Tissue accessing and anchoring device and method
a tissue accessing and tissue technology, applied in the field of medical devices and methods, can solve the problems of exposing physicians to accidental injury during tissue excision, affecting the accuracy of surgical procedures, so as to improve the anchoring and demarcation of the location, avoid delay and imprecision, and simplify and reduce the cost of such procedures.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
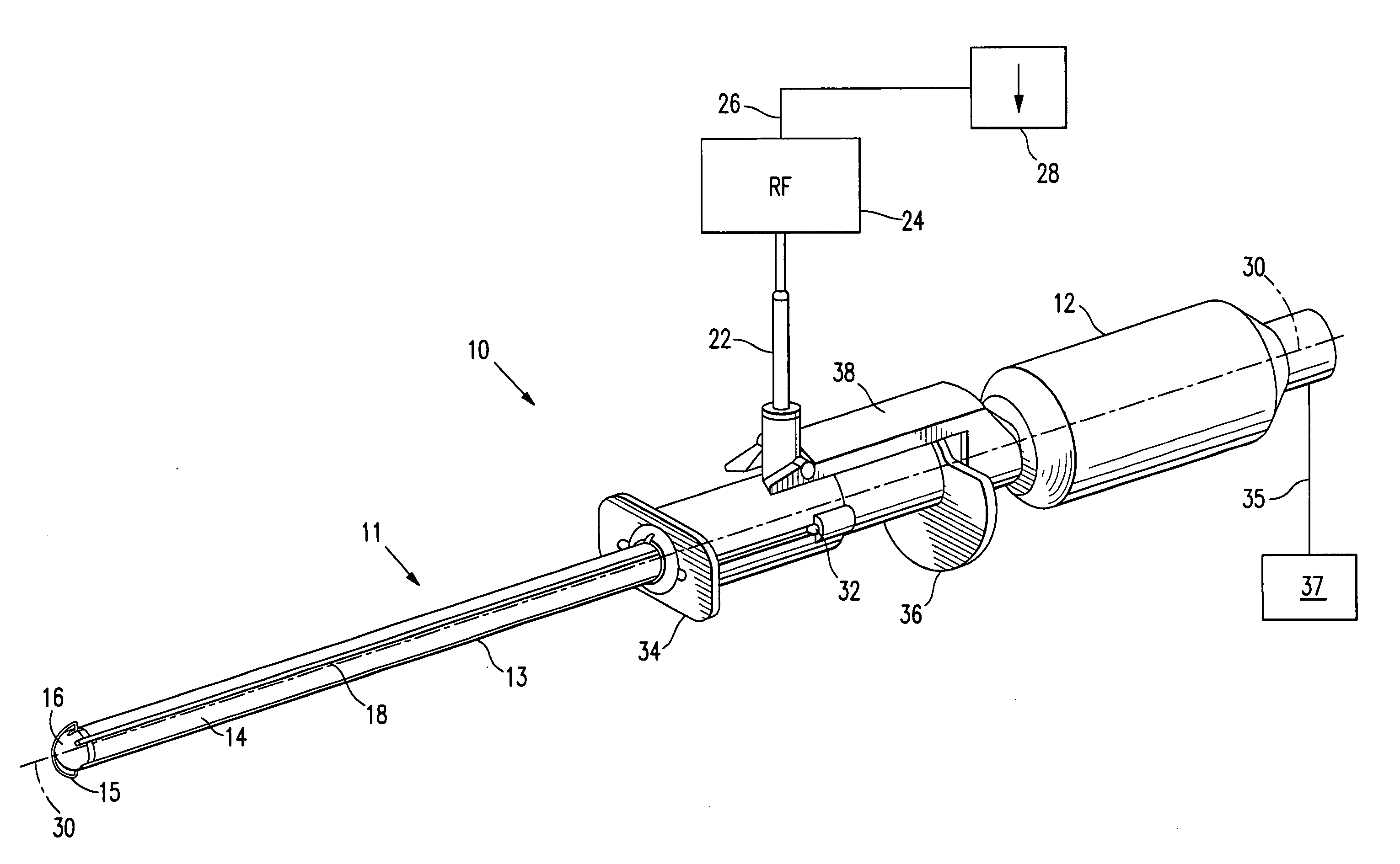
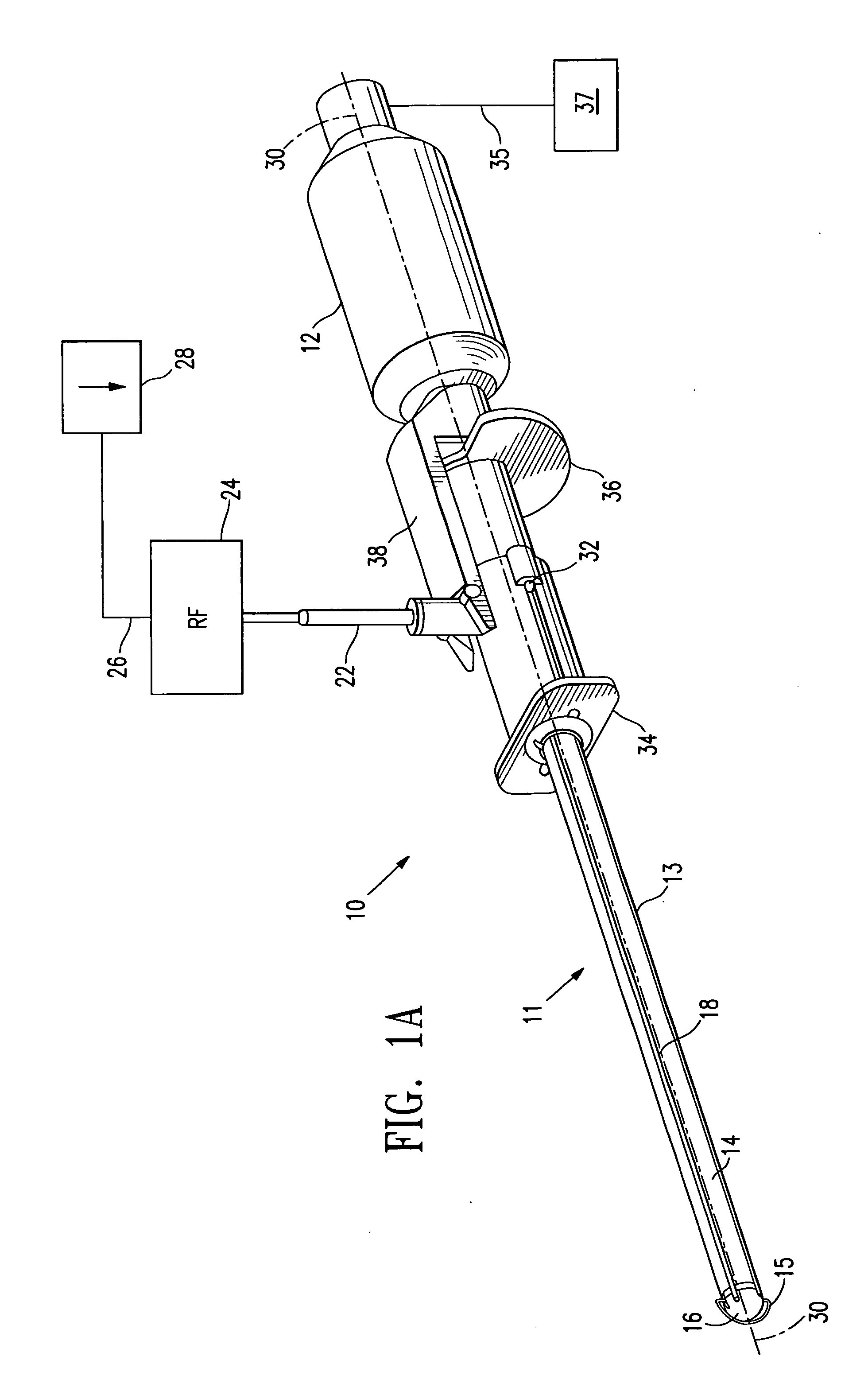
