Device, system and method for cutting, cleaving or separating a substrate material
A substrate and cutting line technology, applied in the field of cutting and separation, can solve problems such as inability to have flexibility, achieve the effect of reducing or reducing micro-cracks and ensuring linearity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0076] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention are described with reference to the drawings.
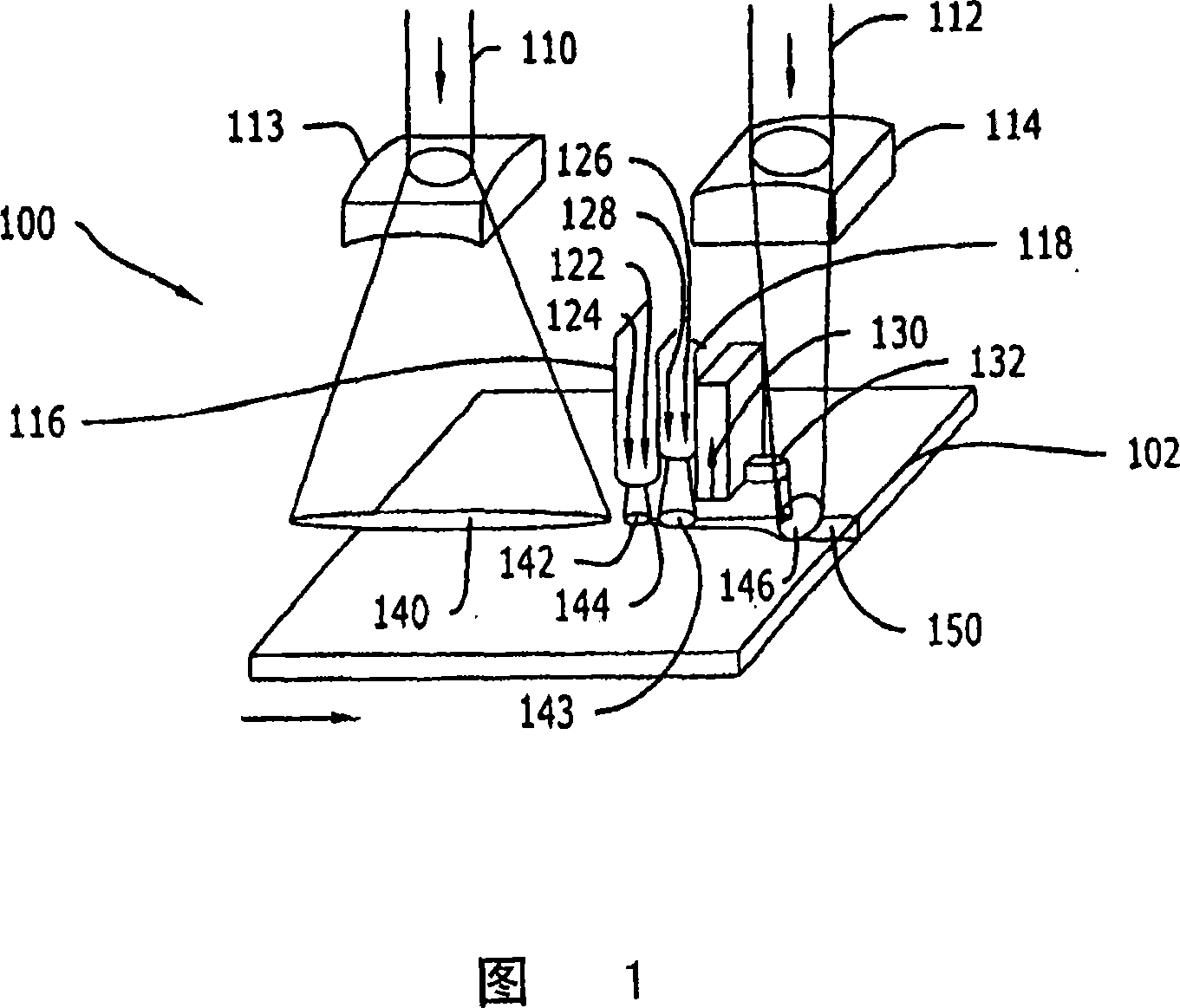
[0077] Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of an apparatus for separating non-metallic materials according to the present invention. A separation apparatus, generally indicated by reference numeral 100 , for separating non-metallic material 102 includes two laser beams 110 and 112 and at least two quench nozzles 116 and 118 .
