Particle detection system
a particle detection and particle technology, applied in particle and sedimentation analysis, measurement devices, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of accurate particle size determination and increased submicron particle detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
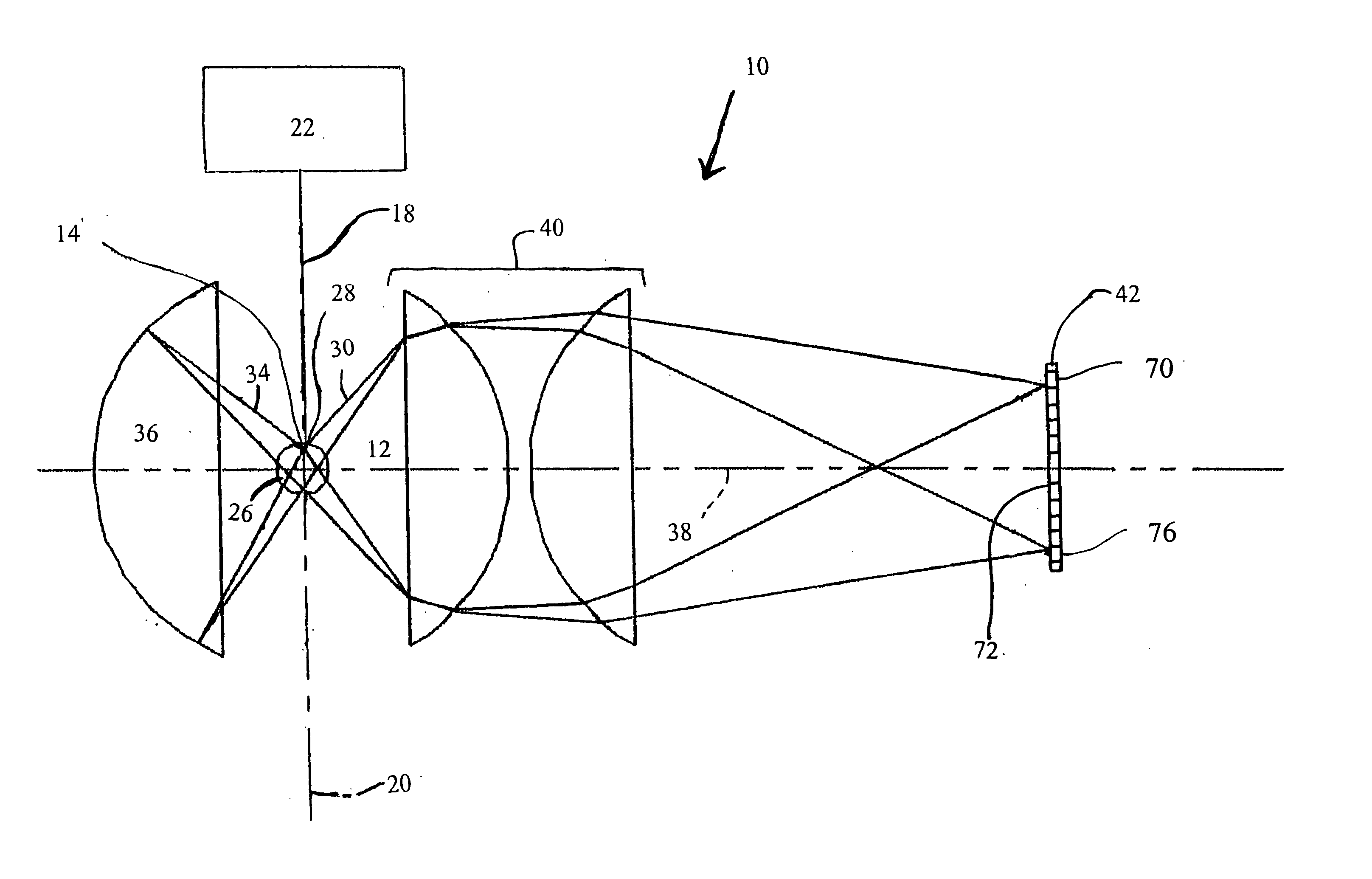
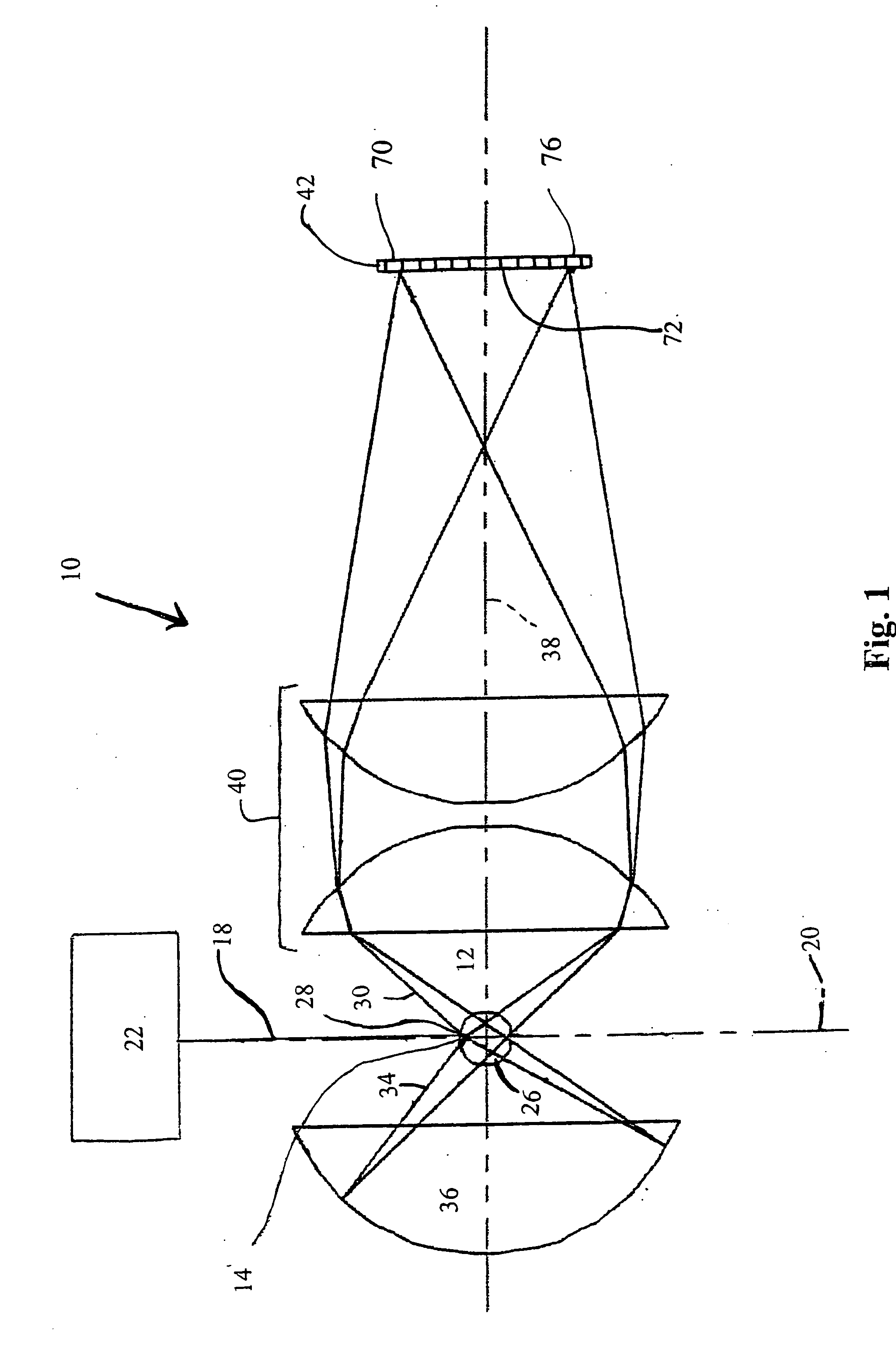
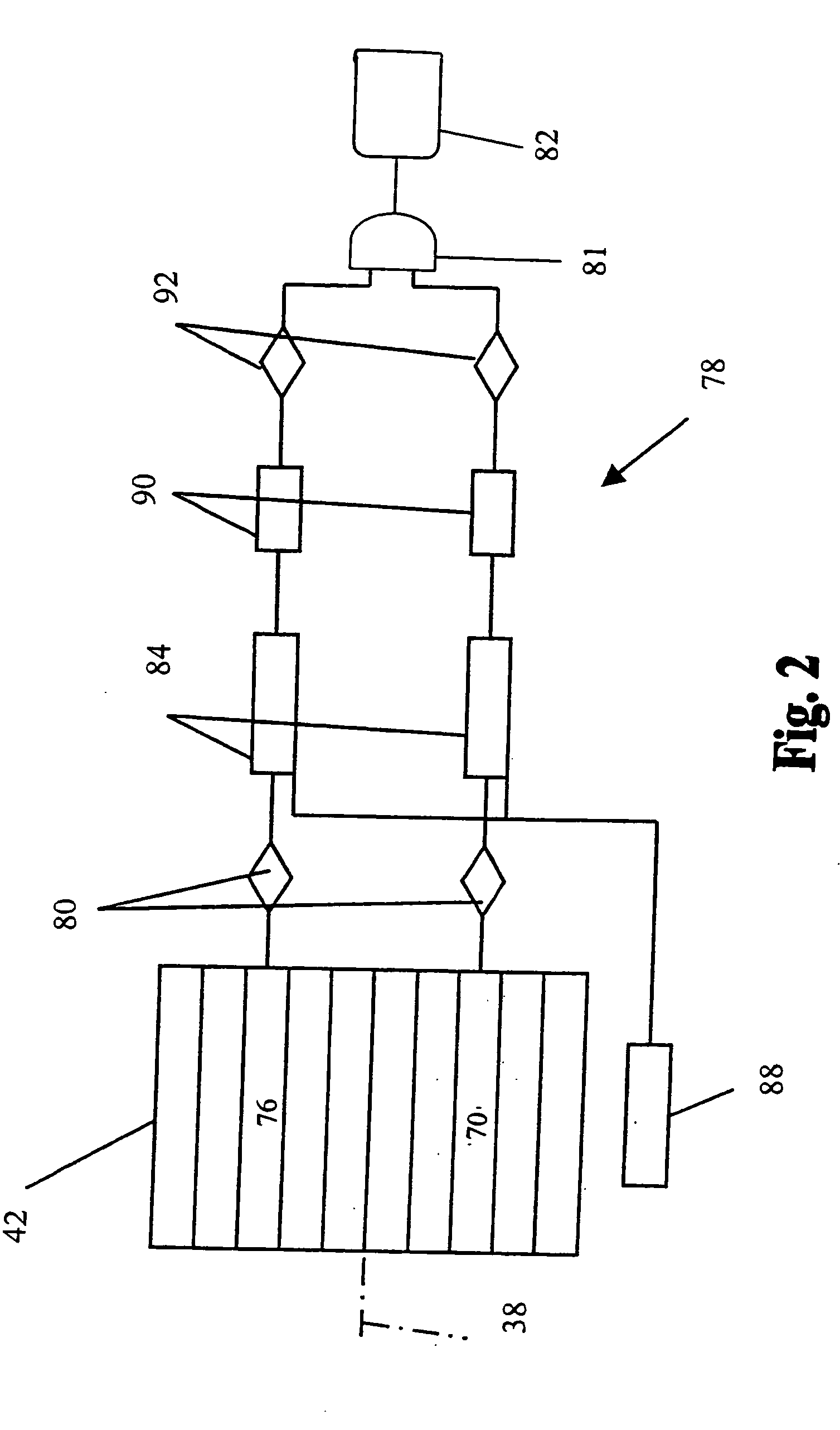
[0018] The particle detection system of the present invention has an increased ability to distinguish between noise and pulse output signals generated by small particles incident upon a light beam. This increased ability results from the incorporation of a light reflector, a pair of detector elements that detect correlated portions of a light beam scattered in multiple directions by a particle, and a coincidence circuit that determines whether the detector elements in the pair concurrently generate pulse output signals exceeding a predetermined threshold. If both detector elements of the pair concurrently generate pulse output signals, there is a high probability that the signals were caused by the incidence of a sample particle on the light beam rather than by noise variations in the particle detection system. The ability of the particle detection system of the present invention to distinguish low-amplitude pulse output signals from noise enables the system to detect smaller diamet...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| distances | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| threshold | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com