Intrusion resistant glass laminates
a technology of glass laminates and glass fibers, applied in the direction of film/foil adhesives, synthetic resin layered products, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problem of not disclosing the modulus or the construction of laminates, and achieve the effect of enhancing stiffness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-15
[0044] Glass laminates about 45×60 cm (18×24 in) were constructed of the materials indicated in Table 1.
TABLE 1Laminate No.Layer Assembly1glass / PBV2 / glass2glass / PVB3 / glass3glass / PVB4 / glass4glass / PVB1 / PET2 / PVB1 / glass5glass / PVB5 / PVB5 / glass6glass / PVB7 / PET2 / PVB7 / glass7glass / PVB6 / PET2 / PVB6 / glass8glass / PVB7 / PET1 / PVB7 / glass9glass / PVB2 / PET1 / PVB2 / glass10glass / PVB6 / PET1 / PVB6 / glass11glass / PVB5 / PET2 / PVB5 / glass12glass / IONOMER / glass13glass / PVB2 / PET2 / PVB2 / glass14glass / PVB5 / glass15glass / PVB1 / PVB5 / PVB1 / glass
[0045] The laminates were evaluated for impact resistance by striking with a 9.5 kilogram hammer-head at the end of a 1400 mm pendulum arm from a drop height of 700 mm according to British Standard BS AU 209, Part 4a modified in that the glass laminate was mounted in a vertically oriented test frame of the type shown in FIG. 5A; the hammer was set to strike at five points of a diamond pattern measuring 70 mm on a square side (in sequence, the top, left center, center, right center and bottom). ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
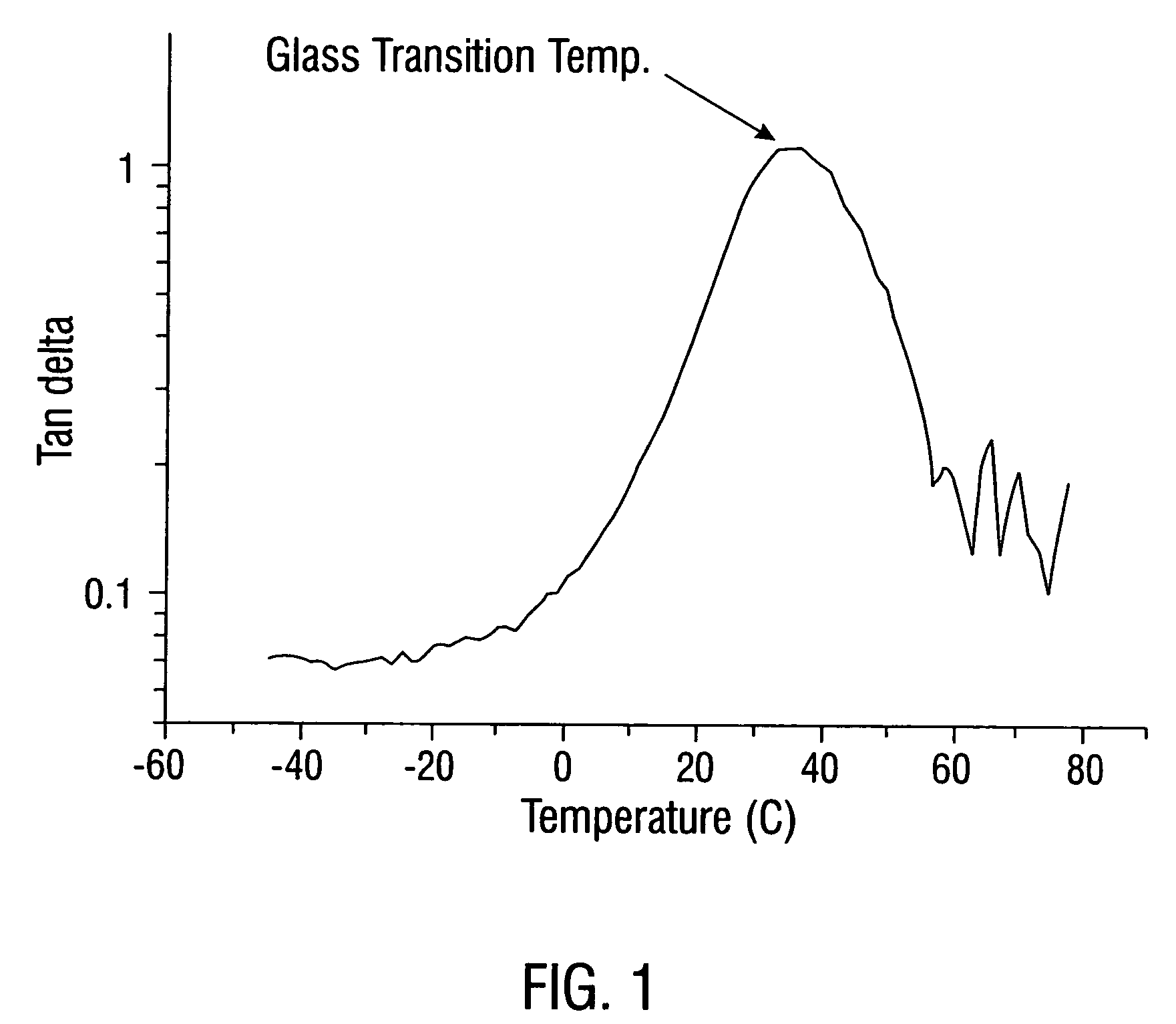
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com