Patents
Literature
271results about "Carpets" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
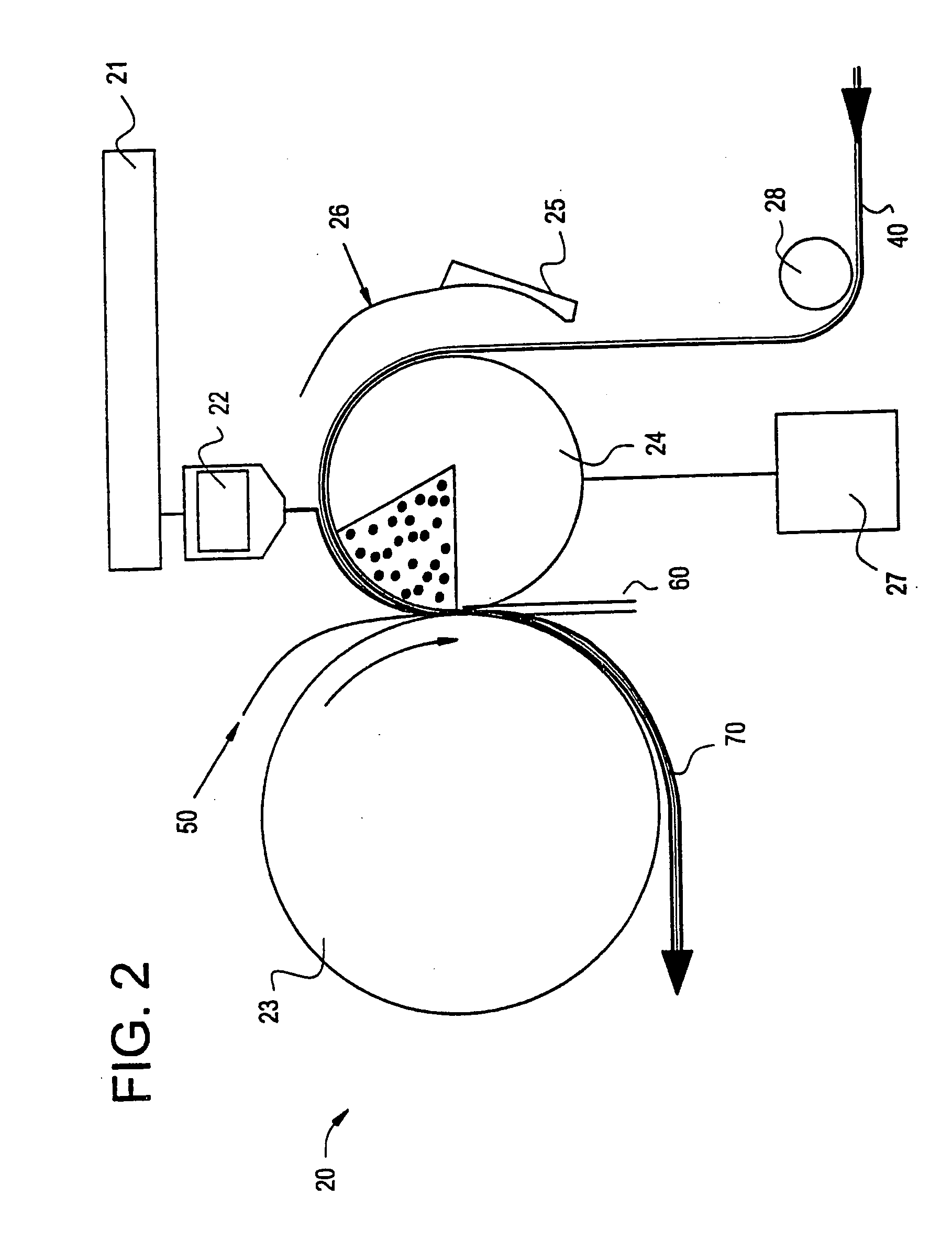
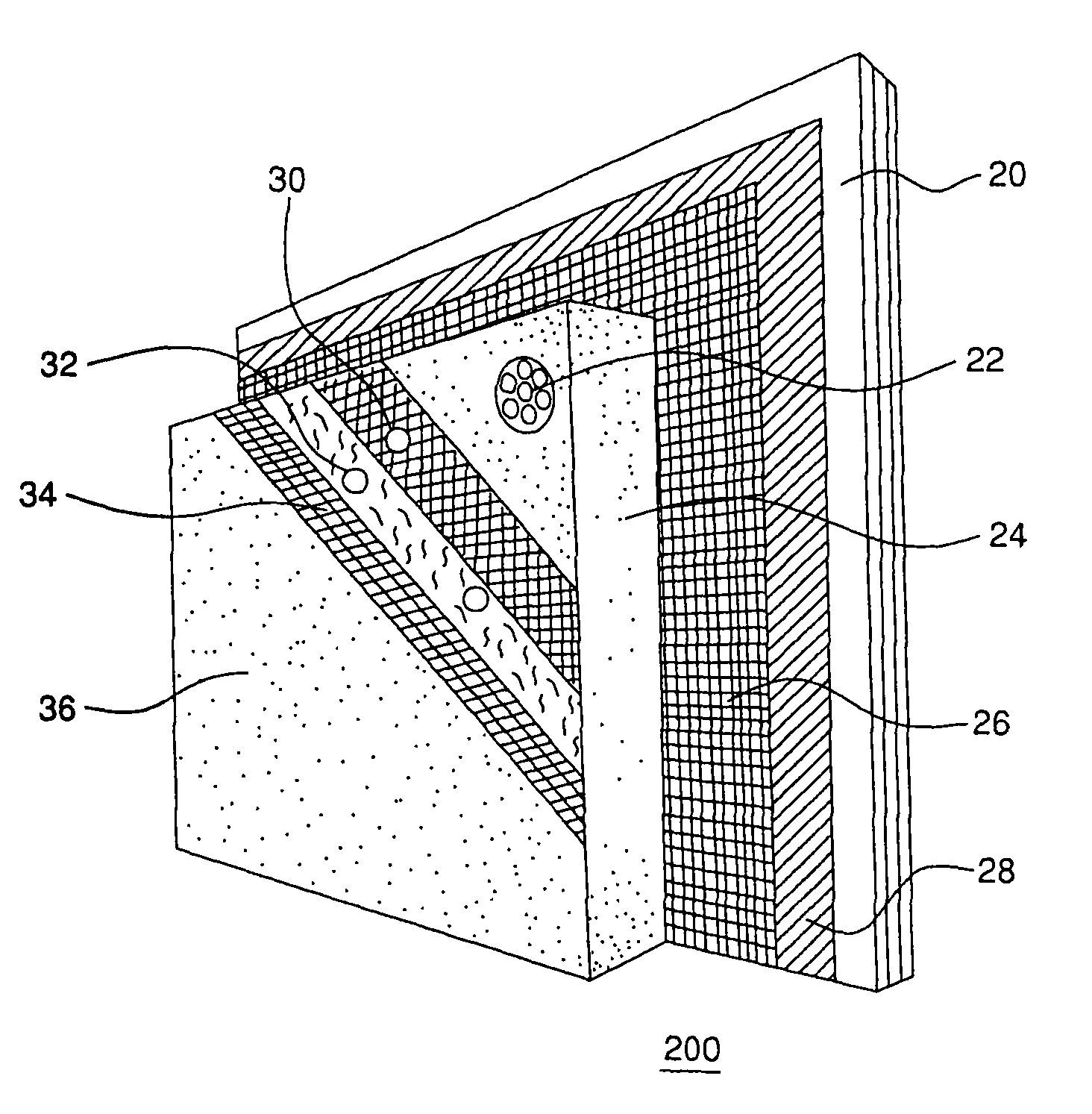
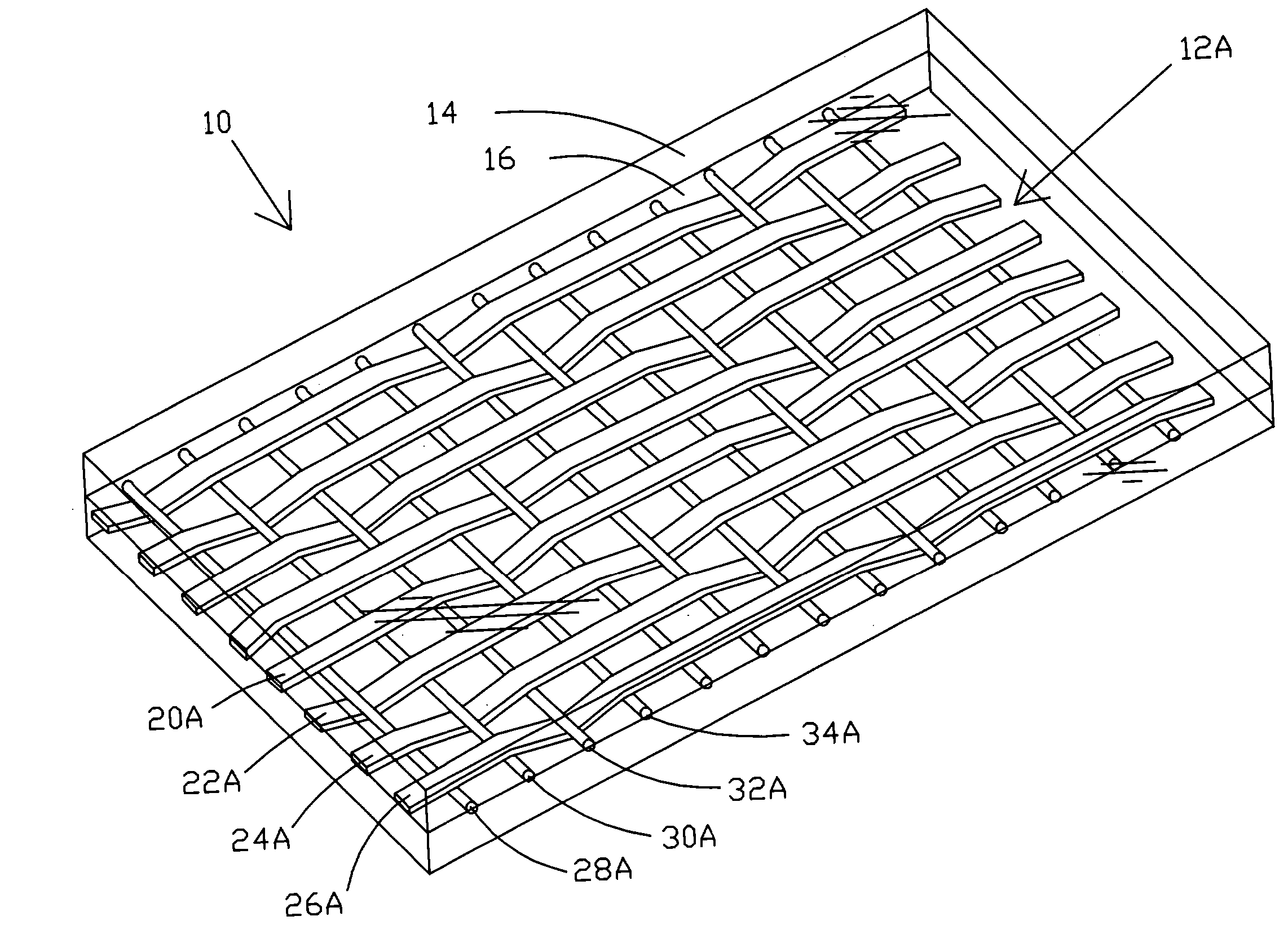
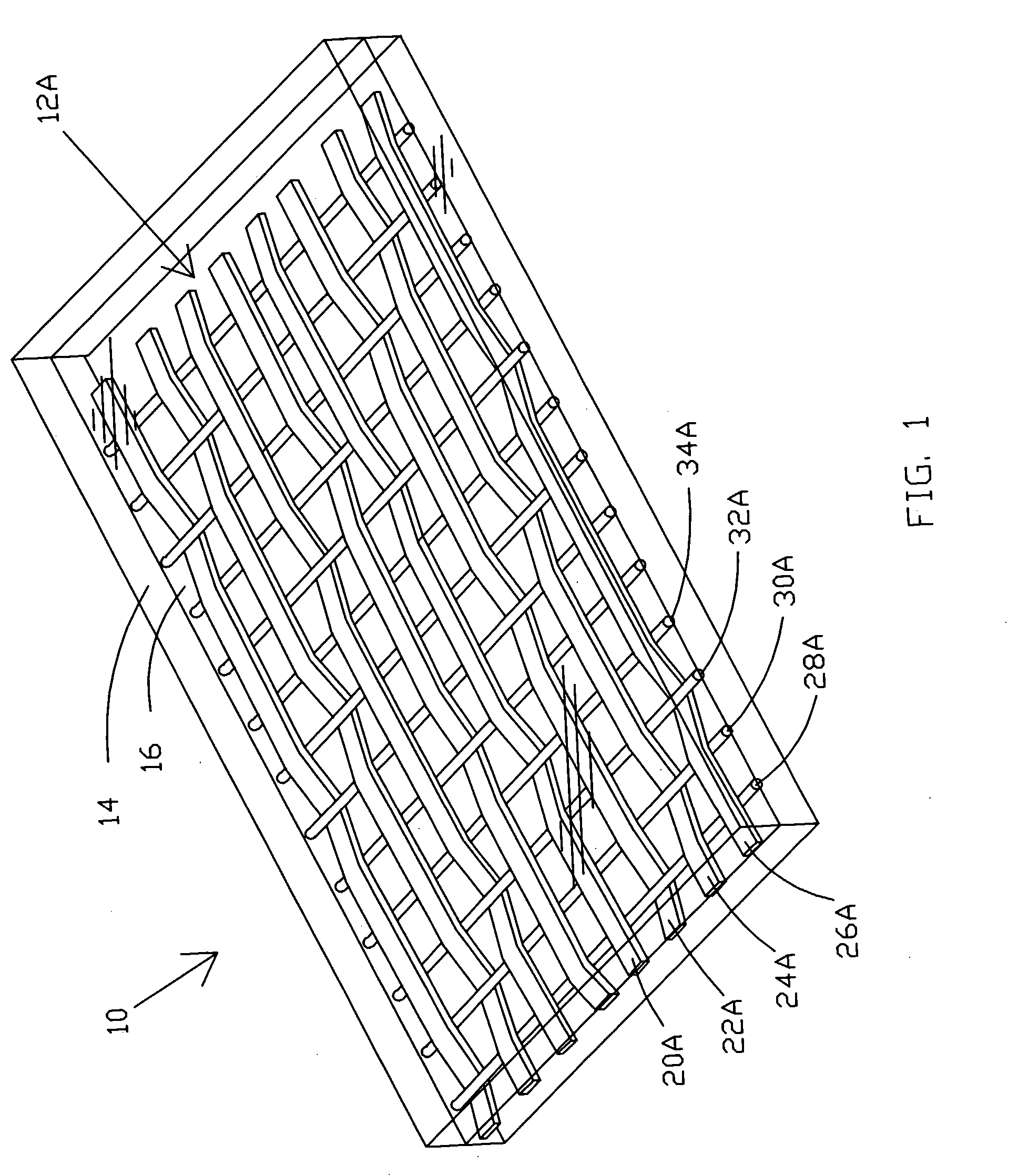
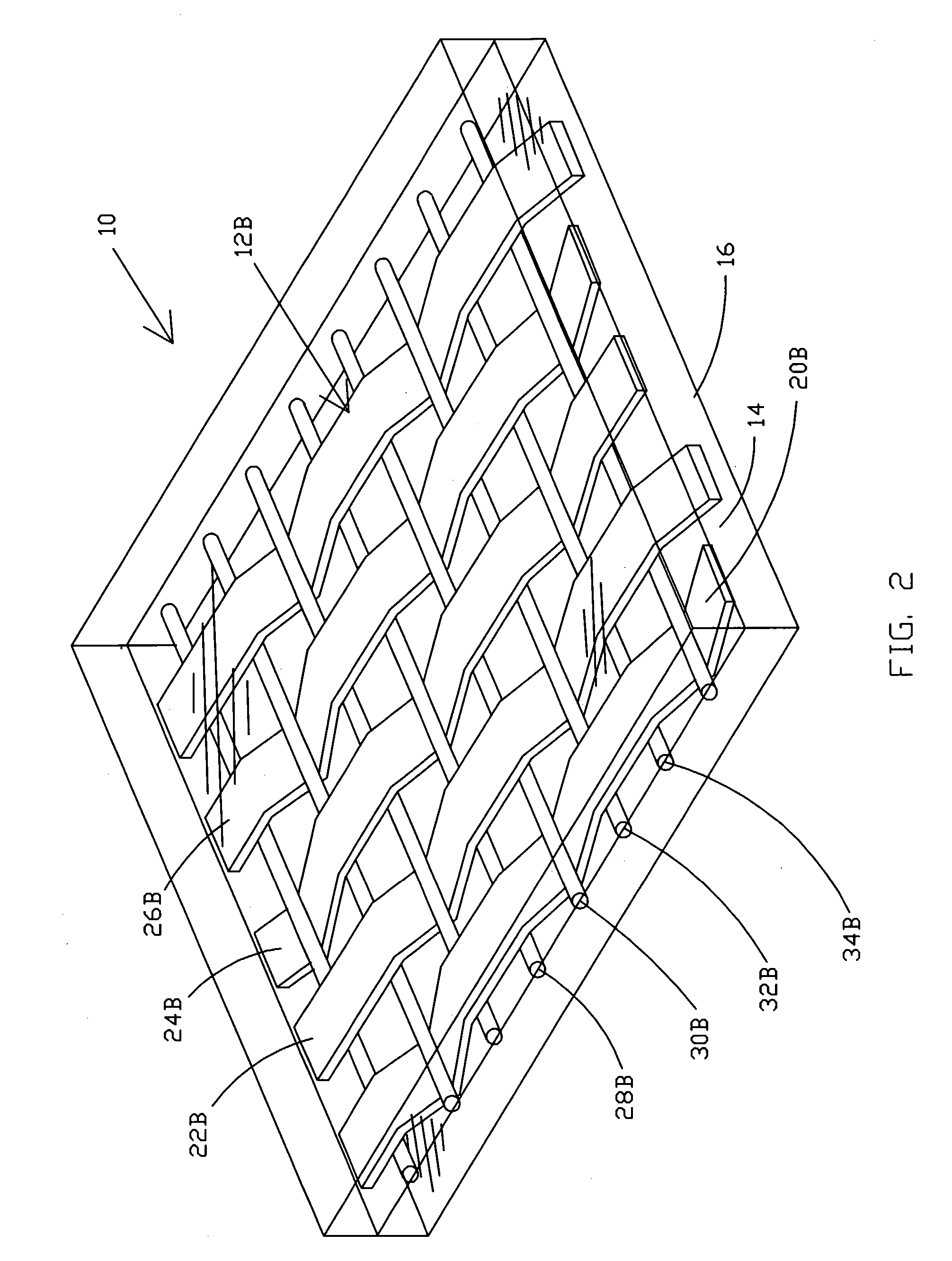
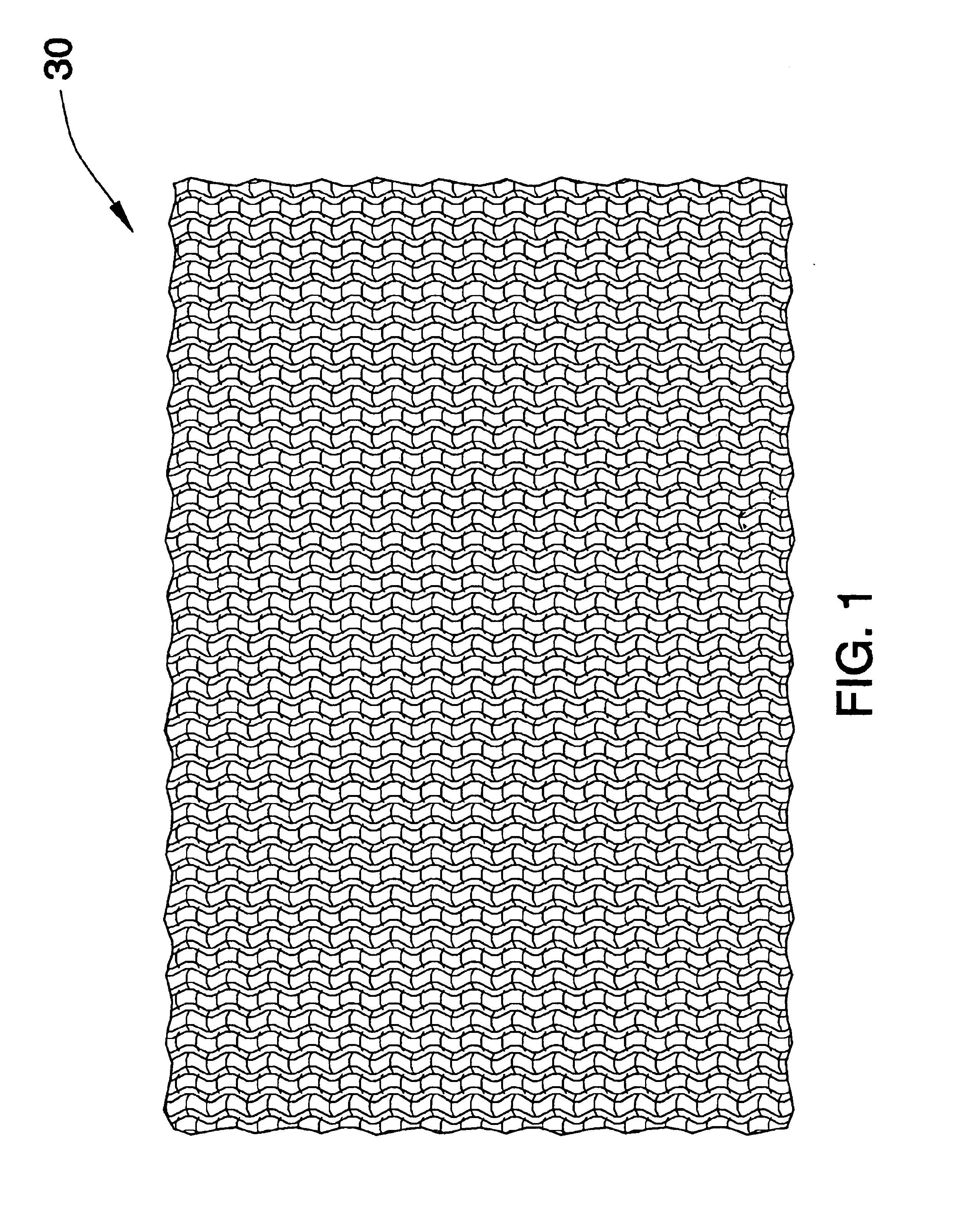
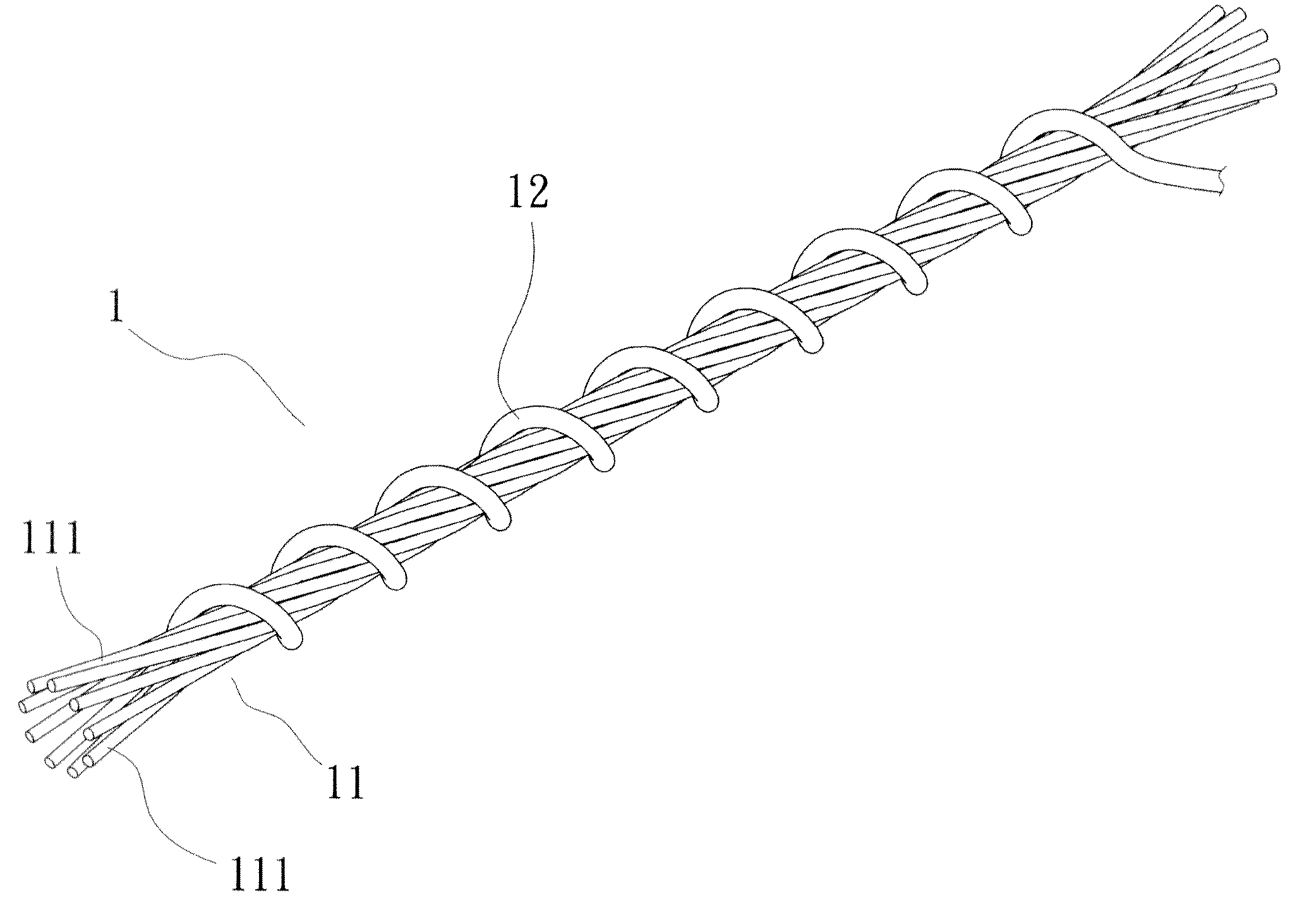
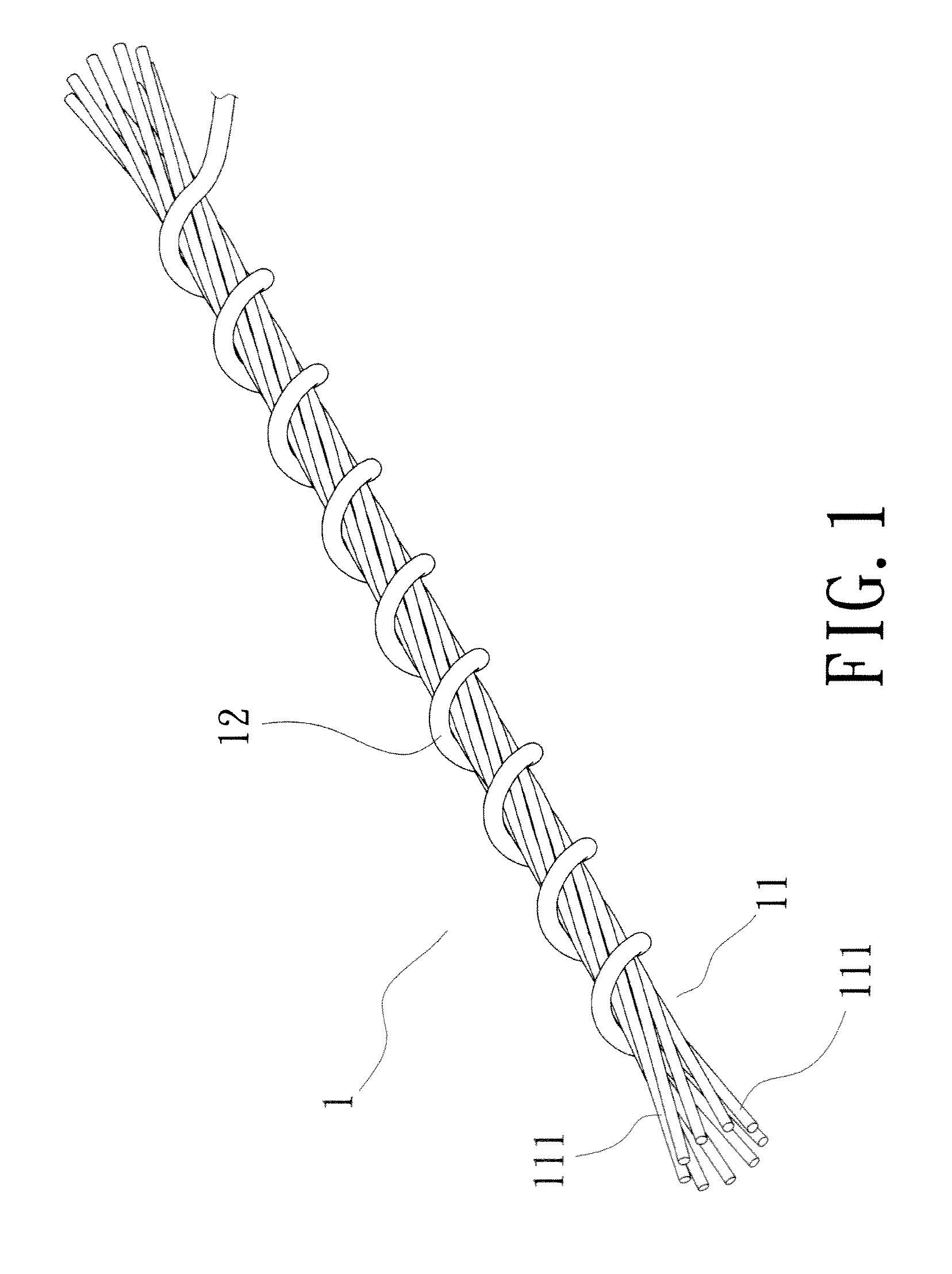
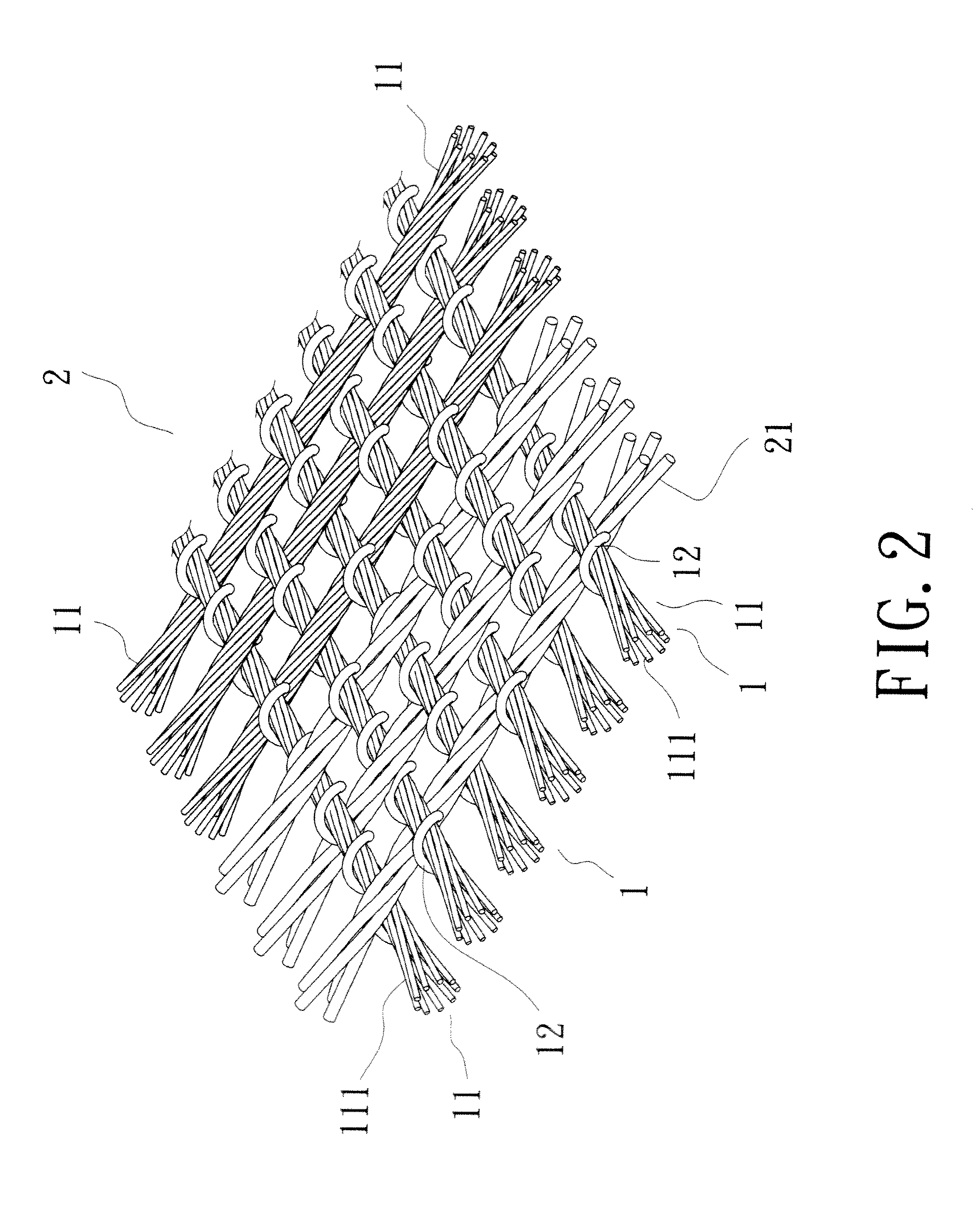
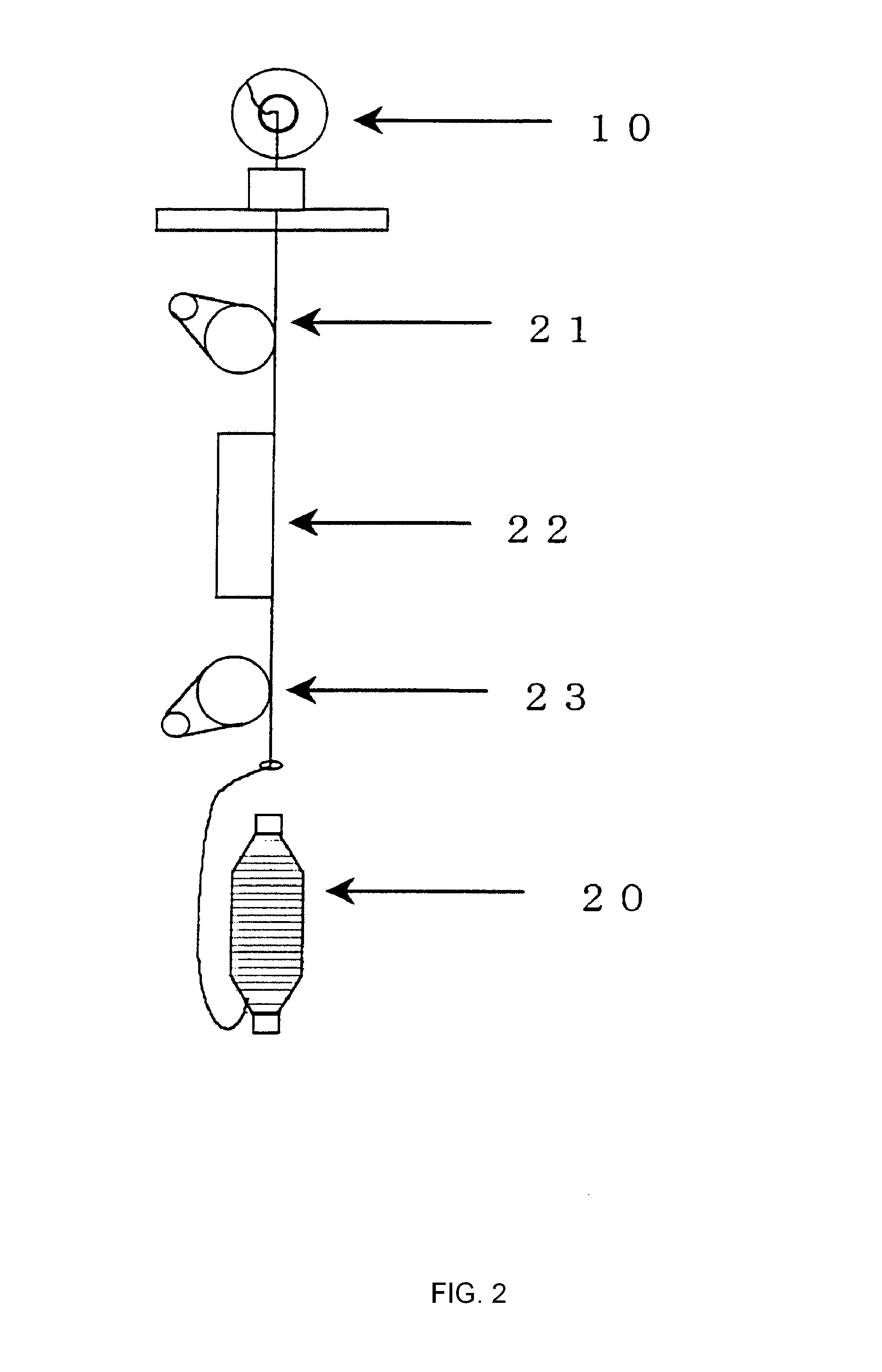
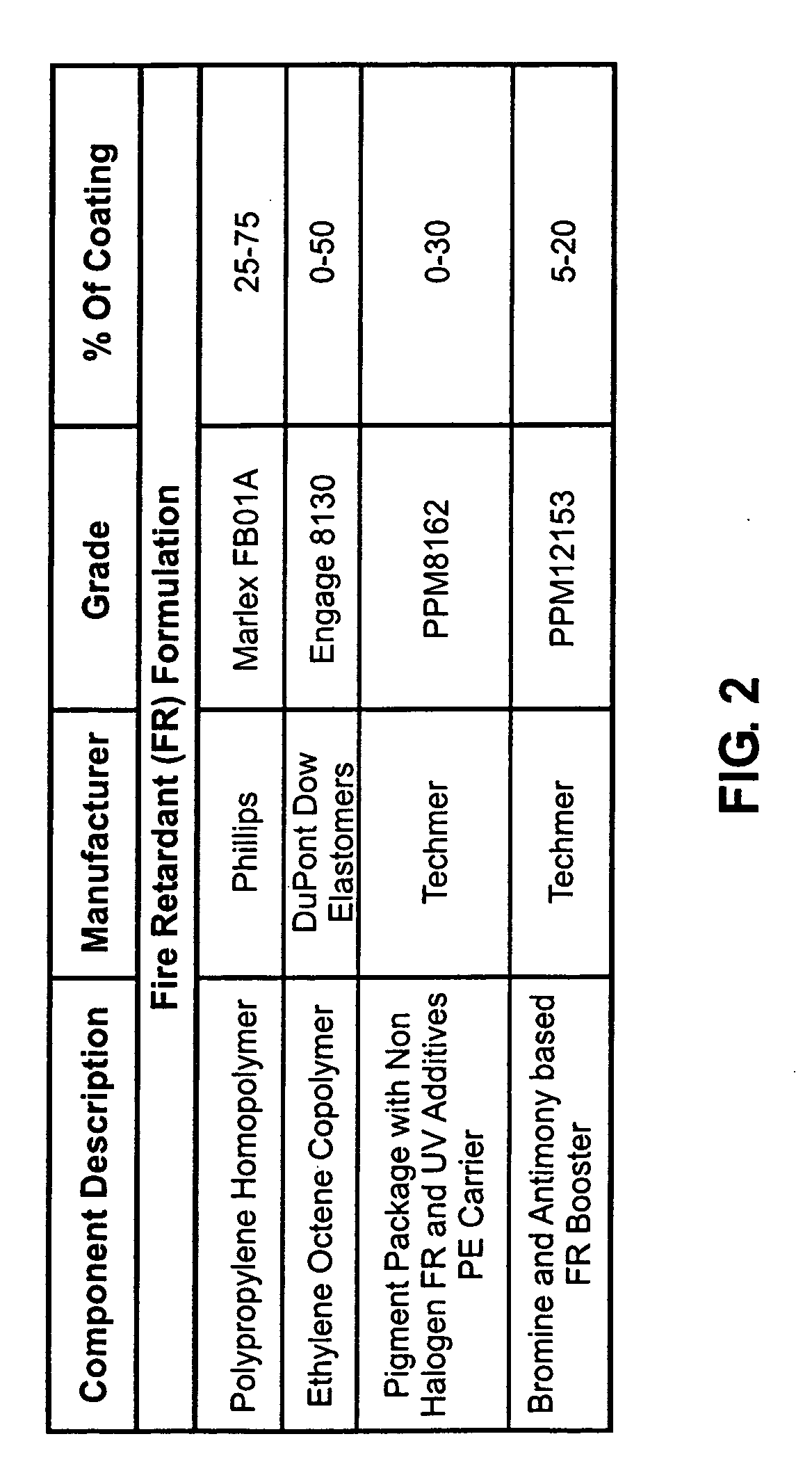
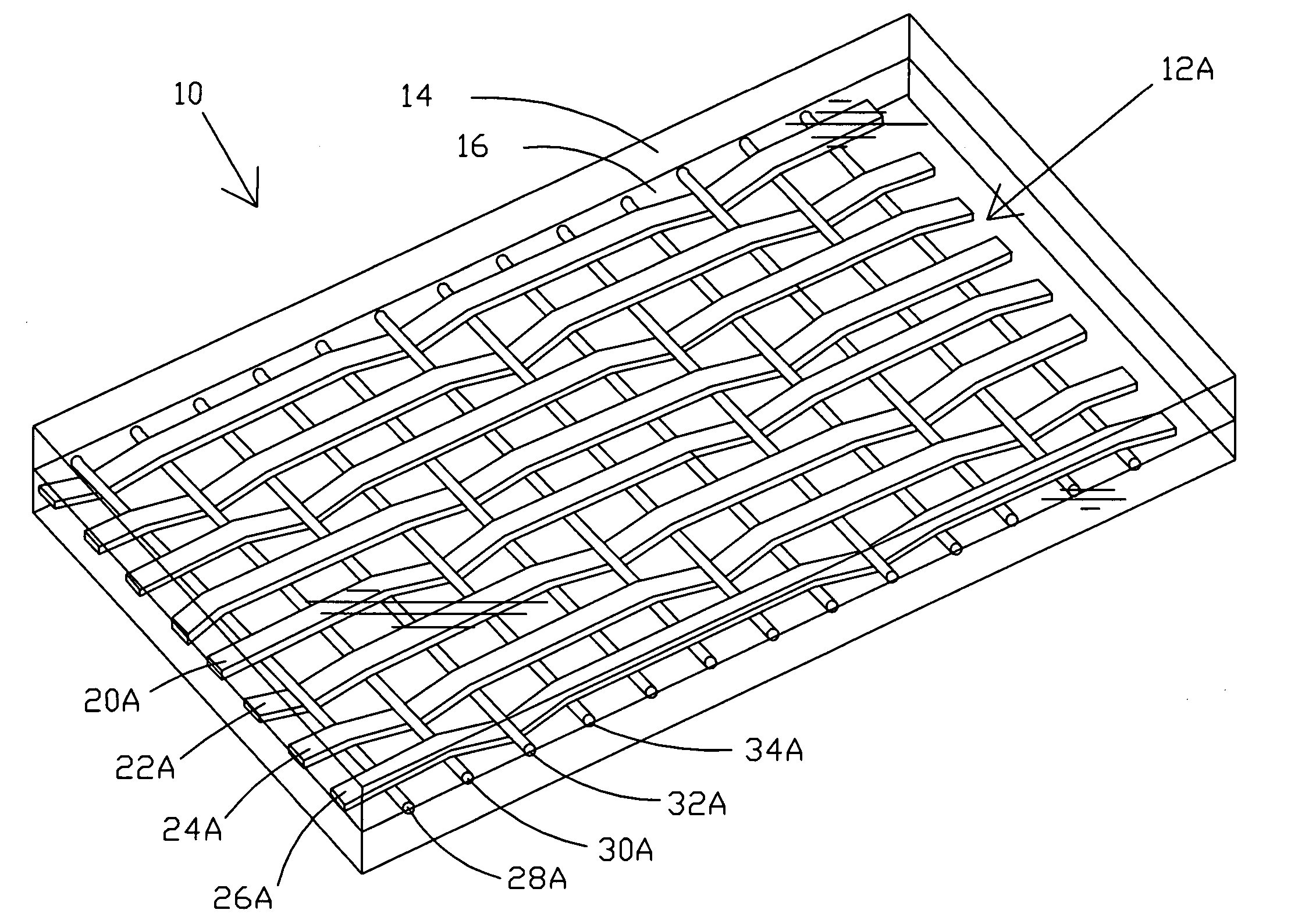
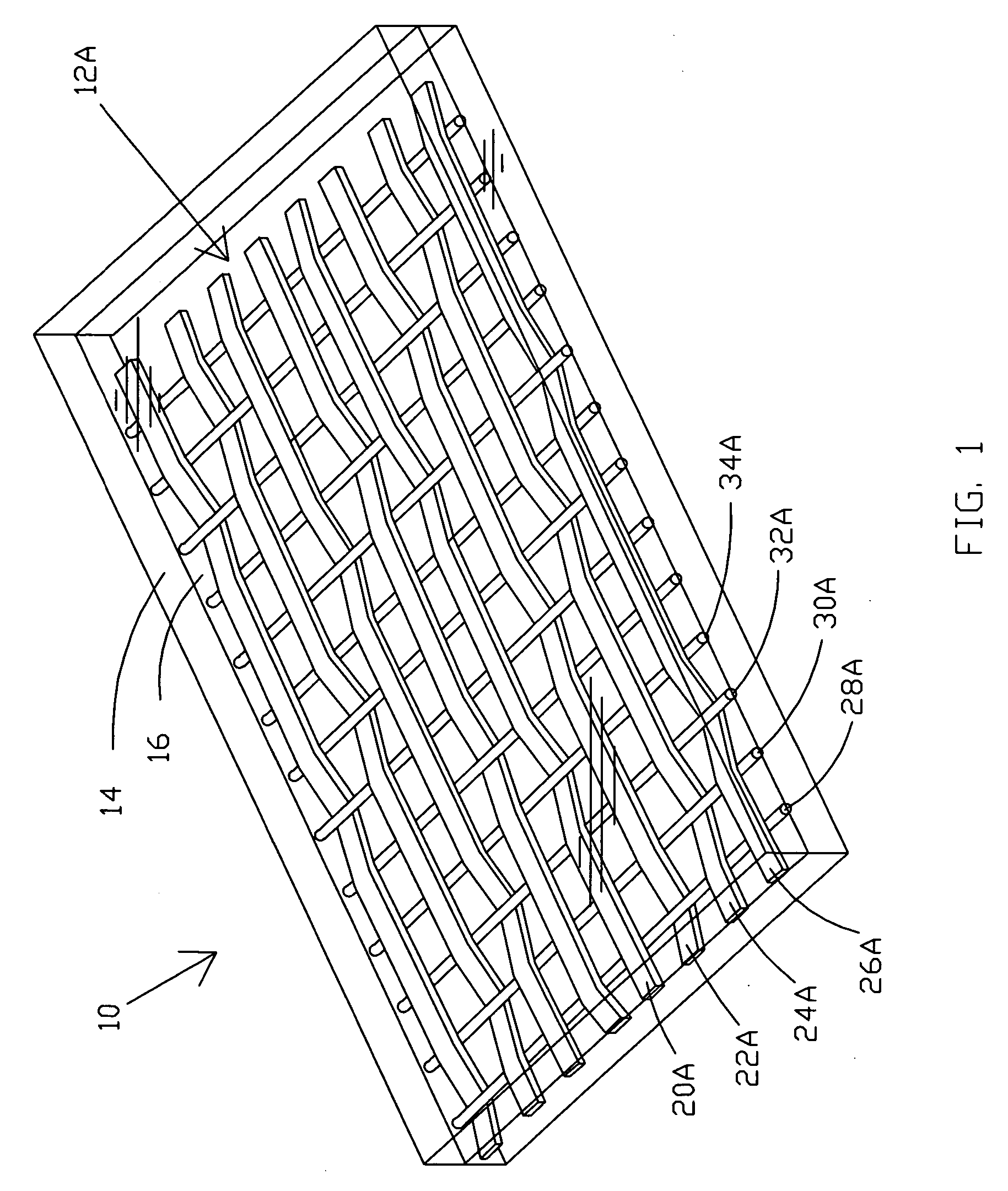
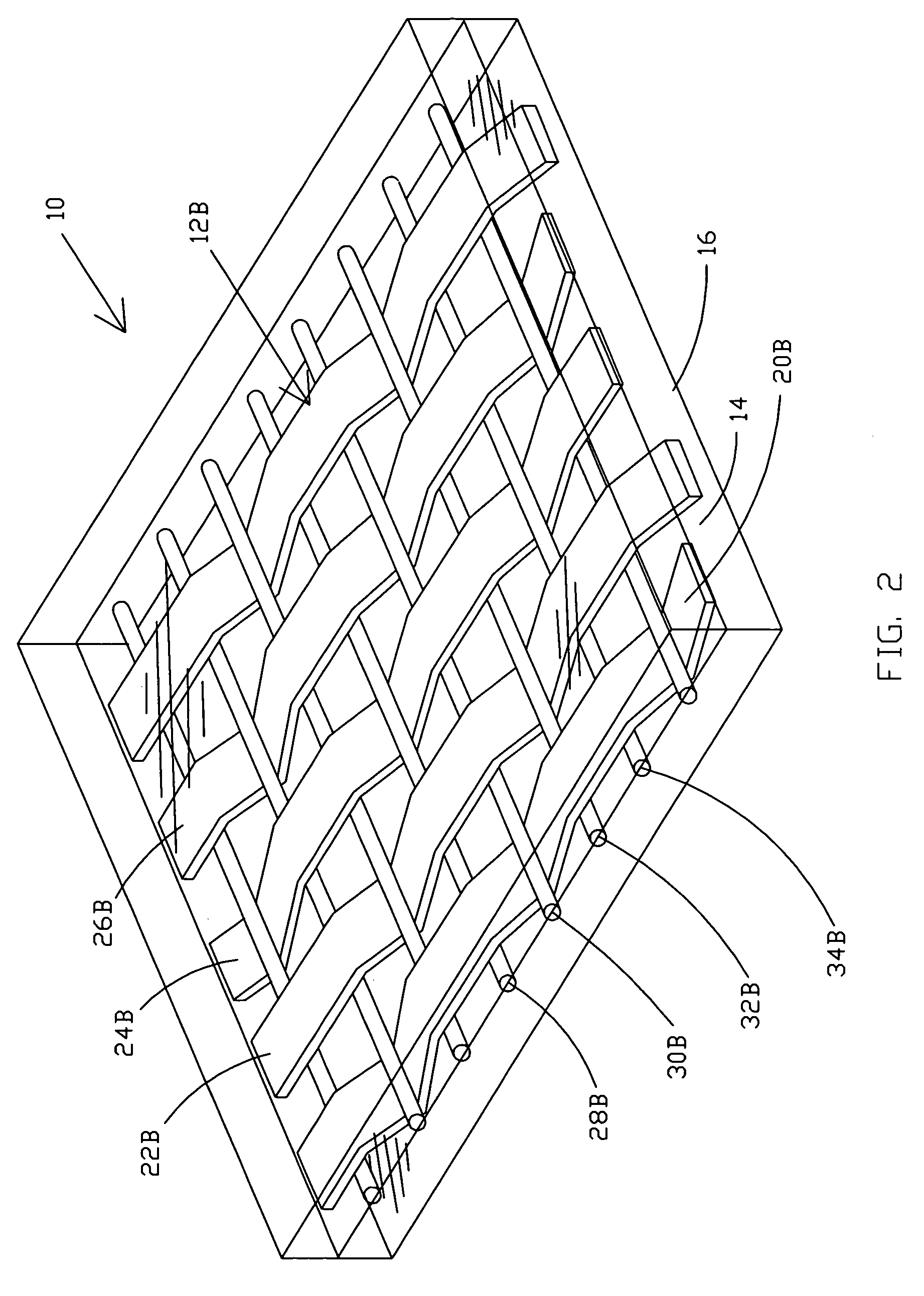
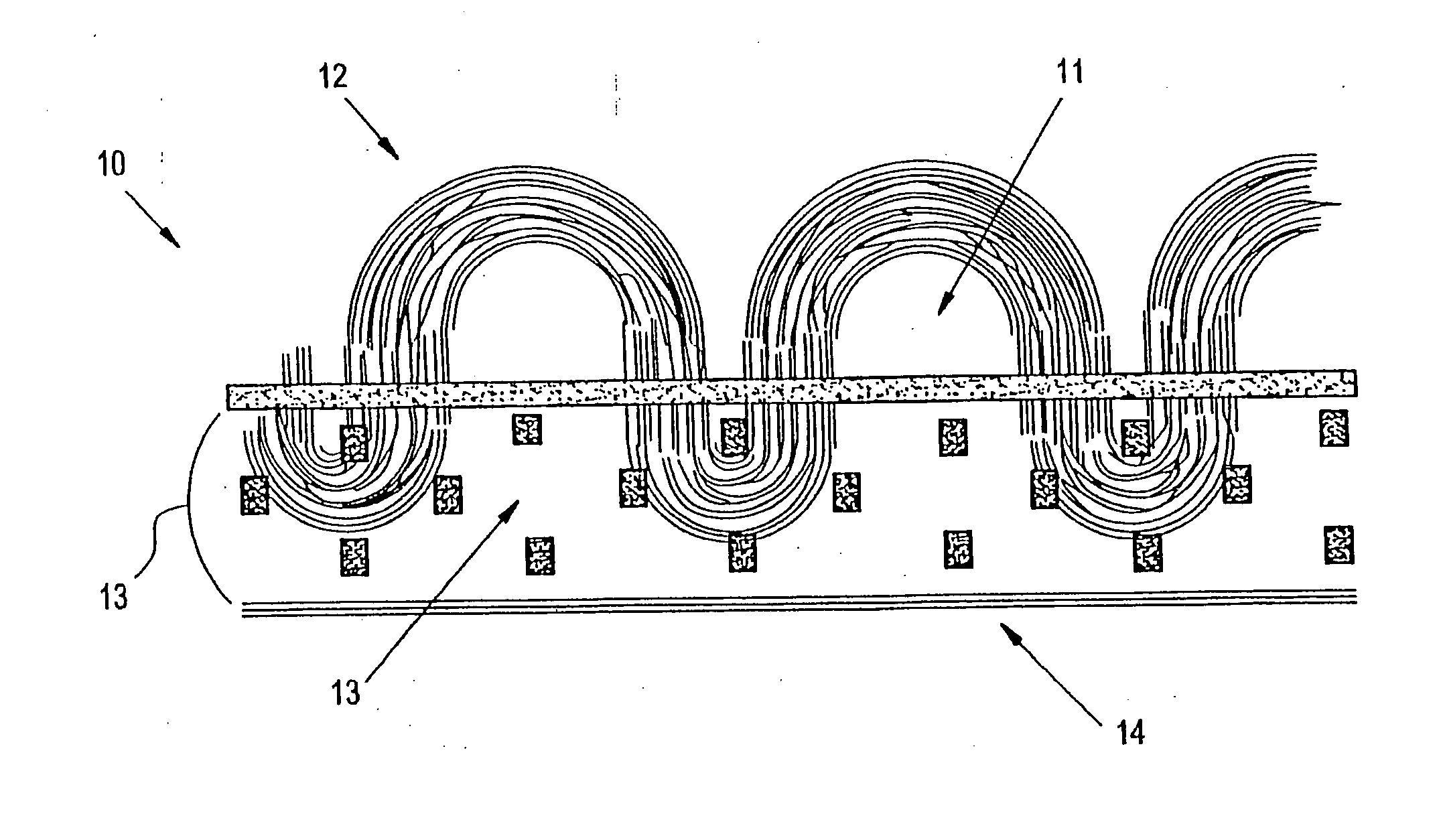
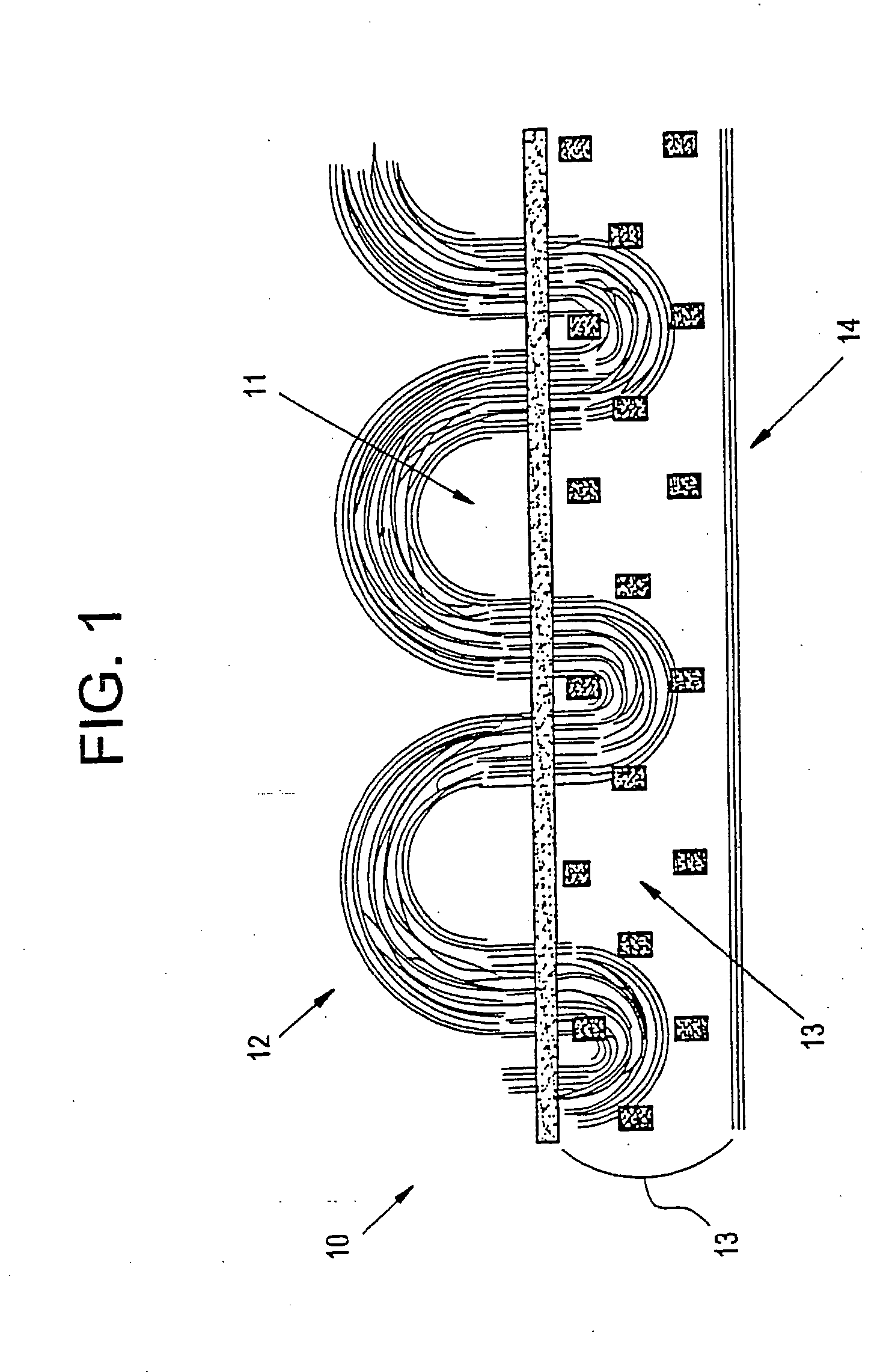
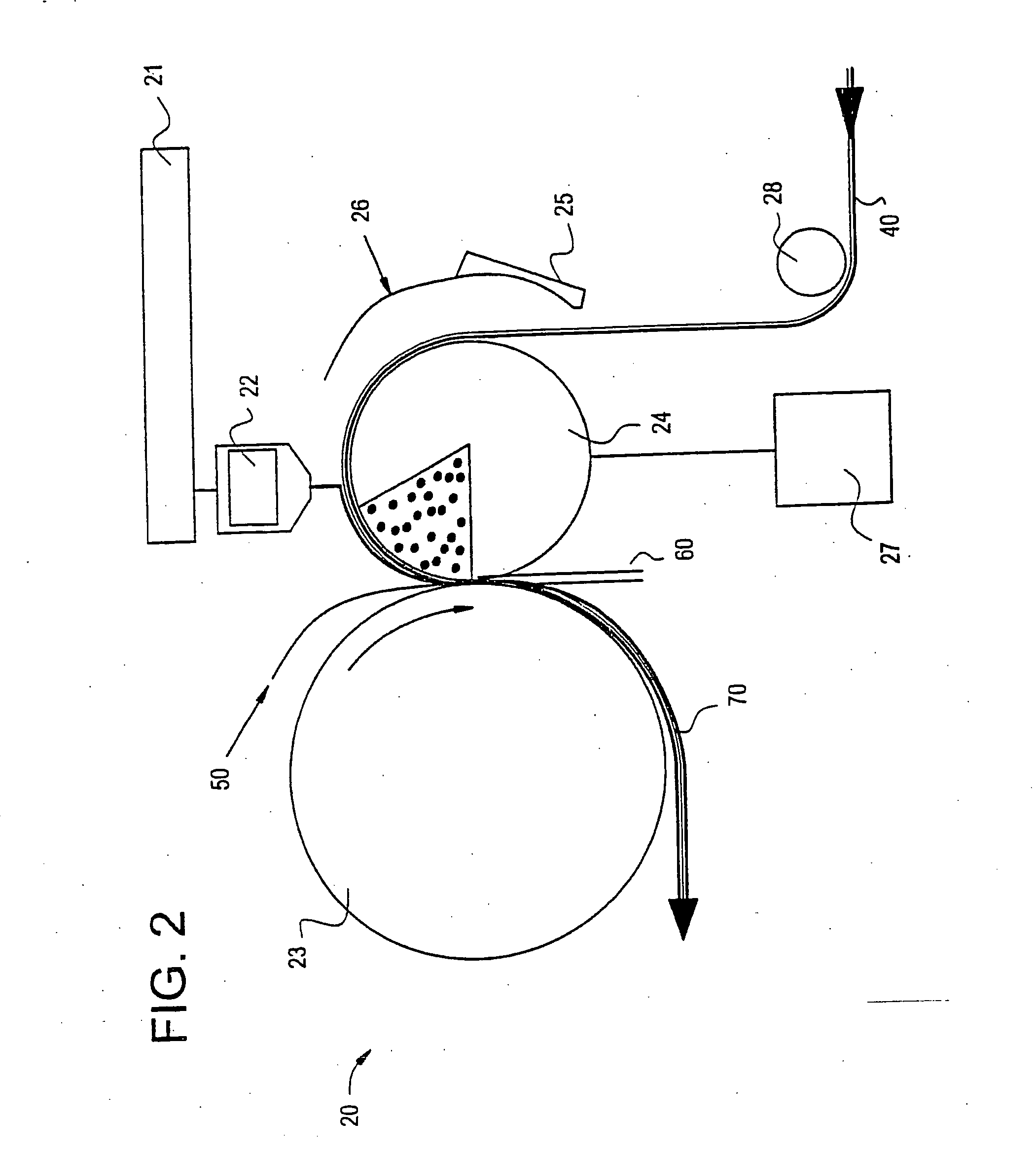
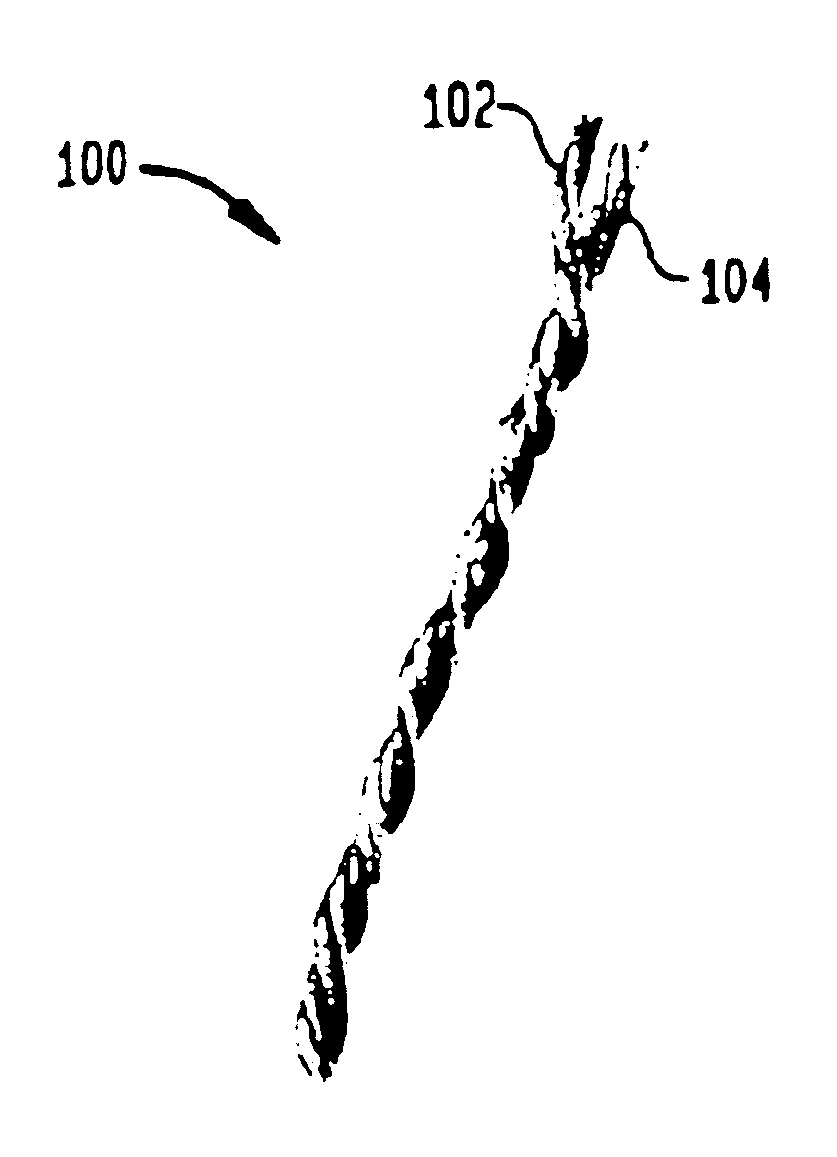
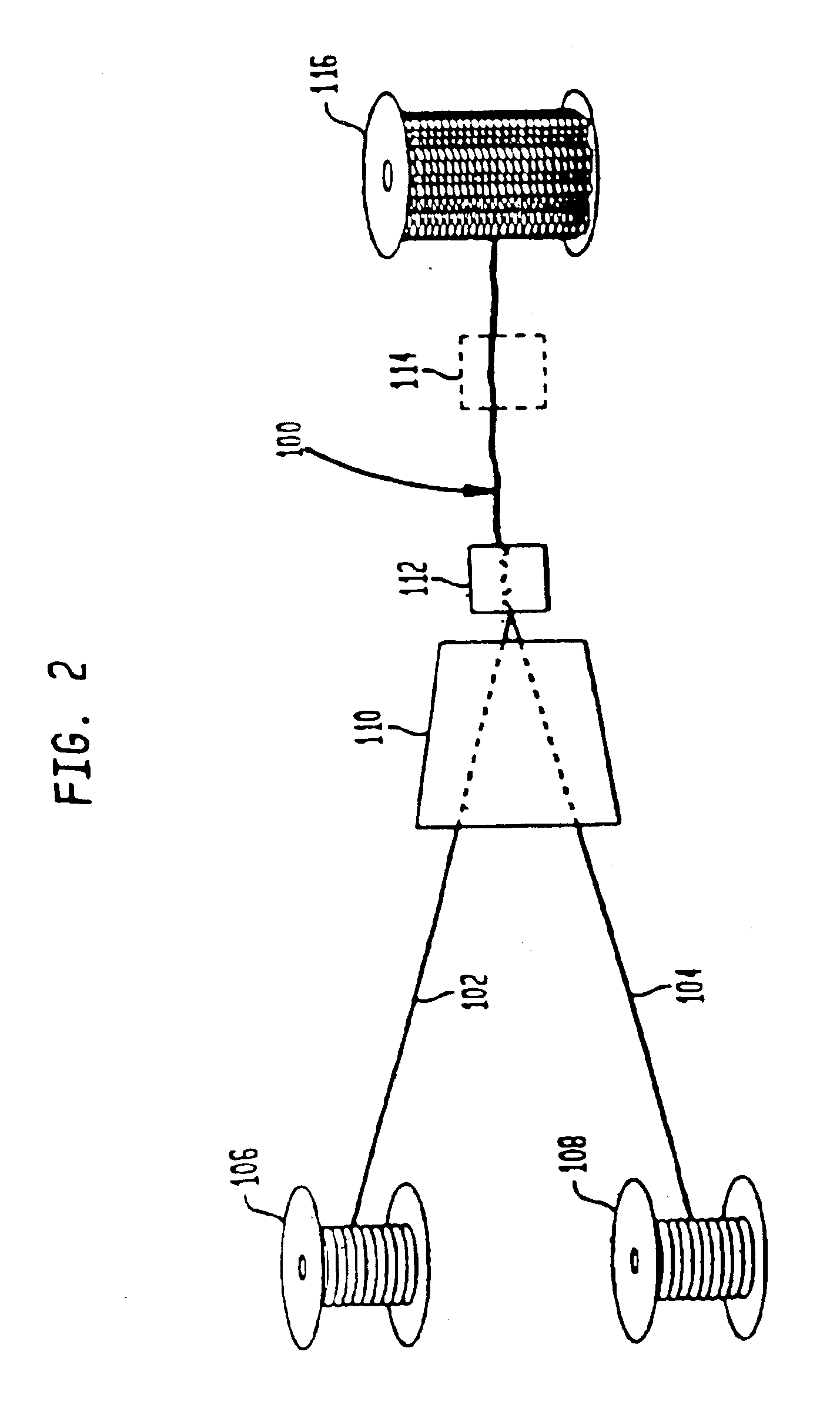
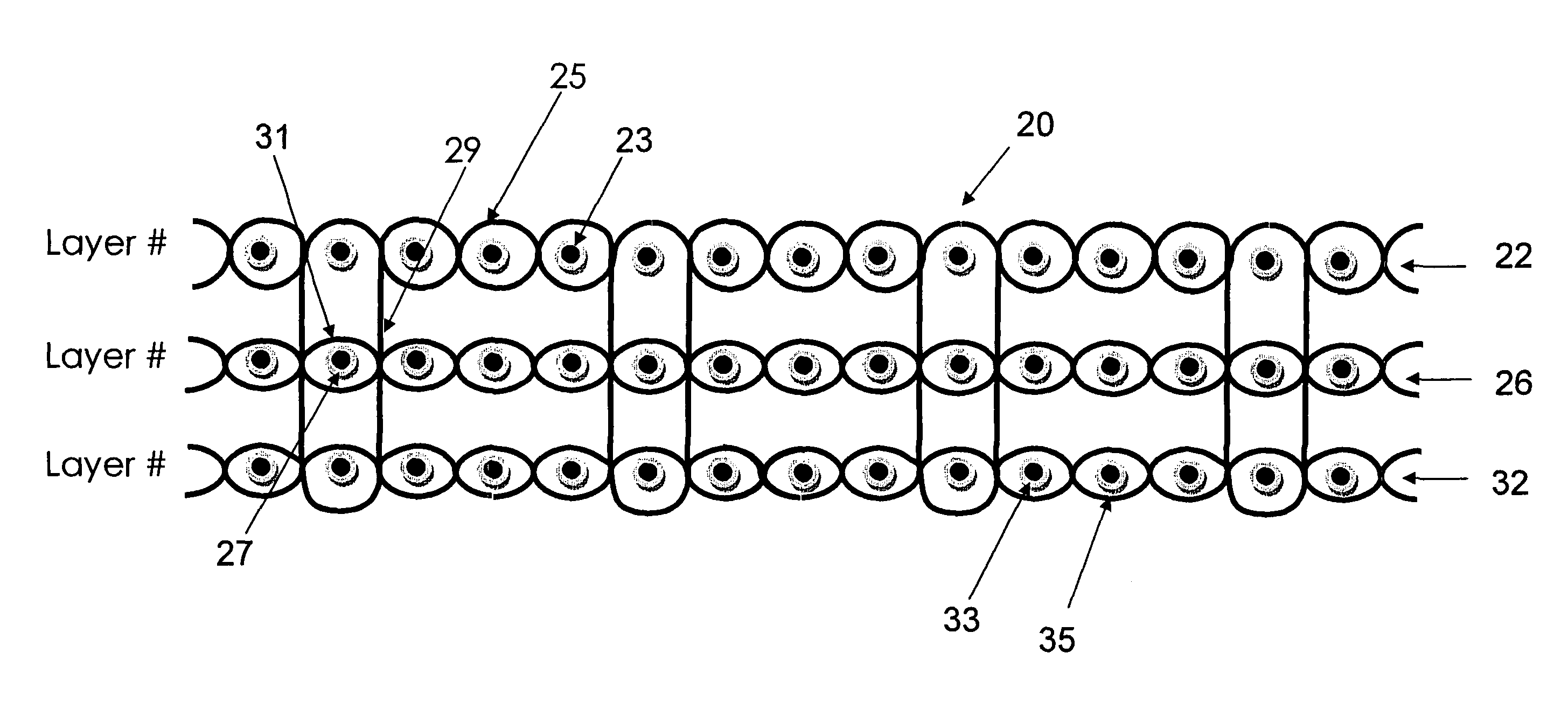
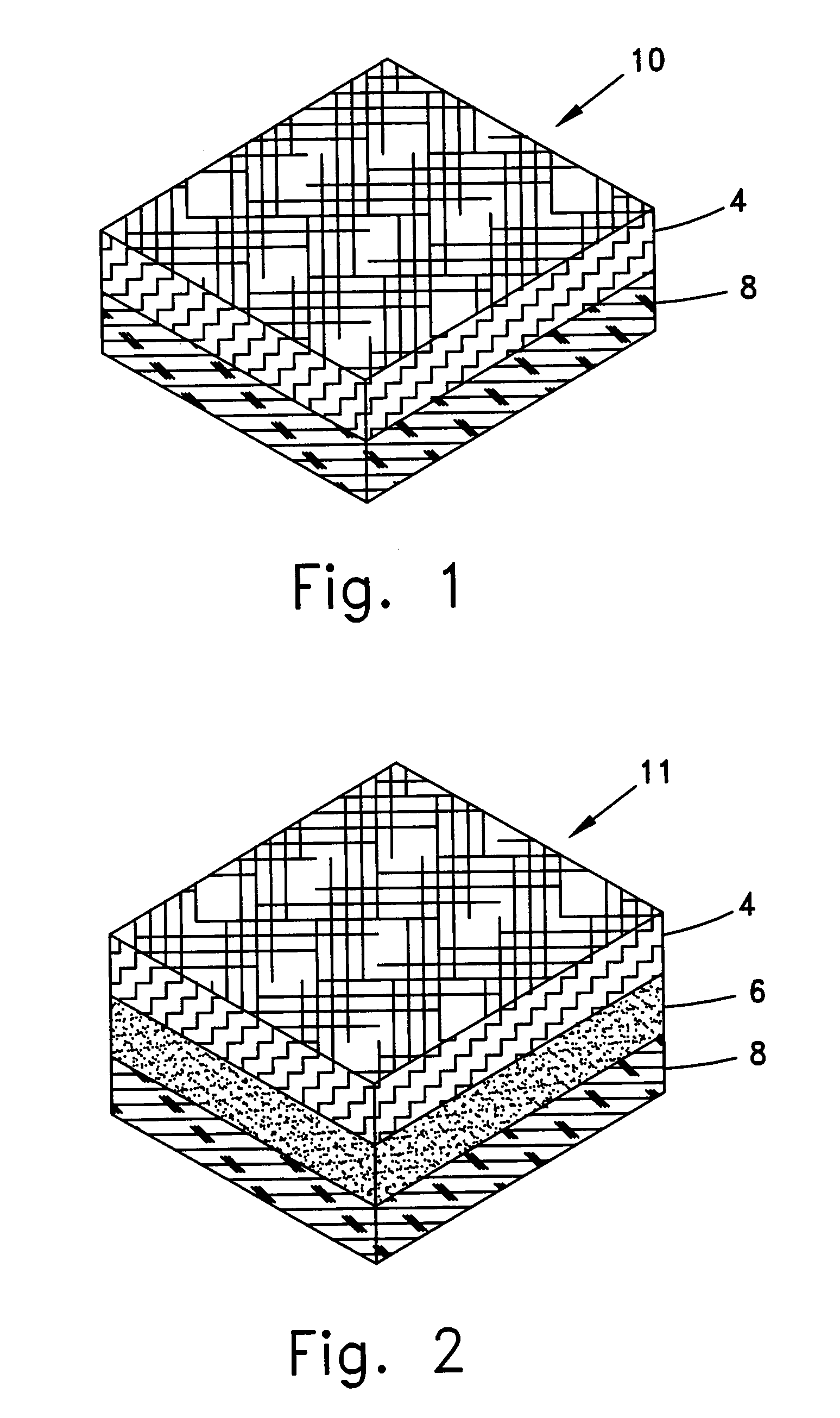
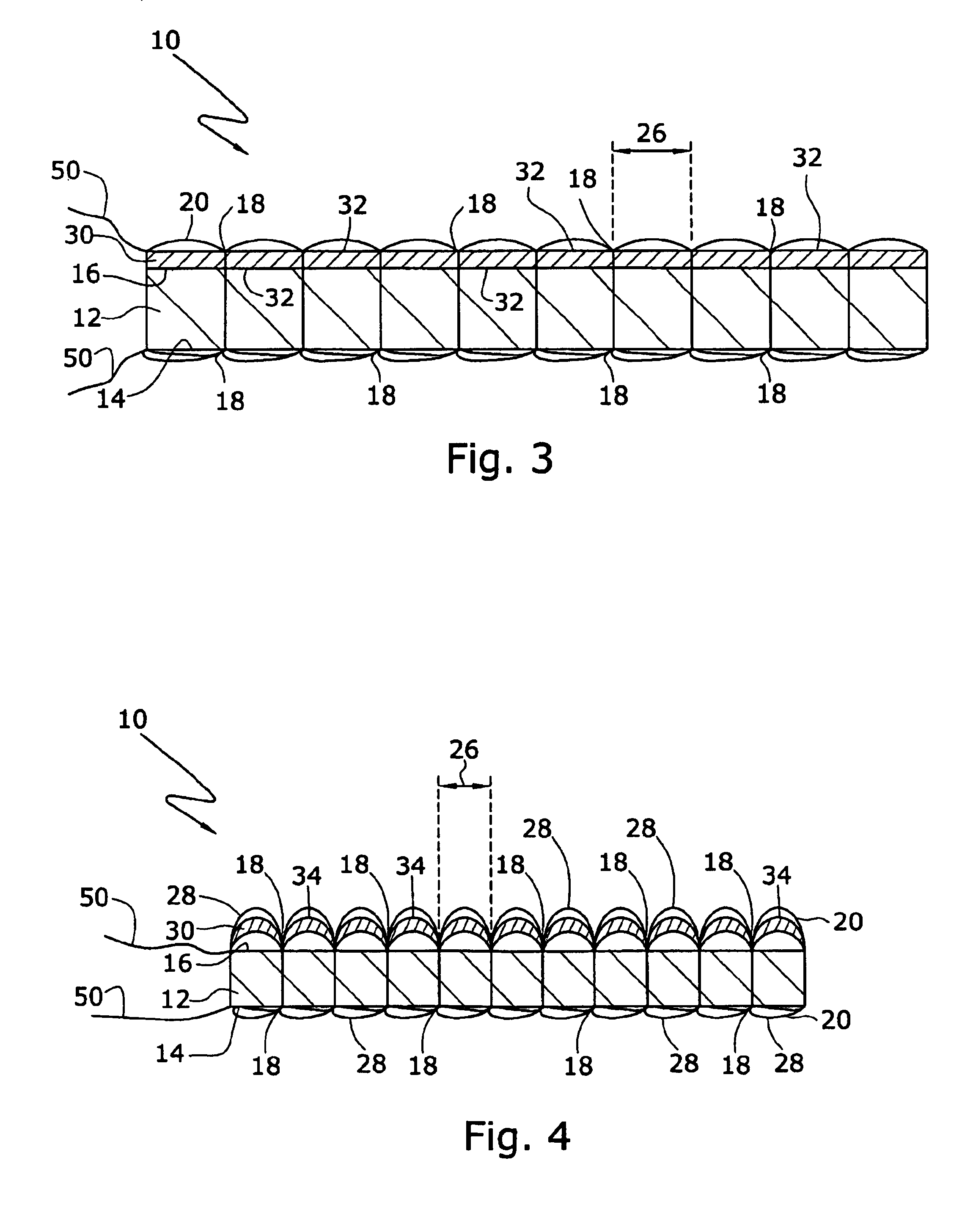
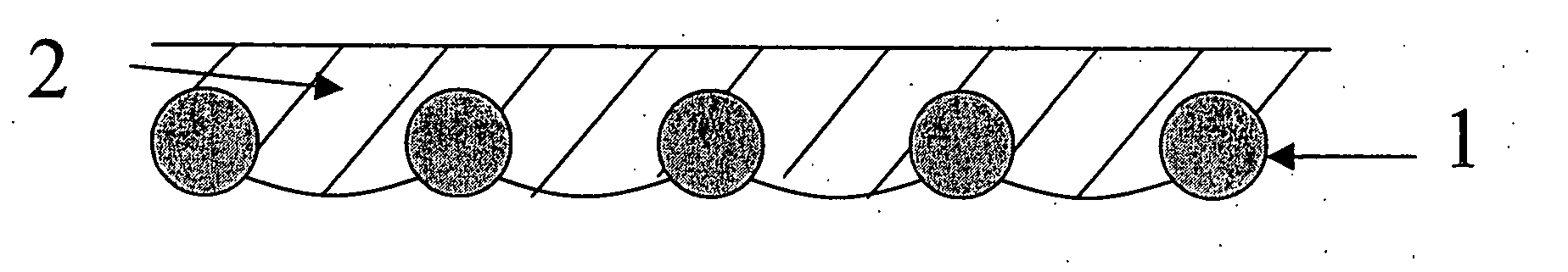
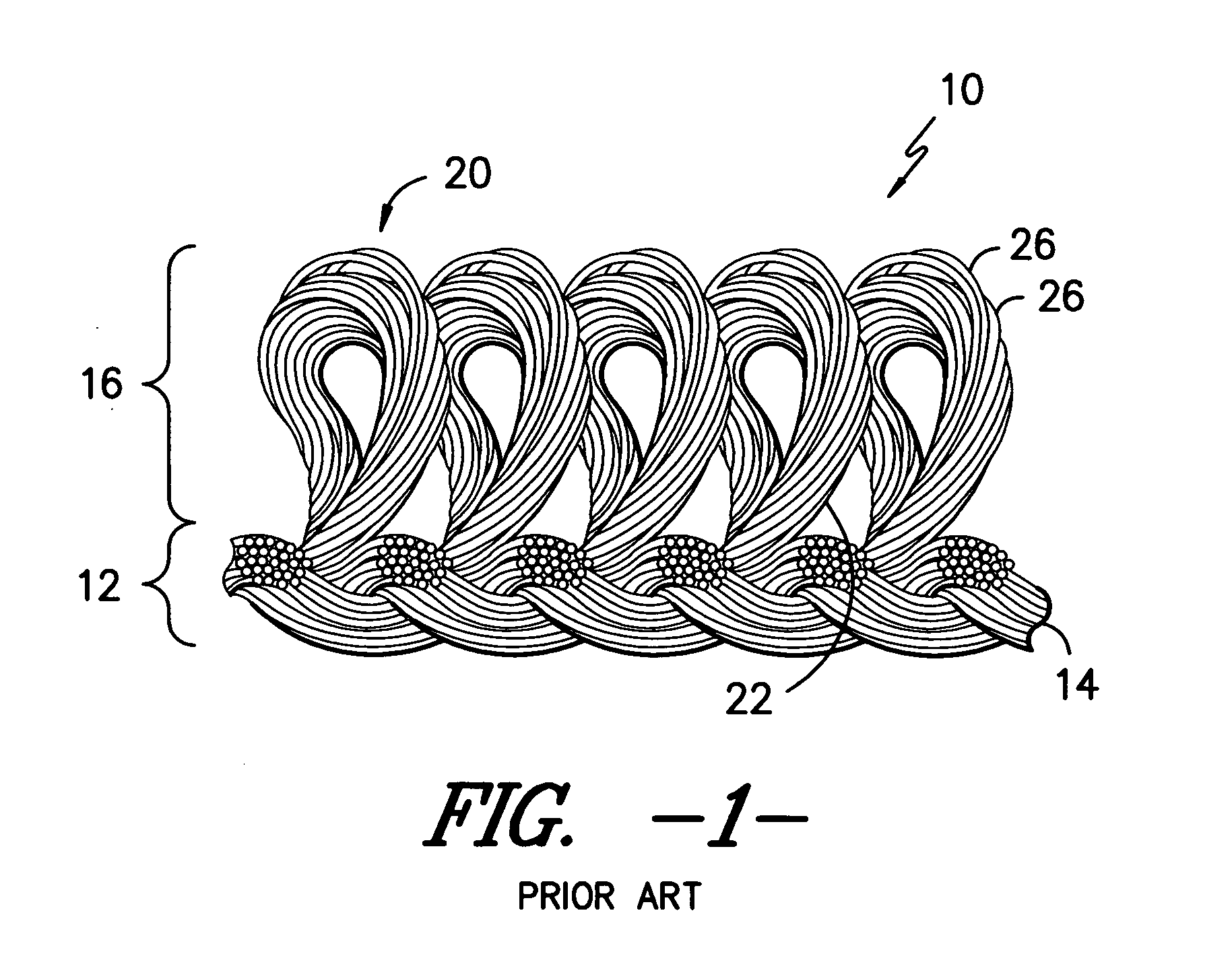
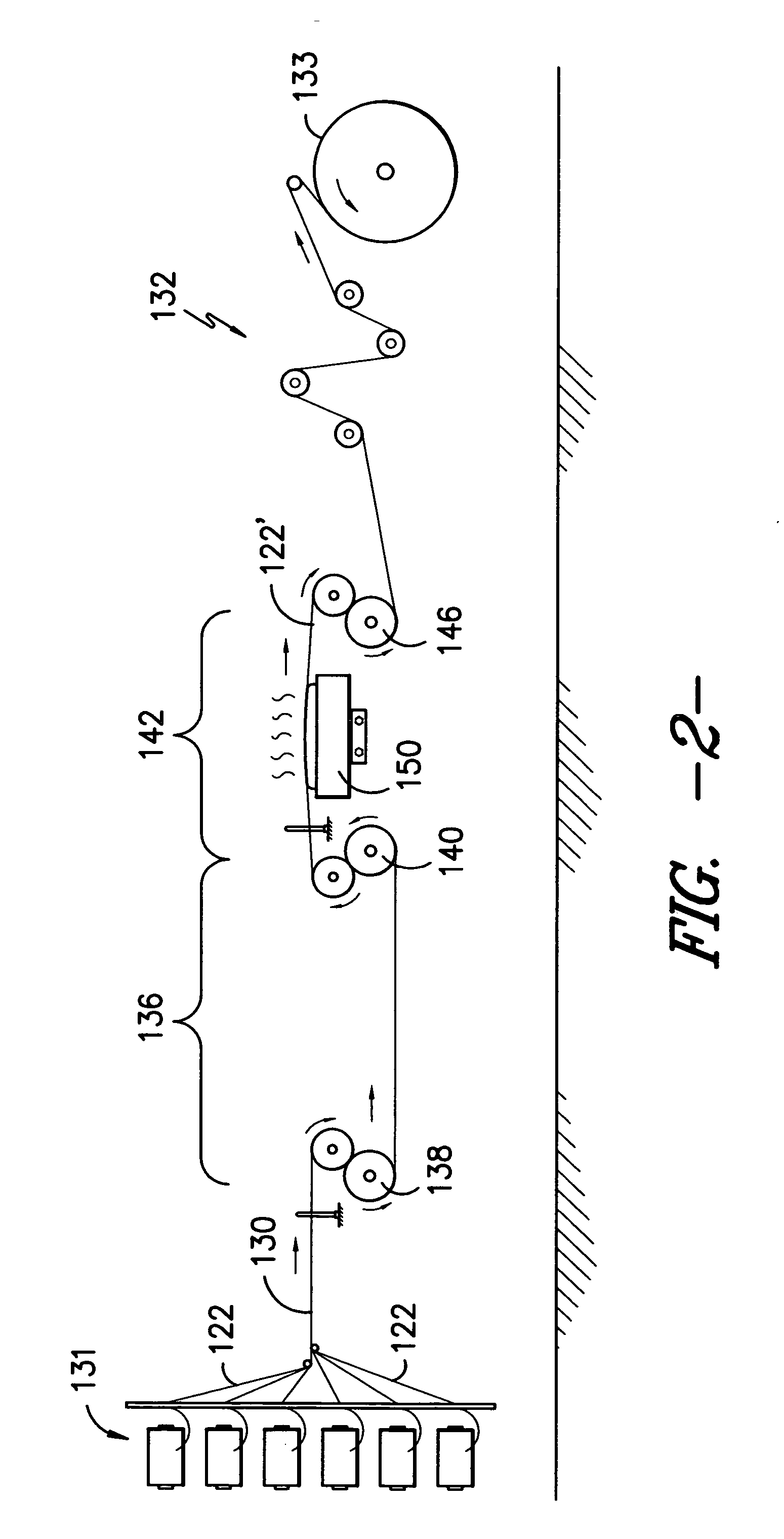
Carpet Construction and Carpet Backings for Same
Owner:PROPEX OPERATING
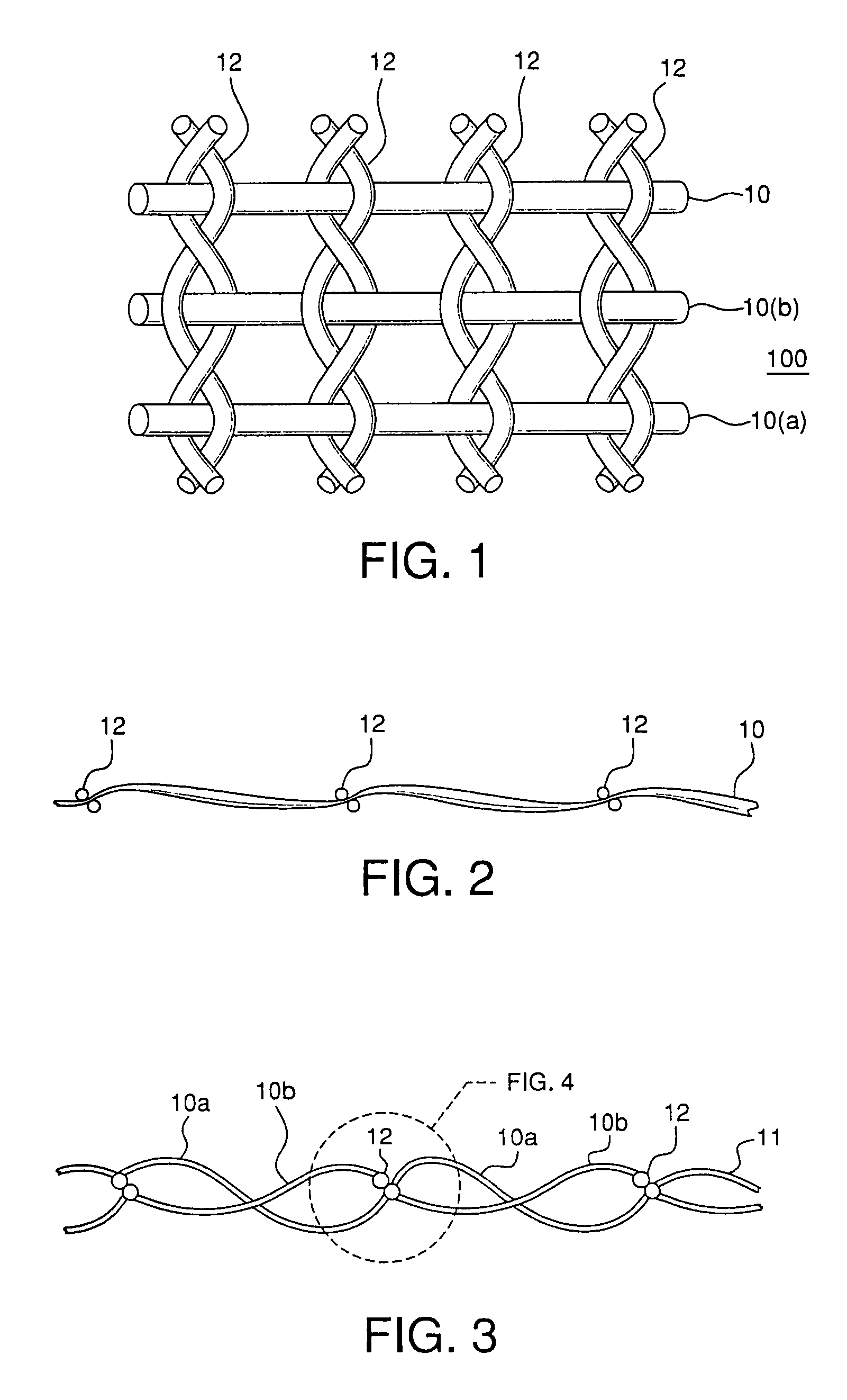
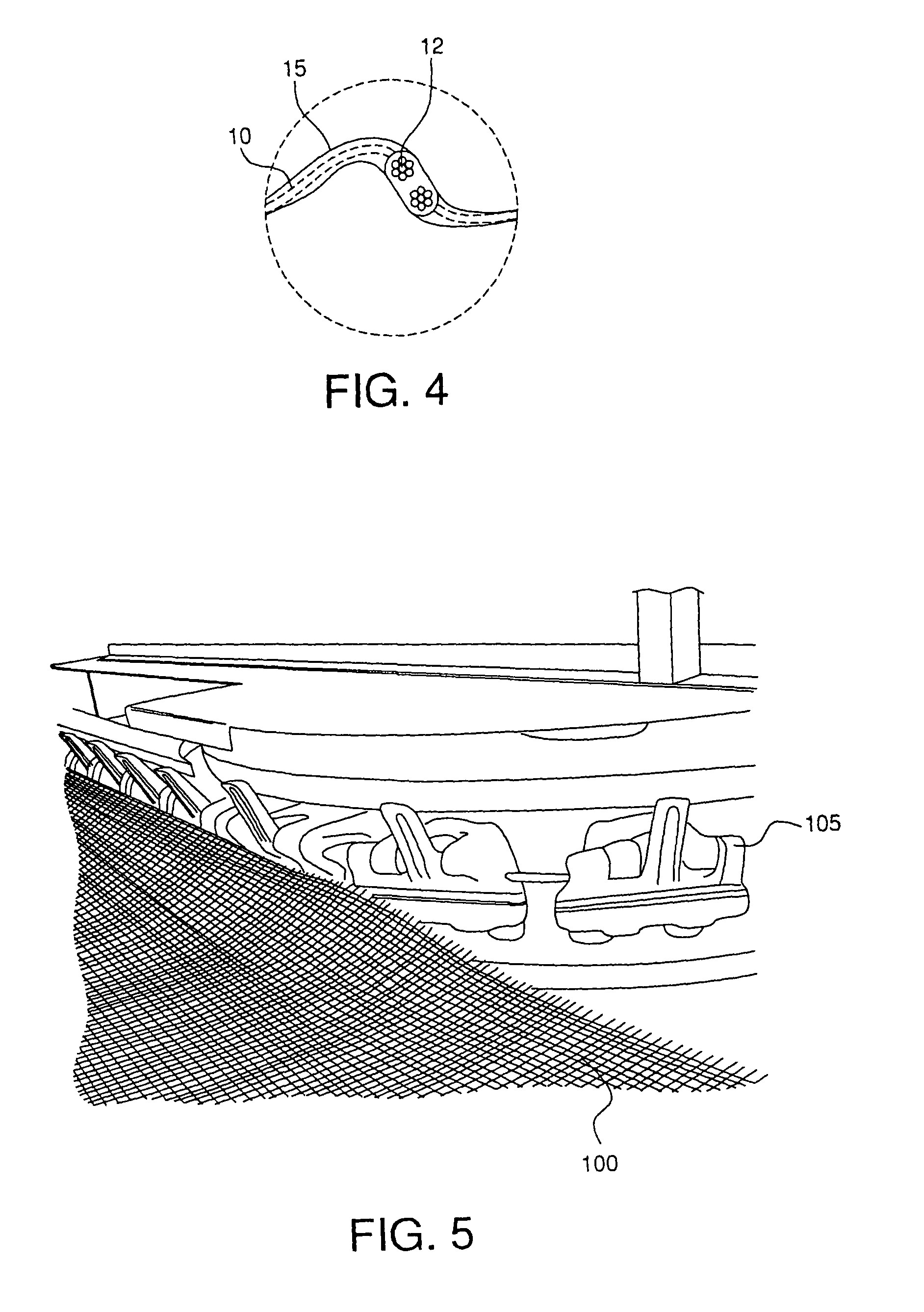
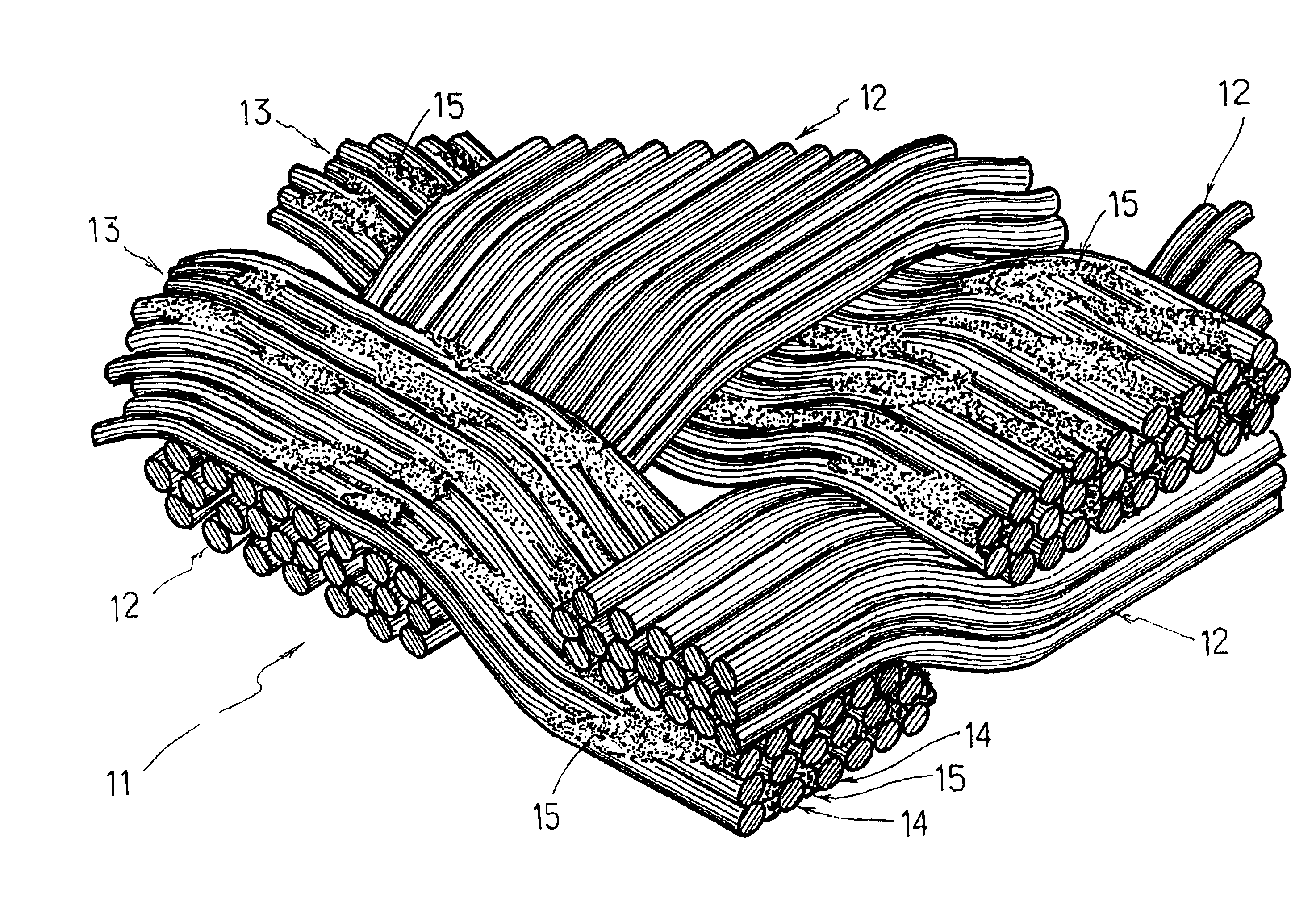
Textile fabric structure
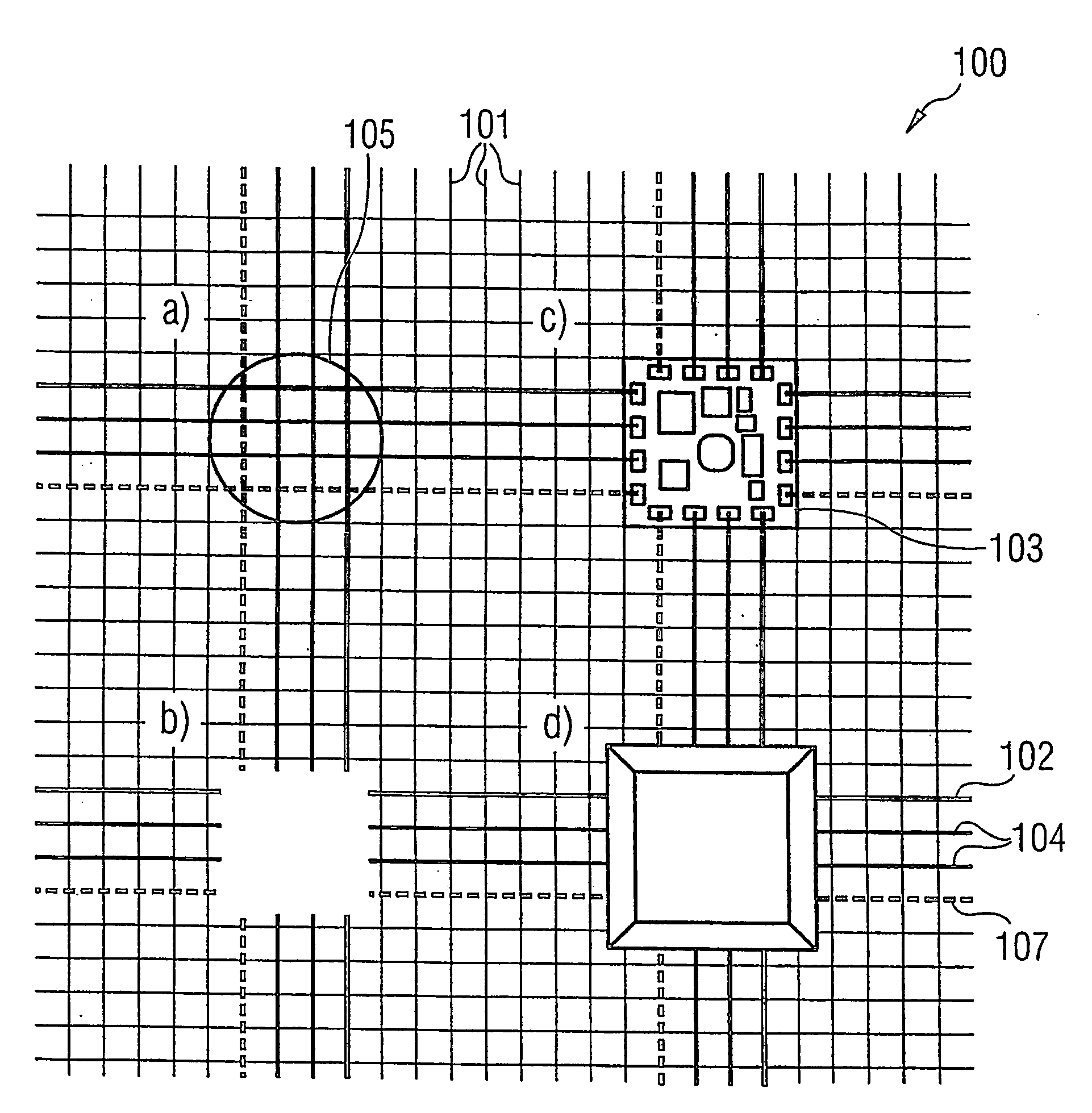
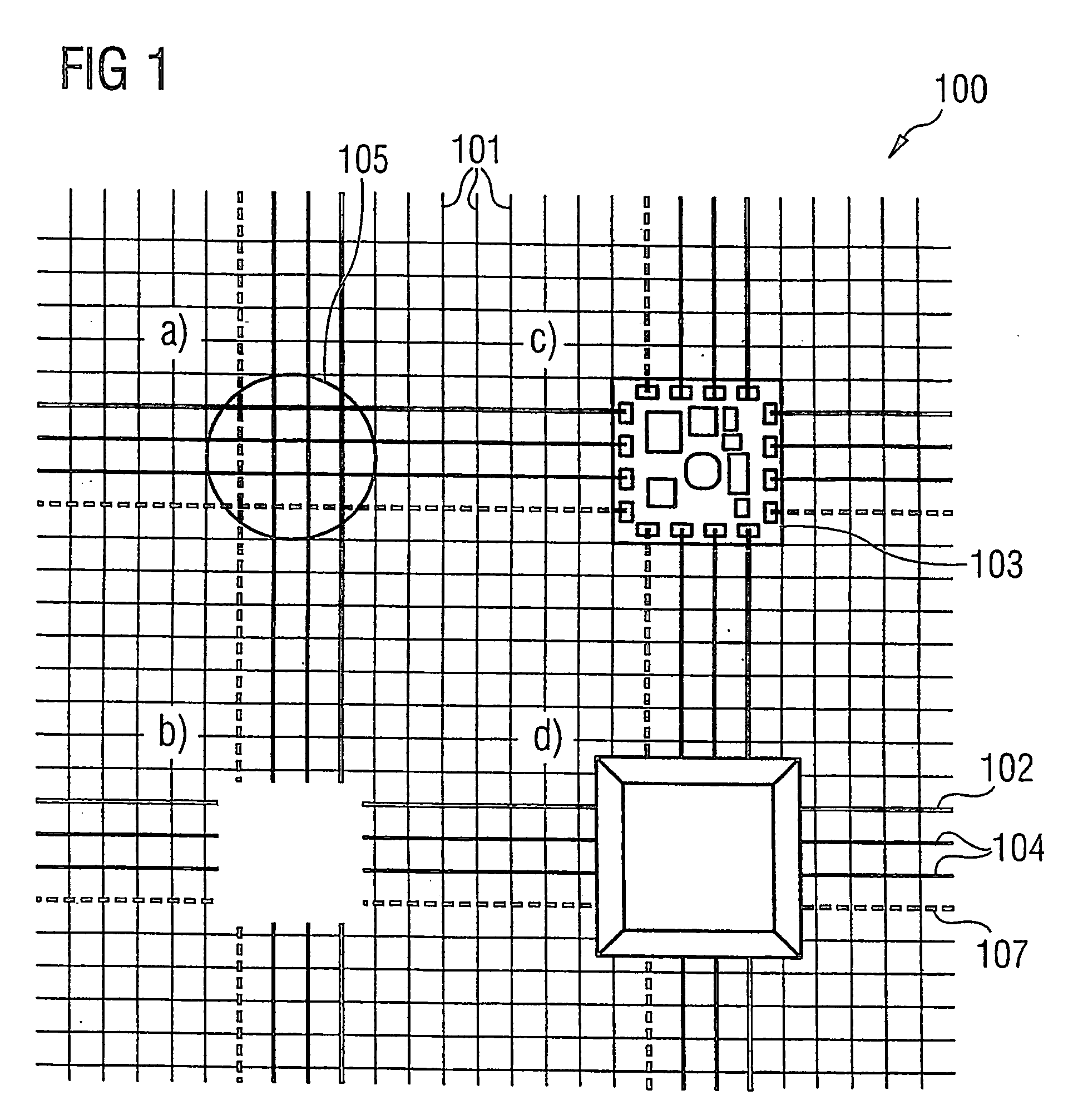
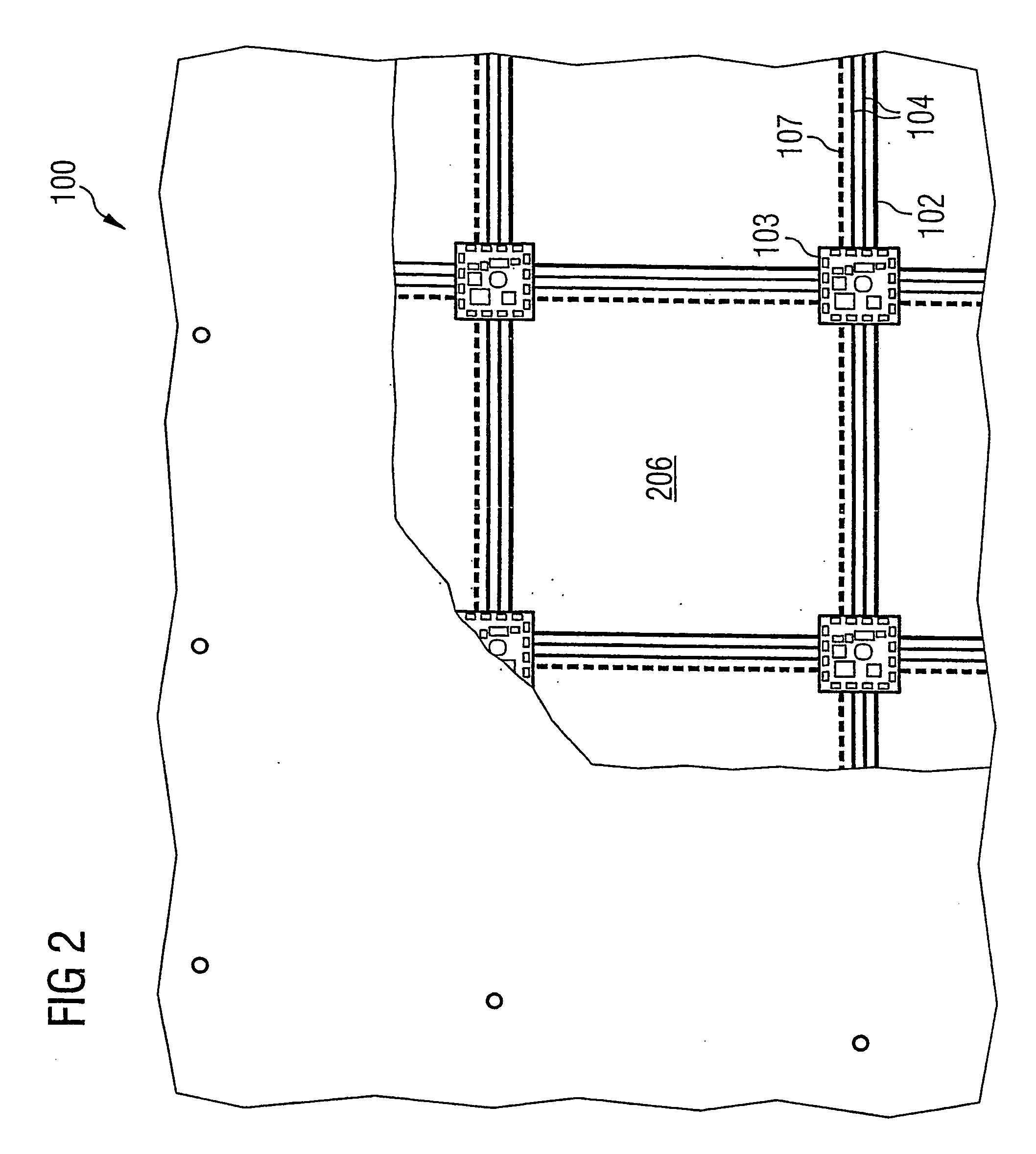
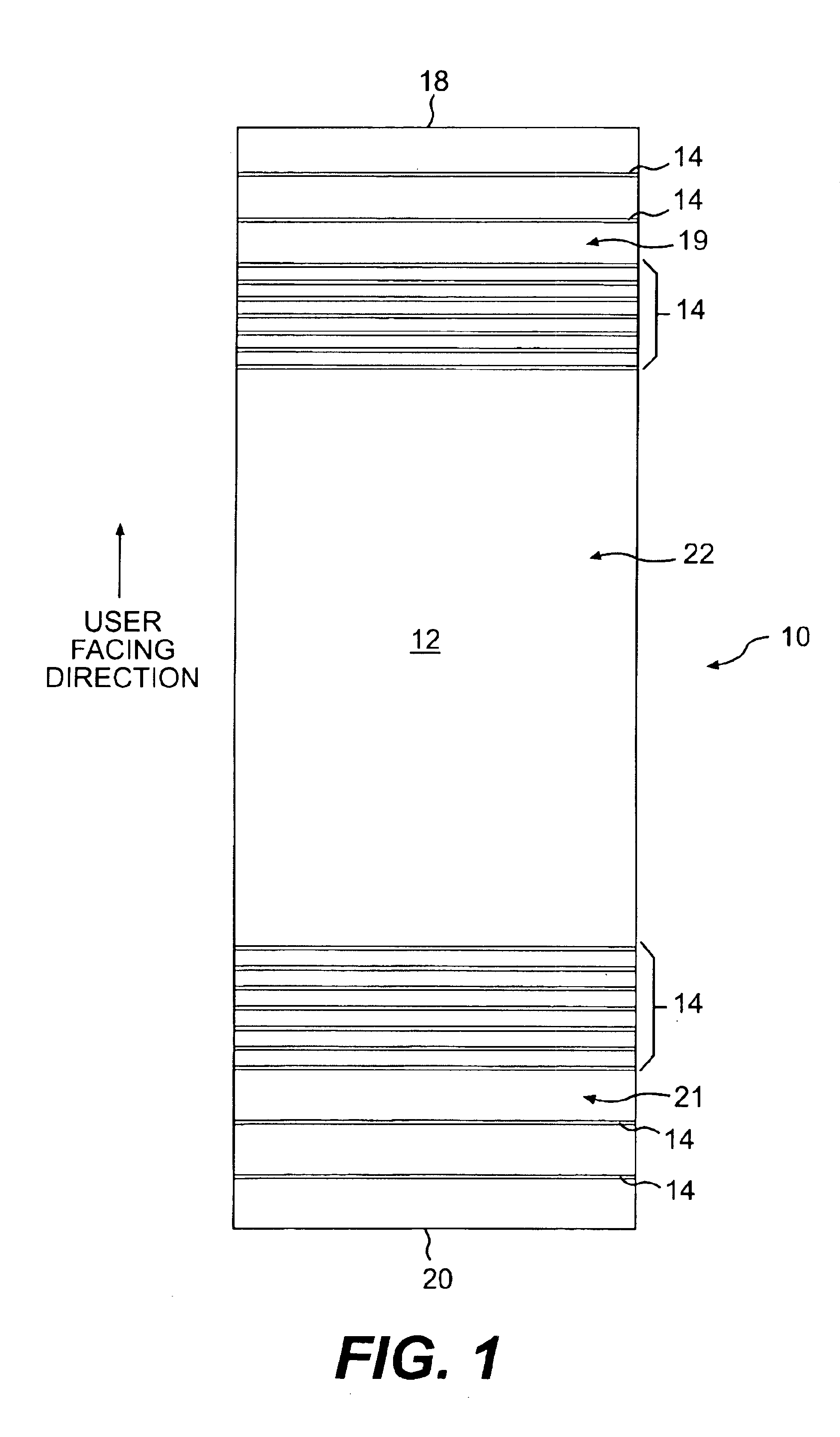
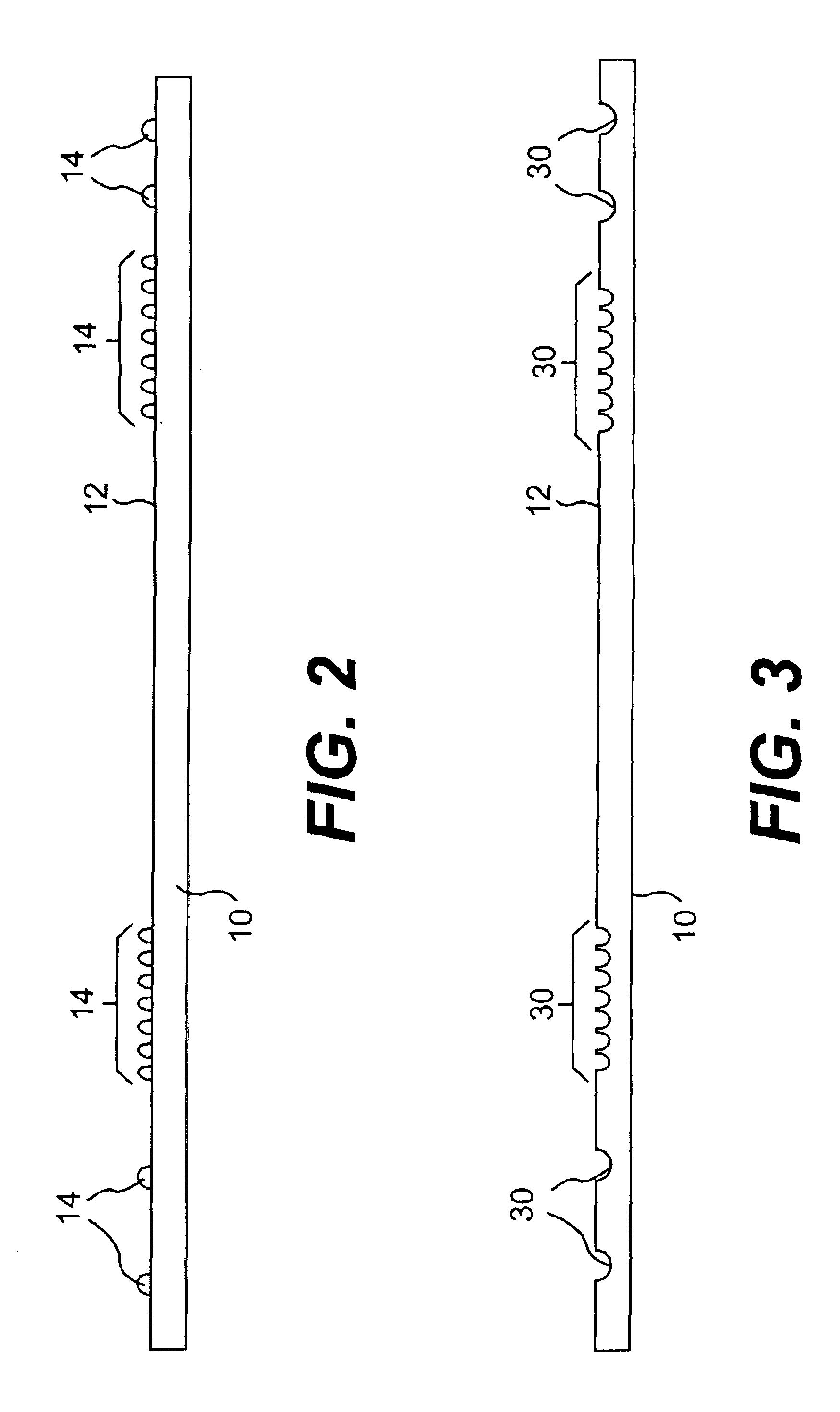
InactiveUS20060035554A1Circuit optical detailsPrinted circuit aspectsData transmissionFabric structure
