Moving mechanism, and compact camera, goniometer and fiberscope using the moving mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
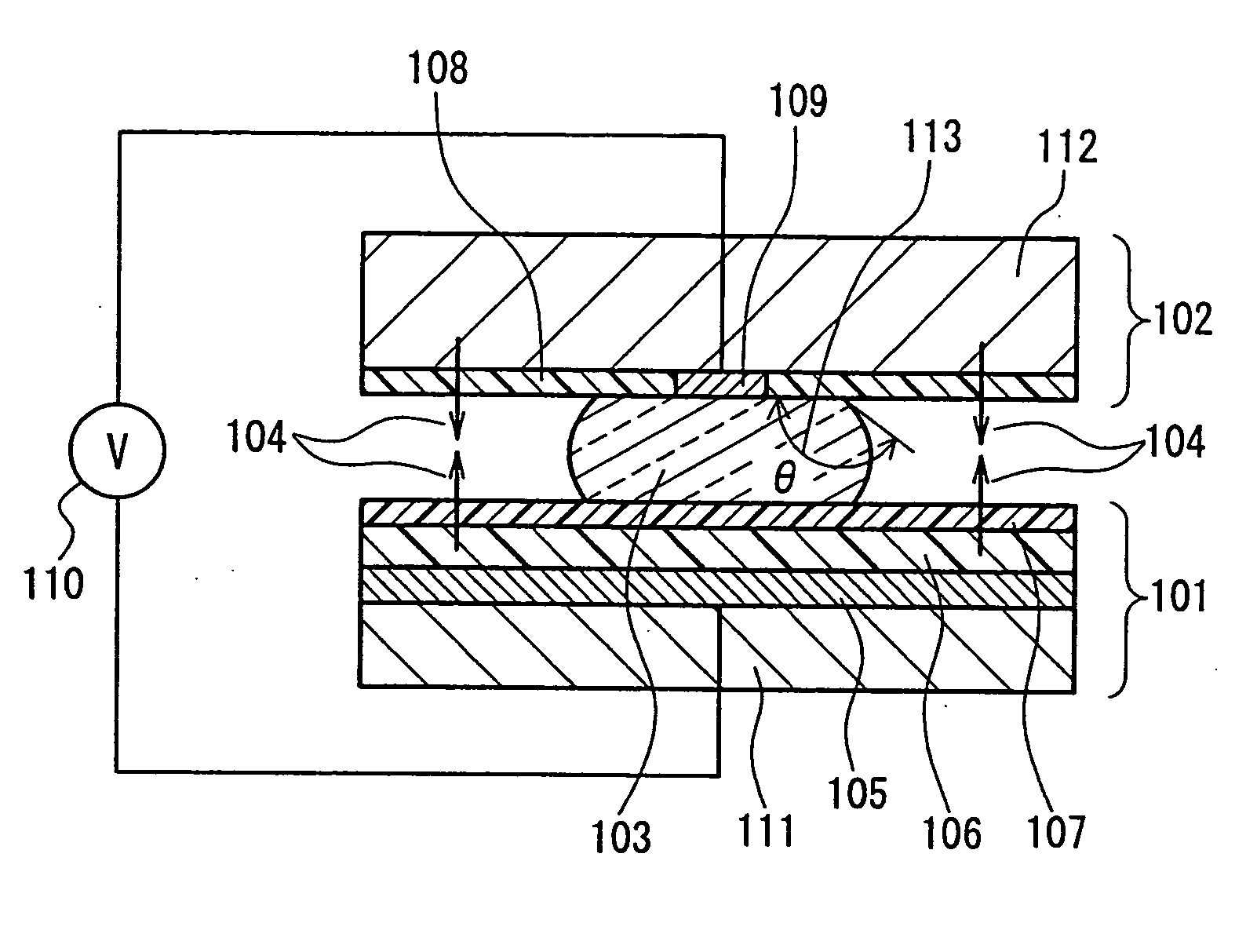
[0070]FIG. 12 is a schematic view showing a position movement mechanism of the present invention. A cross-sectional view of the vicinity of the first structural member 101, the liquid 103 and the second structural member 102 are shown in FIG. 1. In the present embodiment, the first structural member is one part of a bottom face of a fixed tube 404. The second structural member 102 is arranged such that it can move in the vertical direction within the tube. In the picture, gravity acts in the downward direction. Consequently, in the diagram, gravity is the binding force that acts on the second structural member 104.
