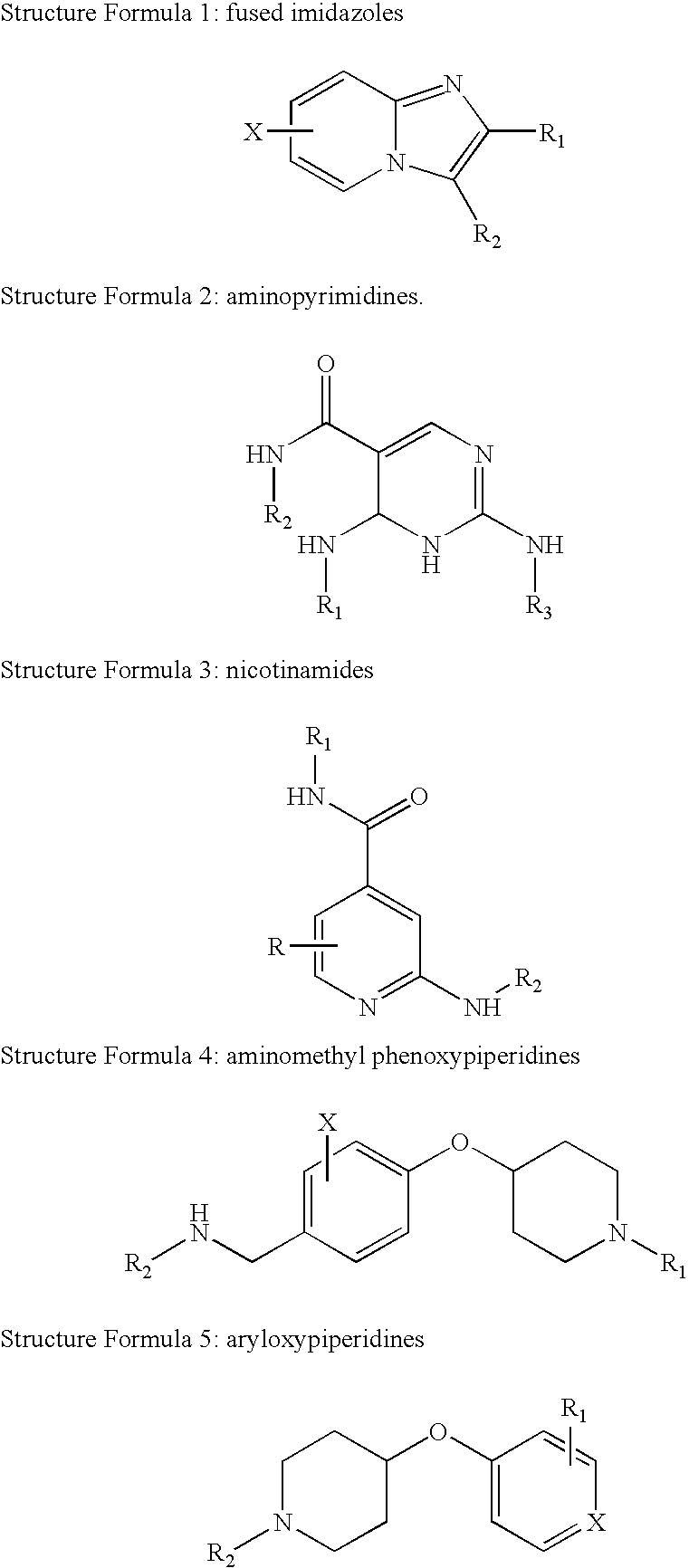
Method for discovering neurogenic agents
a neurogenic agent and method technology, applied in the field of neurogenic agent discovery, can solve the problems of poor plating efficiency, inhibition of neurogenesis, interference with assay,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0117] Selection of a positive control.