A textile fabric structure having a plurality of microelectronic components, which are arranged in the textile fabric structure, electrically conductive threads, which couple the plurality of microelectronic components to one another, conductive data transmission threads, which couple the plurality of microelectronic components to one another, and electrically nonconductive threads. The conductive threads and the conductive data transmission threads at the edge of the textile fabric structure are each provided with an electric interface and a data transmission interface.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Connection member, method of manufacturing the same and connection structure
InactiveUS20120156926A1Easy to implementReduce in quantityLine/current collector detailsCarpetsBand shapeElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK
Fibers excellent in magnetic field responsiveness and conductivity and product consisting of it
InactiveUS20070003761A1Improve responseStable specific resistance valueCurtain accessoriesWarp knittingFiberHeat resistance
Owner:TORAY IND INC
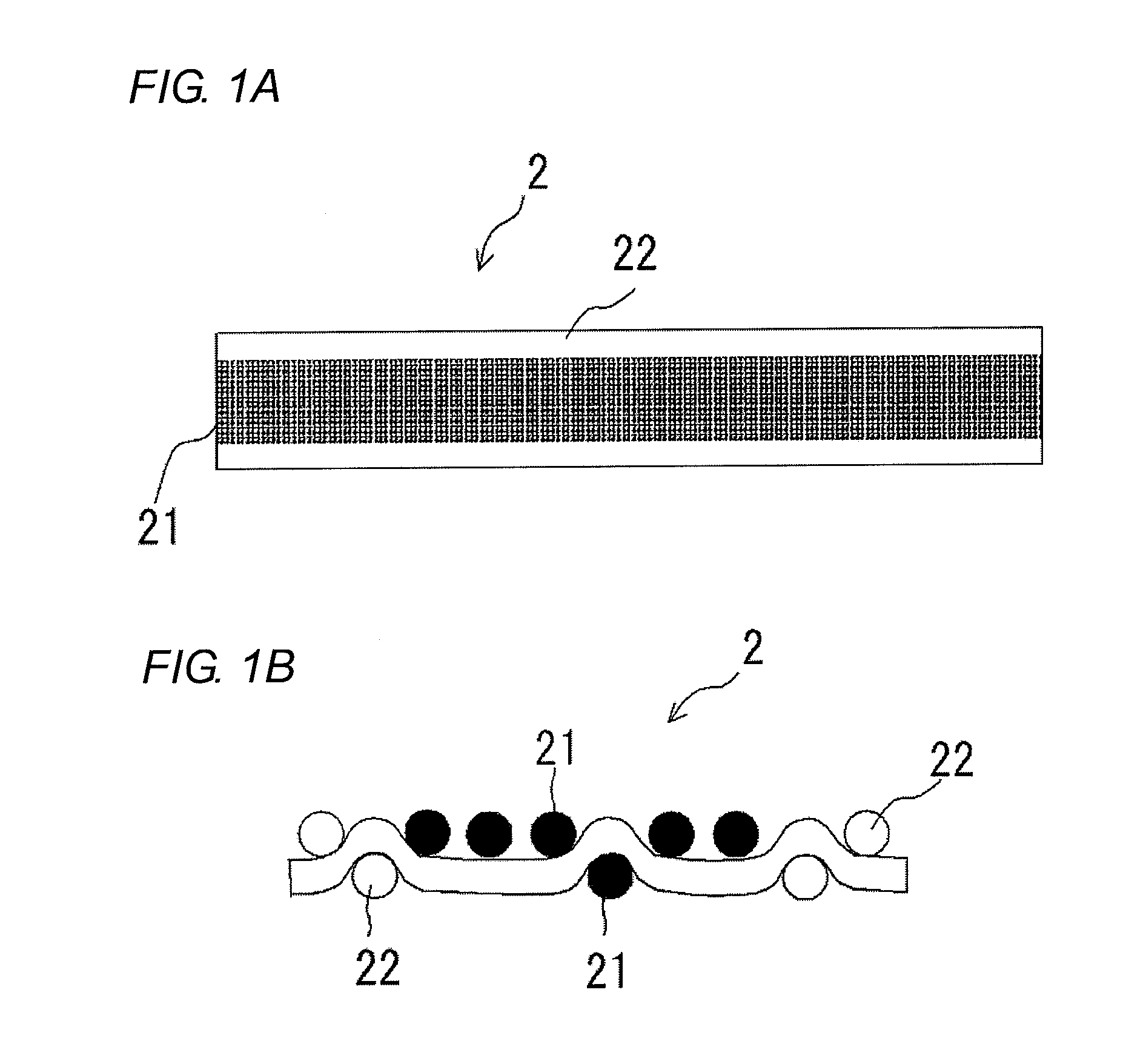
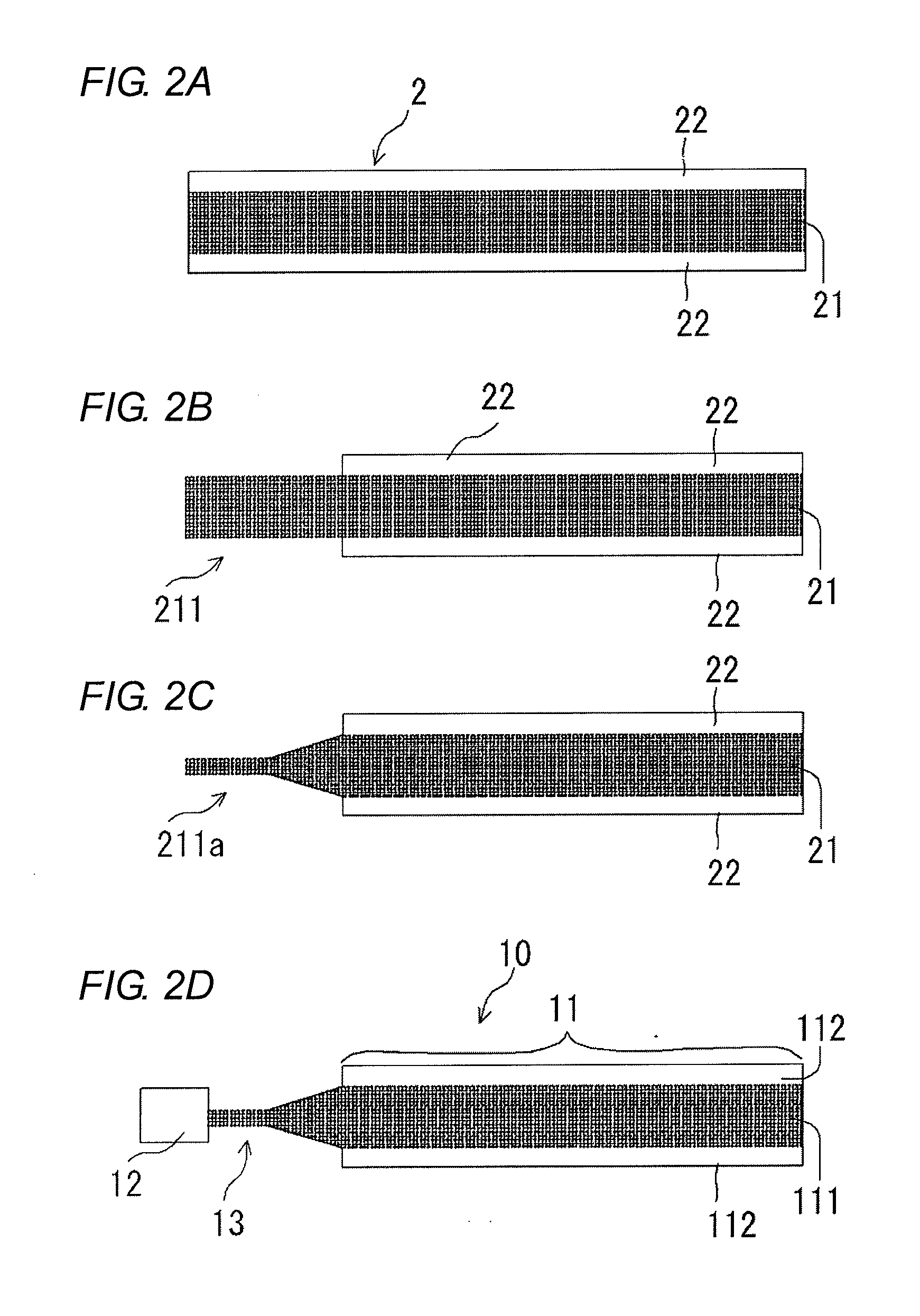
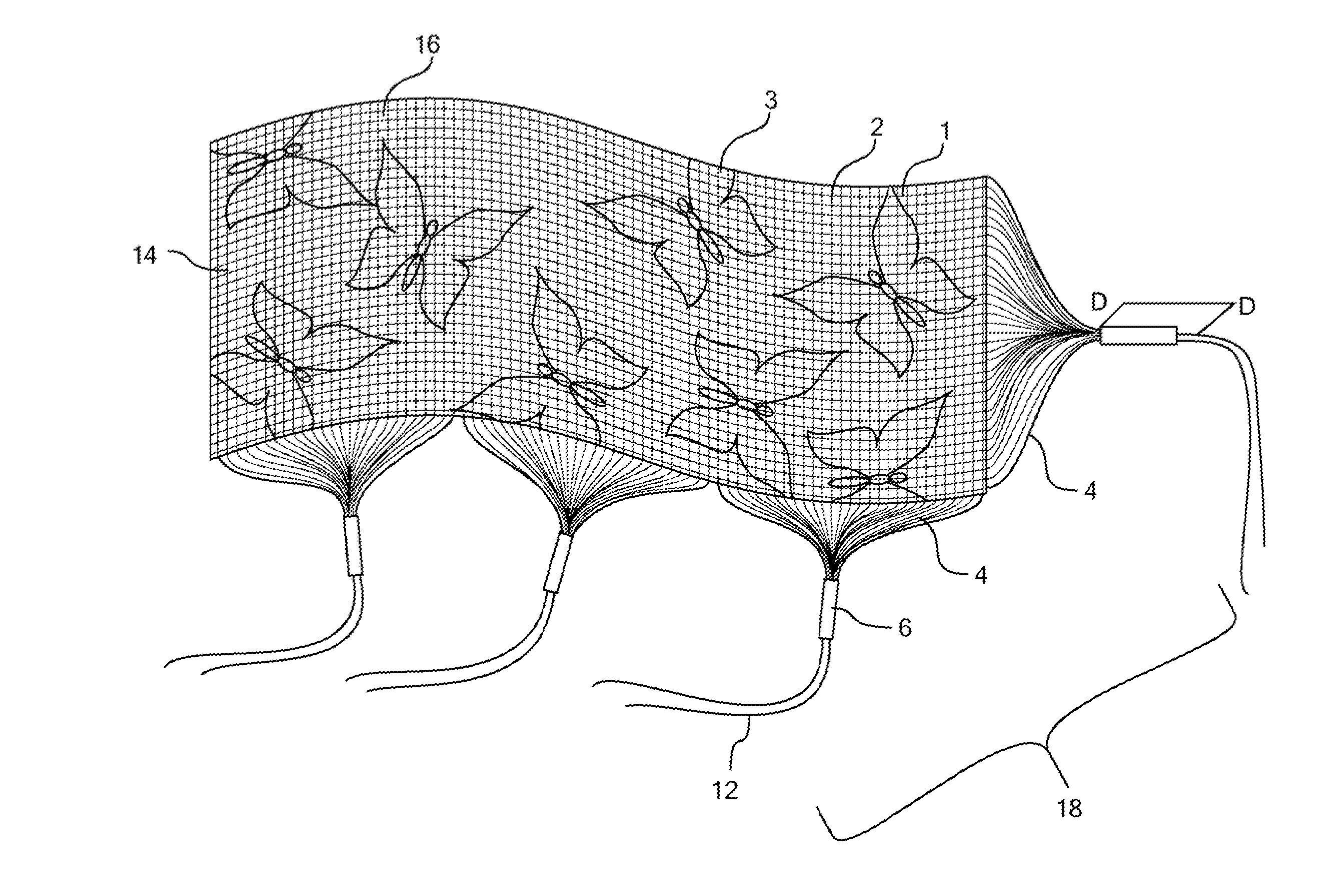
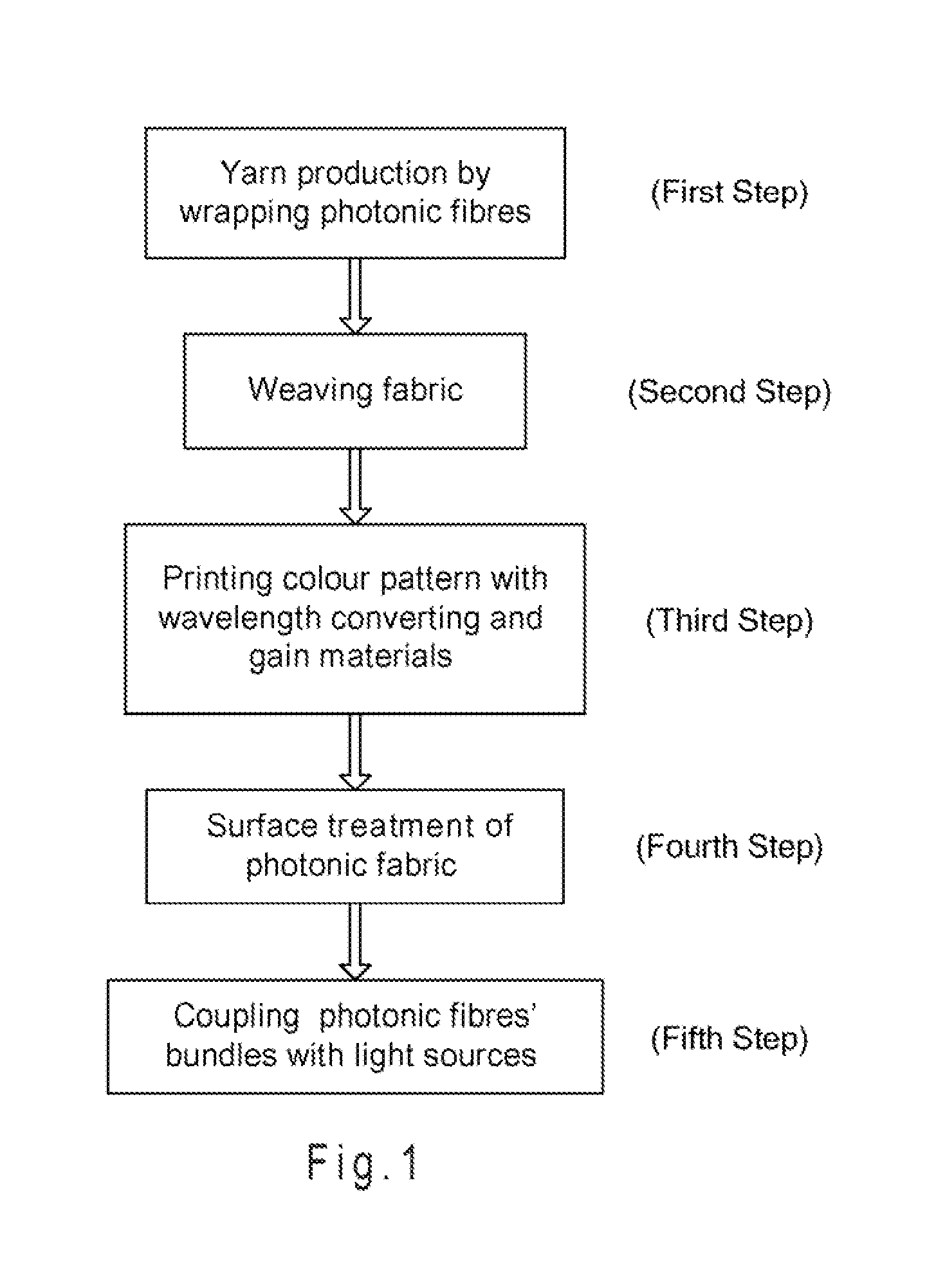
Photonic fabric display with controlled pattern, color, luminescence intensity, scattering intensity and light self-amplification
A method of making a photonic fabric display includes wrapping photonic fibers with a yarn, weaving the wrapped photonic fibers to form a fabric, printing a pattern on the fabric, surface treating the fabric, and coupling the photonic fibers with a light source to form a photonic fabric display.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Polyester and modified fluoropolymer blends
