Acoustically enhanced electro-dynamic loudspeakers
a technology of electro-dynamic loudspeakers and amplifiers, applied in the field of electro-dynamic loudspeakers, can solve the problems of difficult to achieve the desired performance of the audio system, use of loudspeakers, and inability to position or orient the desired loudspeakers, so as to enhance the acoustical properties of electro-dynamic loudspeakers and reduce standing waves
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
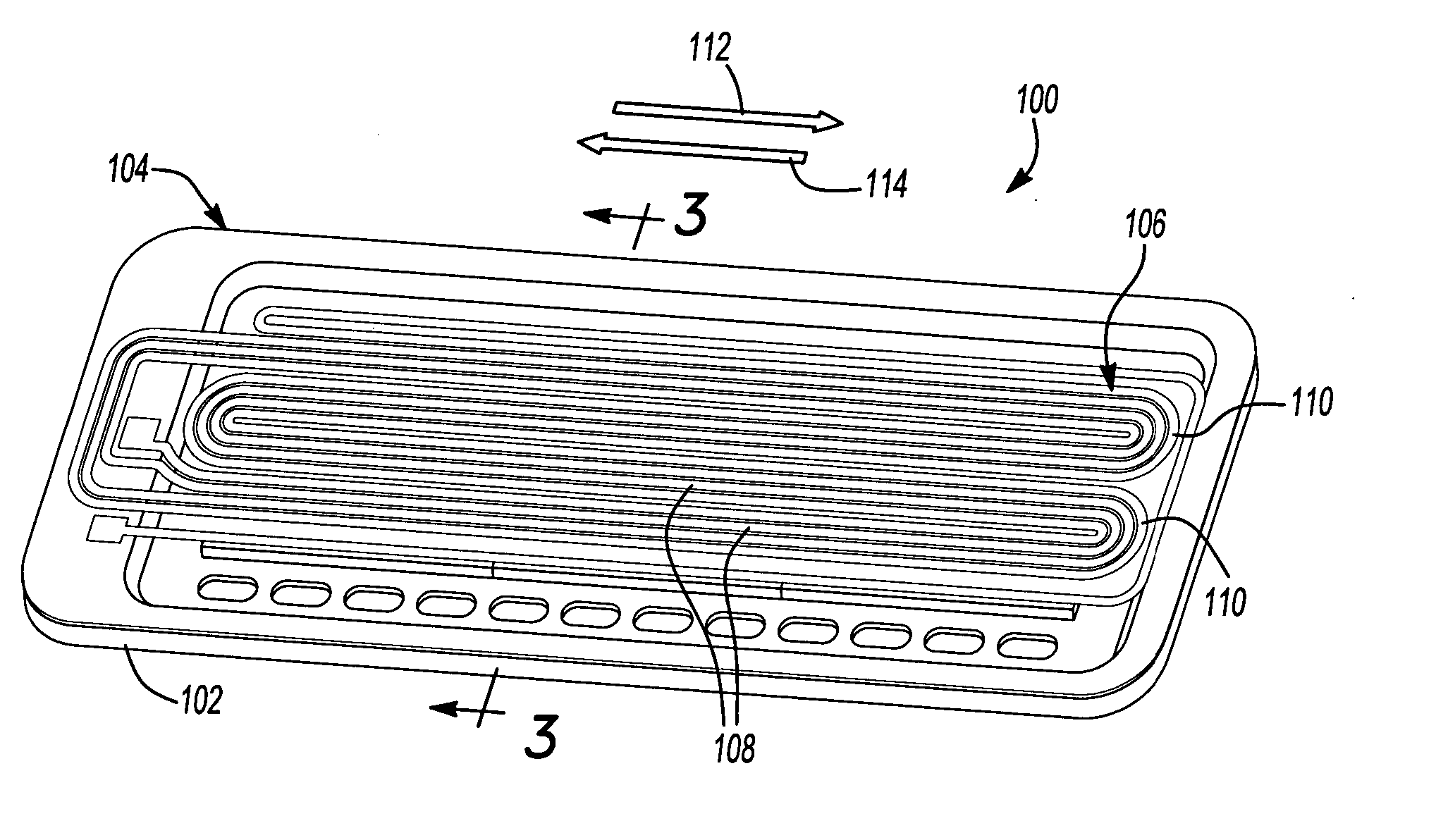
