Identification of novel IgE epitopes
An amino acid and sequence technology, applied in the field of identification of new IgE epitopes, can solve problems such as the risk of inducing allergic antibodies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0107] Preparation of High Affinity Antibodies
[0108] Once the parent antibody has been identified and isolated, one or more amino acid residues in one or more variable regions of the parent antibody may be altered. Alternatively, one or more framework residues may be substituted in the parent antibody such that the binding affinity of the antibody, eg, for human IgE, is improved. Framework region residues to be modified include, for example, residues that bind non-covalently directly to the target (Amit et al. Science 233:747-753 (1986)); those that interact with / affect the conformation of the CDR (Chothia et al. J. Mol. Biol. 196:901-917 (1987)); and / or residues involved in the VL-VH interface (EP 239 400 B1 ). In certain embodiments, modification of one or more such framework region residues results in increased binding affinity of the antibody for the target of interest.
[0109] Modification of the biological properties of an antibody can be achieved by selecting subs...
Embodiment 1
[0202] Example 1: Humanization of anti-IgE murine MAb TES-C21
[0203] The heavy chain variable region (V H ) and the light chain variable region (V L ) were compared to human antibody germline sequences obtained from public databases. When deciding on a template as described in step 1 above, a number of criteria are used, including full length, similar CDR positions within the framework, overall homology, size of the CDRs, and the like. Considering all of these criteria holistically allows selection of the optimal human template, as shown in the sequence alignment between the TES-C21 MAb heavy and light chain sequences and representative human template sequences, shown in Figures 3A and 3B.
[0204] In this case, the antibody was designed using more than one human framework template. for V H The human template for chain selection was the combination of DP88 (amino acid residues 1-95) and JH4b (amino acid residues 103-113) (see Figure 3B). for V L The human template for ...
Embodiment 2
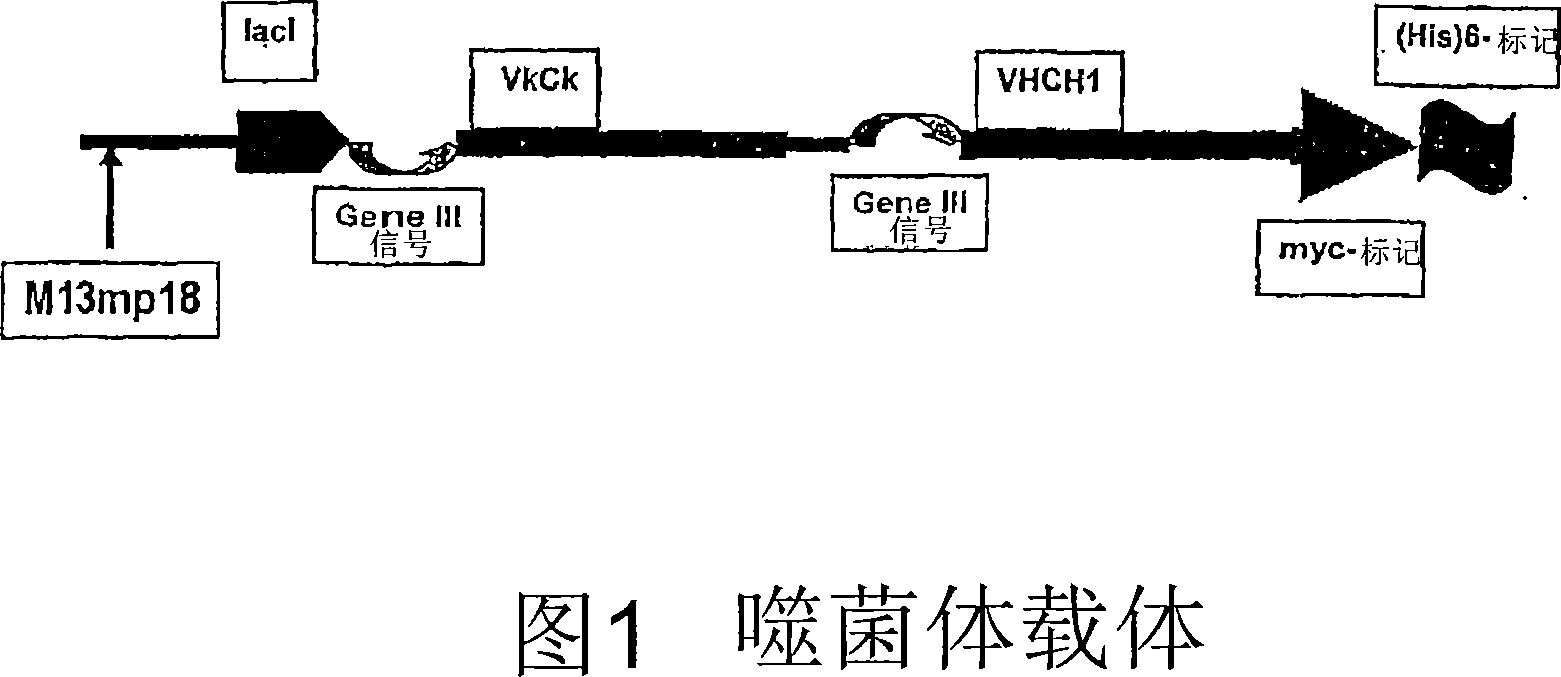
[0211] Example 2: V H and V L Cloned into phage expression vector
[0212] V H and V L Cloned into a phage expression vector. Uridylated templates were obtained by infecting CJ236 Escherichia coli strain (dut - ung - ) and prepared.