InactiveUS20070232170A1Improved resistance to contaminationImproved to abrasionMachine wet endCarpetsFiberPolymer science
Disclosed are blends of a polyester resin and fluoropolymer resin having compatibilizing side groups, such as maleic anhydride. Also disclosed are fibers and fabrics containing that composition. The fabrics are particularly suitable for use in belts in papermaking machines.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Carpet, carpet backings and methods
The present invention pertains to carpet and method of making it. In one aspect, the carpet includes (a) a primary backing which has a face and a back surface, (b) a plurality of fibers attached to the primary backing and extending from the face of the primary backing and exposed at the back surface of the primary backing, (c) an adhesive backing, (d) an optional secondary backing adjacent to the adhesive backing, and (e) at least one homogeneously branched linear ethylene polymer. The method includes extrusion coating at least one homogeneously branched linear ethylene polymer onto the back surface of a primary backing to provide an adhesive backing. The method can include additional steps or procedures, either separately or in various combinations. Additional steps and procedures include preheating the primary backing prior the extrusion step, multilayer adhesive backings, washing or scouring the primary backing prior the extrusion step, and utilizing adhesive polymeric additives, high heat content fillers, blowing agents and / or implosion agents. The constructions and methods described herein are particularly suited for making carpet tile.
Owner:BRUMBELOW JULIE +7
Exterior finishing system and building wall containing a corrosion-resistant enhanced thickness fabric and method of constructing same
A corrosion-resistant lath is provided for use in exterior finishing systems, such as stucco systems and exterior insulation and finish systems (“EIFS”). The lath includes in a first embodiment an open, woven fabric comprising weft and warp yarns containing non-metallic fibers, such as glass fibers. A portion of the weft yarns are undulated, resulting in an increased thickness for the fabric. The fabric is coated with a polymeric resin for substantially binding the weft yarns in the undulated condition. This invention also includes methods for making an exterior finish system and building wall including an exterior finish system using such a lath.
Owner:BASF LEC CONSTR CHEM
Wire mesh panel and method
InactiveUS20050014429A1Easy to cleanFlat surfaceWeft knittingCurtain accessoriesEngineeringWire mesh
An assembly and method is provided for a decorative screen, wall, or other surface to provide a desired amount of light passing through, reflected by, and / or diffused by the decorative screen. In one preferred embodiment, at least one screen is formed of a plurality of wires that are woven together. The screen is preferably affixed within one or more transparent panels. In one embodiment, the screen may preferably have an arrangement with a number of wires having wire diameters in a selected weave or knitted pattern such that only between zero and eighty-five percent of the surface area of the screen is open area. The wire is preferably treated such that a desired level or amount metal luster is provided to control reflection / absorbtion properties of the screen. The screen may be utilized as building material such as walls, counters, shower enclosures, or to make other articles such as furniture.
