Method for assigning a priority to a data transfer in a network, and network node using the method
A technology of data transmission and network nodes, which is applied in the field of network communication to achieve the effect of preventing network congestion, improving data throughput, and improving data throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The present invention is described by taking an owner zone based on a peer-to-peer network structure as an example, in which nodes have individual node identifiers and a common peer group identifier, and nodes belonging to the peer group can freely communicate with each other, exchange messages and other data, etc. It can also be applied to other types of networks, and is particularly advantageous for networks whose nodes are organized fairly autonomously.
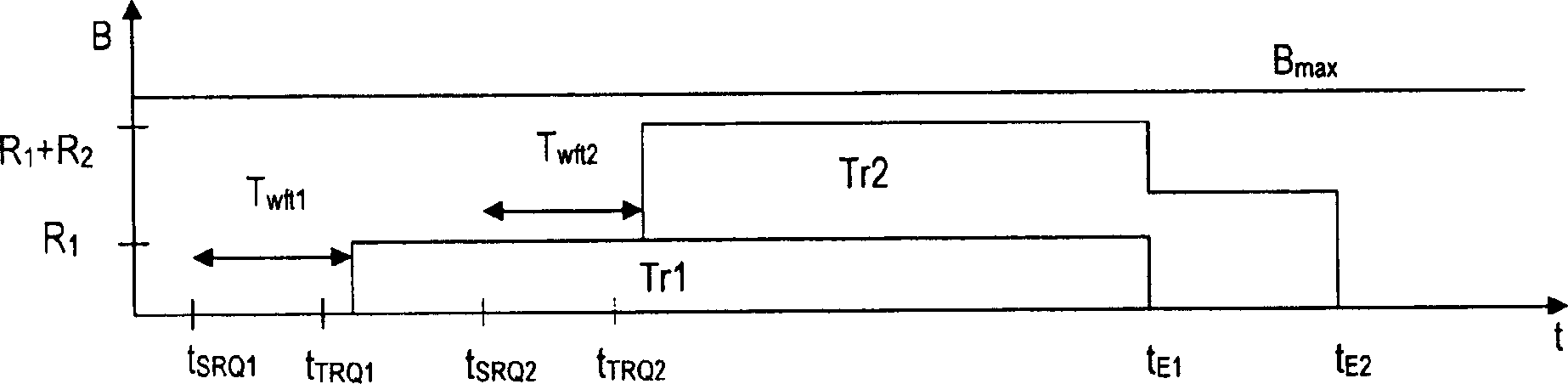
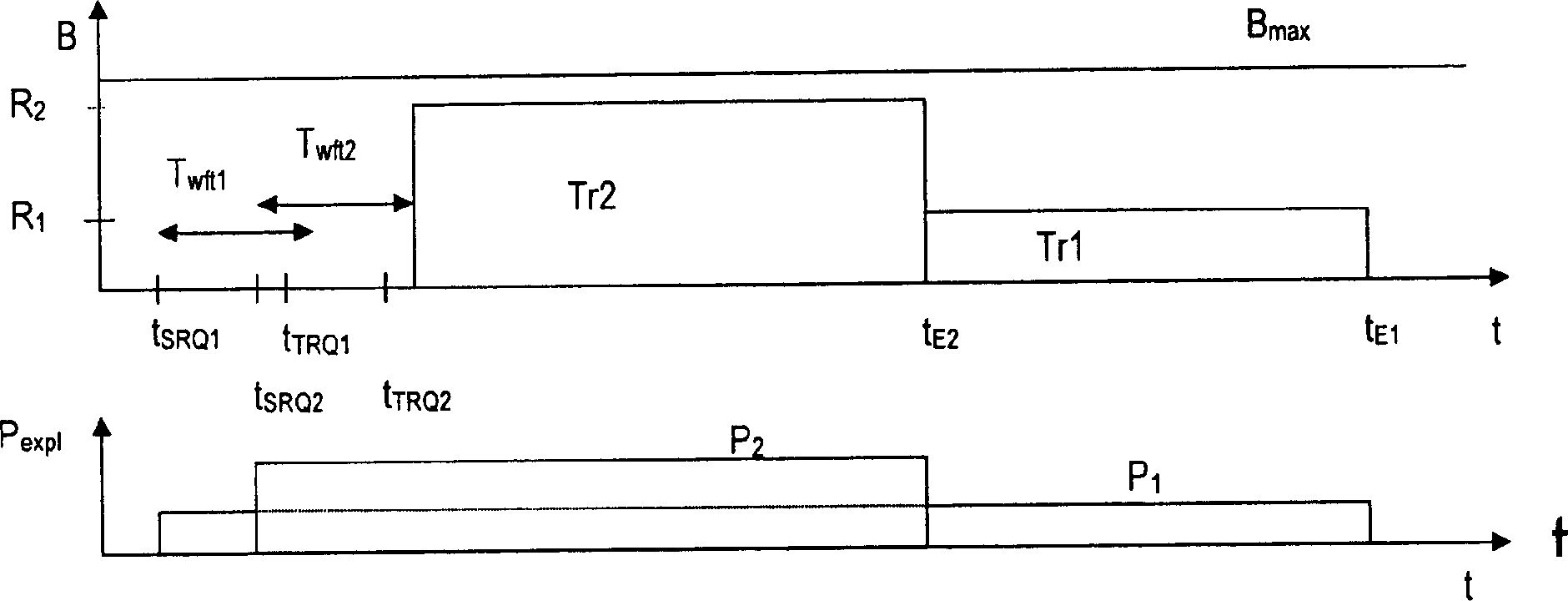
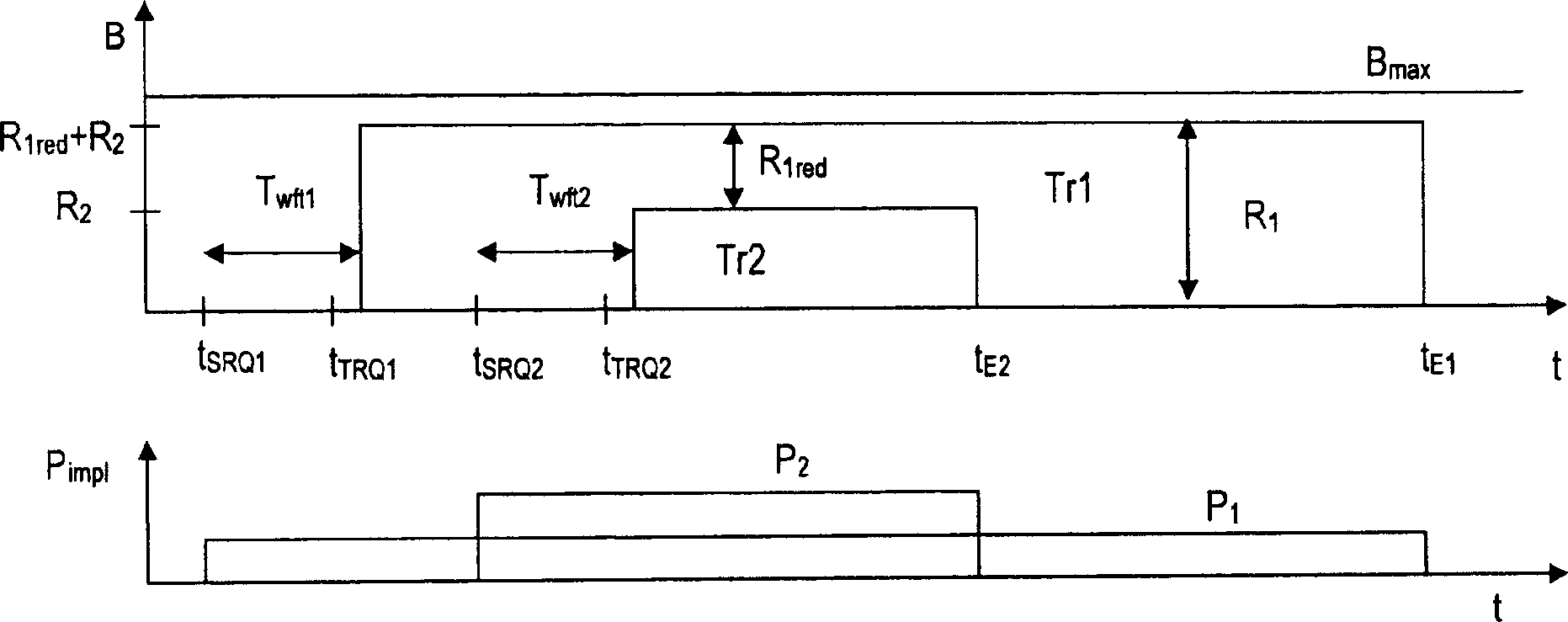
[0024] 1. The concept of priority
[0025] The present invention introduces the idea of a two-level concept, involving the distinction between first-level and second-level priorities: first-level or implicit priority is a relative priority, or priority relationship to which the included nodes conform, For example, peers in the owner zone. It does not have an explicit value associated with it, such as numeric priority or numbers. Thus, the set of implicit priorities represents a node's internal "knowledge" of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com