Multi-processing financial transaction processing system
a financial transaction and multi-processing technology, applied in the field of can solve the problems of complex financial transaction processing system, and increased complexity of computerized data processing system, and achieve the effect of improving efficiency, enhancing auditability of financial data, and long and complex flow of control transaction processing modules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
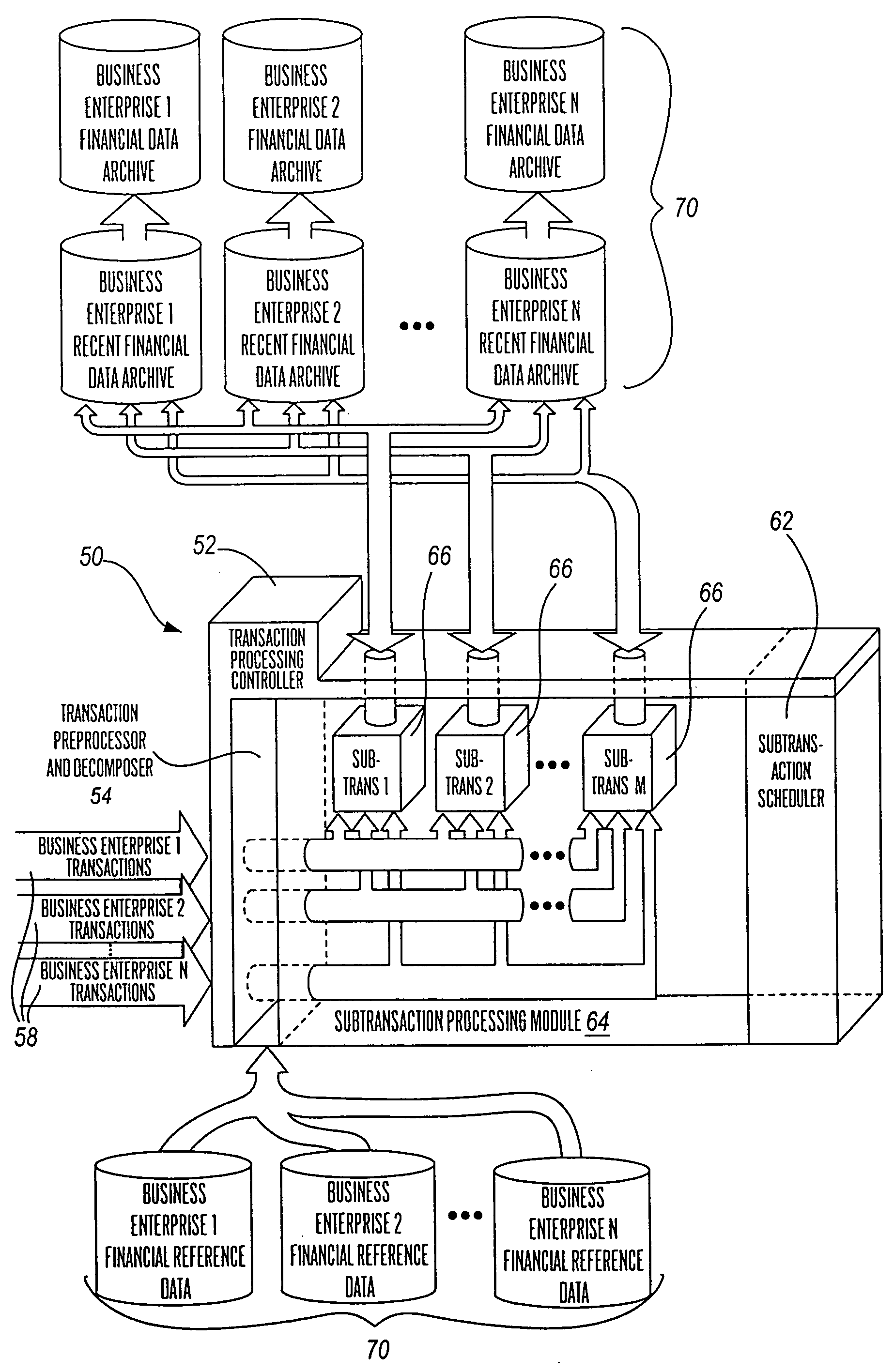
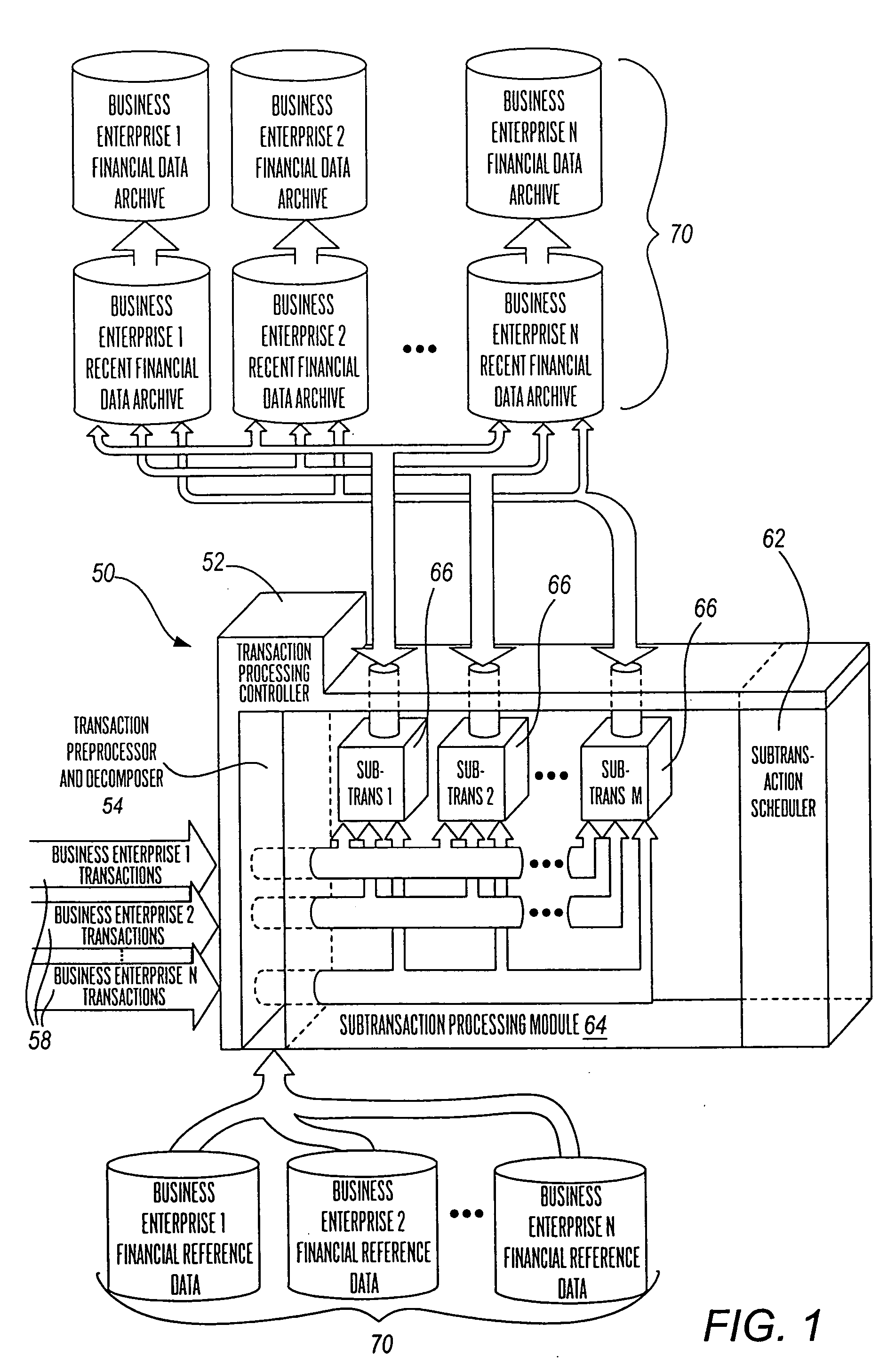