Owner:DORSTENER WIRE TECH
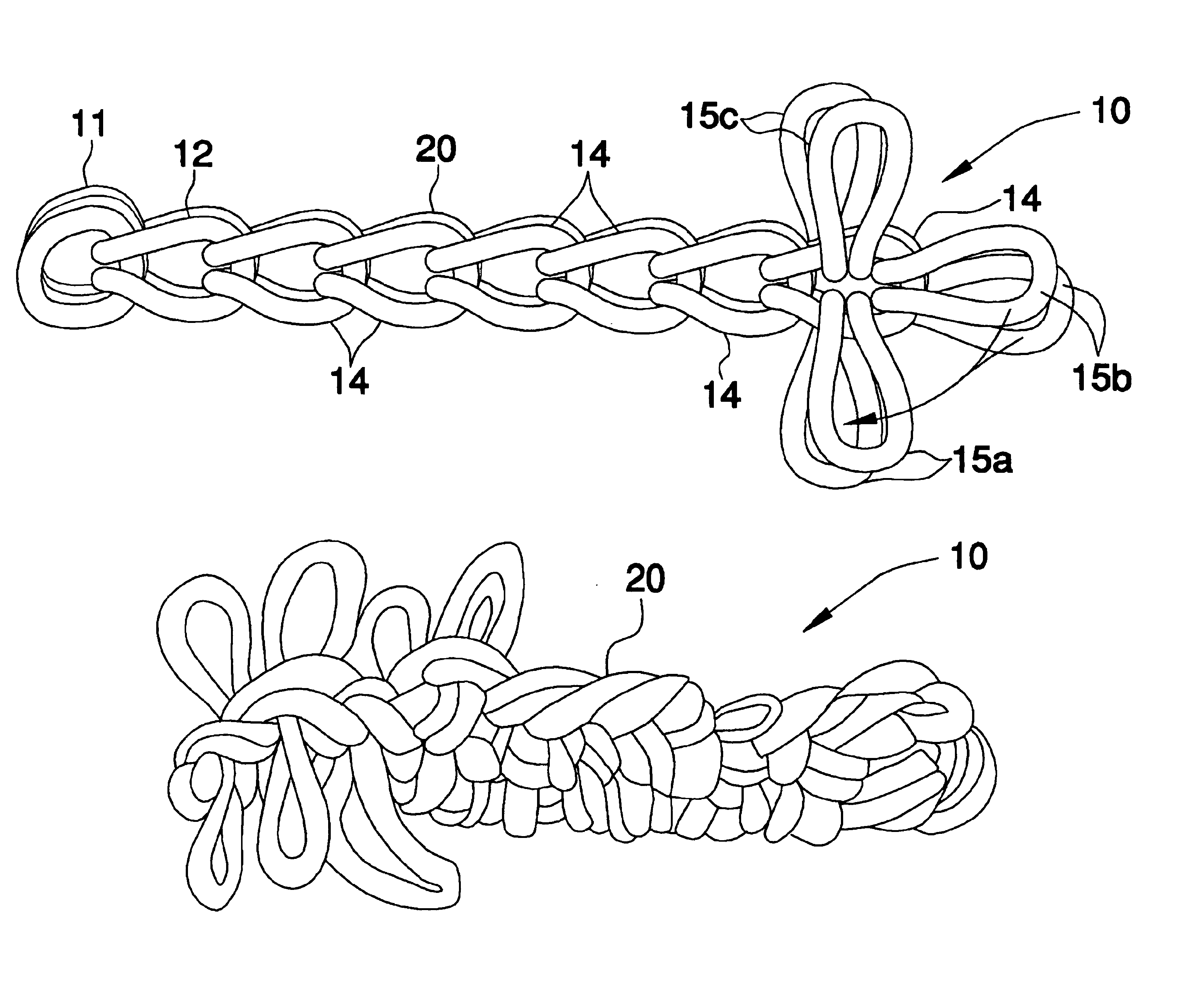
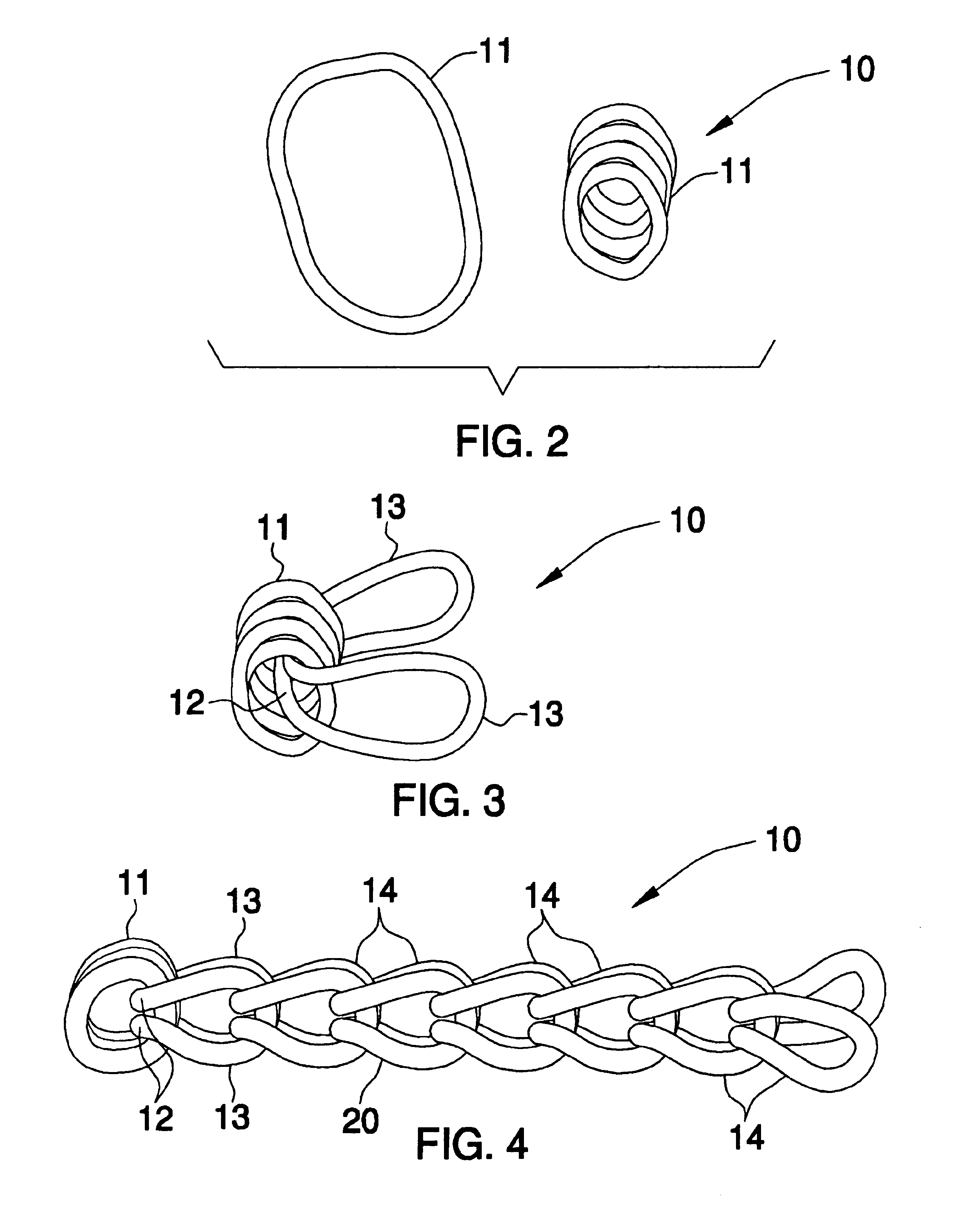
Method for hand-crafting a rug
A method for hand-crafting a rug includes obtaining a first sock loop and twisting the first sock loop to form one loop four strands thick. A second sock loop is pushed halfway through the one loop and a new sock loop is pushed through the two end loops of the second sock loop. Additional sock loops are drawn through selected socks and through each other. This step is repeated until a chain is formed. Another sock loop is wrapped around the chain and pushed through one of the additional sock loops. A new one of the successive sock loops is pushed through the first sock loop and a newer one of the successive sock loops is pushed through a space closest to the old loop. The old loop is pushed over the new successive loop until reaching an opposite end of the chain.
Owner:CLARKE DAISY M
Process of making poly (trimethylene dicarboxylate) fibers
InactiveUS6923925B2Raise the draw ratioGood orientationLayered productsDrafting machinesPolymer scienceSpinning
A process for preparing poly(trimethylene dicarboxylate) multifilament yarns and monofilaments. One process for preparing poly(trimethylene dicarboxylate) multifilament yarns includes (a) providing a polymer blend including poly(trimethylene dicarboxylate) and about 0.1 to about 10 weight % styrene polymer, by weight of the polymer in the polymer blend, (b) spinning the polymer blend to form poly(trimethylene