Three-dimensional image processing apparatus, optical axis adjusting method, and optical axis adjustment supporting method
a technology of image processing apparatus and supporting method, which is applied in the direction of stereoscopic photography, camera body details, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult adjustment of the direction of the optical axes of image processing apparatus, all the more difficult for users without expert knowledge of image processing, and no guarantee that the optical axis passes the center of the image pickup device. , to achieve the effect of high precision and adjustment of directions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
(Configuration of Three-Dimensional Image Processing Apparatus)
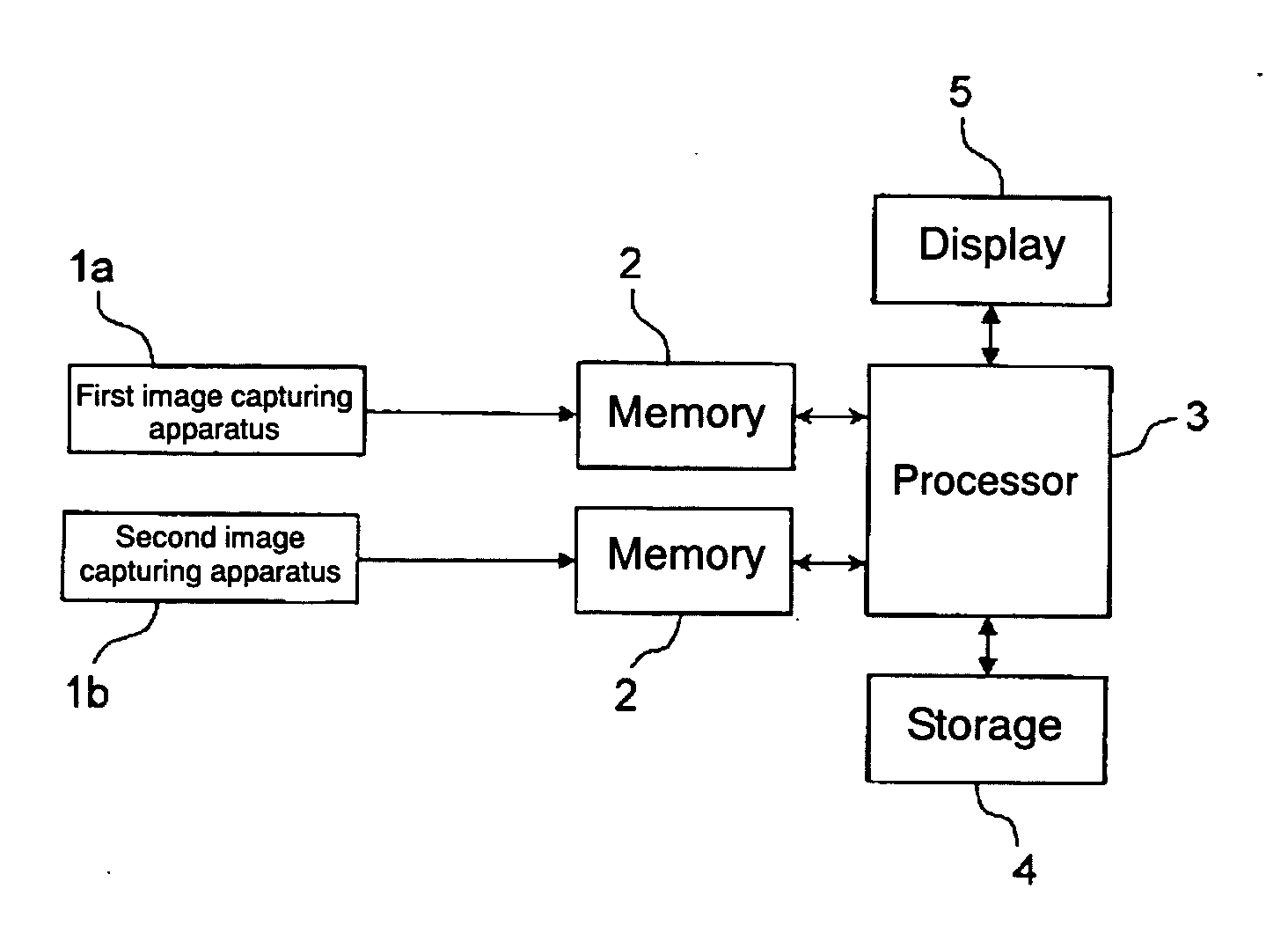
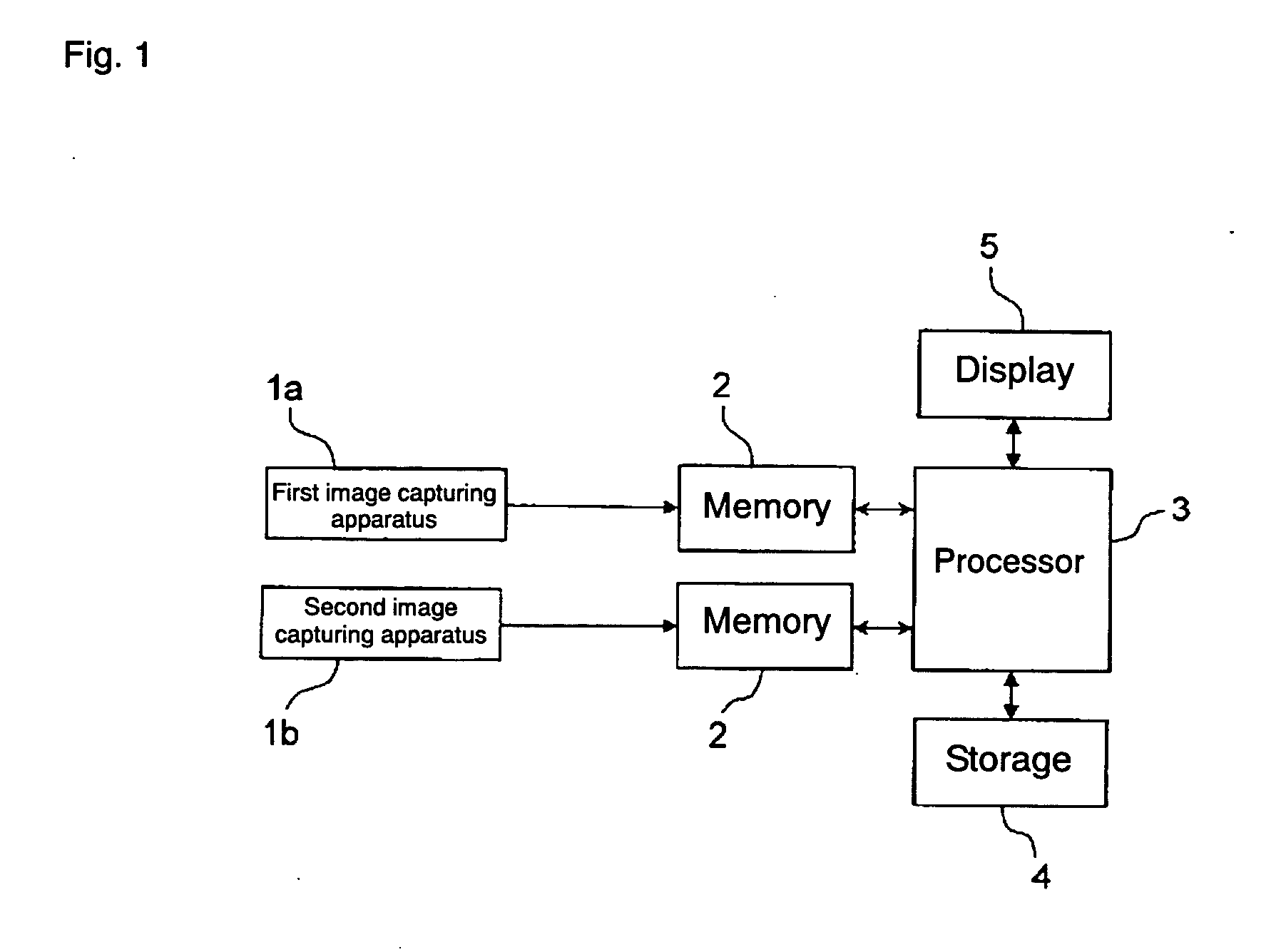
[0037]FIG. 1 shows a block diagram showing a hardware configuration of a three-dimensional image processing apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. The three-dimensional image processing apparatus includes, roughly, a first image capturing apparatus 1a, a second image capturing apparatus 1b, memories 2 and 2 for the image capturing apparatuses, a processor 3, a storage 4, and a display 5.
[0038] Each of the first and second image capturing apparatuses 1a and 1b (hereinbelow, also simply called “image capturing apparatus”) is an image capturing apparatus having an optical system constructed by plural lenses and an image pickup device constructed by a CCD, a CMOS, or the like. Digital images captured by the image capturing apparatuses 1a and 1b are temporarily stored in the memories 2 and, after that, input to the processor 3. The images captured by the image capturing apparatuses 1a and 1b may be ...
