Time-extended cooling system for line-powered apparatus
a cooling system and line-powered technology, applied in the field of cooling systems, can solve the problems of dramatic temperature rise in the parts surrounding the hot component, inability to normalize the cooling cycle, and the heat generating component can get extremely hot, so as to prevent damage to electrical equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
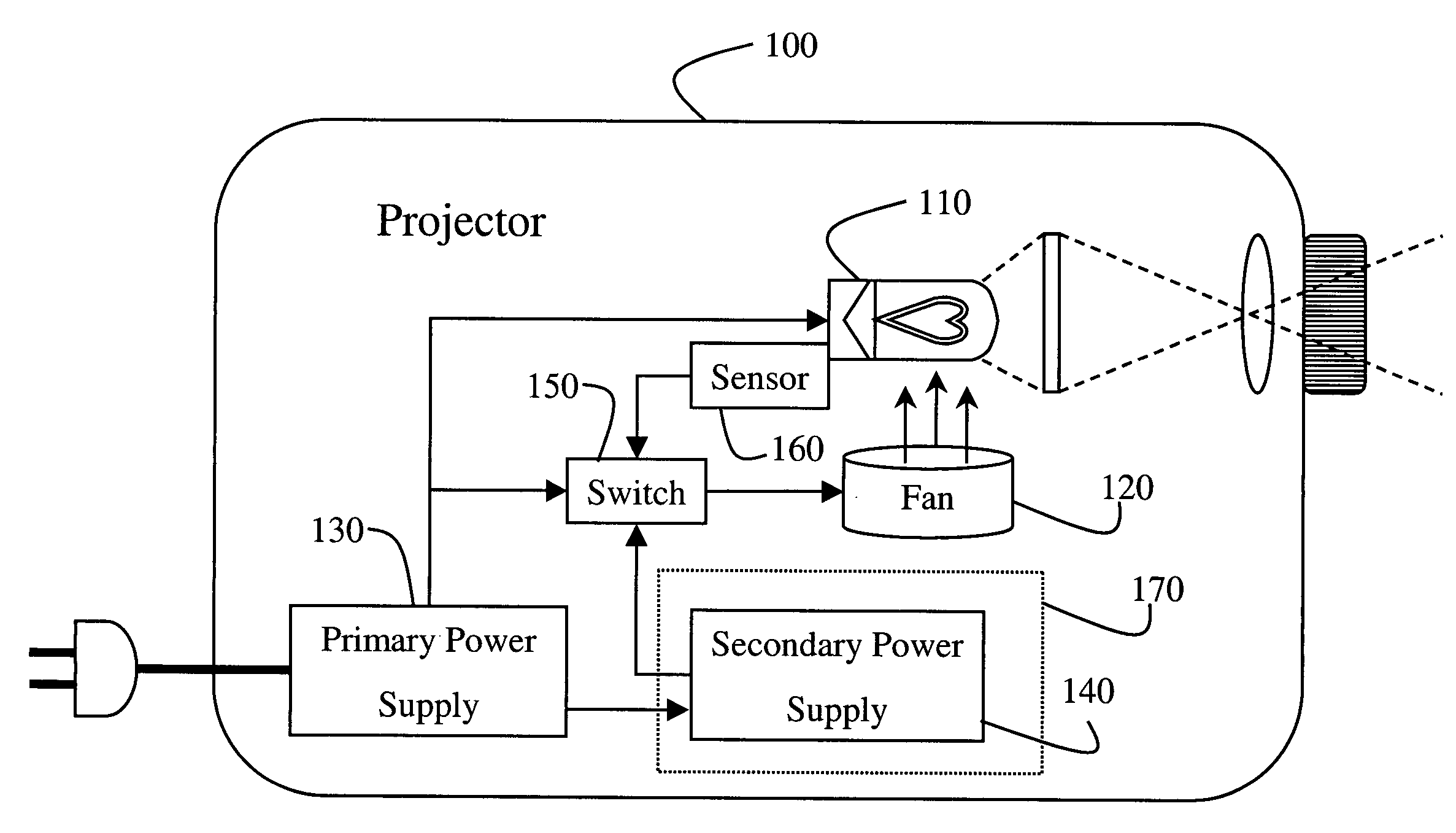
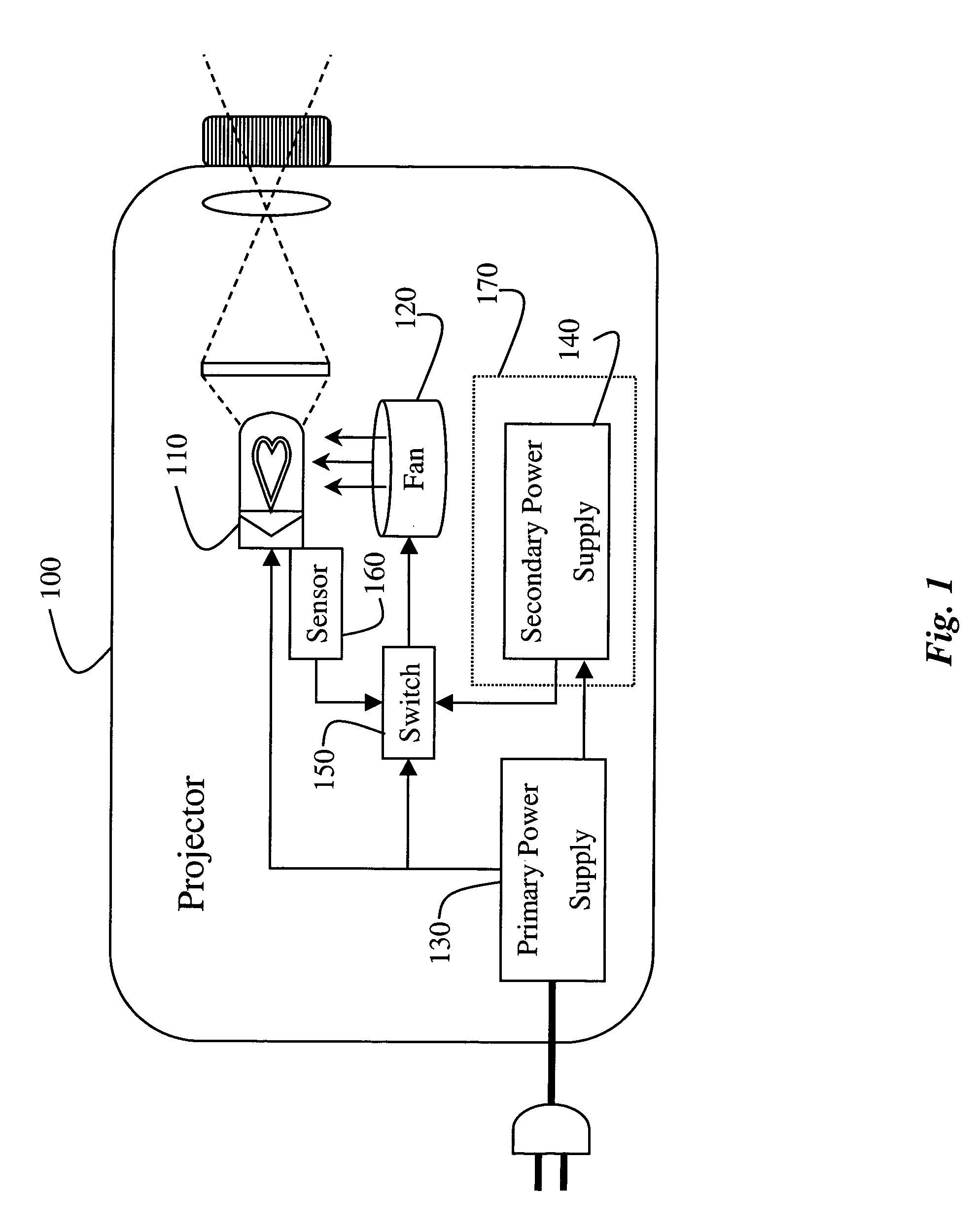
[0017]FIG. 1 shows a projector system 100 that uses the invention. It should be understood that the invention can also be used by other heat generating electrical systems and devices.
[0018] The projector includes a heat source 110, i.e., a lamp. The temperature of the lamp can reach several thousand degrees. If the lamp gets too hot, then it can self-destruct, as well as damage nearby components. Therefore, during normal operation, a fan 120 is used to cool the lamp. The fan is connected to a primary power supply 130, normally a power line.
[0019] In most modern projectors, the fan will continue to run for several minutes after the projector has been shut off to cool the lamp. However, should there be a failure in the power line, damage can still occur.
[0020] Therefore, the projector 100 also includes a secondary power supply 140, for example, a rechargeable battery. Should there be a failure in the primary power supply, then a switch 150 can cause the fan 120 to be operated from ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com