Bipolar transistor and radio frequency amplifier circuit
一种双极型晶体管、高频放大的技术,应用在高频放大器、放大器组合等方向,能够解决高频特性恶化、高频电力损失变大、无法增大Vbe负反馈电压等问题,达到布线设计简单化、消除高频增益的降低、防止部件数的增加的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0071] Figure 7A It is a cross-sectional view showing the structure of a bipolar transistor in the high-frequency amplifier circuit of the present embodiment. Figure 7B is a cross-sectional view of the structure of the transistor 1 of this embodiment, and the cross-sectional view along the dotted line a-a' in the figure is Figure 7A . But when Figure 7A The emitter wiring 20 is omitted. exist Figure 7A in, with Figure 5A The difference between the structural cross-sectional view of the conventional bipolar transistor 101 is that the DC terminal 3 to which a direct current (DC) bias is supplied and the RF terminal 4 to which a high frequency (RF) power is supplied are provided separately. That is, DC bias and RF power are supplied to the base layer 8 from different electrodes (respectively, the base electrode 6 for DC and the base electrode 7 for RF). The more essential difference is that the base electrode 6 for DC and the base electrode 7 for RF 7 is electrically ...
no. 2 approach
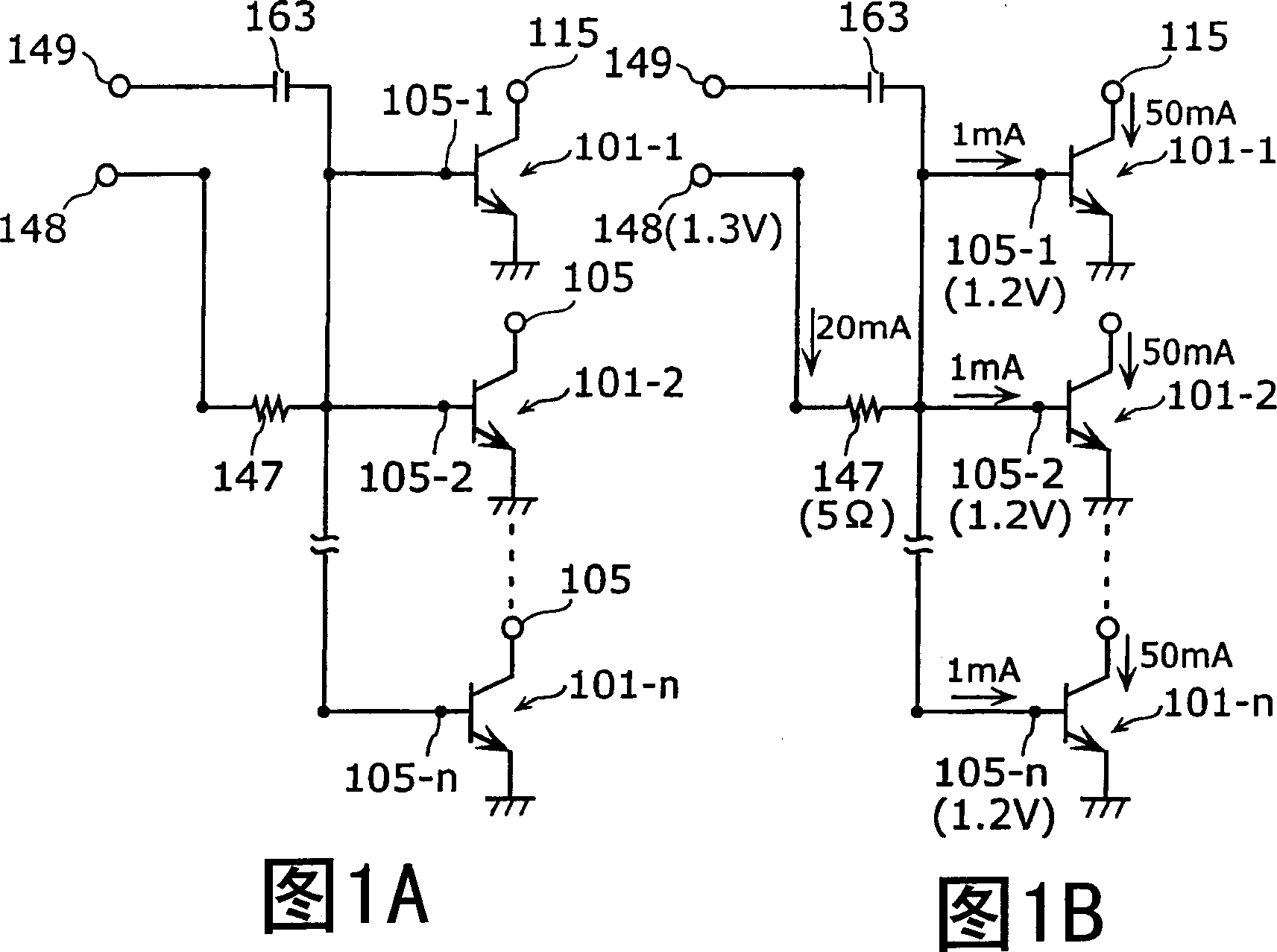
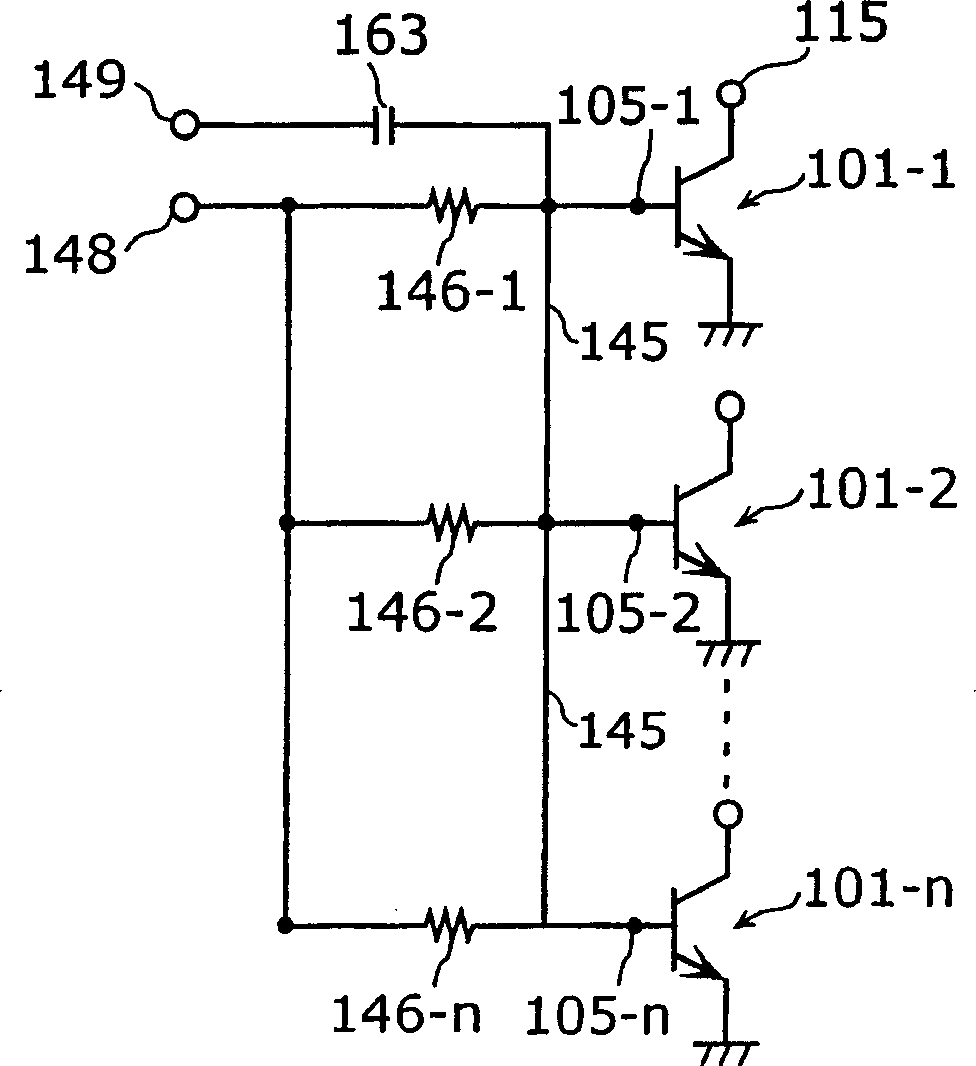
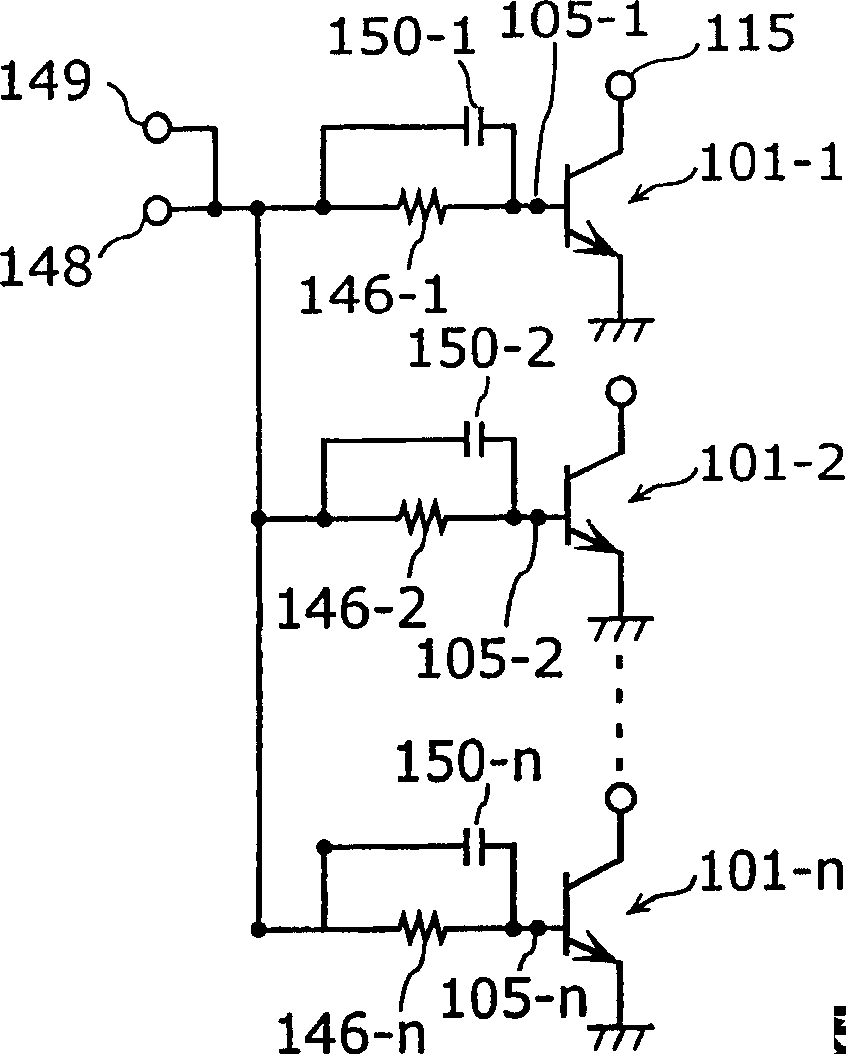
[0088] Next, in the first embodiment Figure 10 In the high-frequency amplifying circuit described in , it is considered that a collector current of 70 mA, which is 1.4 times that of other bipolar transistors, flows through the bipolar transistor 1-2. Such as Figure 11 As shown, the hFE of the bipolar transistors 1-1~1-n is 50, therefore, the base current flowing through the resistor 47-2 is 1.4mA, the voltage drop generated in the resistor 47-2 is 0.14V, and the electrode 6 The potential of -2 is 1.16V. On the other hand, the potential of the electrode 7-2 is 1.175V. At this time, the potential (1.175 V) of the electrode 7-2 is higher than the potential (1.16 V) of the electrode 6-2, so the base current of the bipolar transistor 1-2 is supplied from the electrode 7-2. That is, the negative feedback voltage of Vbe becomes 0.025V which subtracts 1.175V from 1.2V. On the other hand, the collector current of bipolar transistor 1-2 increases from 50mA to 70mA, whereby the jun...
no. 3 approach
[0096] Figure 14 It is a cross-sectional view of the structure of the bipolar transistor 70 in the high-frequency amplifier circuit of the third embodiment. with in Figure 12 The bipolar transistor 60 of the second embodiment shown is different in that it has a plurality of DC base electrodes 6-1, 6-2 and also has a plurality of emitter layers 11-1, 11-2. and Figure 12 Compared with the bipolar transistor 60, the emitter area is doubled, and the current capacity can be doubled in the unit cell. And, with Figure 12 Similarly, the bipolar transistor 60 is set to 3 μm by setting the distance from the DC base electrode 6-1 to the emitter layer 11-1 and the distance 61 from the DC base electrode 6-2 to the emitter layer 11-2. , the distance 16 from the RF base electrode 7 to the emitter layers 11-1, 11-2 is 0.5 μm, and Figure 12 The bipolar transistor 60 also, for any current concentration of the bipolar transistor, damage caused by thermal runaway of the bipolar transist...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com