Method of making pile fabric
a pile fabric and pile technology, applied in the directions of knitting, knotting, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of visual “break” in the surface coverage provided, undesirable surface coverage breakage, and uneven pile formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
The initial fiber samples of the invention in Samples A and B of Table 2 below were run using round polyester partially oriented yarn (POY), designated M-3M001, which was obtained from Nanya Plastics Company of South Carolina USA, according to the following conditions.
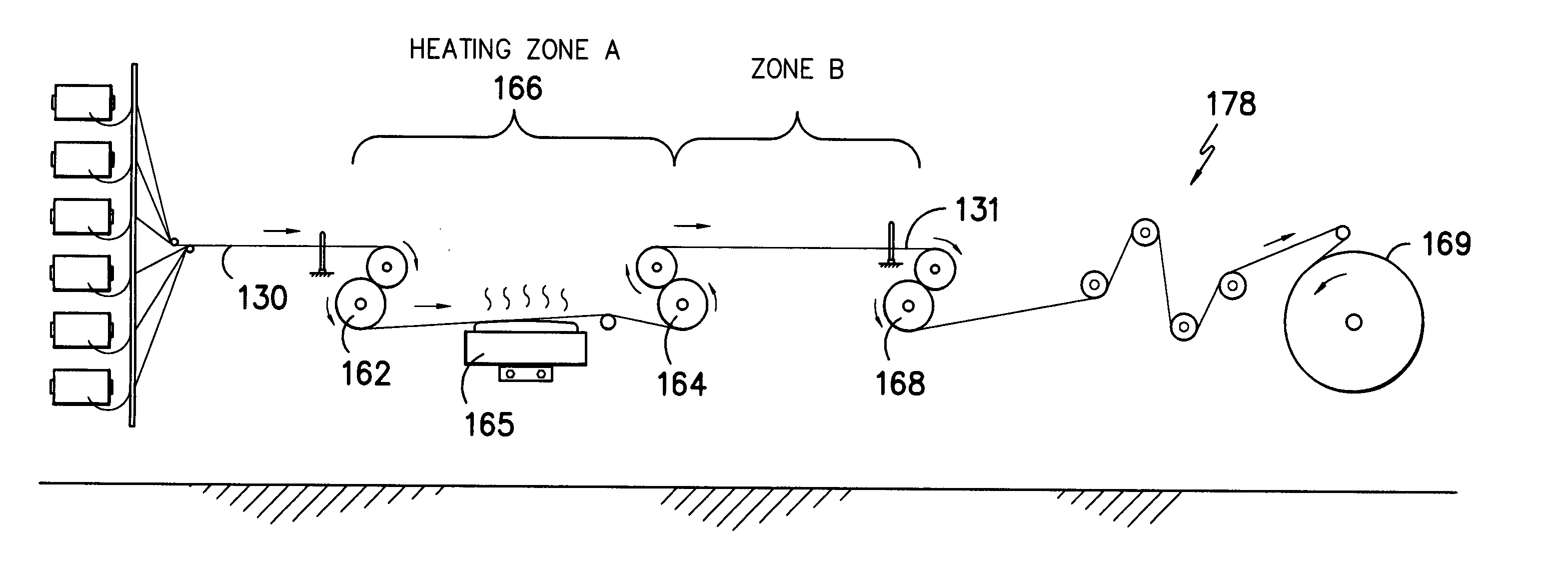
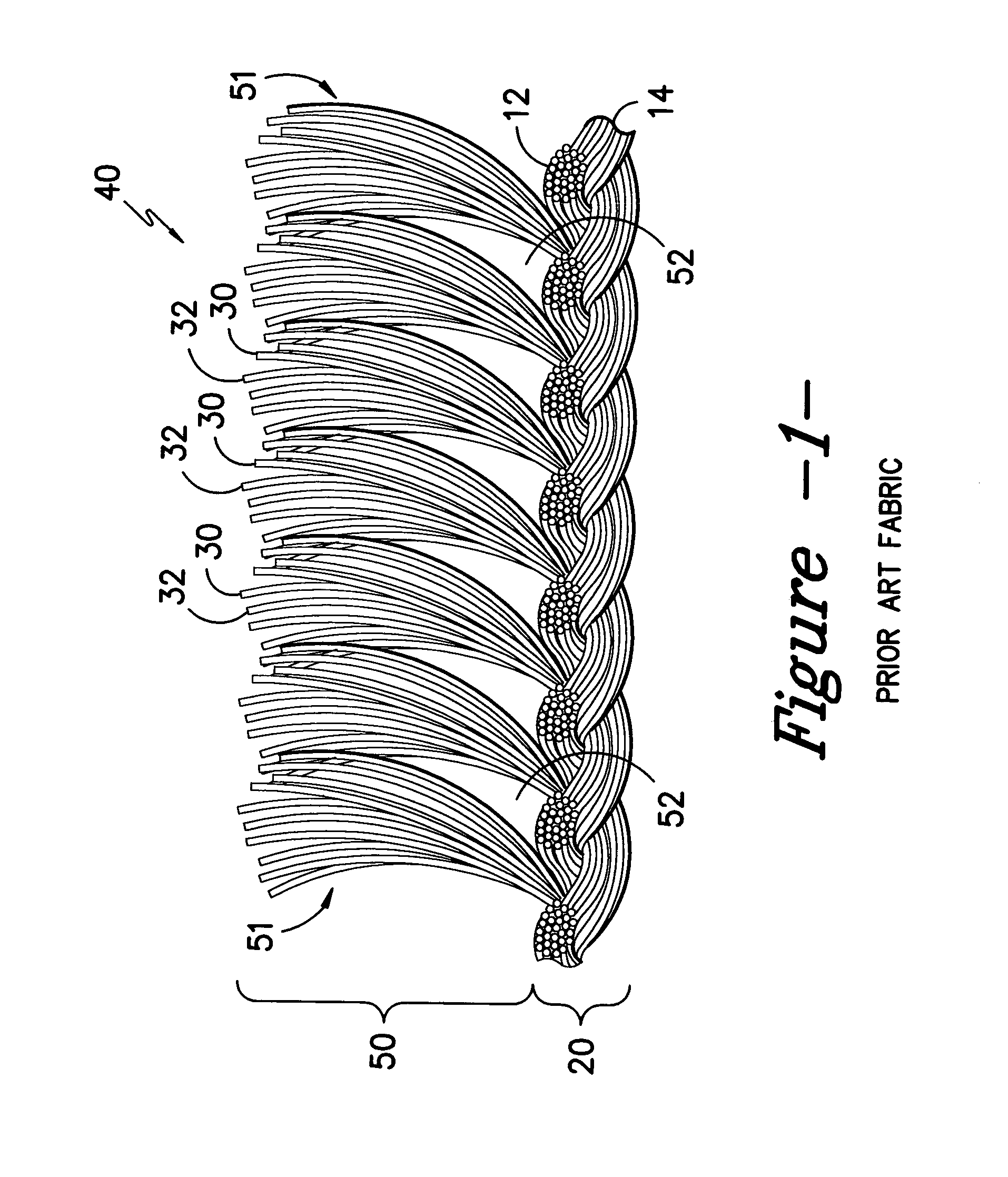
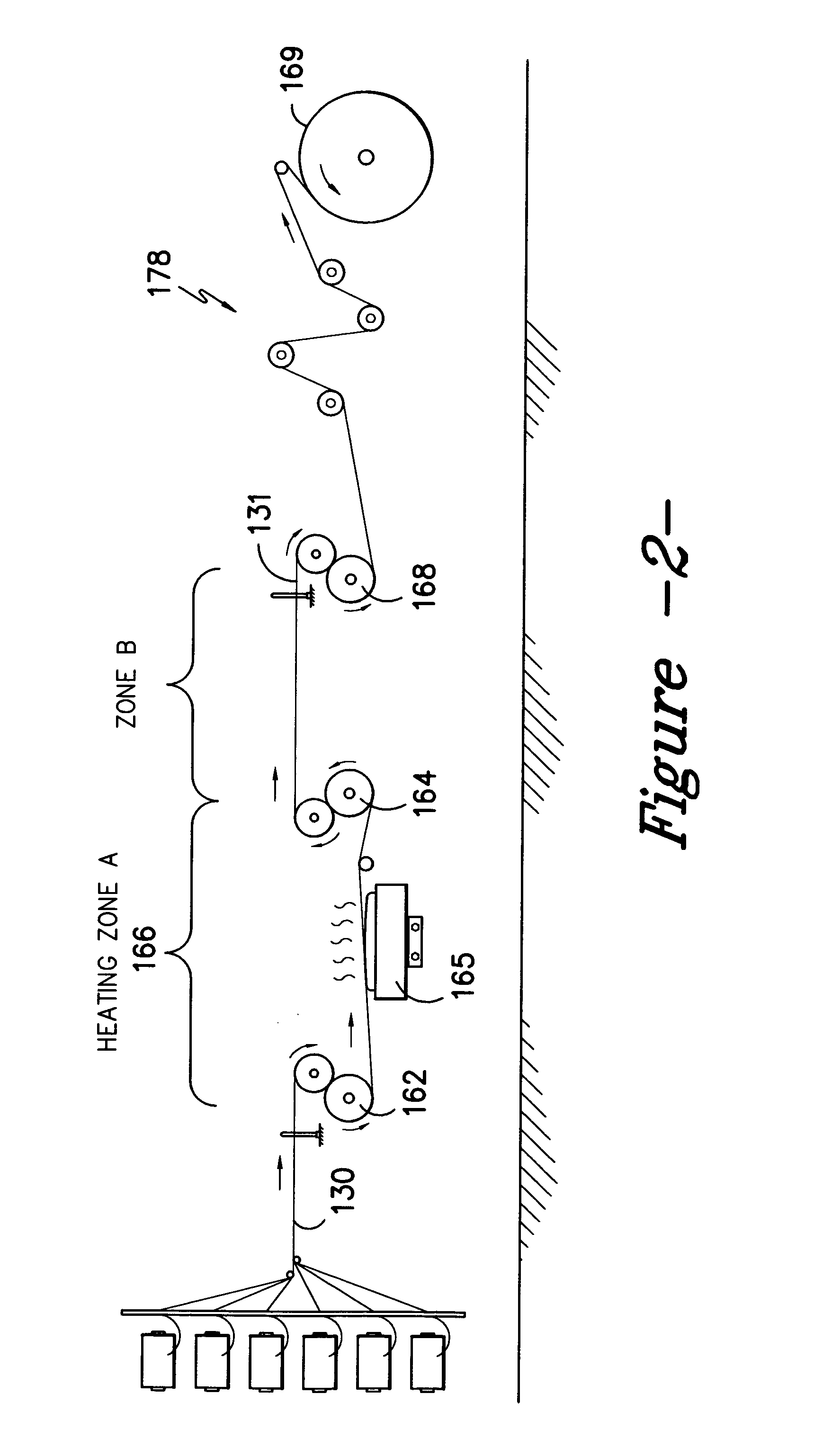
Formation and processing parameters for the fabrics of Samples A and B are set forth in Table 1 below. The knitting of each was accomplished upon a 32 Gauge Double Needle Bar Warp Knitting machine. The fabric was formed in a “sandwich” structure at a six bar construction with ground yarns (forming the fabric base) carried in bars 1, 2, 5 and 6 and pile yarns carried in bars 3 and 4. The pile-forming yarns were characterized by the meta stable state, due to the heat shock effects provided in the practice of the invention.
TABLE 1Formation and Processing ParametersBack Bar YarnBars 1 and 6(260) 212 / 36 semi-dull round polyesterRunner Length = 120.0″Mid Bar YarnBars 2 and 5(260) 150 / 36 semi-dull round polyesterRunner L...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com