Disc reproduction device and method
A device and audio data technology, applied in magneto-optical discs, read-only discs, disc-shaped record carriers, etc., can solve the problems of complex disc playback equipment and time-consuming jump operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
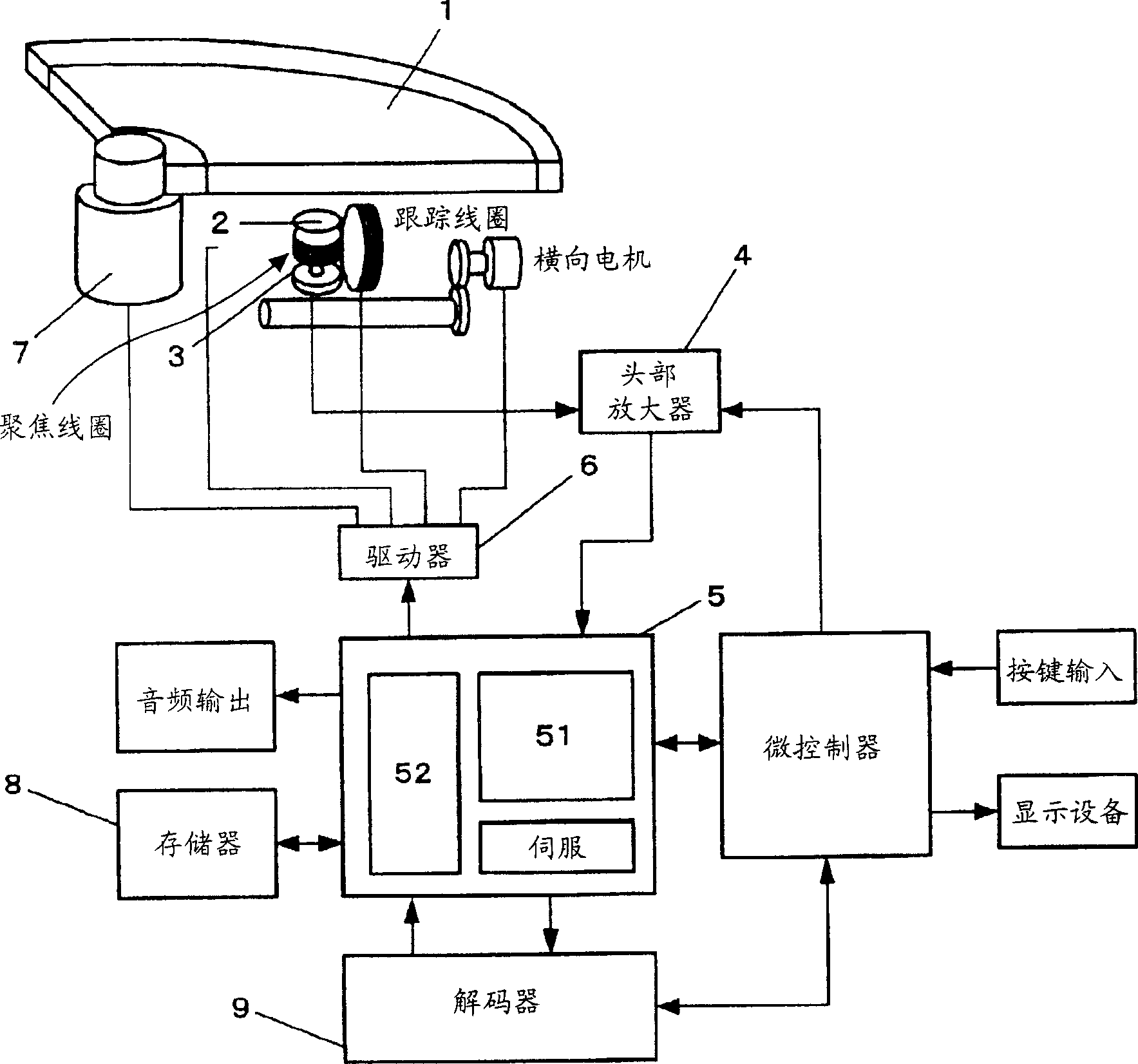
[0059] Next, an optical disc playback device according to a first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings. first, Figure 5 A map within memory 8 is shown. The memory 8 having a ring buffer structure is divided into: an area called a work area for storing audio data having a specific length and belonging to a plurality of tracks; The remaining audio data of one track following the audio data having a certain length is stored and output.
[0060] In the processing belonging to the track head search, the basic requirement is to divide the work area into some tracks recorded in the optical disc 1, and to store the audio data sequentially from the head of the music selection to the tracks in the work area. The head position of the corresponding segmented region of the track (WP n ). The basic requirement for the amount of audio data to be stored in each divided area of the audio track is greater than the amount of dat...
no. 2 approach
[0073] Next, an optical disc playback device according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0074] The AB repeat process between two points on the track is described by referring to FIGS. 12 and 13 .
[0075] First, when point A is set, the read pointer is moved to the head position (WP) of the work area (step S1211). To set the work range of the read pointer to (work area+track buffer), the ring buffer MAX is set to the end (WPe) of the work area (step S1212). In the write process, the target position to which the optical pickup 3 is to be moved by the jump operation is set as the position of point A on the disc, while the write pointer is set to the same position as the read position (step S1213).
[0076] Subsequently, write processing is performed (step S1214), such as Figure 7 shown in . When a predetermined amount of data is stored in the memory 8, output of the audio data written in the memo...
no. 3 approach
[0084] Next, an optical disc playback device according to a third embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0085] When a request to set point A is issued during playback of audio data, the audio data stored in the track buffer is transferred to the work area by DMA (Direct Memory Access) transfer. In this case, as Figure 14 As shown in , the write MAX is set to the current read position so that the audio data to be newly written in the track buffer does not overwrite the audio data stored in the write buffer (S1401). Subsequently, the current read position is set as a DMA transfer start position (S1402). DMA transfer is started (S1403). When the transfer of audio data has reached the end of the work area, the transfer is terminated (S1404). Figure 15 The state of the read and write pointers during this process is shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com