dicarboxylate) multiconstituent filaments containing dispersed styrene polymer, and (c) processing the multiconstituent filaments into poly(trimethylene dicarboxylate) multifilament yarn including poly(trimethylene dicarboxylate) multiconstituent filaments containing styrene polymer dispersed throughout the filaments. Another process includes spinning at a speed of at least 3,000 m / m and processing a blend including poly(trimethylene dicarboxylate) to form partially oriented poly(trimethylene dicarboxylate) multifilament yarn. A poly(trimethylene terephthalate) yarn including poly(trimethylene terephthalate) multiconstituent filament containing styrene polymer dispersed throughout the multiconstituent filament. The invention is also directed to uses of the filament yarns and monofilament.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
Conductive yarn and cloth containing the same
InactiveUS20110047957A1High energy consumptionEnergy lossCurtain accessoriesBed linenFiberElectricity
A conductive yarn and a cloth containing the same are revealed. A plurality of fibers is wound with a heating element in a spiral form so as to form a yarn with electrical conductivity and flexibility. The conductive yarn is used as a thread in a first direction while regular yarns with conductive metal wires arranged at the two sides thereof are used as threads in a second direction. Thus the threads are woven into a cloth that generates heat while being conducted with electricity. Thereby the cloth can be made into mattress, curtains, textile wall coverings, oversleeves, knee braces, waist supports, foot pads, seat cushions, and carpets etc so as to replace various heating equipment.
