Method and device for the determination of the actual position of a geodesic instrument
A technology of actual position and geodetic measurement, applied in the direction of measuring instruments, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as adverse effects of the measurement process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
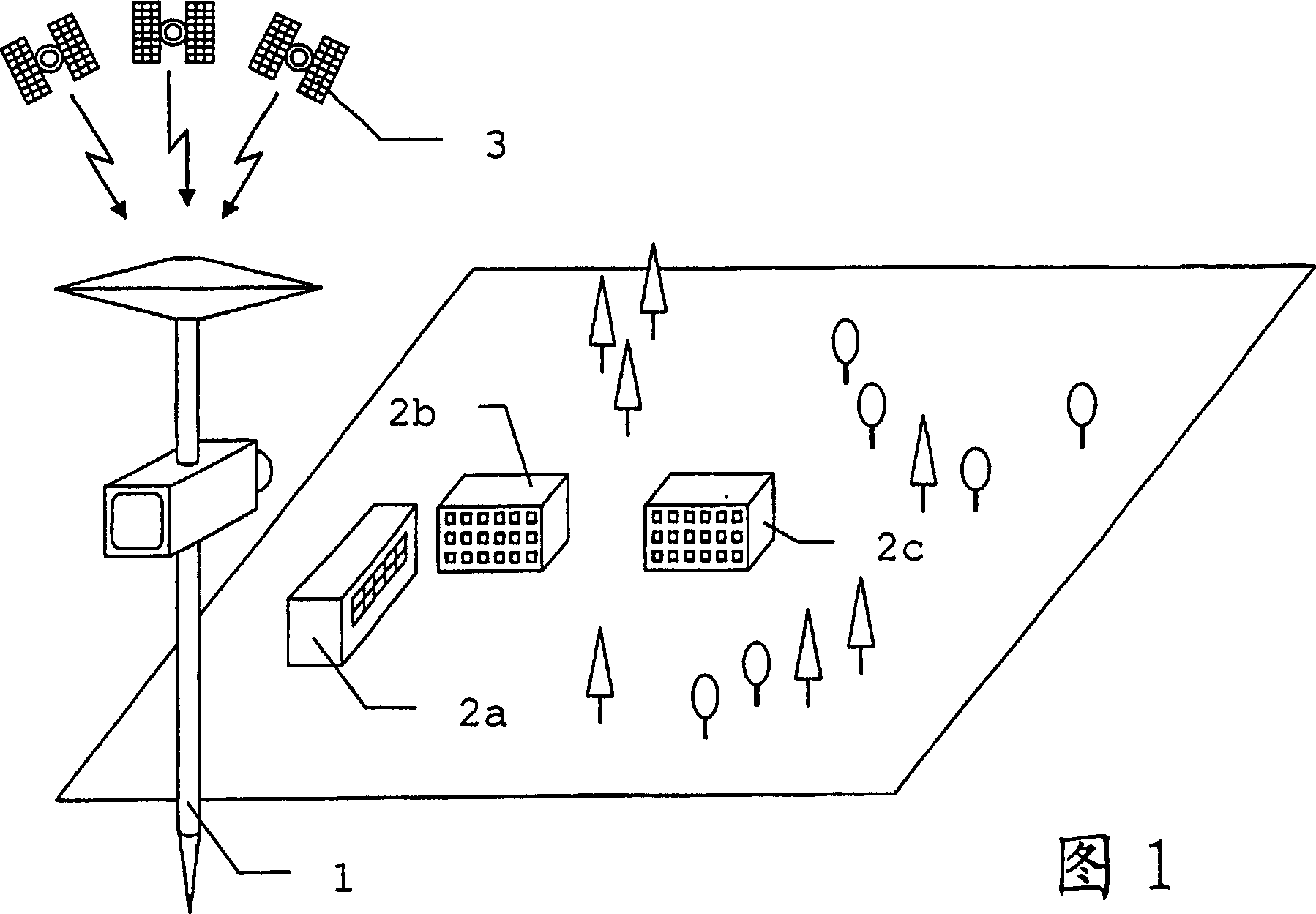
[0045] Figure 1 shows a typical survey task using a positioning system. The purpose of the survey is to determine the position of various points on the object 2c arranged in the complex together with the auditorium 2a and the building 2b. The surveying is carried out using a geodetic instrument 1 which has the components required for the respective surveying task. The actual position of the instrument 1 can be determined on the basis of signals of a positioning system, which is here assumed to be a satellite-supported system purely by way of example, representing in each case the current position to be determined for the survey. The actual position can be derived from the signal of the satellite 3, which is received by the satellite receiver of the instrument 1 and which travels substantially in a straight line.
