Interlocking IM nails with outer screw
a technology of im nails and screws, applied in the field of interlocking im nails with outer screws, can solve the problems of increasing the fixation in the cortical bone, not helping the screw-nail interface, and loss of reduction, so as to achieve stable fixation and eliminate the play of the screw-nail interface
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
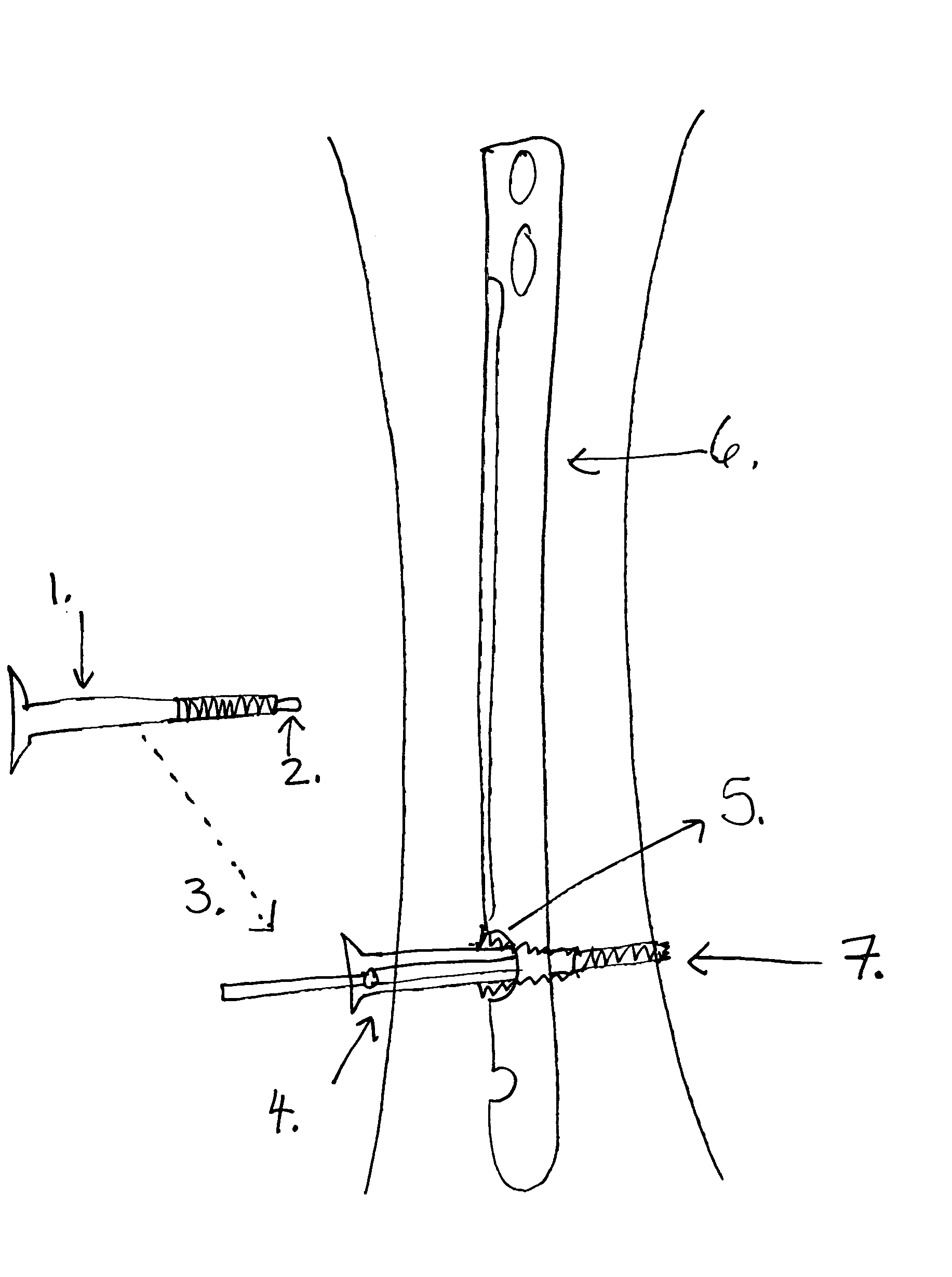
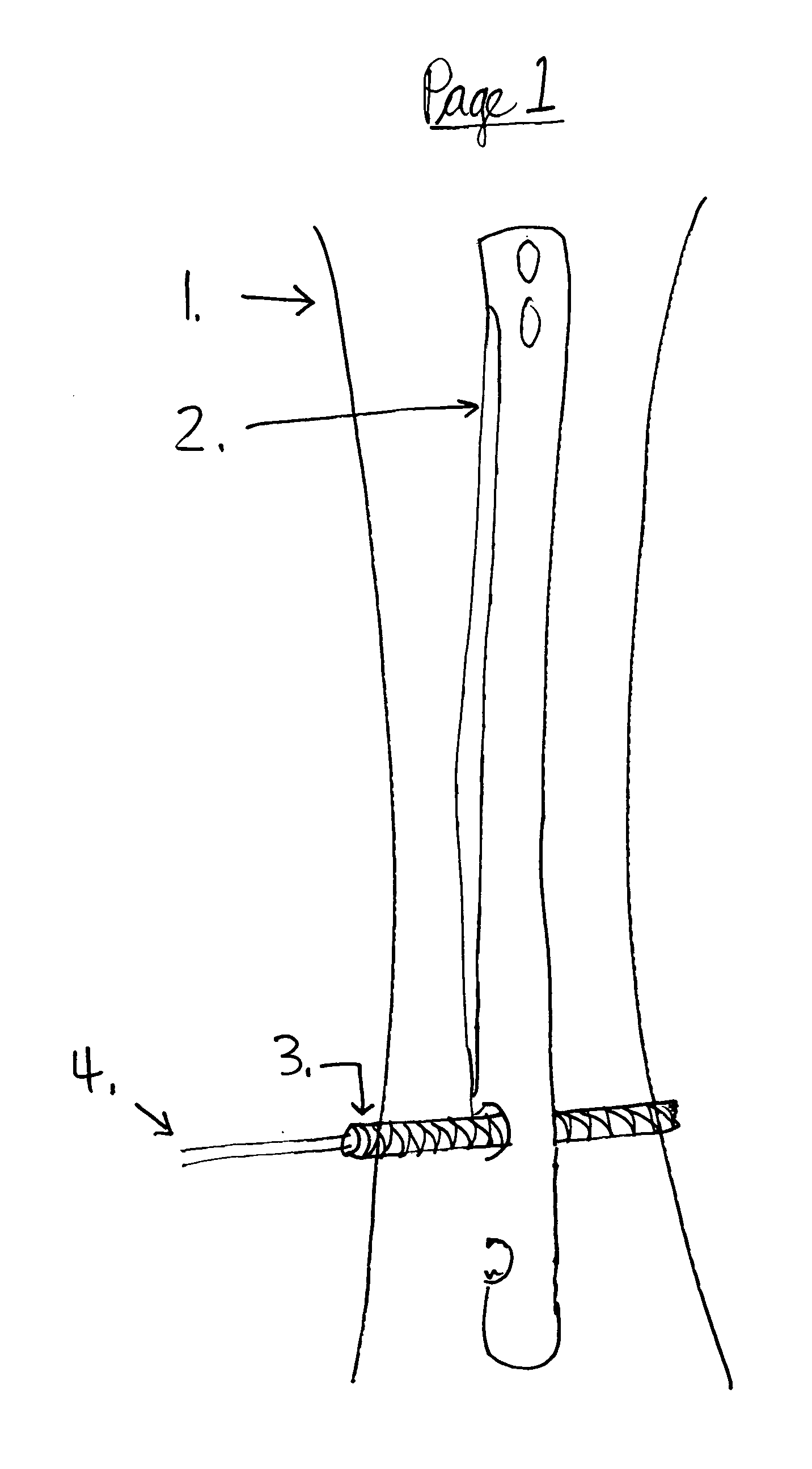
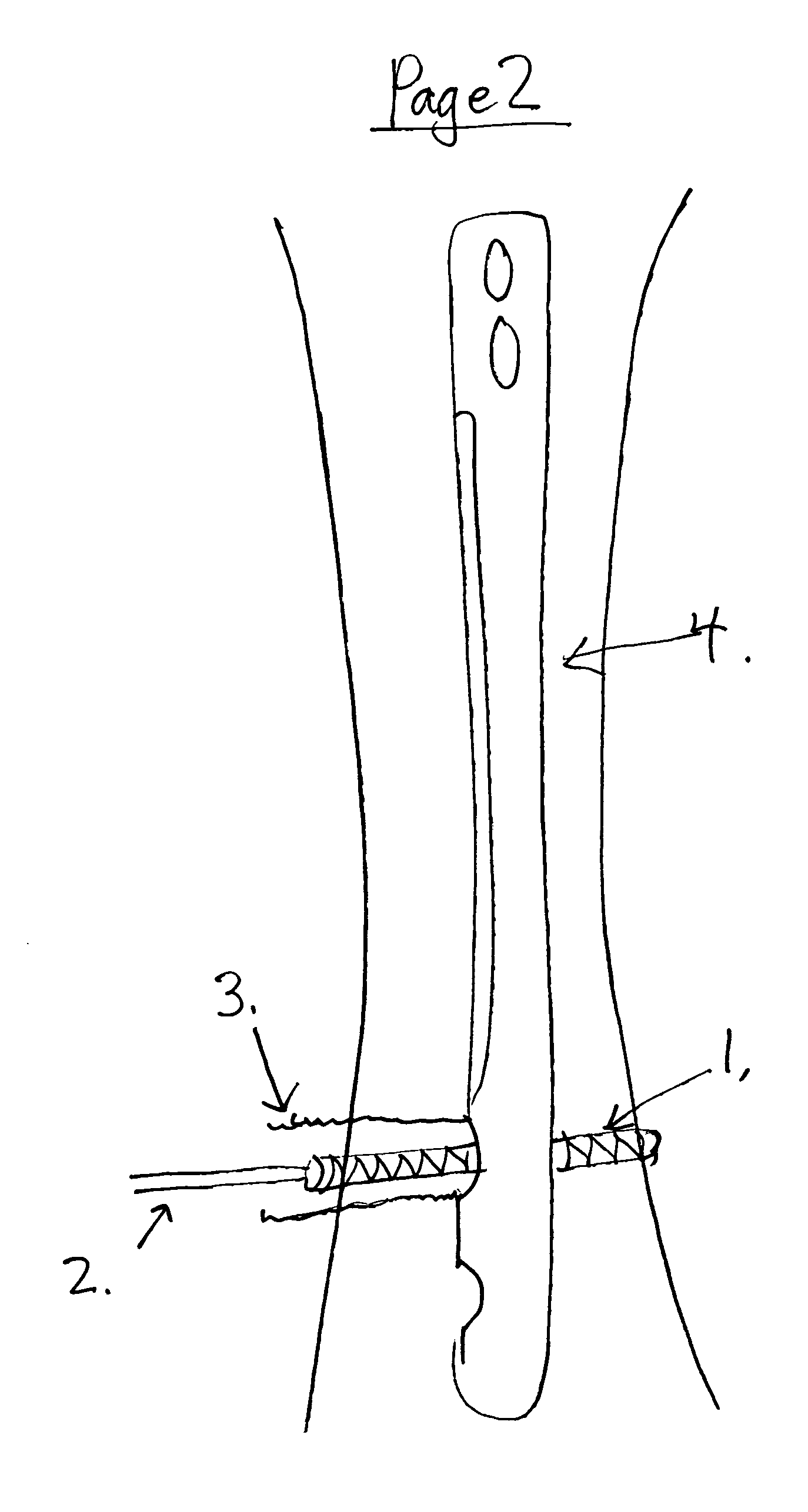
[0052] The IM Nails and screws are manufactured with cobalt-chrome, titanium or other materials for strength and durability. The current methods do not address screw-nail interface locking and can cause loss in reduction. In this invention, the IM Nail is secured by headless screws and canulated outer screws that cap the headless screws; this will secure and eliminate movement of the screws to the IM Nail.
[0053] The screwdriver for placing the headless screw remains attached to this headless screw after insertion. A decision is made on the length of the outer screw (the one that encapsulates the headless screw) to be placed so that the intramedullary nail is kept at a fixed distance from the cortex of the bone. The headless screw is then over drilled with a canulated drill. The outer screw is then placed over the modular screwdriver and then over the headless screw. The outer screw engages threads on the nail, locking the outer screw to the nail. The opening of the nail may be tape...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com