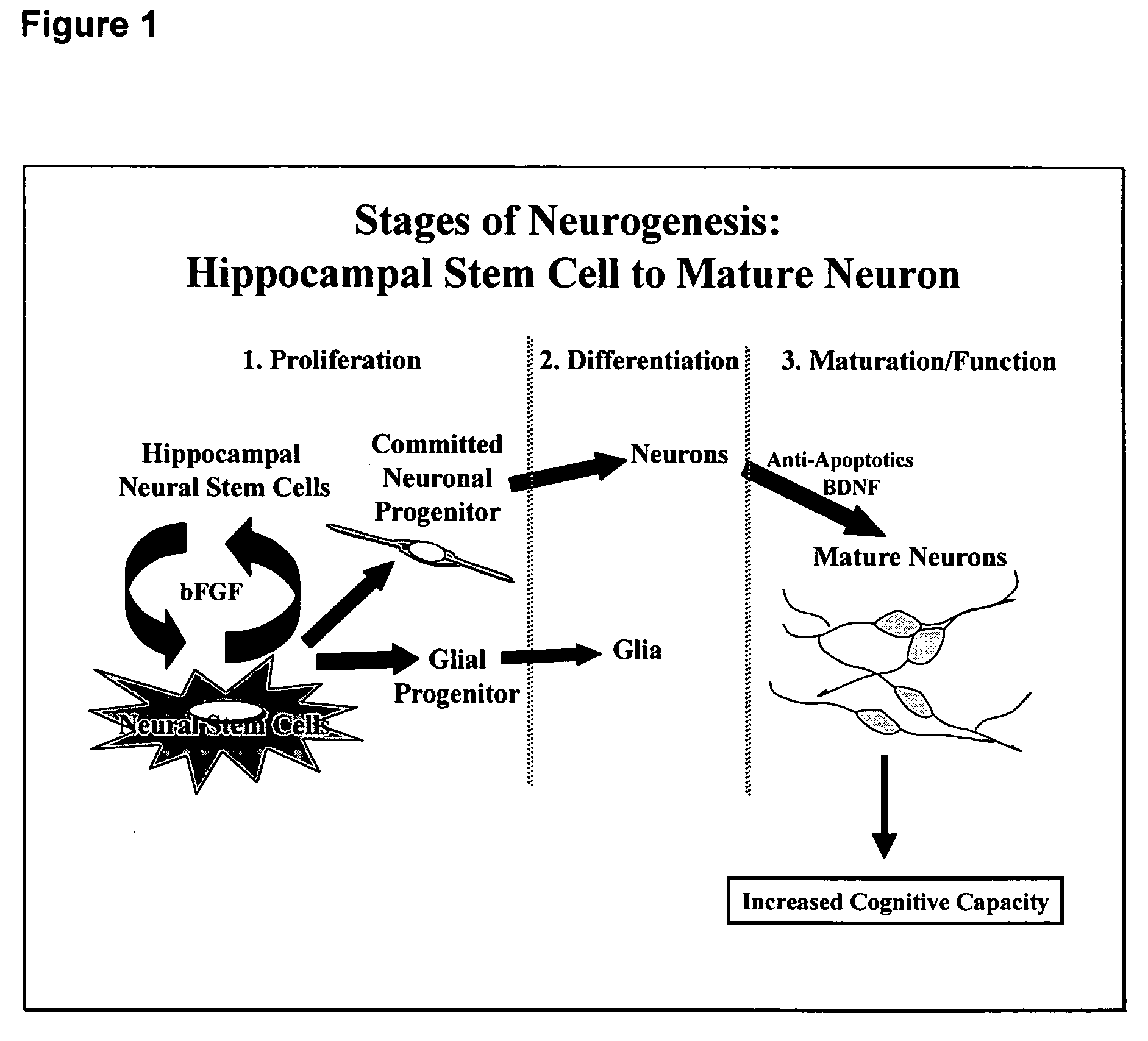
[0118] Several neurotrophic factors--including brain-derived neurotrophic factor, glia-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophic factor-3, and leukemia inhibitory factor--suggested to have neurogenic properties were tested in the assay described above. Only one (leukemia inhibitory factor) was effective (FIGS. 3A and 3B). Thus, the assay can discriminate test agents for selectively having a neurogenic activity. The positive control utilized is leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), a cytokine growth factor, at 20 ng / ml. The selection of LIF as the positive control is based on its properties to increase by 2-3 fold the number of neurons and glia. This effect validates both the neural stem cell system, in which, should a compound be effective in neurogenesis, the cells respond appropriately by enhanced differentiation and / or mitosis, and the assay method in which such cellular responses can be measured reproducibly and quantifiably.
example 2
[0119] Primary screening of unknown compounds.