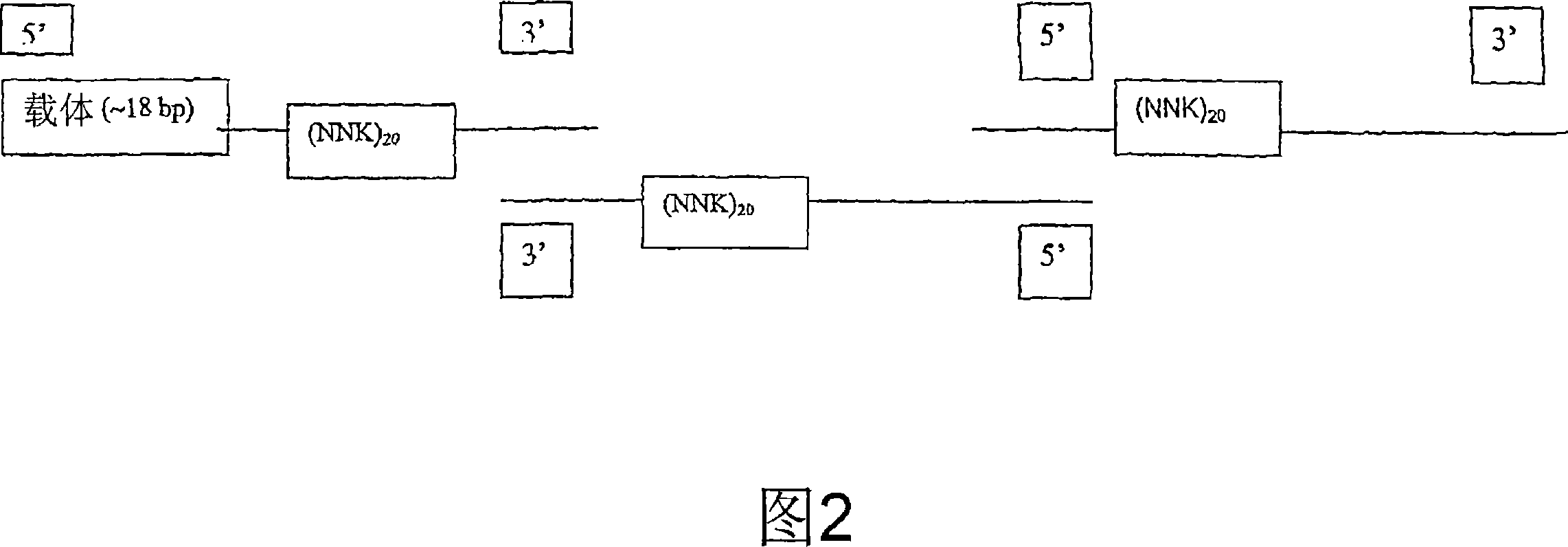
[0213] The following components [200ng uridine acidified phage vector (8.49kb); 92ng phosphorylated single chain H chain (489 bases); 100ng phosphorylated single chain L chain (525 bases); 1μL 10× annealing buffer, with ddH 2 O adjust the volume to 10 μL] Annealing was performed by PCR maintaining the temperature at 85° C. for 5 minutes (denaturation), followed by a gradient down to 55° C. over 1 hour (approximately 8-fold molar ratio of insert to vector). The samples were chilled on ice.
[0214] Add the following components to the annealed product: 1.4 μL 10× synthesis buffer, 0.5 μL T4 DNA ligase (1 unit / μL), 1 μL T4 DNA polymerase (1 unit / μL), and then incubate on ice for 5 minutes at 37 Incubate for 1.5 hours at °C. The product wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com