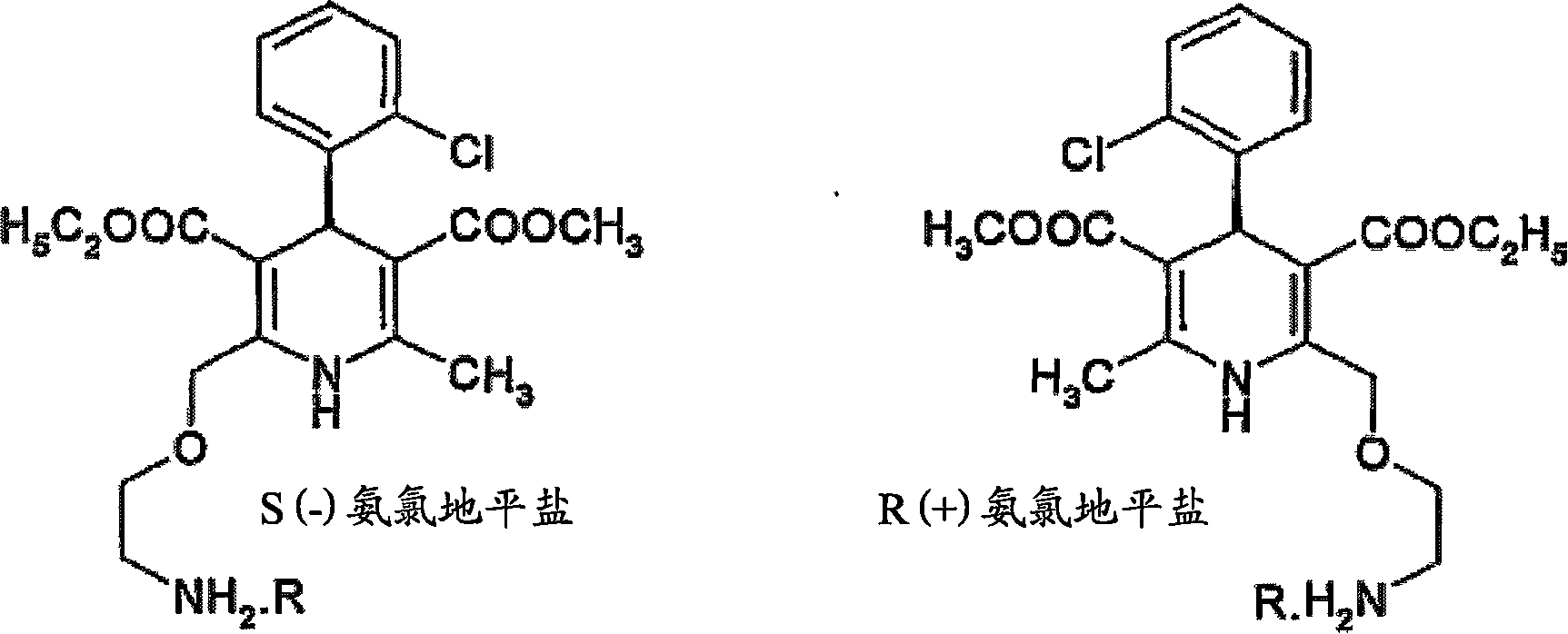
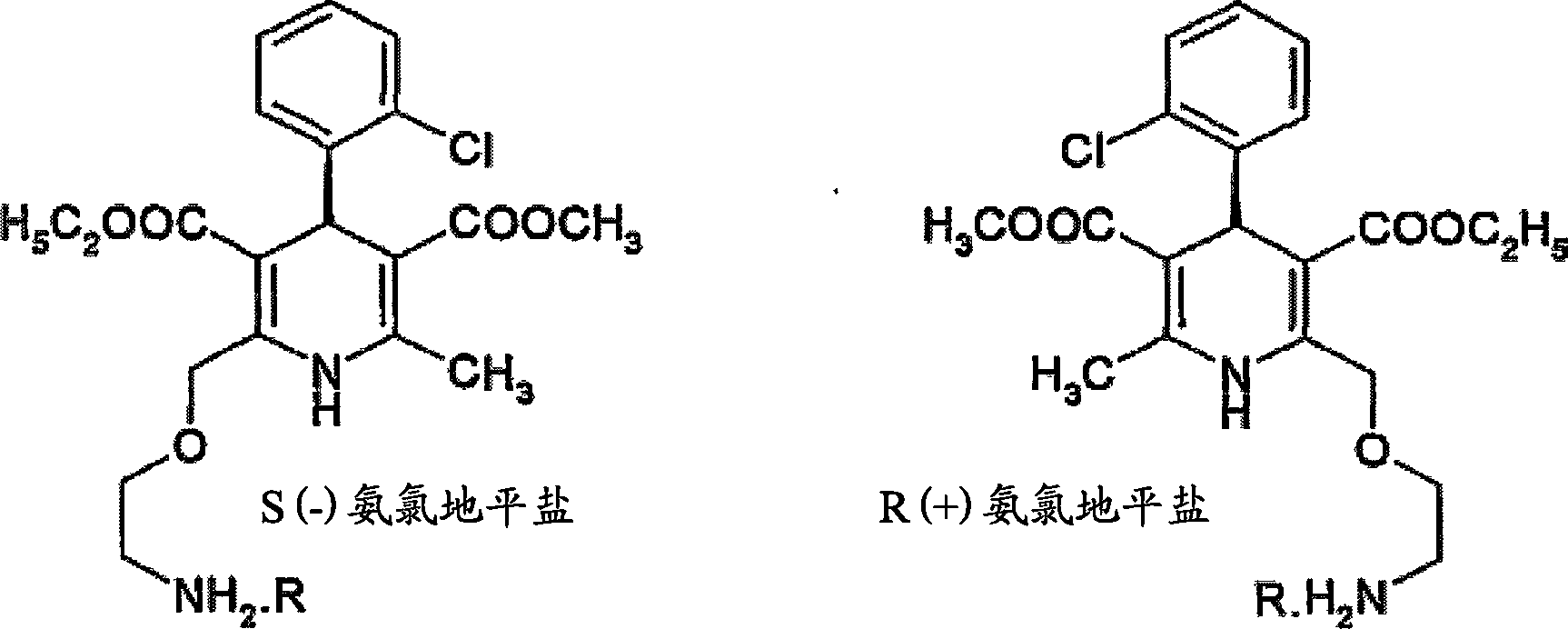
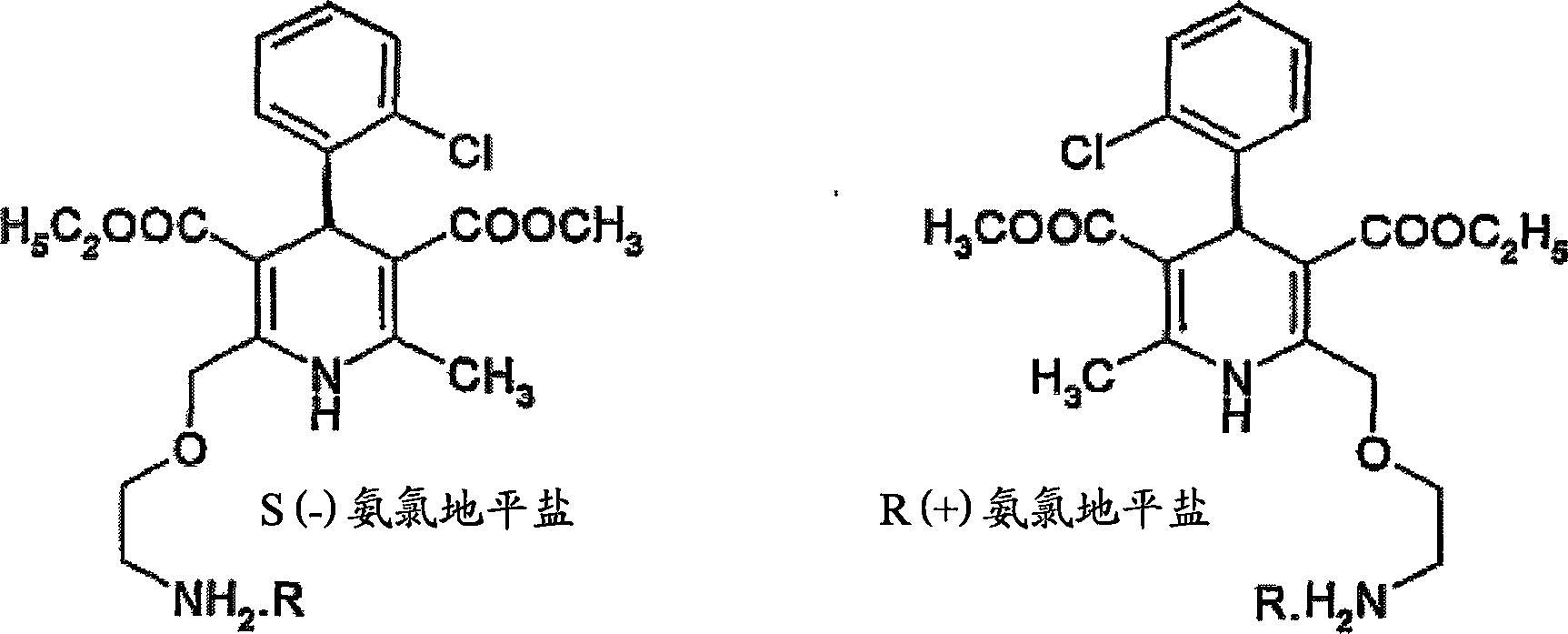
Process for preparation of chiral amlodipine salts
A kind of amlodipine salt, amlodipine technology, applied in the field of preparation of chiral amlodipine salt, can solve the problem of low yield of split salt
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047]Example 1: Preparation of R(+) amlodipine hemi-L(+) tartrate monoDMSO solvate from RS amlodipine
[0048] To a stirred solution of 10.50 g (0.0256 mole) RS amlodipine in 30 ml DMSO was added a solution of 1.93 g (0.0128 moles, 0.5 equivalent (eq.)) L(+) tartaric acid in 30 ml DMSO. Within 5-10 minutes, solids began to separate from the clear solution. The reaction was stirred for 