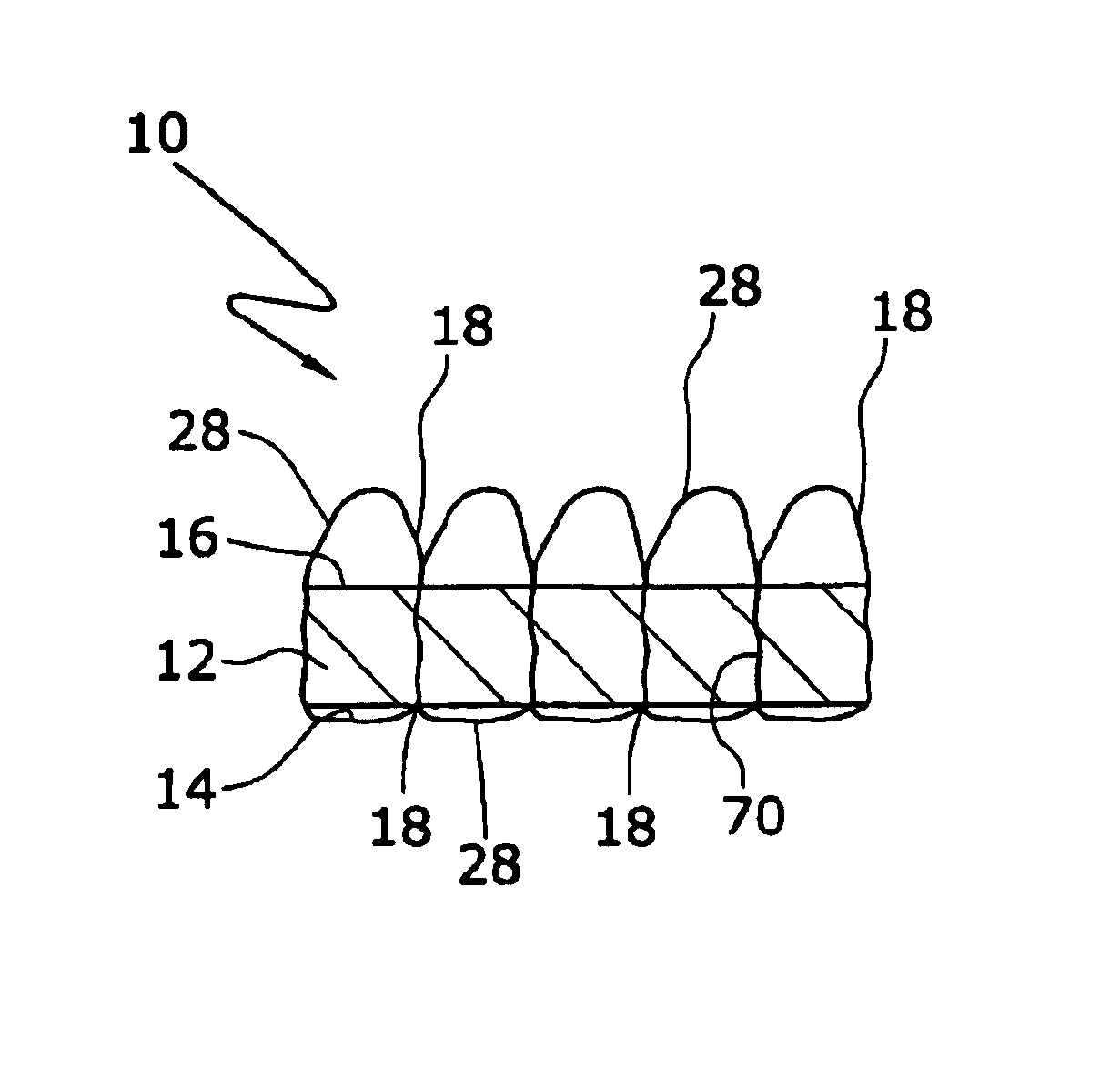
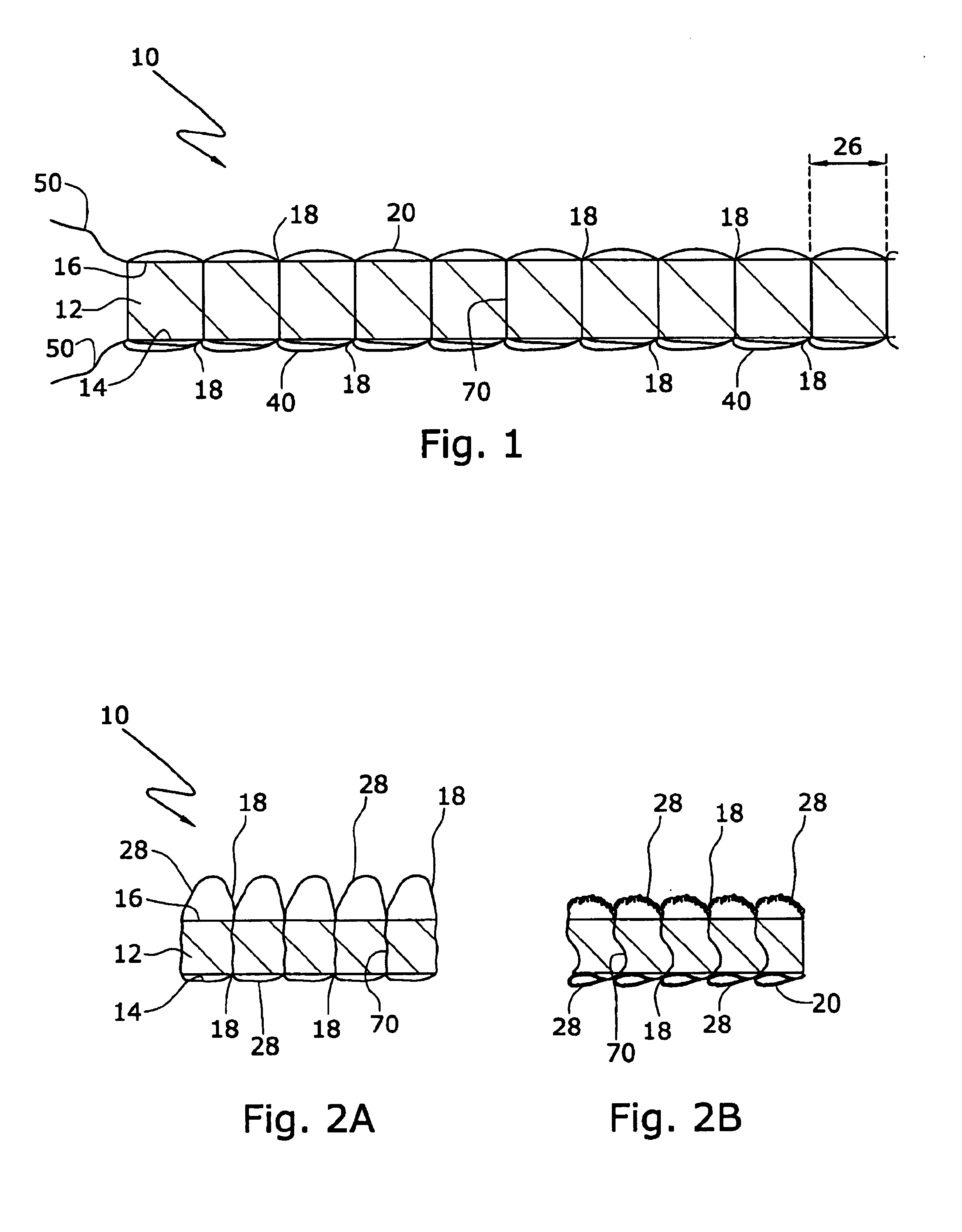
Carpet construction and carpet backings for same
Tufted carpet having good tuft bind and fuzz resistance comprising pile face yams, a backing fabric and an adhesive binder free of inorganic and latex materials. The adhesive binder comprises a thermoplastic fabric, which melts to secure the pile to the backing.
Owner:PROPEX
Polylactic acid resin, textile products obtained therefrom, and processes for producing textile products
InactiveUS7445841B1Deterioration of propertyLow tensile strengthEngine sealsCarpetsYarnRelative viscosity
A polylactic acid resin suitable for use especially in textile products; textile products obtained from the resin as a raw material (a fiber, multifilament, monofilament, staple, false-twist yarn, long-fiber nonwoven fabric, etc.); and processes for producing these textile products. The polylactic acid resin is a resin consisting mainly of a polylactic acid and is characterized in that it is linear, has an L-isomer content of 95 mol % or higher, an Sn content of 30 ppm or lower, a monomer content of 0.50 wt. % or lower, and has a relative viscosity of 2.7 to 3.9 or has a weight-average molecular weight of 120,000 to 220,000 and a number-average molecular weight of 60,000 to 110,000. Each of the textile products comprises the polylactic acid resin as the main material. The textile products each comprises a polylactic acid that is excellent in processability and excellent fiber properties. The free textile products are problems in practical use.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Environmentally friendly yarn and fabric
A monofilament or multifilament, high tenacity, polypropylene, polyethylene, propylene based copolymer, ethylene based copolymer, olefin, or fiberglass core yarn is extruded with a coating comprising a mixture of polypropylene, ethylene octane copolymer to form a monofilament yarn. The coating may also include a flame retardant, a pigment, an ultraviolet inhibitor or a lubricant. This yarn is inherently recyclable, and possesses none of the ecological and health concerns associated with commonly used polyvinyl chloride (PVC) coated yarns. The yarn overcomes the potential health risks, meets flame resistance standards, and ideally replaces PVC products. Bonded, woven fabrics employing the yarn are also recyclable, environmentally friendly, and perform as well as fabrics utilizing a PVC coated yarn. Such fabric makes an ideal interior window shades, wall coverings, and seating material in typical commercial, residential, or automotive interior applications.
Owner:TWITCHELL CORP
Wire mesh panel and method
Owner:DORSTENER WIRE TECH
Carpet, carpet backings and methods
InactiveUS20040202817A1Good flexibilityImprove cohesionFibre treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsFiberPolymer science
The present invention pertains to carpet and method of making it. In one aspect, the carpet includes (a) a primary backing which has a face and a back surface, (b) a plurality of fibers attached to the primary backing and extending from the face of the primary backing and exposed at the back surface of the primary backing, (c) an adhesive backing, (d) an optional secondary backing adjacent to the adhesive backing, and (e) at least one homogeneously branched linear ethylene polymer. The method includes extrusion coating at least one homogeneously branched linear ethylene polymer onto the back surface of a primary backing to provide an adhesive backing. The method can include additional steps or procedures, either separately or in various combinations. Additional steps and procedures include preheating the primary backing prior the extrusion step, multilayer adhesive backings, washing or scouring the primary backing prior the extrusion step, and utilizing adhesive polymeric additives, high heat content fillers, blowing agents and / or implosion agents. The constructions and methods described herein are particularly suited for making carpet tile.
Owner:COLUMBIA INSURANCE CO
Exercise rug with contours
A woven exercise rug having contours on the exercise surface for the purpose of reducing the chance of a user slipping during exercise is disclosed. The woven characteristic of the exercise rug provides for some moisture absorption and the contours provide additional gripping for the user of the rug to help reduce the chance of slipping due to moisture accumulation on the rug, due, for example, to perspiration. The contours of the rug may be provided by supplementary wefts or warps in the weave of the rug which are not required for the structural stability of the rug.
Owner:BUCKLEY CHRISTINE
Fabric stimulating the plant structure for moisture management
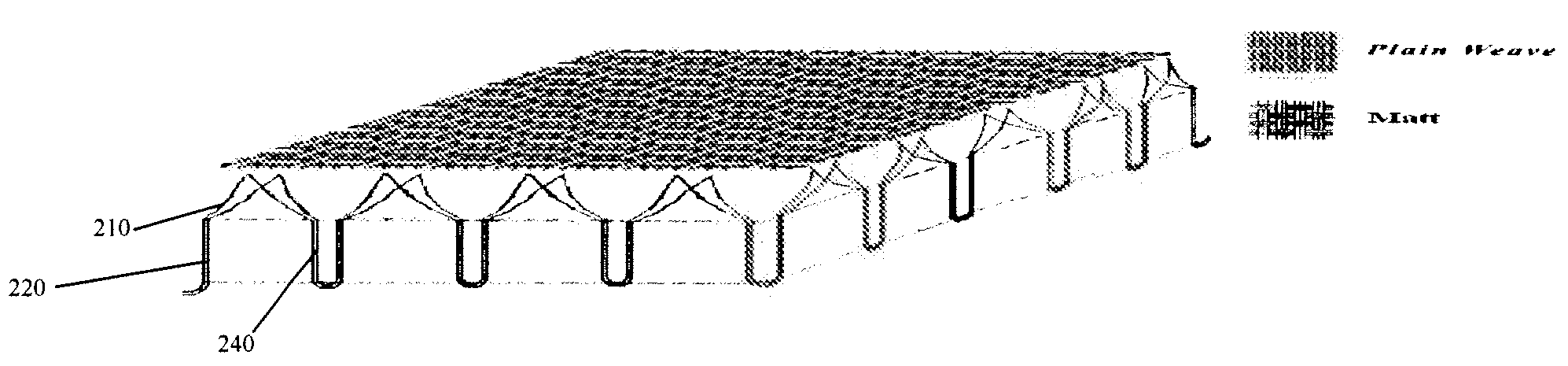
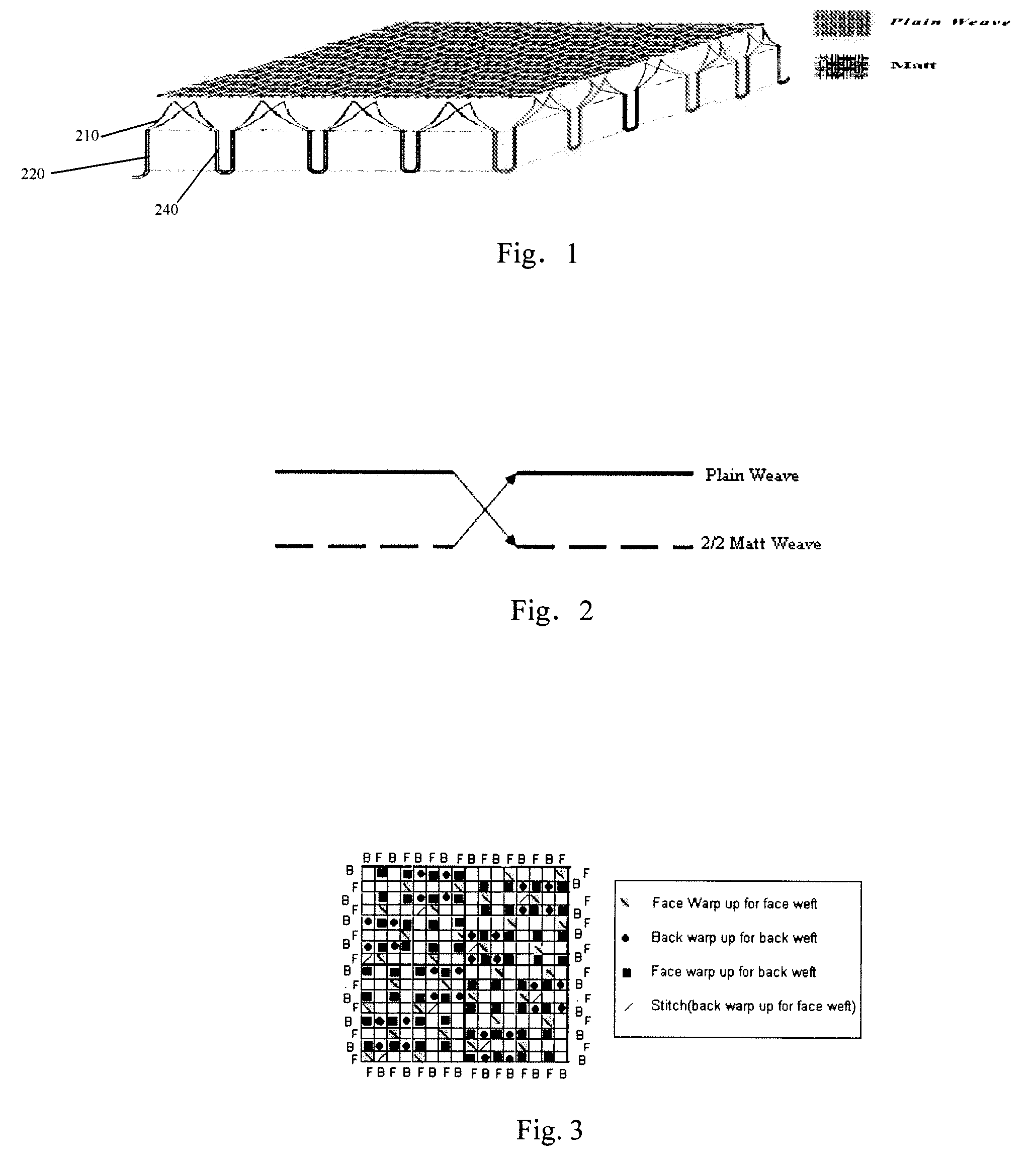
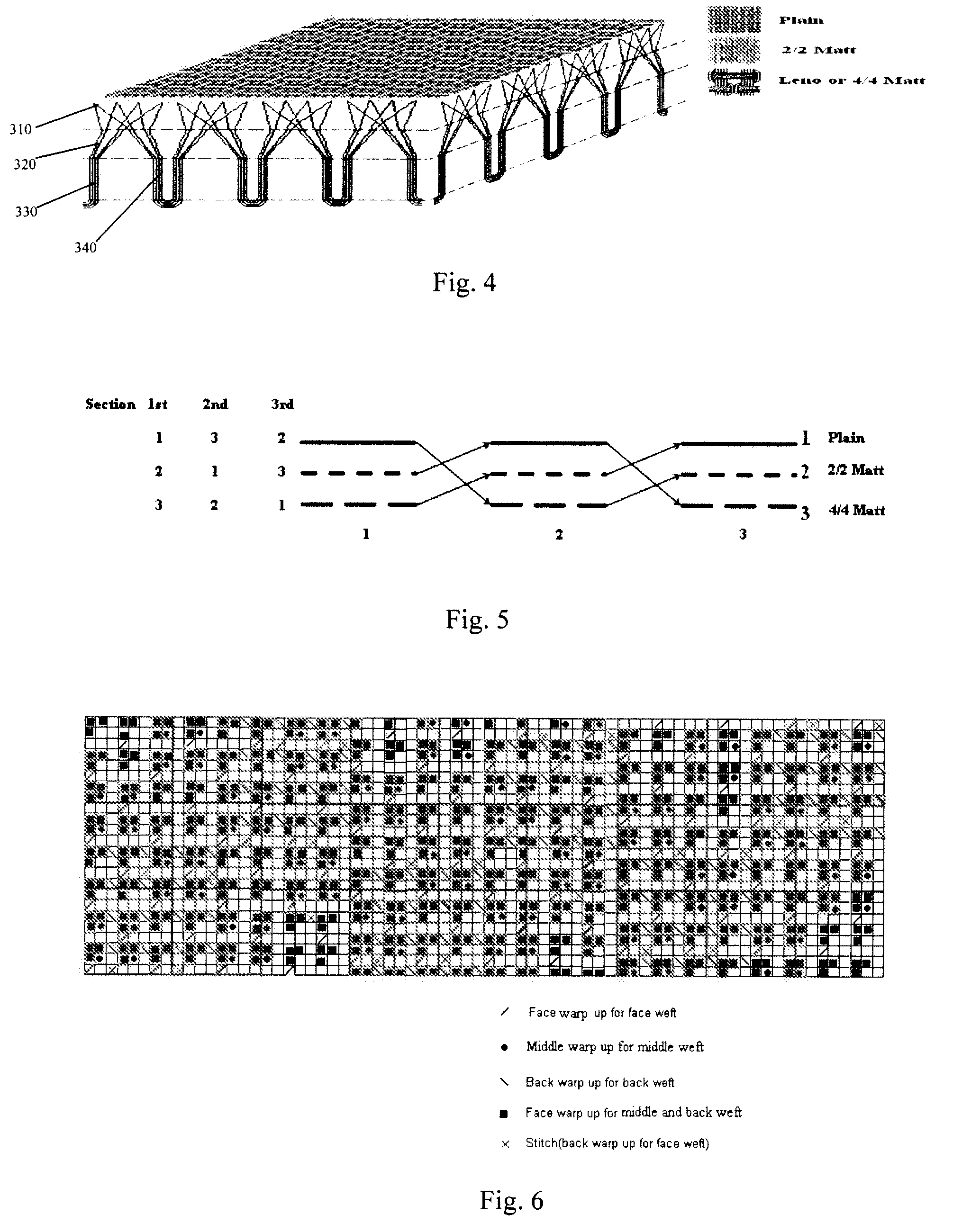
ActiveUS20080220185A1Excellent water transport propertyKeep coolGarment special featuresDead plant preservationPlant StructuresEngineering
A fabric having moisture management function, which has a structure simulating plant structure and comprises at least two layers as follows: a bottom layer, which is of a leno or matt structure simulating main stem of plant, in which a number of yarns are grouped together to form a plurality of fabric units; said bottom layer can be adapted to be in contact with human skin; a top layer, which is of a plain weave structure, in which the yarns of said fabric unit further split in the top layer to form such a plain weave structure, simulating the branching in plant structure; wherein, in said fabric, water can be transported from the bottom layer to the middle layer and further to the top layer where it evaporates due to the improved capillarity of the yarns so as to provide better moisture management function.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
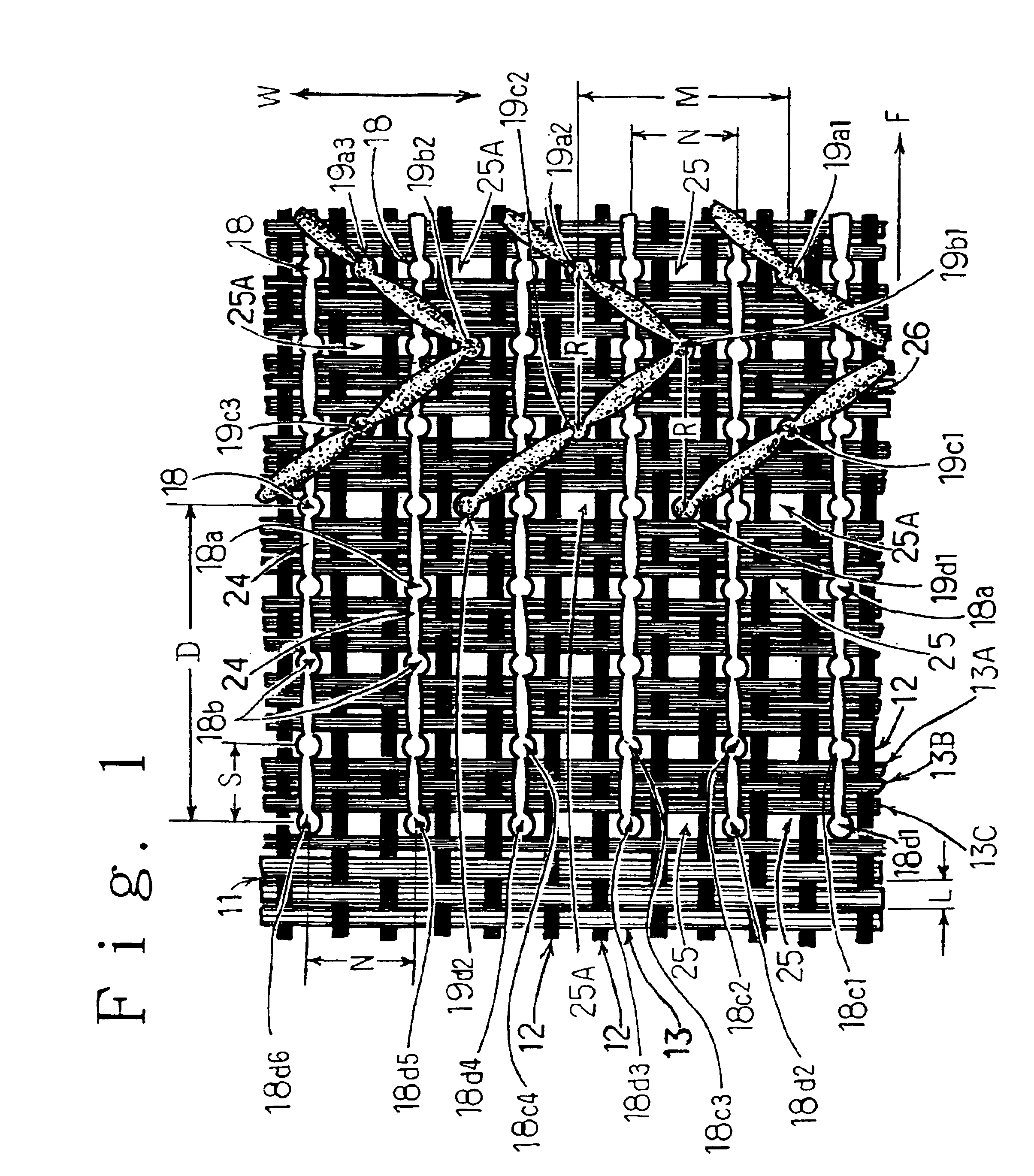
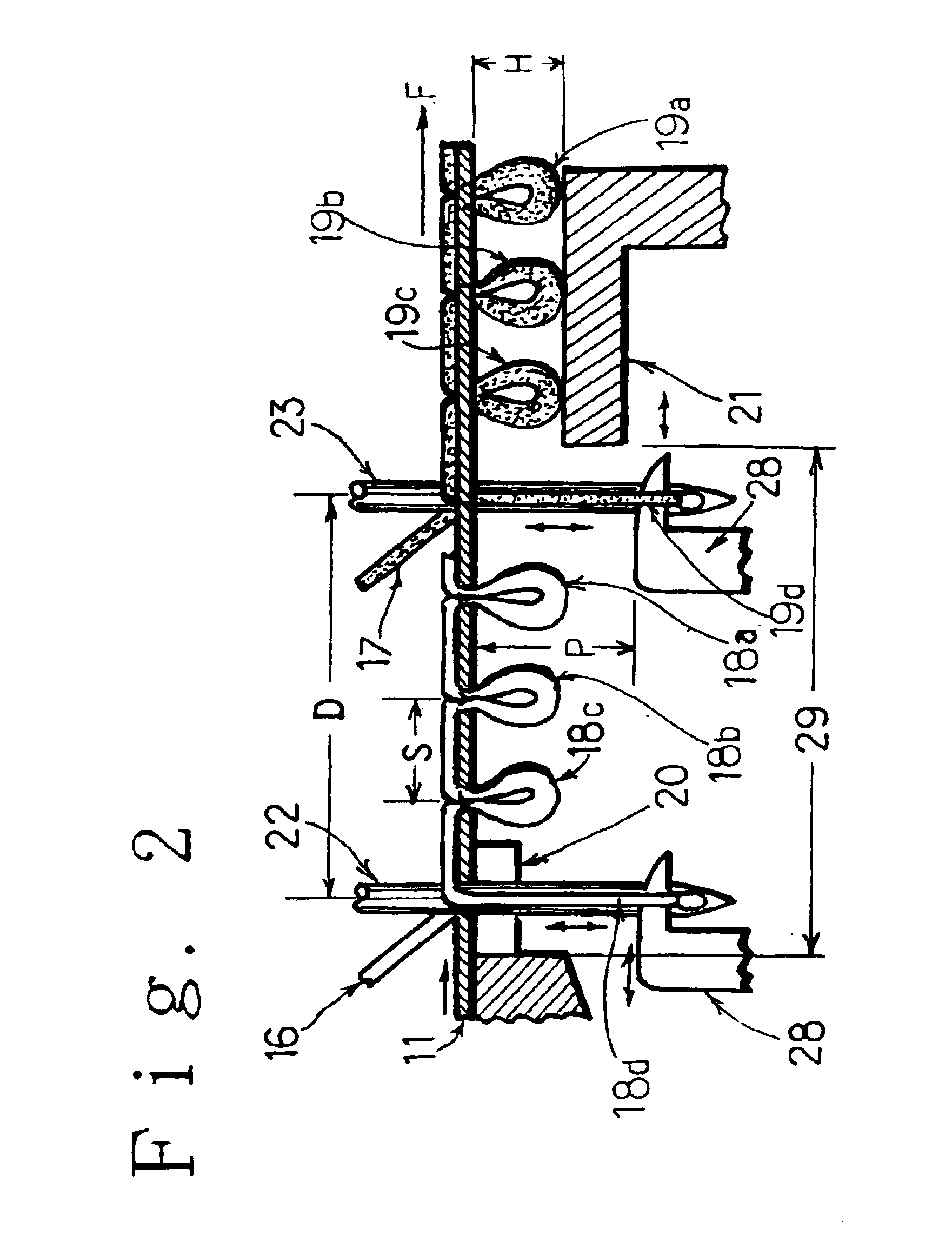
Tufted carpet and backing fabric
A carpet which is suitable for use in a vehicular passageway, includes a backing fabric that is woven by using the multi-filament yarns for the warps and wefts. A binding resin is applied to the filaments which compose the weft. The filaments which make up the weft are partially fixed to one another through the binding resin. The warp and the weft are partially fixed through the binding resin sticking on the filament of the weft before the tufting process.
