Optical disc drive and optical pickup
a technology of optical disc drives and optical pickups, applied in the direction of data recording, instruments, disposition/mounting of heads, etc., can solve the problems of increasing thickness, reducing response characteristics, and inability to achieve appropriate wavefront correction for compensating aberrations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
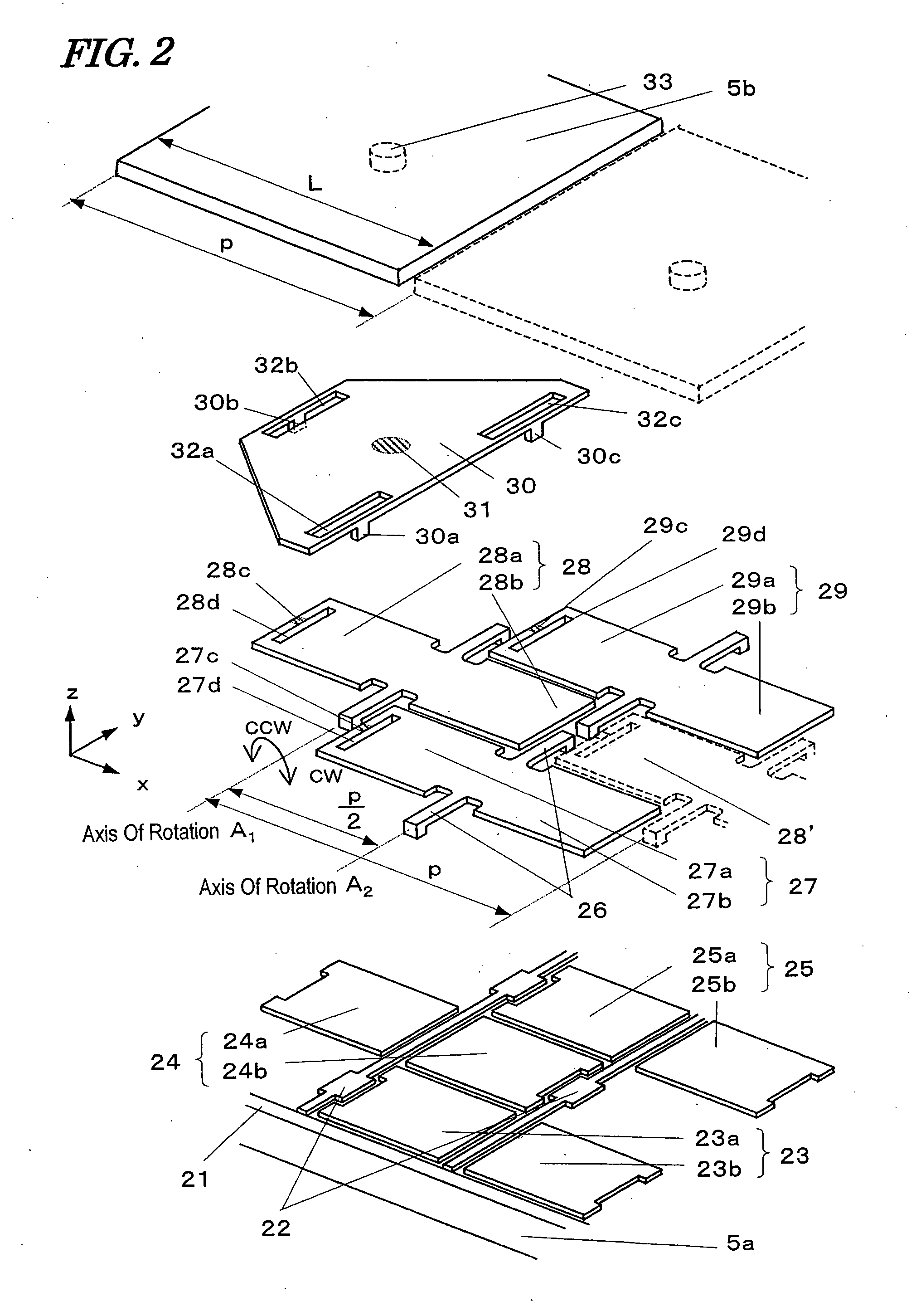
Hereinafter, an apparatus according to a first specific preferred embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 through 7. In the following preferred embodiment, the apparatus is implemented as an optical disc drive.