[0071] The fixed tube 404 has a shape whose internal diameter is 10 mm and whose height is 30 mm, and its material is polycarbonate resin. The first structural member 101 is made from a silicon substrate 111 that has a thickness of 100 μm (see FIG. 1. In FIG. 12, this is included as a part of the first structural member 101), a platinum electrode 105 that has a thickness ...
embodiment 2
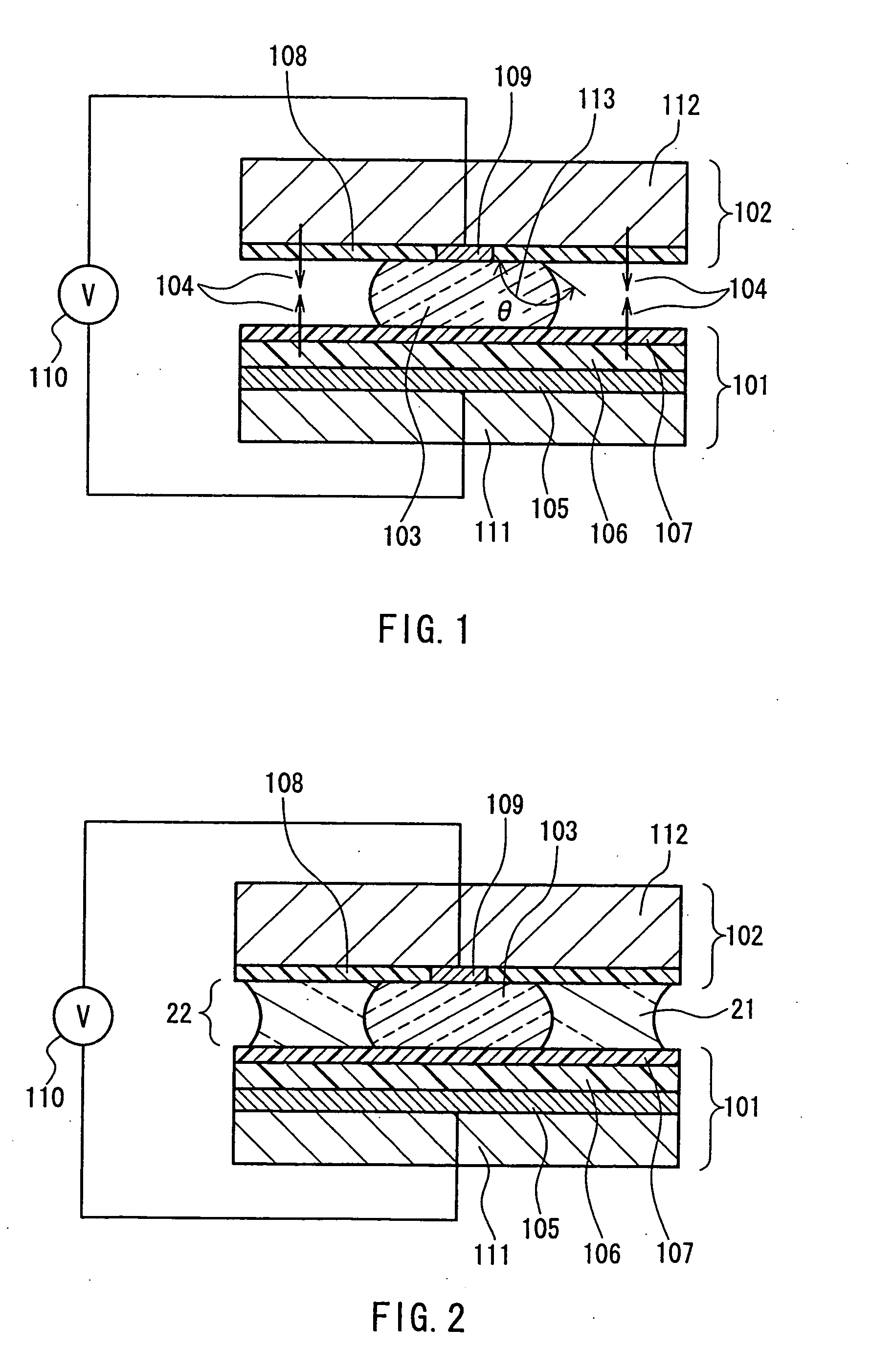
[0081]FIG. 13 is a schematic view showing a position movement mechanism of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of the vicinity of the first structural member 101, the liquid 103 and the second structural member 102. The basic structure of the present invention is the same as in Embodiment 1, however a filler liquid 21 has been added. Numeral 1001 is a fixed tube. In the present embodiment, a modified organic silicone oil (phenylmethylsiloxane homopolymer, manufactured by Gelest) with a specific gravity of 1.0 and a viscosity of 10 cPs is used as the filler liquid. The amount of filler liquid is adjusted such that the liquid 103 is completely enclosed within it, that no air bubbles are contained within it, and moreover, that it does not protrude from the gap between the first structural member and the second structural member. The surface tension of the filler liquid is on the order of 30 dyne / cm, and at the time of filling, the liquid surface has a concave shape....
