Method of and apparatus for molding multi-layer polymer plastic articles having inner, outer and interior or core layers, with control of relative volumetric flow rates of the inner and outer layers enabling relative shifting of the position of the core layer and control of the relative thickness of the inner and outer layers in the molded articles
a multi-layer polymer and plastic article technology, applied in the direction of food shaping, dough shaping, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of uneven penetration of the leading edge of the interior core, particularly severe, and affecting the uniform penetration of the interior cor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
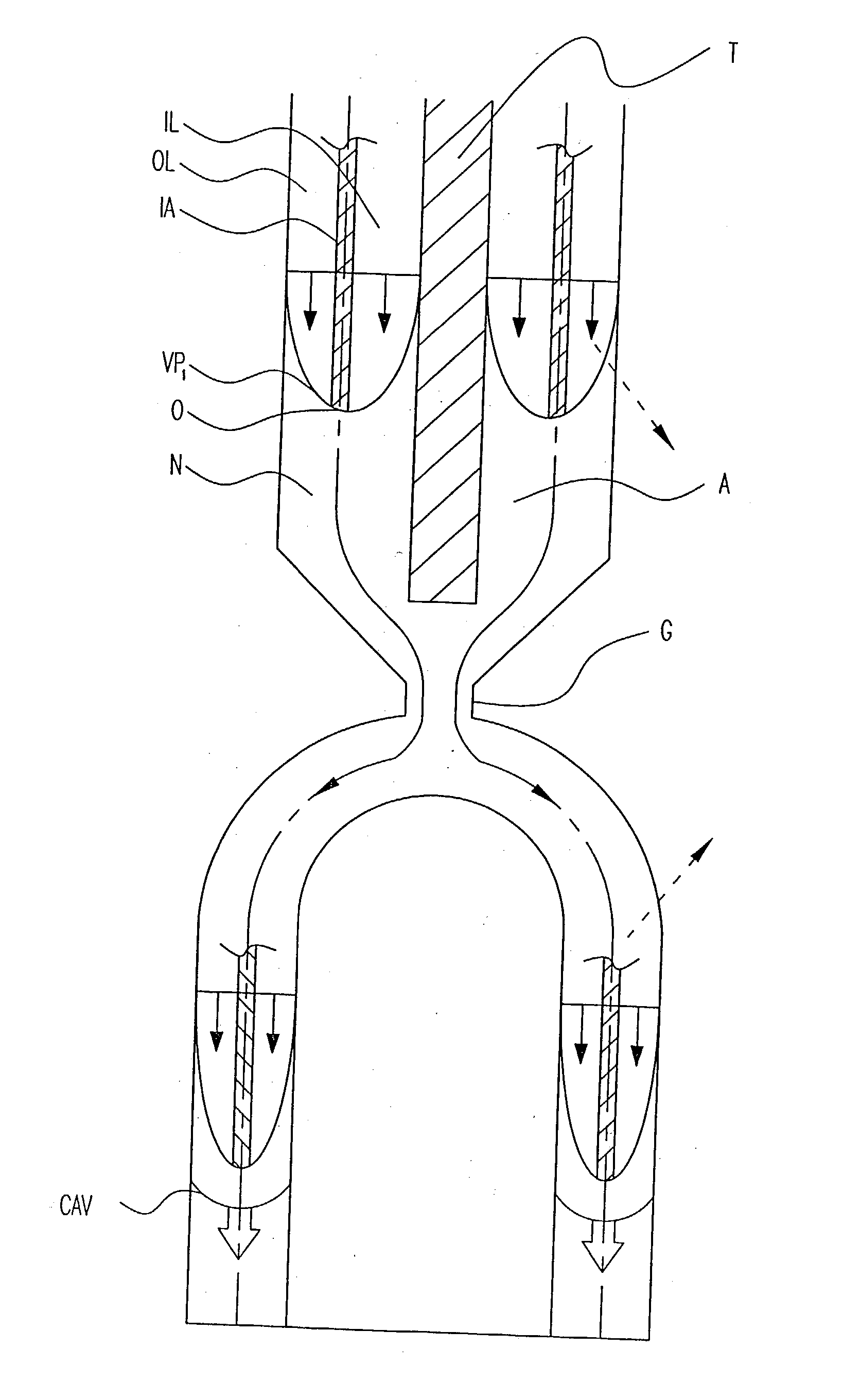
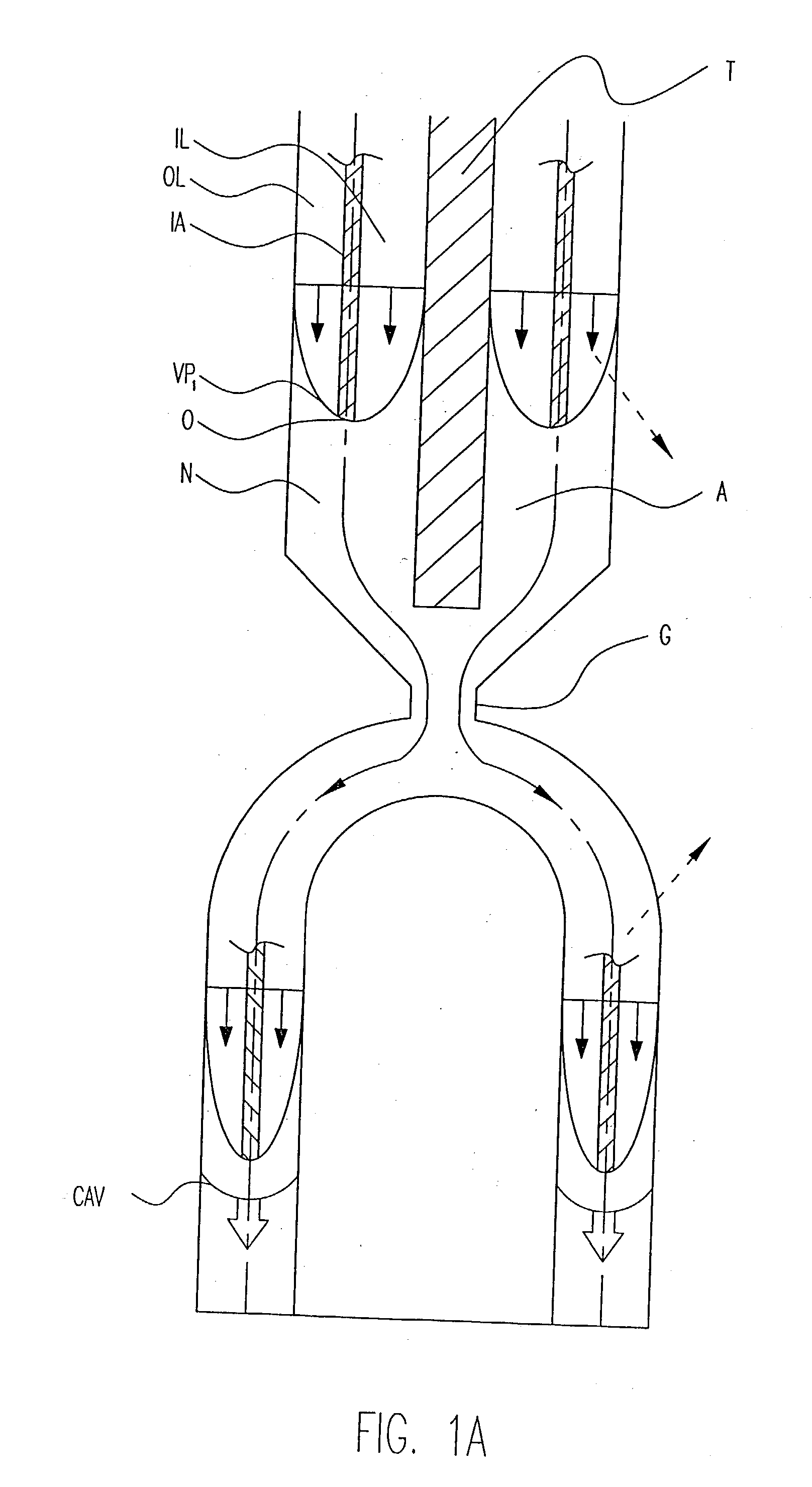
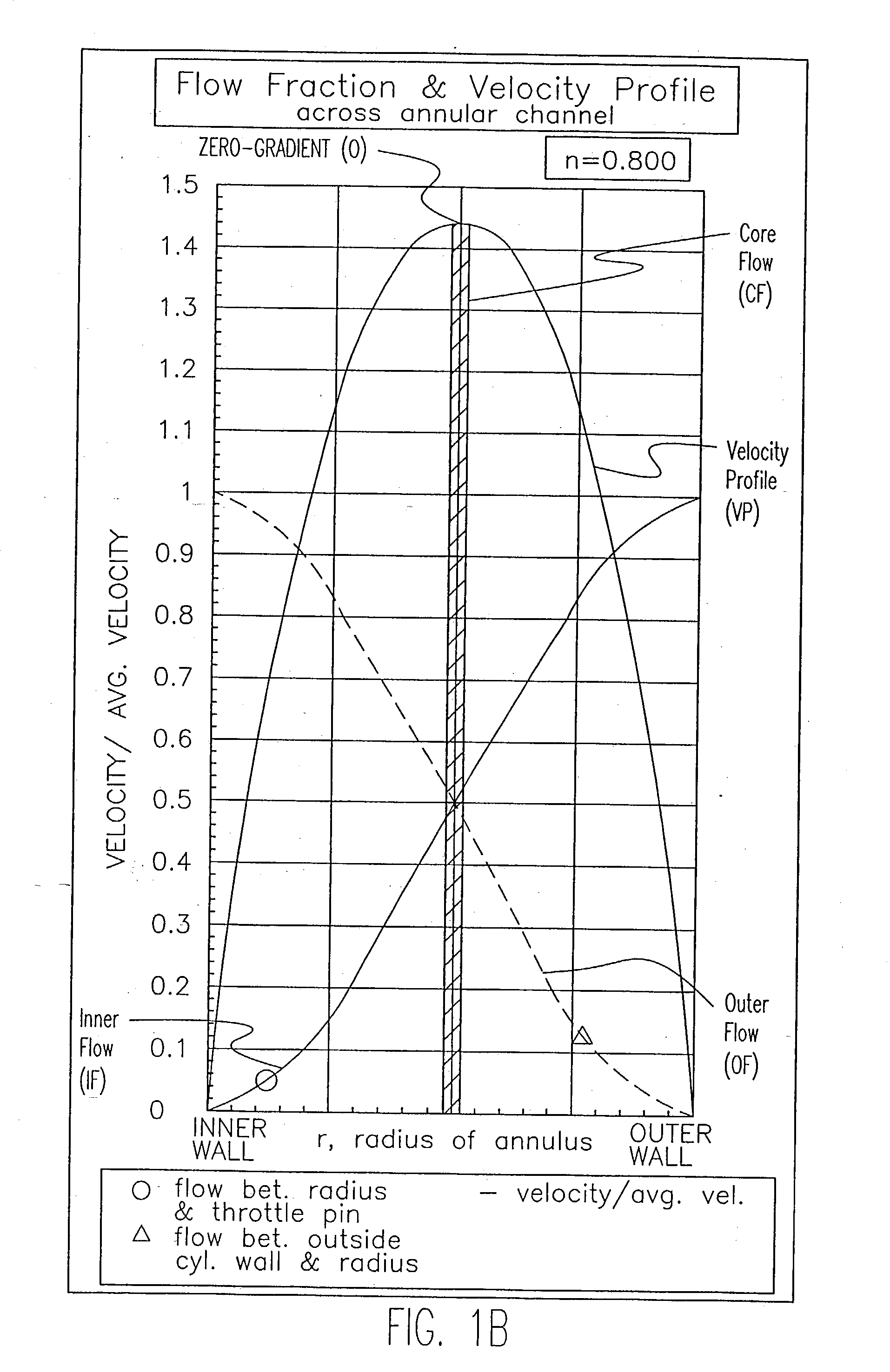
[0037] In my before-referenced prior co-extrusion patent, at least two-polymer plastic materials are provided as a 3-layer combined flow stream; a first material L which forms the ultimate outer and inner molded covering layers of the ultimate molded product, article or part from the inner and outer flow stream layers (IL and OL), injected as annular streams; and a second material (I) which forms the middle, inner or interior core of the product formed from an injected concentric annular interior stream (IA) encased within the inner and outer annular stream layers of the covering material.
[0038] The preferred apparatus employs a multiple-plastic stream co-extruder as for injection molding cavities in which the extruder is internally provided therewithin and therealong with a restrictor or throttle pin, rod or element that forces combined plastic materials streams, formed with an interior core stream encased in outer and inner stream layers, into corresponding concentric co-extensive...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volumetric flow rates | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexibility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| penetration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com