3 hours and the solid was filtered off, washed with acetone and dried to afford 6.66 g (46.2%) of R(+) amlodipine hemi L(+) tartrate monoDMSO solvate. Melting point (mp.) 160-162°C, determined by chiral HPLC to be 95.2%d.e. M. Kremser.].
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Preparation of R(+) amlodipine hemi-L(+) tartrate monoDMSO solvate from RS amlodipine
[0050] To a stirred solution of 100 g (0.245 mole) RS amlodipine in 300 ml DMSO was added a solution of 9.2 g (0.06 mole, 0.25 equivalent (eq.)) L(+) tartaric acid in 300 ml DMSO. Within 5-10 minutes, solids began to separate from the clear solution. The reaction was stirred for 3 hours and the solid was filtered off, washed with acetone and dried to yield 52.3 g (36.2%) of R(+) amlodipine hemi-L(+) tartrate monoDMSO solvate. Melting point (mp.) 160-162°C, 98.2% d.e. by chiral HPLC.
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3: Preparation of R(+) amlodipine hemi-L(+) tartrate monoDMSO solvate from RS amlodipine
[0052] To a stirred solution of 100 g (0.245 mole) RS amlodipine in 150 ml DMSO was added a solution of 9.2 g (0.06 mole, 0.25 equivalent (eq.)) L(+) tartaric acid in 100 ml DMSO. Within 5-10 minutes, solids began to separate from the clear solution. The reaction was stirred for 3 hours and the solid was filtered off, washed with acetone and dried to yield 58.6 g (40.5%) of R(+) amlodipine hemi L(+) tartrate monoDMSO solvate. Melting point (mp.) 160-162°C, 96.8% d.e. by chiral HPLC.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com