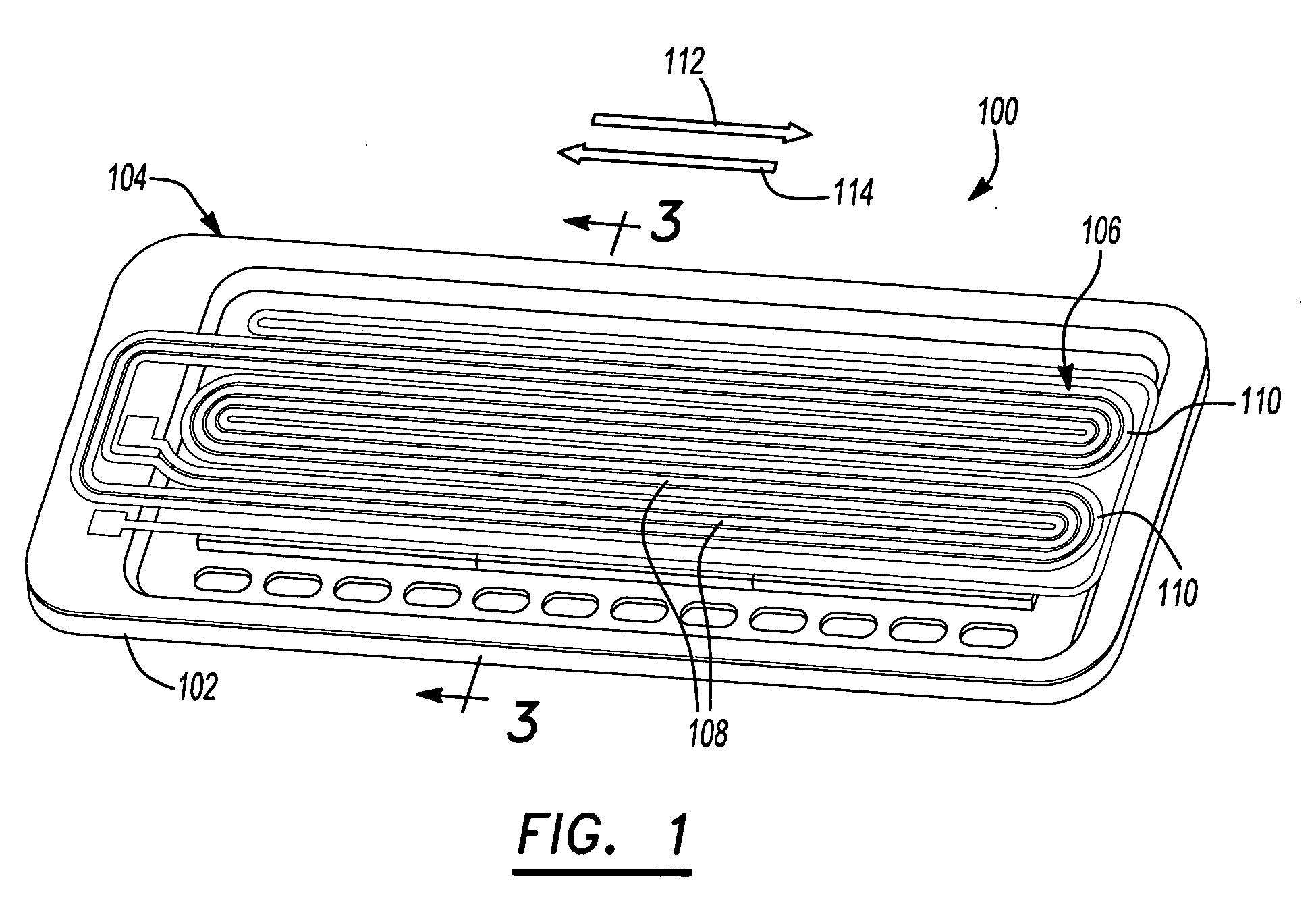
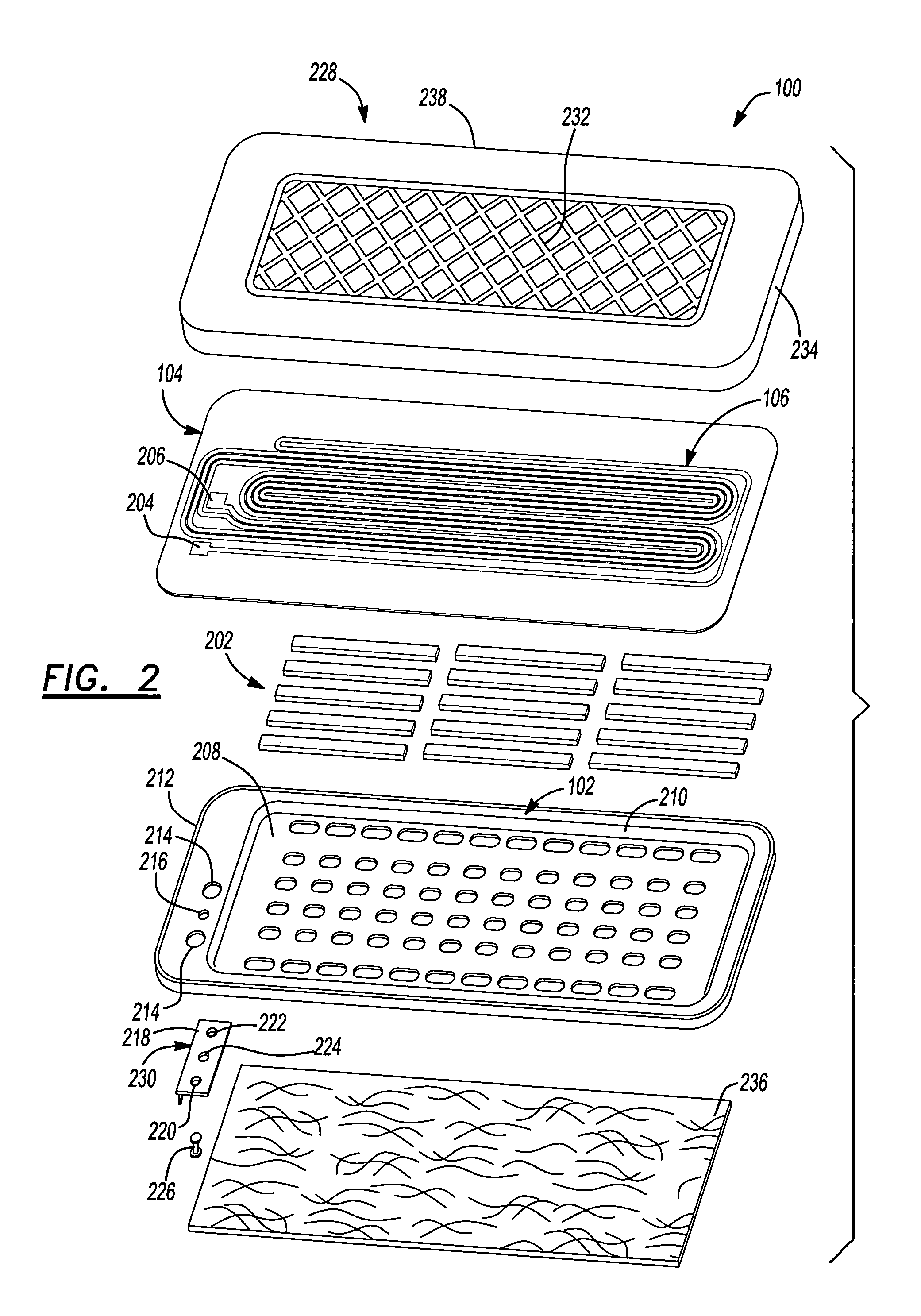
[0039]FIG. 1 is a perspective view of an electro-dynamic loudspeaker 100 of the invention. As shown in FIG. 1, the electro-dynamic loudspeaker is a generally planar loudspeaker having a frame 102 with a diaphragm 104 attached in tension to the frame 102. A conductor 106 is positioned on the diaphragm 104. The conductor 106 is shaped in serpentine fashion having a plurality of substantially linear sections (or traces) 108 longitudinally extending along the diaphragm interconnected by radii 110 to form a single current path. Permanent magnets 202 (shown in FIG. 2) are positioned on the frame 102 underneath the diaphragm 104, creating a magnetic field.
[0040] Linear sections 108 are positioned within the flux fields generated by permanent magnets 202. The linear sections 108 carry current in a first direction 112 and are positioned within magnetic flux fields having similar directional polarization. Linear sections 108 of conductor 106 having current flowing in a second direction 114, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com