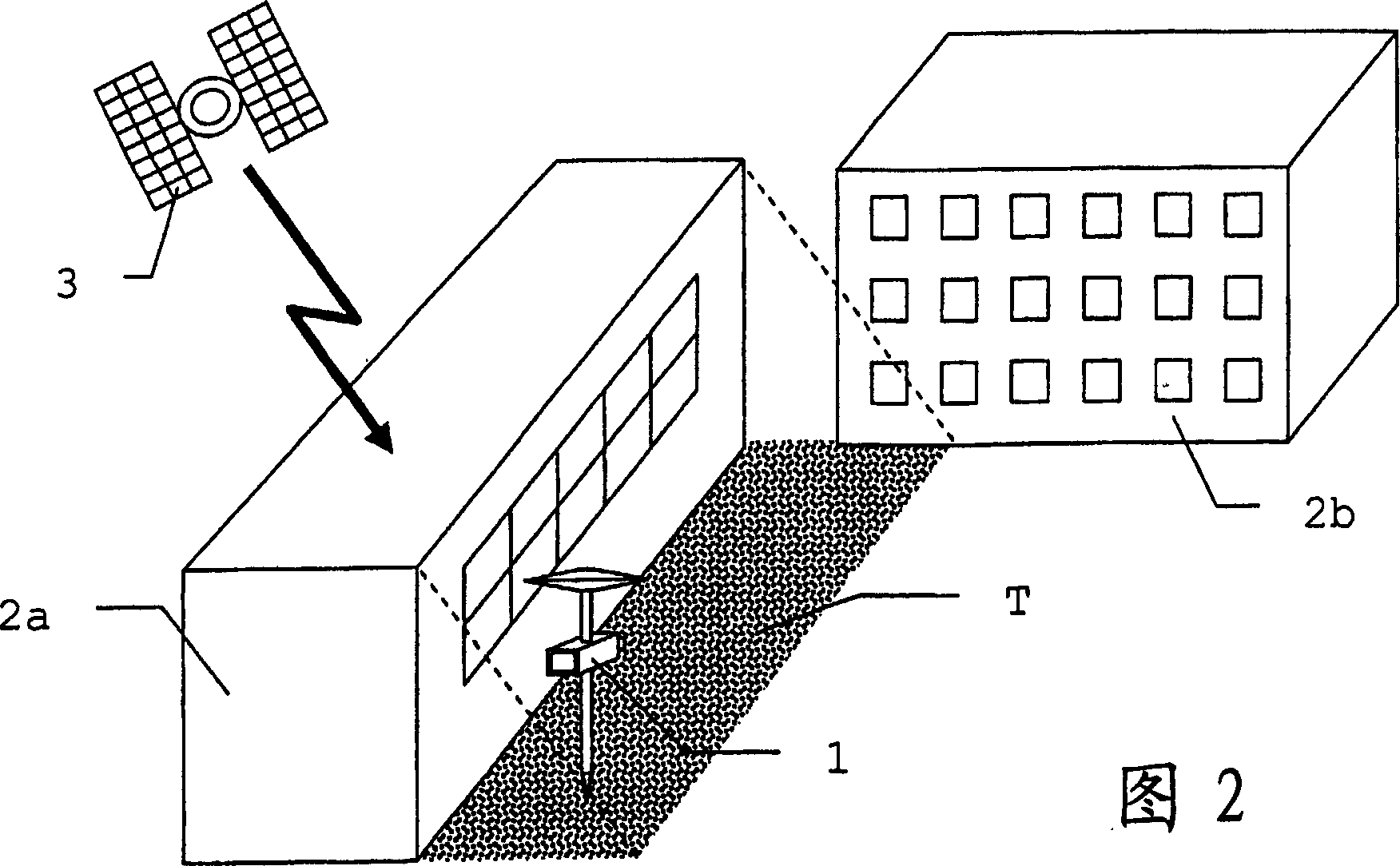
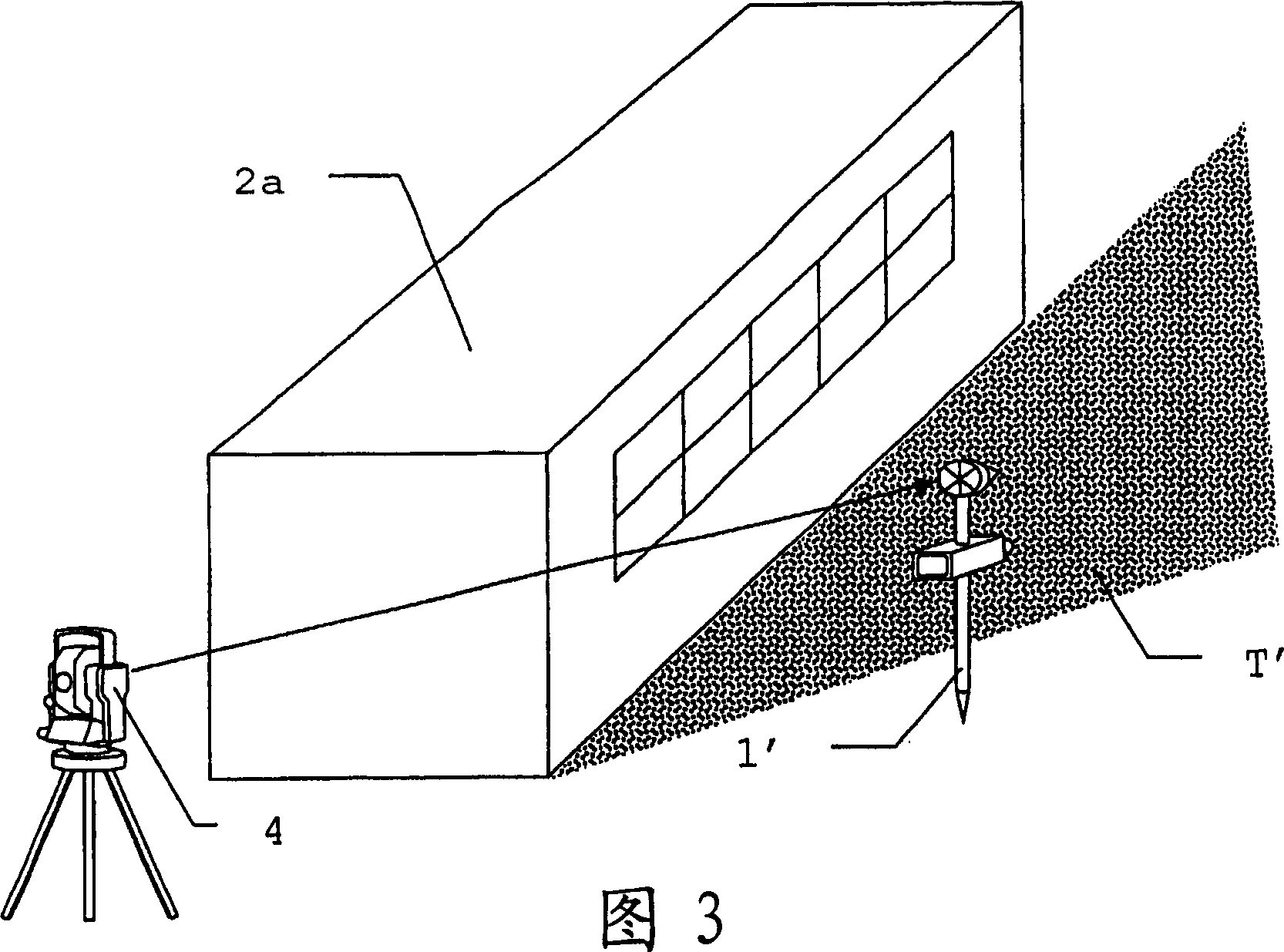
[0046] FIG. 2 schematically shows the situation in the immediate vicinity of the object to be surveyed. If for survey purposes it is necessary to place the instrum...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com