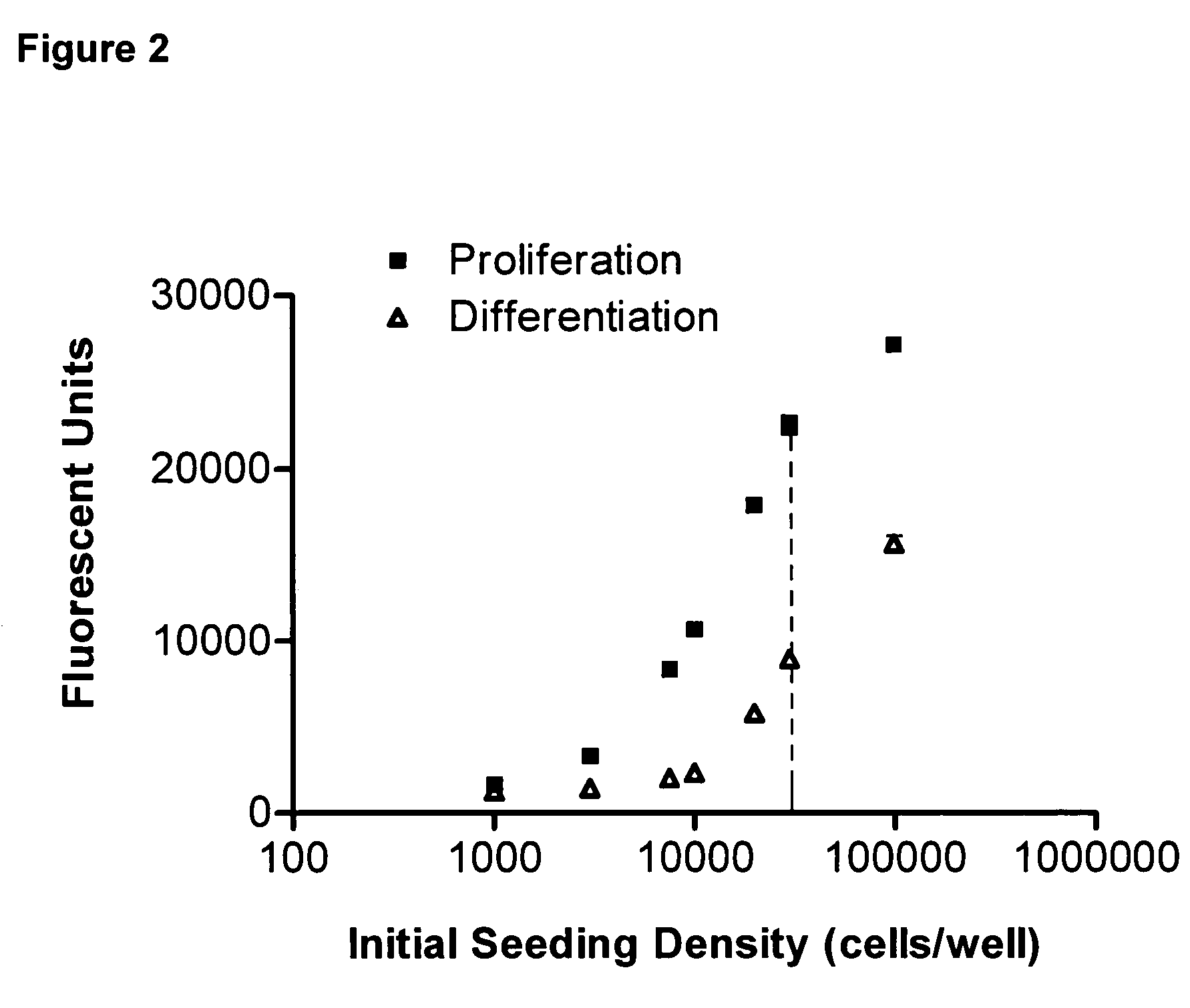
[0120] 5,628 synthetic compounds of the type Fused Imidazoles, Aminopyrimidines, Nicotinamides, Aminomethyl Phenoxypiperidines and Aryloxypiperidines are evaluated for their effect on neurogenesis according the assay method described above. From the preliminary analysis using the fluorescent plate reader, over 300 compounds to date showed initial positive activity. Those were re-analyzed by quantitative neuron counting. Among them, 30 compounds significantly increased cell number ("proliferation", FIG. 4); 53 increased the number of neurons ("neurogenesis", FIG. 5 & FIG. 6); and 7 showed significant activity in both. The significance level was empirically set at an activity above 30% change over the vehicle control for proliferation and above 10% change for neurogenesis. A summary of the result in the compound screening is provided in Table I.
1TABLE I Summary of Compound Screening Primary Hits Proliferation Neurogenesis Double Screen Con...
example 3
[0121] Dose-response profiles.
[0122] Linearity of dose-response and in vitro neurotoxicity are used to further filter down desired compounds from the primary screen. The dose-response curve measures neurogenesis over a concentration range of 100 picaM to 100 microM. The rationale for this is to eliminate early on those compounds with pronounced toxicity and those without a dose-dependent effect on neurogenesis. Examples of several primary hits fully analyzed for dose-response are shown in FIG. 7. Significantly, most compounds exhibit a linear response over several log concentrations below 1 microM. This indicates that the assay for primary screening is reliable and that the quality of the compound library is high. Table II contains the summary of EC50 of each compound tested. On the other hand, at high concentrations (100 microM), some, but not all showed high level of neurotoxicity, indicating that analyzing dose-response curves will be discriminatory and serve as an effective earl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com