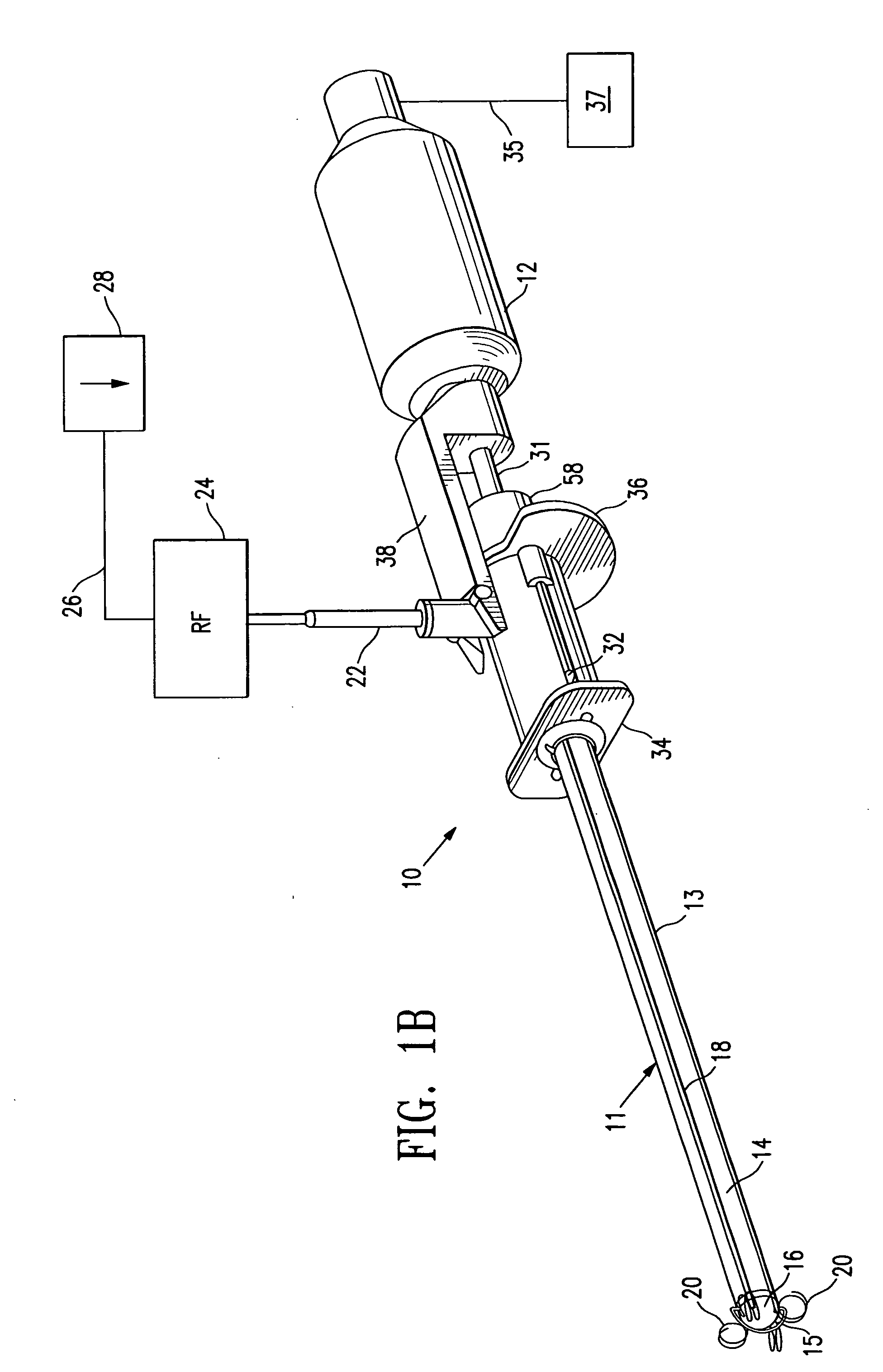
[0059]FIGS. 1A and 1B show a system 10 embodying features of the invention, which includes a sentinel node accessing and anchoring device 11, and an elongated radiation detector 12. The accessing and anchoring device has a shaft 13 with a proximal portion and a distal portion 14 with a cutting wire 15 at its tip 16; and a source of radio frequency (RF) power 24 connected to the cutting wire 15 via RF connector 22. The shaft 13 and radiation detector 12 lie generally along longitudinal axis 30. As shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B, cutting wire 15 is a tissue cutting member that may be activated by RF energy and is configured to ablate and penetrate tissue. It is shown as an arcuate wire spaced distally from the tip 16 of shaft 13. In alternative embodiments, cutting wire 15 may take other shapes and may be in contact with or form part of tip 16.
[0060] Radiation energy detector 12 includes an elongated probe 31, shown in FIGS. 4 and 6, and may be, e.g., a gamma probe. Radiation energy detect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com