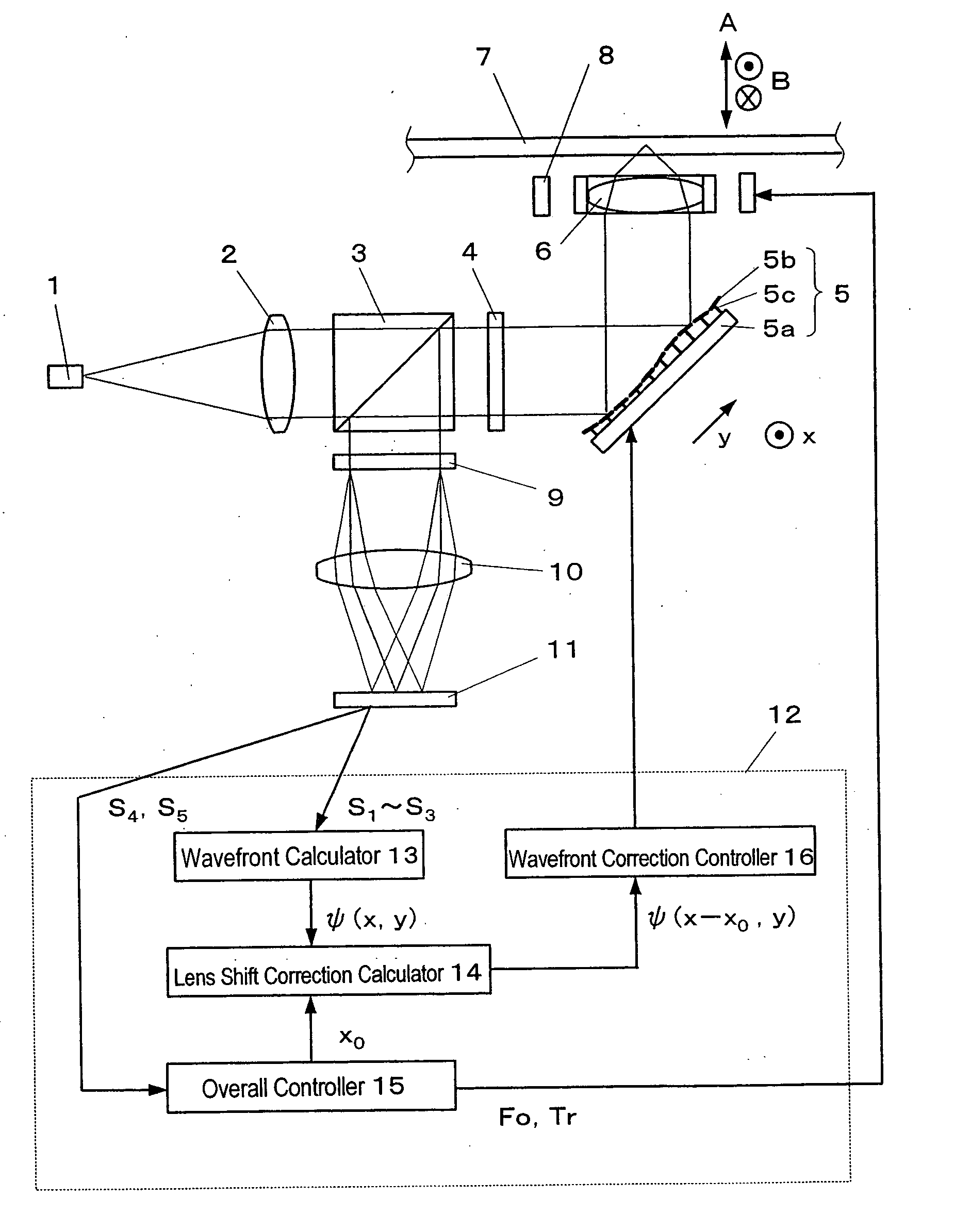
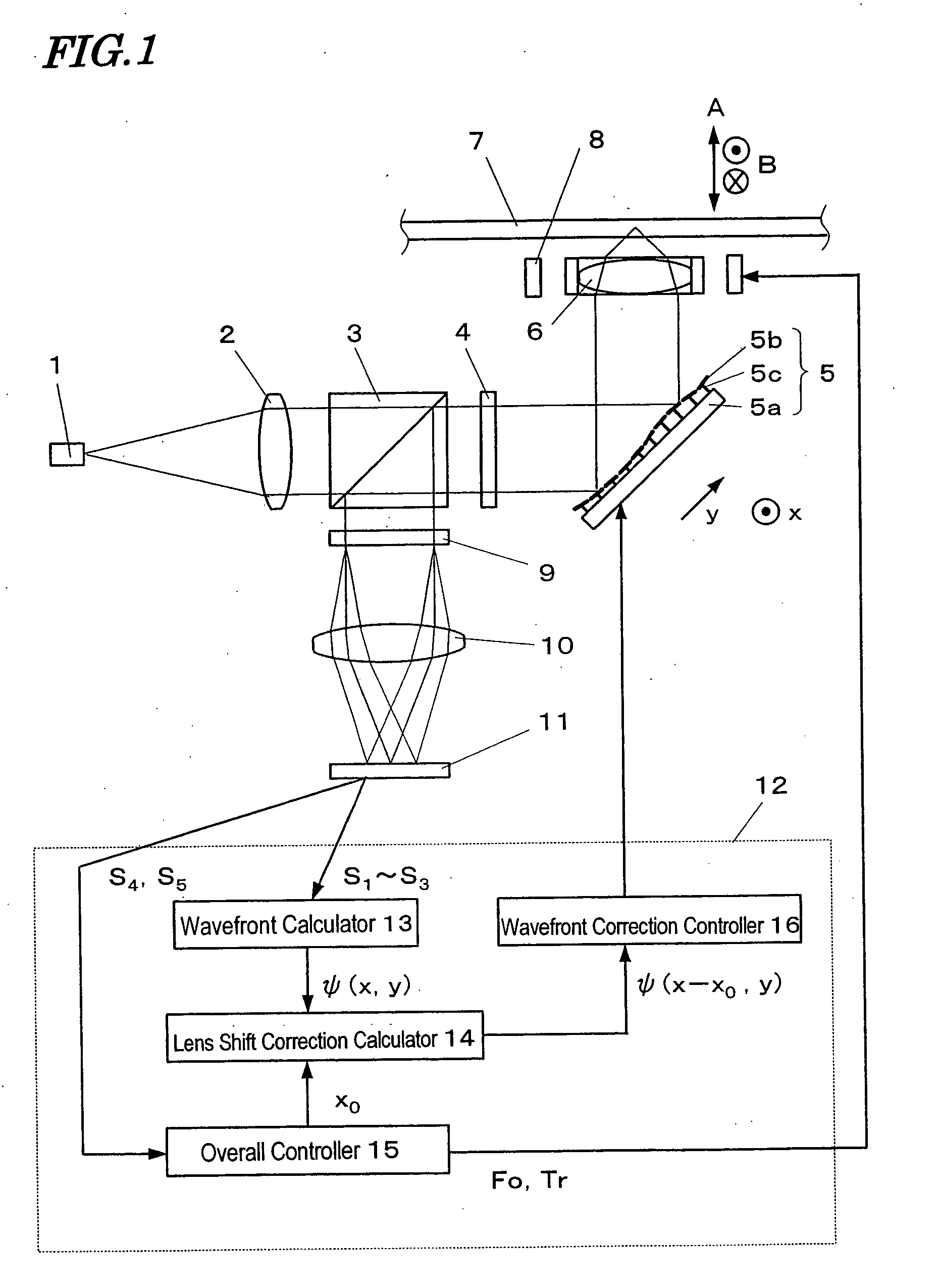
First, referring to FIG. 1, illustrated is a schematic configuration for an optical disc drive according to this first preferred embodiment. This optical disc drive is an apparatus for reading and / or writing data from / on a given medium (i.e., an optical disc in this case).
A light beam emitted from a light source 1 such as a GaN laser diode is transformed by a collimator lens 2 into an parallel light beam, which is then incident onto a polarization beam splitter 3. Only the P-polarized component of this light beam is transmitted through the polarization beam splitter 3, while the remaining S-polarized component is reflected from the polarization beam splitter 3 so as to enter a front light monitor (not shown). Thereafter, the transmi...
embodiment 2
Hereinafter, an optical disc drive according to a second specific preferred embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 8, which schematically illustrates a configuration for the optical disc drive of this second preferred embodiment.
In this second preferred embodiment, the light source 1, collimator lens 2, deformable mirror 5, objective lens 6, optical disc 7, objective lens actuator 8, photodetector 11, control section 12, wavefront calculator 13, lens shift correction calculator 14, overall controller 15 and wavefront correction controller 16 are identical with the counterparts that have already been described for the first preferred embodiment.
A light beam emitted from the light source 1 is transformed by the collimator lens 2 into an parallel light beam, which is then incident onto a half mirror 50. A portion of the light beam that has been transmitted through the half mirror 50 is incident onto a polarization beam splitter 51. Only the P-...
embodiment 3
Hereinafter, an optical disc drive according to a third specific preferred embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 10, which schematically illustrates a configuration for the optical disc drive of this third preferred embodiment.
In this third preferred embodiment, the structures and operations of the light source 1, collimator lens 2, polarization beam splitter 3, quarter-wave plate 4, deformable mirror 5, objective lens 6, optical disc 7, objective lens actuator 8, lens 10, lens shift correction calculator 14, and wavefront correction controller 16 are identical with those of the counterparts that have already been described for the first preferred embodiment.
The light beam that has returned from the optical disc 7 to the polarization beam splitter 3 is reflected from the polarization beam splitter 3, passed through the lens 10, given astigmatism by a cylindrical lens 20 and then incident onto a photodetector 11b. The photodetector 11b incl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com