Owner:TB KAWASHIMA CO LTD +2
Method of making furniture with synthetic woven material
An article of furniture is made from elongated polymer filaments. The polymer filaments may be monofilaments or plural filaments which are twisted together and heat set to prevent their untwisting during the subsequent weaving process. The heat setting of the polymer filaments is achieved by heating the polymer material either before or after the twisting process.
Owner:CASUAL LIVING WORLDWIDE
Composite fabric product and production process therefor
A composite fabric product comprises at least one layer of textile material and at least one layer of melted plastic material, wherein non-melting textile material is embedded in at least one of the said layers of melted plastic material, and wherein filaments or yarns located in at least one of said layers of textile material extend into said at least one layer of melted plastic material and interlace with the non-melting textile material embedded therein.
Owner:TEXOPLAST
Stitch-bonded and gathered composites
InactiveUS6936327B2Good dimensional stabilityStretchabilityWarp knittingLaminationYarnMaterials science
Owner:J&J FLOORING GRP LLC
Composite structure made of urethane and woven backing materials
The present invention relates to composite structures comprising an open weave, natural or synthetic fabric or backing having fibers and a urethane froth foam, wherein the fibers of the fabric or backing are at least partially penetrated and / or embedded by the urethane froth. This invention also relates to a process for the production of a composite structure comprising A) applying a reactive urethane froth to an open weave, natural or synthetic fabric or secondary backing having fibers, B) passing the fabric or backing coated with the reactive urethane froth under a doctoring device such that the reactive urethane froth at least partially penetrates and / or embeds the fibers of the fabric or backing, and C) curing the reactive urethane froth.
Owner:HOLESCHOVSKY ULRICH B
Textile fabric structure and method for determining the interspacing of microelectronic elements of the textile fabric structure
The invention relates to a textile fabric structure having a plurality of microelectronic components, which are arranged in the textile fabric structure, electrically conductive threads, which couple the plurality of microelectronic components to one another, conductive data transmission threads, which couple the plurality of microelectronic components to one another, and electrically nonconductive threads. The conductive threads and the conductive data transmission threads at the edge of the textile fabric structure are each provided with an electric interface and a data transmission interface.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
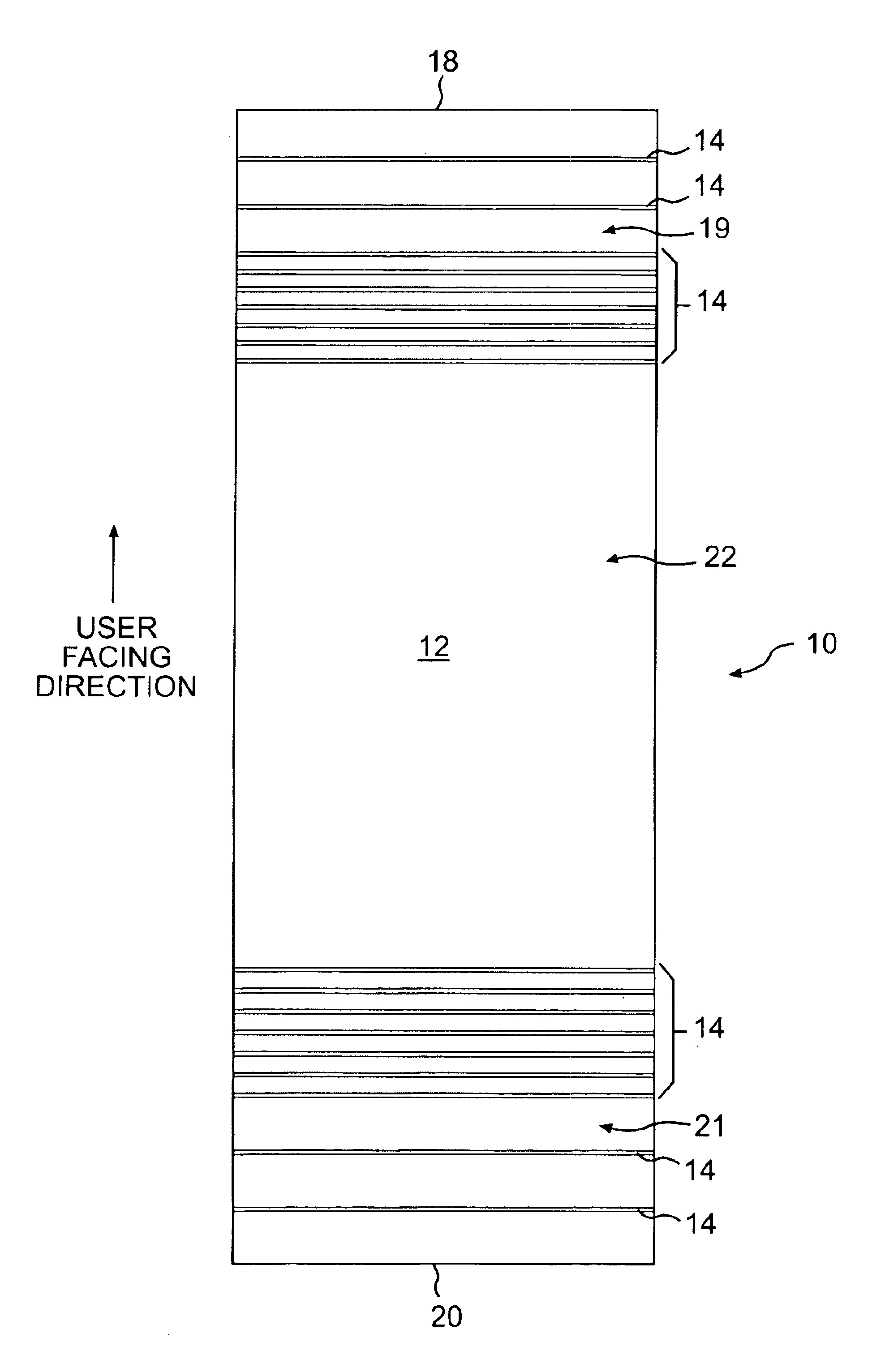
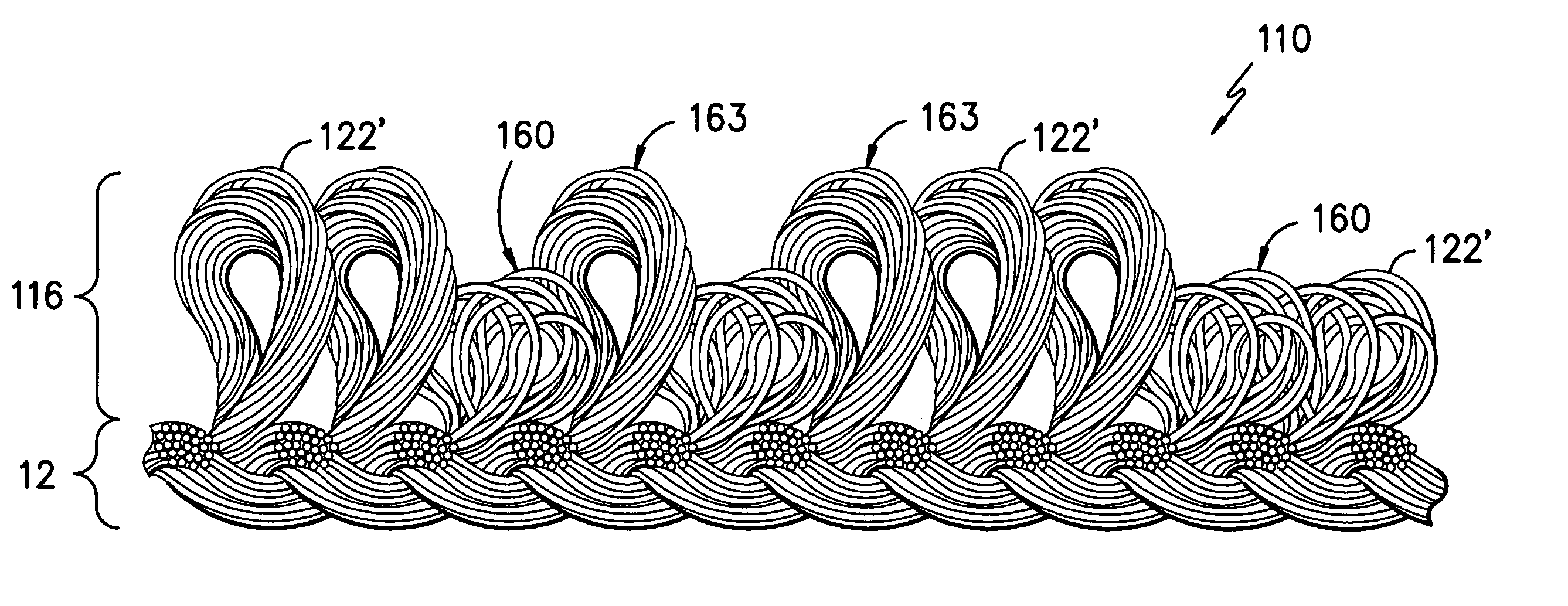
Loop pile fabric having randomly arranged loops of variable height
A loop pile fabric wherein the pile portion has a first group of yarn loops projecting outwardly from the base portion to a first height and at least a second group of yarn loops projecting outwardly from the base portion to a second height lower than the first height. At least a portion of the first group of yarn loops and at least a portion of the second group of yarn loops are formed from segments of a common yarn. In the fabric the segments of the common yarn forming the second group of yarn loops are formed from yarn filaments having an average cross sectional area which is greater than the average cross sectional area of yarn filaments in the segments of the common yarn forming the first group of yarn loops.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Combination weave using twisted and nontwisted yarn
An article of furniture is made from elongated polymer filaments. The polymer filaments may be monofilaments or plural filaments, which are twisted together and woven with polymer strands of non-twisted yarn to form a woven portion of material. The woven portion can be used to form the seat or back rest of a seating article of furniture for indoor or outdoor use.
Owner:CASUAL LIVING WORLDWIDE
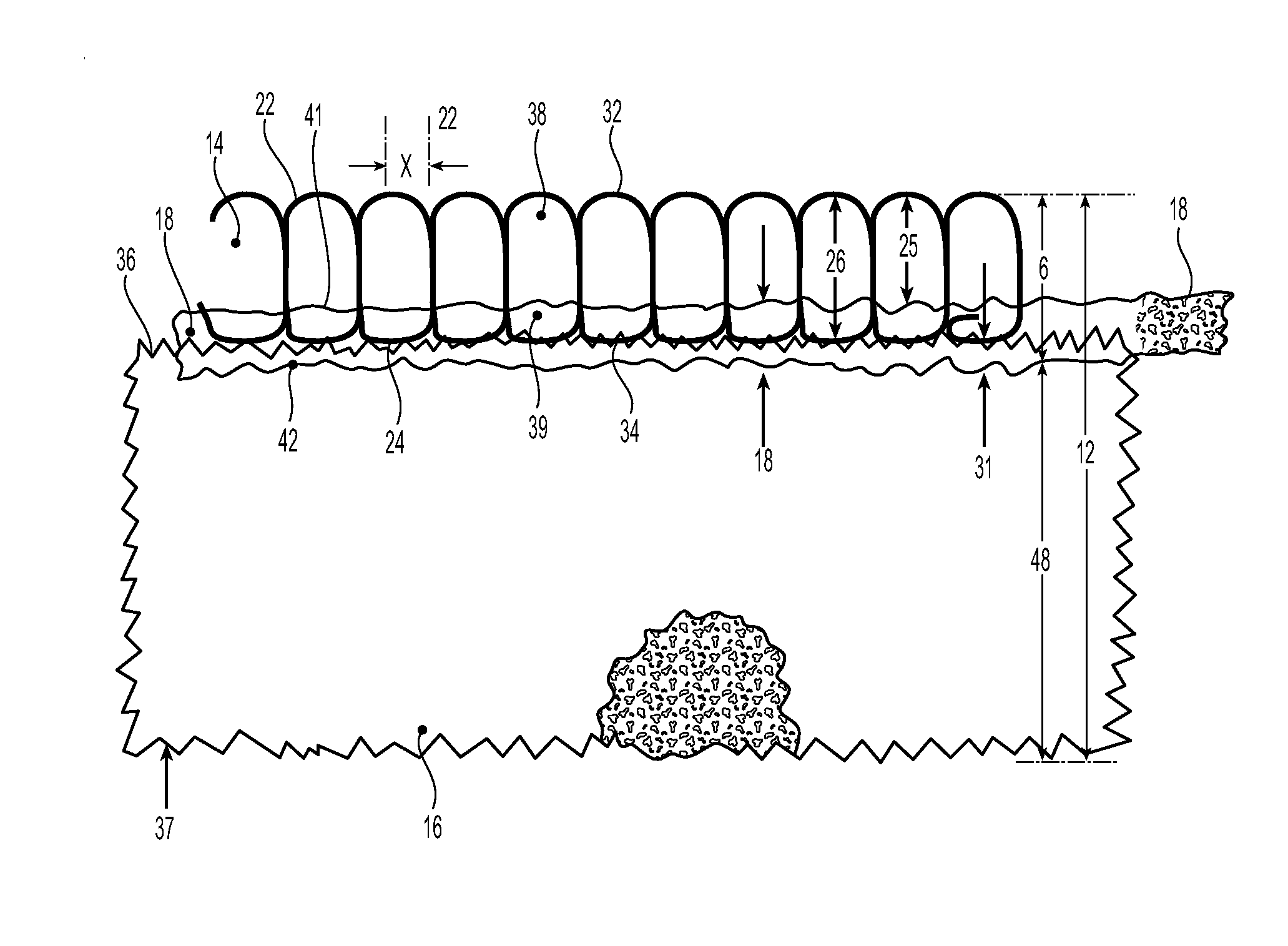
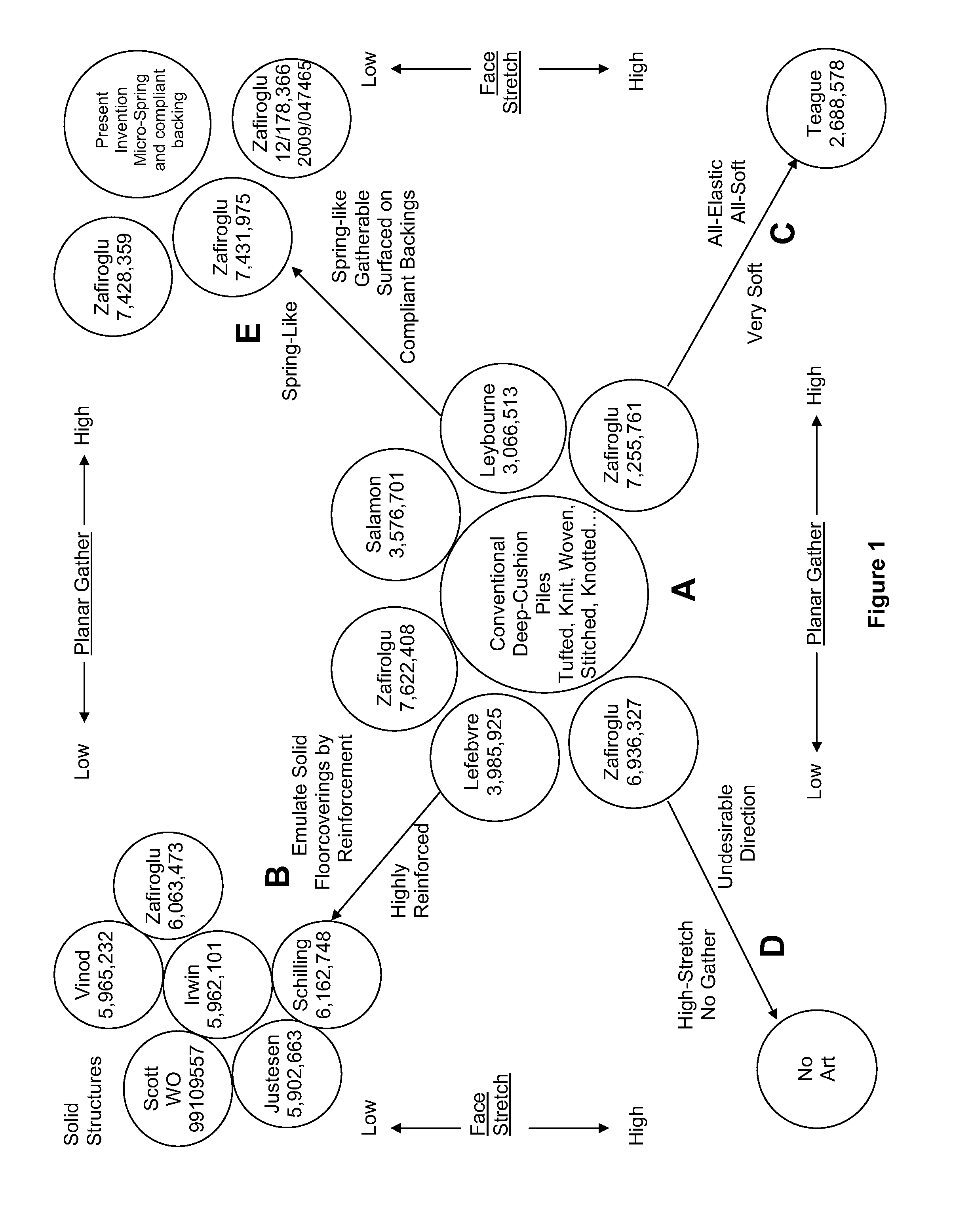
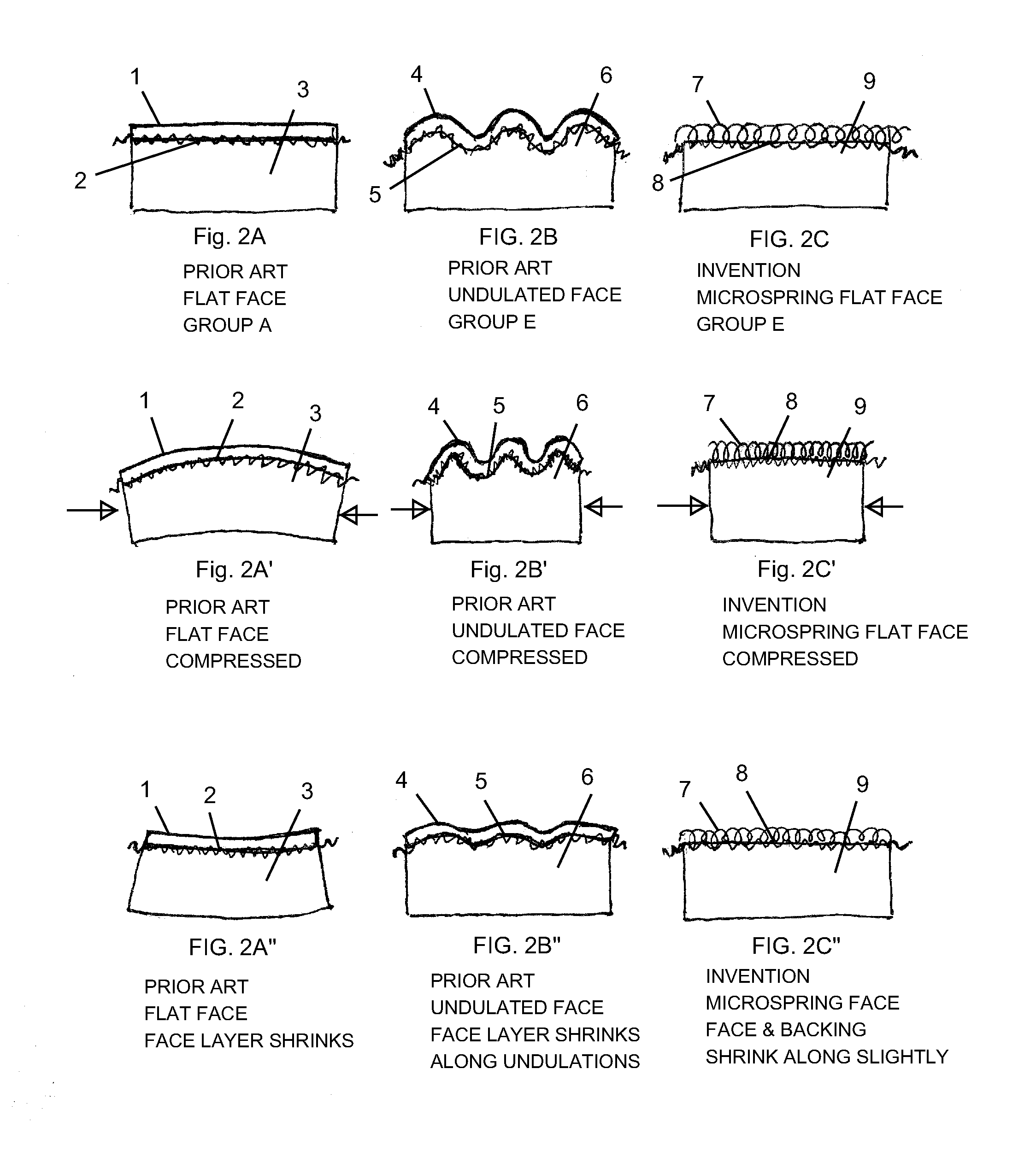
Fabric-Faced Floor Coverings with Micro-Spring Face Structures
The present invention is directed to multiple-layer composites suitable for use as floor-coverings in the form of cut tiles or broadloom sheets, providing a durable and highly stable structure that can lay flat and remain flat with variations in temperature and humidity and provide a durable and yet soft textile face. The composite comprises a laterally-compressible fabric face bonded with an adhesive layer to a highly conformable stress-absorbing cushioning layer. The face fabric comprises closely packed looped yarns reciprocating between the top and the bottom of the fabric, protruding into the adhesive layer and emerging from the adhesive layer to the surface forming micro-spring structures. The weight, properties, density and level of penetration of adhesive are controlled to maintain lateral compressibility for the entire composite and avoid warping.
Owner:J&J FLOORING GRP LLC
Fiberglass corespun fabrics for use in flame resistant drywall installations
Provided is a flame resistant drywall installation, especially those designed to meet ASTM E119. The installations comprise the use of fiberglass corespun flame resistant (FR) woven and fiberglass corespun stitchbonded nonwoven fabrics. The preferred forms of the woven and stitchbonded fabric used in this invention include:WOVEN FABRIC: A 3-8 opsy woven fabric consisting of fiberglass corespun yarns as described below.STITCHBONDED FABRIC: A 4-10 nonwoven batting of 100% cotton, 100% rayon, 100% lyocell, cotton / non-FR fiber blends, rayon / non-FR fiber blends or lyocell / non-FR fiber blends stitched with fiberglass corespun yarns as described below.Fiberglass corespun weaving and stitching yarns, for use in the invention, include those known in the textile industry as Alessandra® yarn (U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,146,759; 6,287,690; 6,410,140; 6,606,846; 6,553,749 by McKinnon Land LLC) and Firegard® yarn (by Springs Industries).The two fabric types mentioned above are used in tandom, between layers of conventional gypsum style drywall paneling to obtain a higher flame rating than would otherwise be able to be obtain in a layered drywall construction which does not include these fabrics. Conventional latex paint or flame resistant coating materials can be used to adhere the fabrics between the drywall paneling.
Owner:BASOFIL FIBERS
Flame-retardant polyester fiber, woven or knitted flame-retardant polyester fiber fabric, nonwoven flame-retardant polyester fiber fabric, and woven or knitted suede fabric
A flame-retardant polyester fiber containing a phosphorus compound copolymerized polyester satisfying the following formulas (1)-(3) and having a phosphorus atom content of 500-50,000 ppm: (formula 1) tan delta max >= 0.1740 , (formula 2) T alpha - 3.77 x 1n (dtpf) <= 137.0; (formula 3) 1.331 <= SG - DELTA n DIVIDED 8.64 <= 1.345 wherein tan delta max is the maximum value of loss tangent in a dynamic viscoelasticity measurement, T alpha is a temperature at which loss tangent reaches the maximum, dtpf is single fiber fineness (dtex), SG is density (g / cm<3>), and DELTA n is birefringence, particularly a flame-retardant polyester fiber showing an L value of not less than 67 and a b value of not more than 10.00 as measured with a Hunter's color-difference meter, a flame-retardant polyester woven, knitted fabric using this flame-retardant polyester fiber at least in a part thereof, and a suede raised woven, knitted fabric which is a raised woven, knitted fabric obtained by applying a raising treatment to this flame-retardant polyester woven, knitted fabric, which has a coefficient of friction of a surface of the woven and knitted fabric by a surface tester KES-FB4 of 0.200-0.300. By this constitution, a flame-retardant polyester fiber, a woven, knitted fabric, a nonwoven fabric and a suede raised woven, knitted fabric superior in dyeing property and mechanical property such as abrasion resistance, heat stability and the like, can be provided, which have extremely fine whiteness, a soft feeling and flame retardancy stable over a long period of time.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com