Methods and media for utilizing symbolic expressions in circuit modules
a circuit module and symbolic expression technology, applied in the field of parametric logic modules, can solve the problems of increasing design complexity, designer cannot deal with the entire design at the gate level, and it is difficult to achieve true hierarchical design for fpgas using currently-available softwar
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example sim
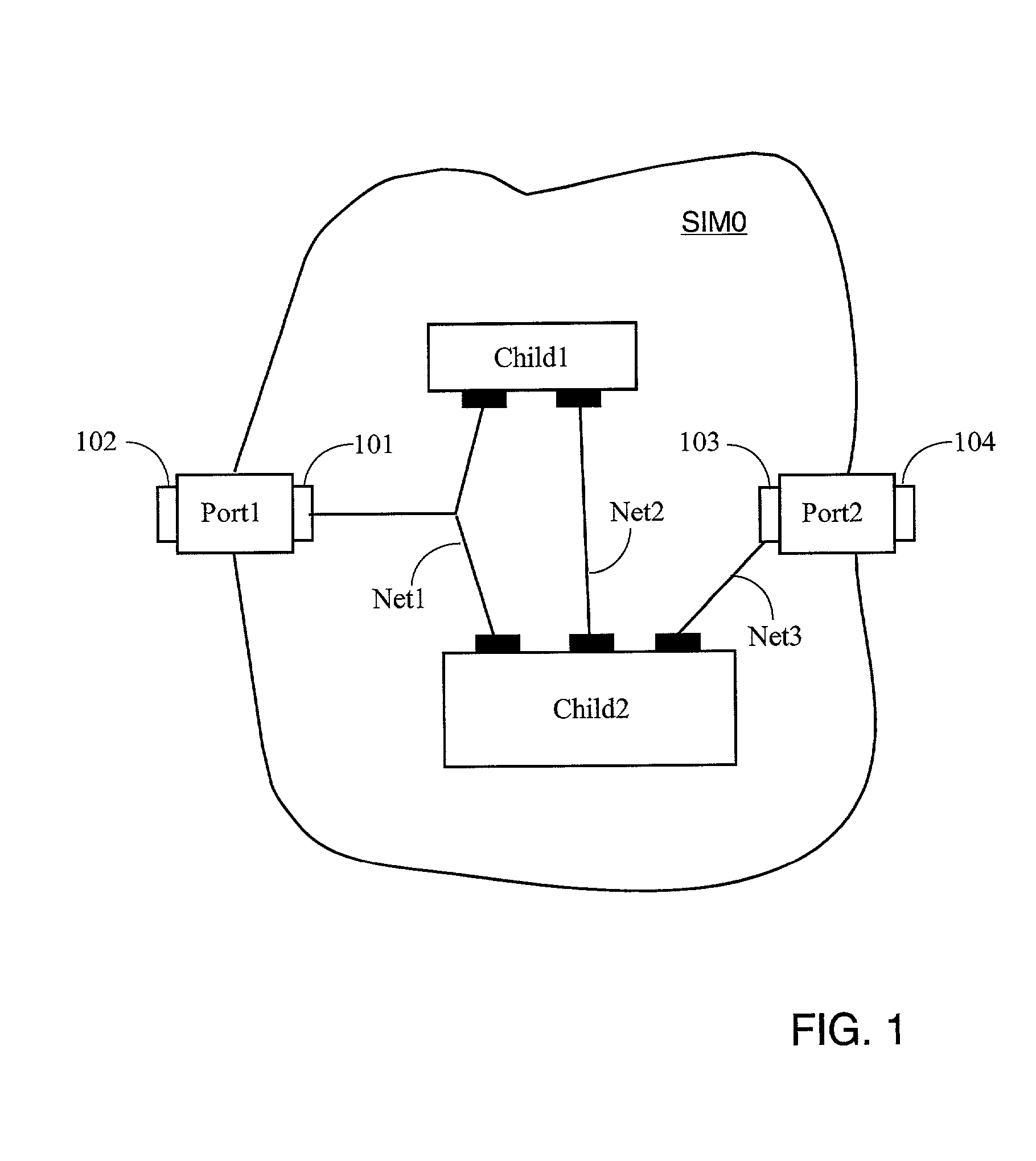
[0156] FIG. 2 shows a partial listing 200 of a SIM called X4keAdderxWReg, which illustrates some of the concepts discussed above. In particular, in the example of FIG. 2 it is seen that the width of the adder is established only when an instance of class X4keAdderxWReg is actually instantiated, by calling the constructor of this class. Therefore, the adder implementation is independent of the adder width. The listing shows three ports, "a", "b", and "sum". The listing also shows two internal nets, "cy" and "clsum". One or more instantiations of SIM "CY4" are then added, the number of child SIMs incorporated depending on the "sampleWidth" width parameter set when the adder SIM is instantiated. In this example, CY4 is a carry logic module for Xilinx XC4000 Series FPGAs and is set to functional mode "ADD-FG-CI". Partial listing 200 illustrates static parameter passing as implemented in programming languages such as Java or C. For example, in FIG. 2, the "sampleWidth" parameter is passe...
planner examples
[0248] FIGS. 18-25 show several examples of Planners using a variety of algorithms.
[0249] FIG. 18 shows a Planner 1800 that cycles through a series of precomputed shapes. The SIM designer or user may have created several implementations and stored them in the SIM's PlaceInfo object. The simple Planner in FIG. 18 cycles through all available implementations, scores each implementation according to a predetermined scoring scheme, and selects the implementation with the best score.
[0250] FIGS. 19 and 20 show a Planner called "RowPlanner" that is a special-purpose linear Planner. (The Planner comprises the code 1900 of FIG. 19 followed by the code 2000 of FIG. 20.) For a SIM that implements a data path, the constituents are often laid out in a simple linear arrangement. The Planner in FIGS. 19 and 20 performs the layout of such a structure, placing the constituent SIMs in a row. Note that the constituent SIMs need not be identical, nor of the same size. The analogous column Planner ("Co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com