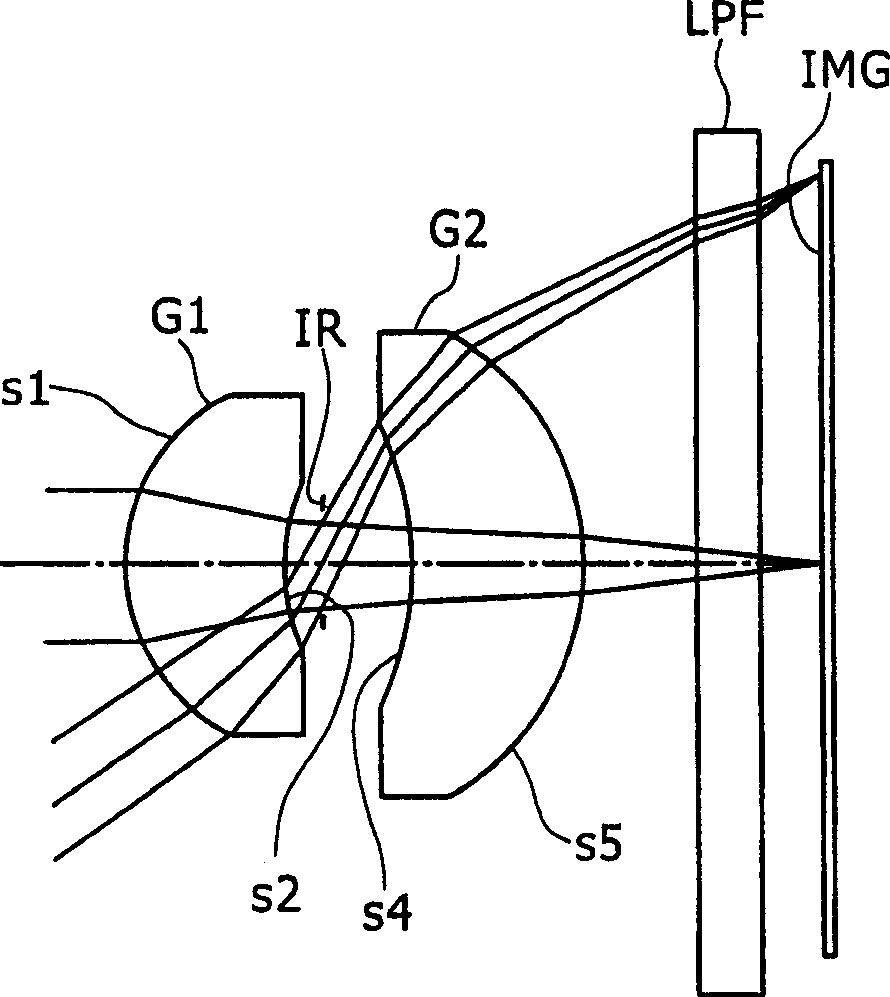
[0104] image 3 is a view of a lens structure according to a second embodiment of the present invention. The imaging lens of the second embodiment is configured by a first lens G1, a second lens G2, and an aperture stop IR arranged in this order from the object side. The first lens G1 has a meniscus shape with a convex surface facing the object side and has a positive refractive index, and the second lens G2 has a meniscus shape with a convex surface facing the image side and has a positive refractive index. "LPF" is a low-pass filter inserted between the second lens G2 and the imaging surface IMG.
[0105] Table 3 shows the data of the optical system according to Numerical Example 2 in the case of applying actual numerical values to the second example.
[0106] table 3
[0107] FNo = 4.0
[0108] f=4.61
[0109] Si
Ri
di
ni
vi
1
1.444 (ASP)
1.21
1.7433
49.3
2
1.460 (ASP)
0.30
3
...
no. 3 example
[0115] Figure 5 is a view of a lens structure according to a third embodiment of the present invention. The imaging lens of the third embodiment is configured by a first lens G1, a second lens G2, and an aperture stop IR arranged in this order from the object side. The first lens G1 has a meniscus shape with a convex surface facing the object side and has a positive refractive index, and the second lens G2 has a meniscus shape with a convex surface facing the image side and has a positive refractive index. "LPF" is a low-pass filter inserted between the second lens G2 and the imaging surface IMG.
[0116] Table 5 shows the data of the optical system according to Numerical Example 3 in the case of applying actual numerical values to the third example.
[0117] table 5
[0118] FNo = 4.0
[0119] f=3.54
[0120]
Si
Ri
di
ni
vi
1
1.389 (ASP)
1.06
1.7433
49.3
2
1.507 (ASP)
0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com