embodiment 3
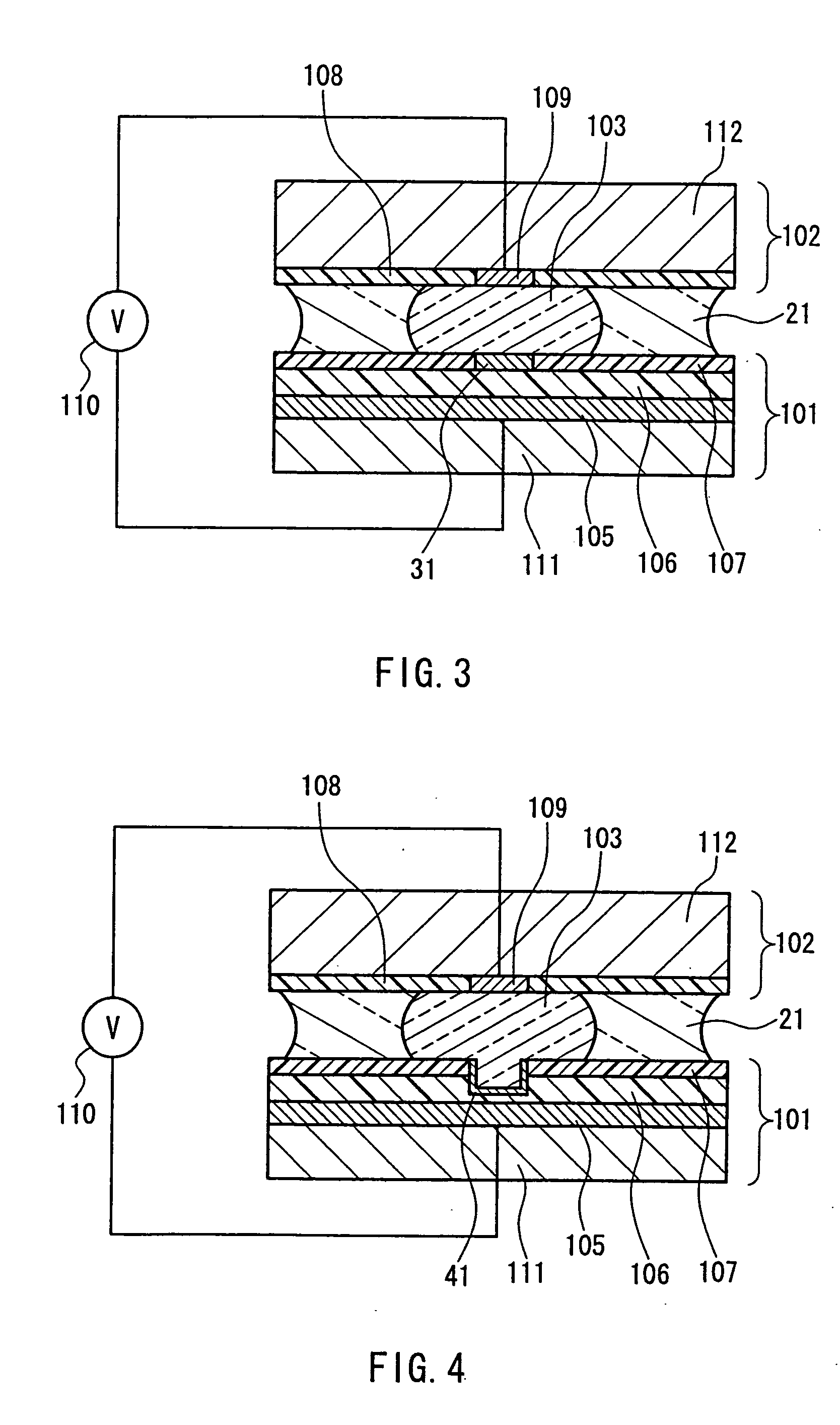
[0085] A position movement mechanism similar to that in Embodiment 2 was formed. However, a hydrophilic region exists on the insulating film of the first structural element wherein the water-repelling film is not formed, and the liquid is in contact with the hydrophilic region. A cross-sectional view of the vicinity of the first structural member, the liquid and the second structural member of the present embodiment is shown in FIG. 3. A circular hydrophilic region 31 with a diameter of 1 mm is formed in the center of the first structural member 101. After formation of the water-repelling film, the hydrophilic region is formed by affixing a metal mask that has circular holes of a diameter of 1 mm to the water-repelling film, and irradiating the metal mask with oxygen plasma. That is to say, the oxygen plasma only hits the water-repelling film in the part of the open holes, removing the water-repelling film, and the PZT is hydrophilically converted at the same time.
[0086] Because th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com