[0064]FIG. 1 shows a high level conceptual block diagram of a transaction processing system 50 according to the present invention. In particular, the present invention is conceptualized in the present figure as including five functional components, these being:
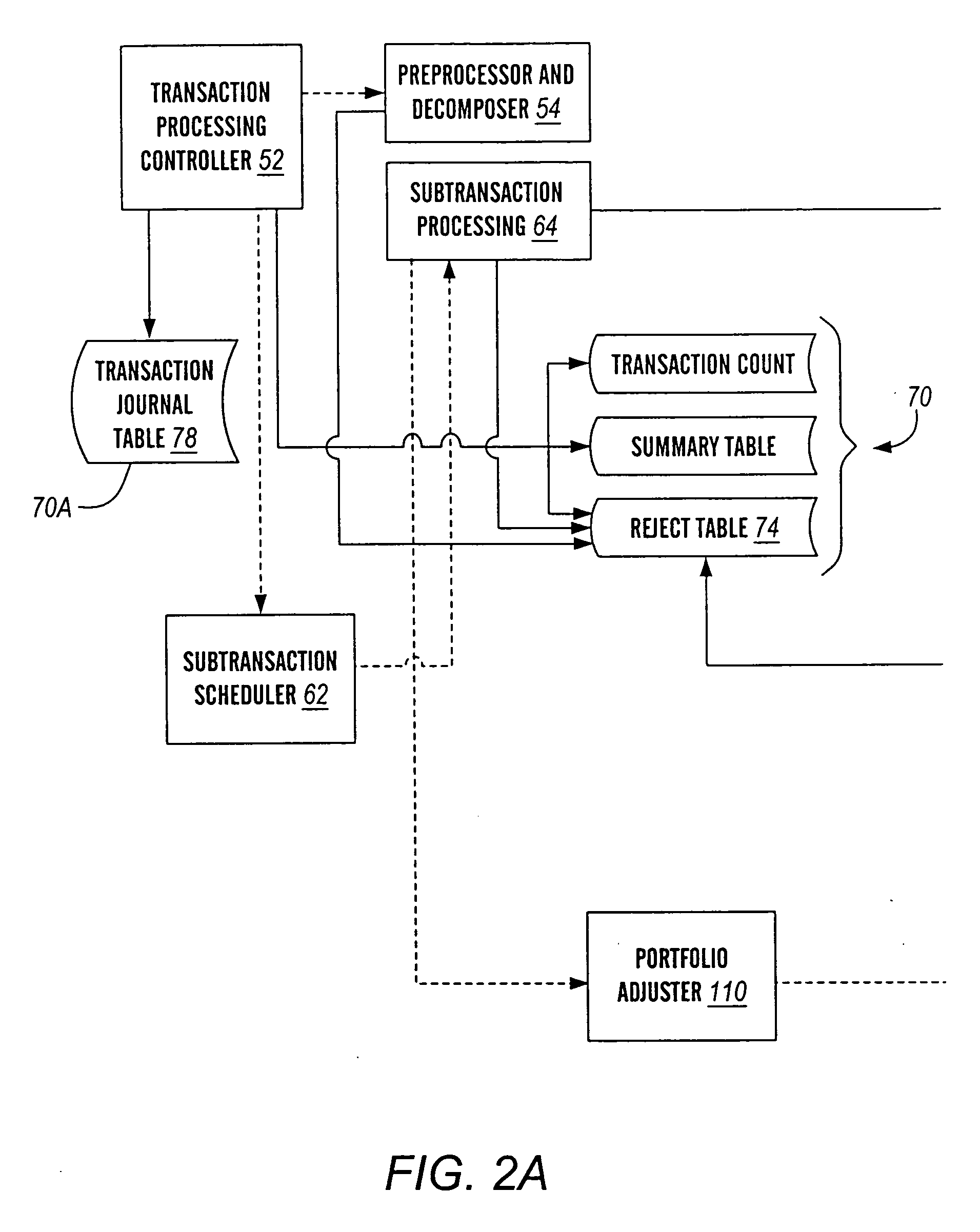
[0065] (a) transaction processing controller 52 for: (i) receiving transactions 58 from business enterprises, (ii) controlling the processing of such transactions, including the scheduling of subtransactions to be performed, and (iii) writing of transaction details to, for example, a transaction journal file or table;
[0066] (b) a transaction preprocessor and decomposer 54 for initially receiving a transaction 58 from any one of a plurality of business enterprises as shown, wherein the preprocessor and decomposer 54 decomposes transactions into subtransactions;
[0067] (c) a subtransaction processing module 64 for performing the instructions for each subtransaction determined by the transaction preprocessor and decomposer 54. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com