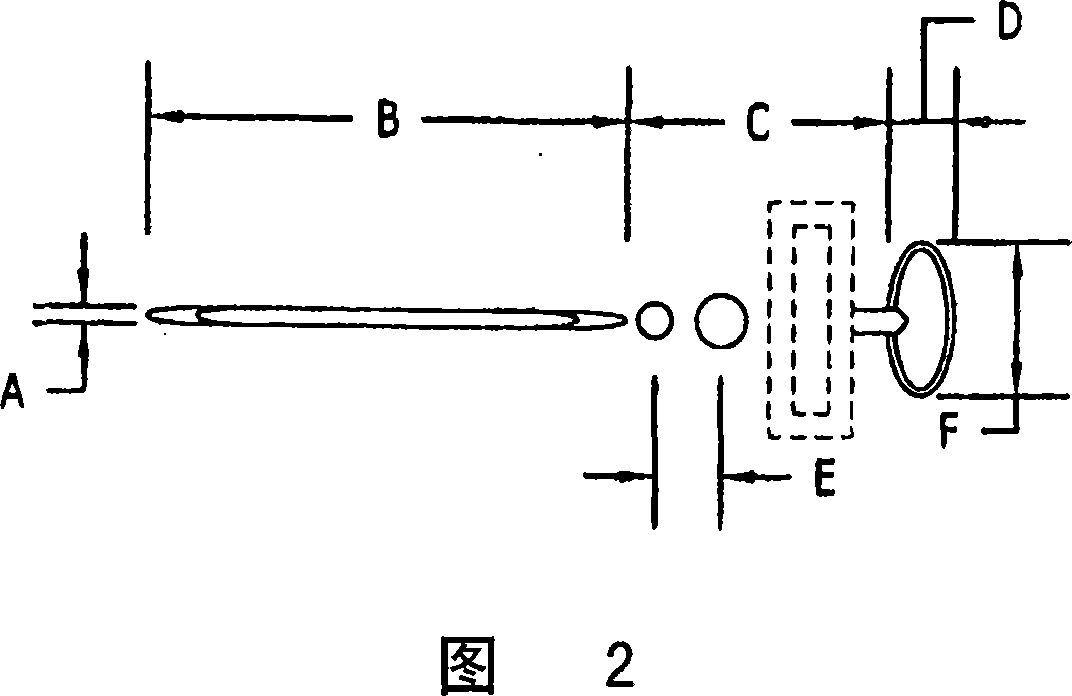
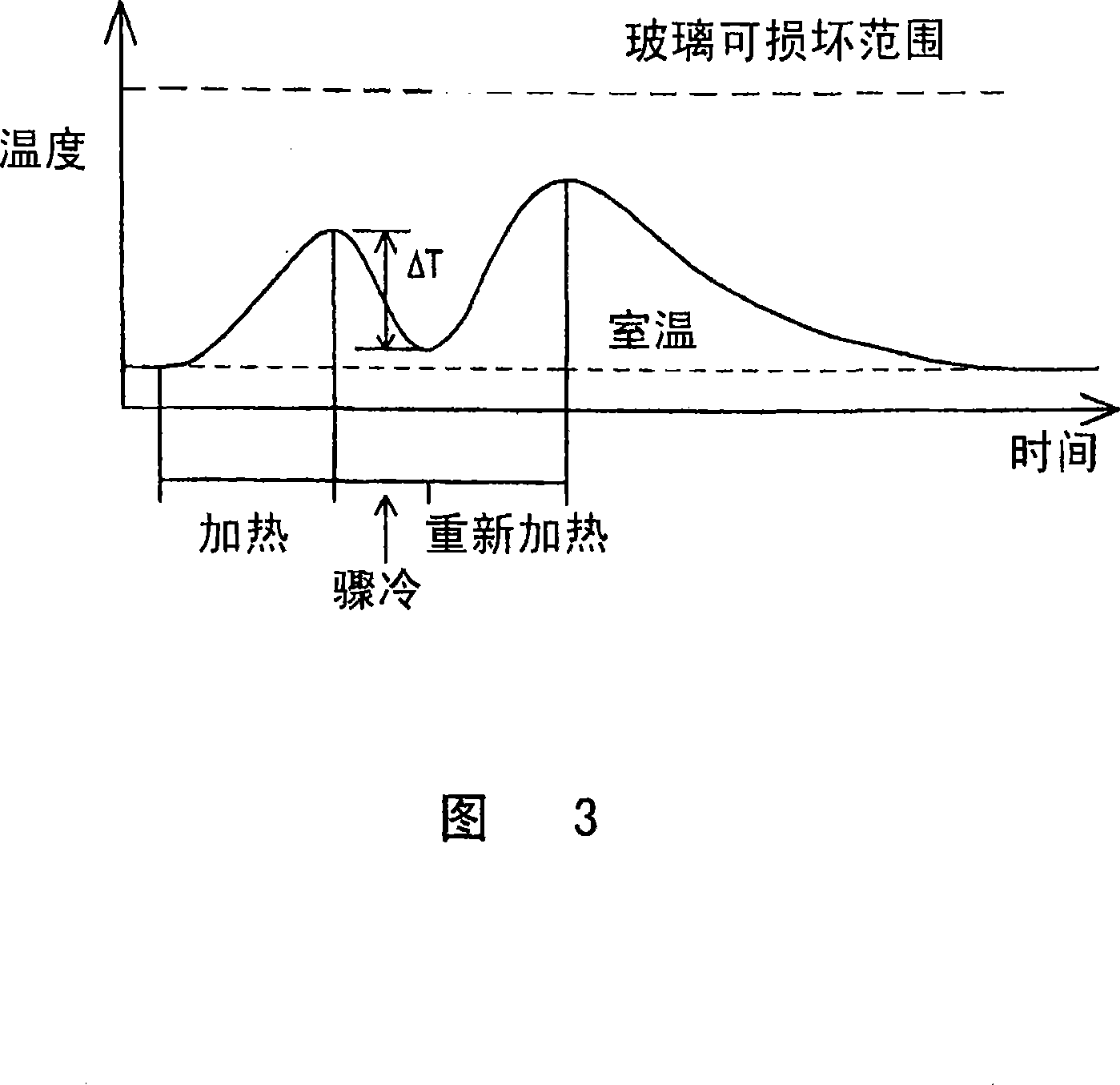
[0078] The non-metallic substrate 102 moves under the non-metallic substrate 102, eg glass, relative to the separation device 100 in the direction indicated by the arrow. Laser beam 110 passes through lens 113 and is focused on scribing unit beam processing region 140 . Two quench nozzles 116 and 118 schematically represent shaped quench regions 142 and 143 respectively on the non-metallic substrate 102 . Between the quench regions 142 and 143 is a score line 144 of diffusion. Laser beam 112 passes through lens 114 and is focused on fracture laser bea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com