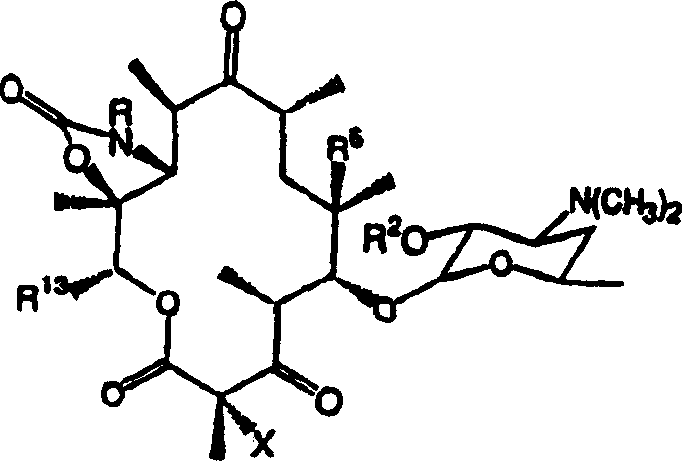
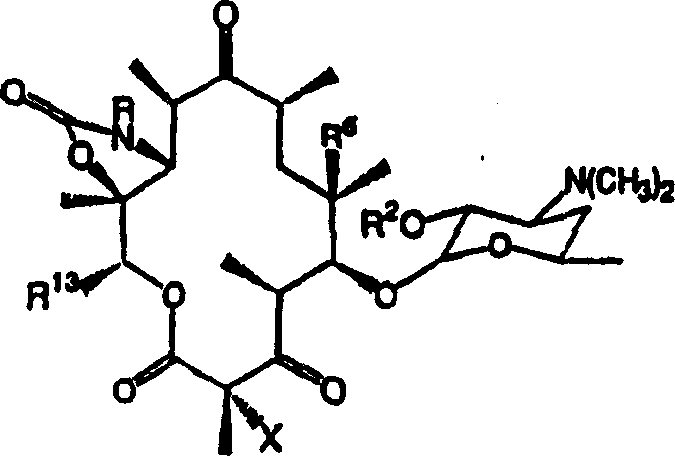
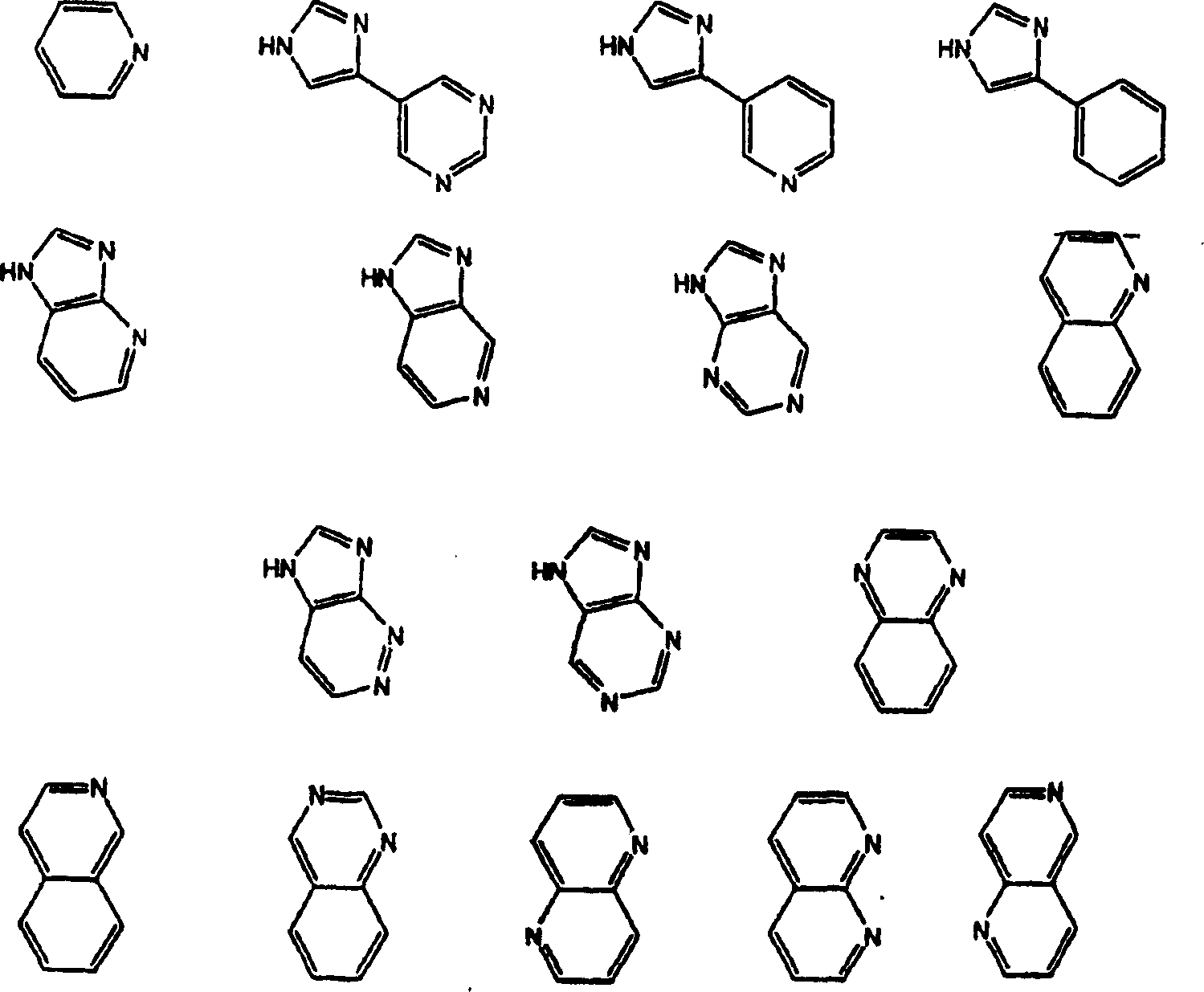
Ketolide antibacterials
A technology of alkyne and alkyl groups, which is applied in the field of ketolide antibacterial agents, and can solve problems such as the complexity of macrolide molecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 10
[0137] Example 10 describes the preparation of C-2-halo compounds of the invention. Specifically, the compound to be halogenated is treated with a base and an electrophilic halogenating reagent such as pyridinium perbromide or N-fluorobenzenesulfonimide. Example 12 describes the removal of cladinose from a derivative of erythromycin A containing a C-6-O-allyl group and the oxidation of the resulting C-3-hydroxyl to a ketone. Example 13 illustrates the transformation of C-6-O-alkyl containing compounds into several intermediates useful in the synthesis of compounds of the invention. Example 14 describes the synthesis of compounds of formula I, where R = H, R 2 = H, X = H and R 6 =O-allyl. Example 15 describes the conversion of macrolides containing 6-O-alkyl and 11,12-cyclic carbamate functional groups to compounds of formula I by the Heck reaction followed by deprotection of the deoxyaminosugar. Example 16 describes the alkylation of the compound to the 6-O-propargyl inter...
Embodiment 21
[0139] Example 21 describes the synthesis of 1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-1-(4-amino-2-butene), an amine useful in the synthesis of compounds of the invention where R=1H - imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine.
[0140] Methods for converting 10,11-anhydro compounds into carbamate derivative compounds of the present invention are described in Examples 22 and 23. The amines used in the synthesis of carbamate derivative compounds of Formula I are either commercially available or can be readily prepared as described in Denis et al., Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett.9:3075-3080 (1999). ground preparation.
Embodiment 1
[0142] Preparation of diketone thioesters
[0143] In this example, the preparation of N-acetyl for feeding recombinant Streptomyces host cells to produce 15-methyl and 14,15-dehydro-6-deoxyerythromycin ring B intermediate compounds is described. Method used for Cysteamine Thioate ("NACS"). The synthetic methods described below are also described in U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 09 / 492,733 (inventors G. Ashley, M. Burlingame, and I. Chan-Kai), which is incorporated herein by reference.
[0144] Thus, from (4S)-N-[(2S,3R)-2-methyl-3-hydroxyhexanoyl]-4-benzyl-2-oxazolidinone (Preparation D) with N-acetylcysteine Amine (Preparation B) reaction to prepare (2S,3R)-2-methyl-3-hydroxyhexanoate NACS (Preparation E), which is used to prepare 15-methyl-6-deoxyerythrolide ring B intermediate. In turn, N-acetyl cysteamine was prepared from N,S-diacetyl cysteamine (Preparation A). Preparation of (4S)-N-[(2S,3R)-2-methyl-3 from (4S)-N-propionyl-4-benzyl-2-oxazolidinone (propionyl-N...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com