second embodiment
[0063] In a second embodiment of the present invention, a function of enlargedly displaying a portion including a mark is added. The other configuration is similar to that of the foregoing embodiment.
[0064] When an enlargement display function is executed in a state where the image of FIG. 6 is displayed on the display 5, the local areas around the marks 53 and 54 in the images 51 and 52 are enlargedly displayed (refer to FIG. 9). By the enlargement, the positioning between the marks and the points on the object 21 is facilitated and fine adjustment and matching of the optical axes can be performed with high precision.
[0065] In the case of digitally enlarging an image, it is sufficient to enlarge a local area in a display image by interpolation in the processor 3. In the case of optically enlarging an image, it is sufficient to increase the focal distance of the image capturing apparatuses 1a and 1b by sending a control signal from the processor 3. In this case, attention has to b...
third embodiment
[0066] In the case where the shape of an object is simple and easily recognized as shown in FIG. 6, the correspondence between the mark and the point on the object can be easily obtained. However, depending on the shape and pattern of an object, it is difficult to determine a point with which the mark is to be matched. There is a case that it is difficult to perform the optical axis adjustment by the method of the first embodiment.
[0067] In a third embodiment of the present invention, a function of superimposing marks of plural image capturing apparatuses on a single image is added. The other configuration is similar to that of the foregoing embodiments.
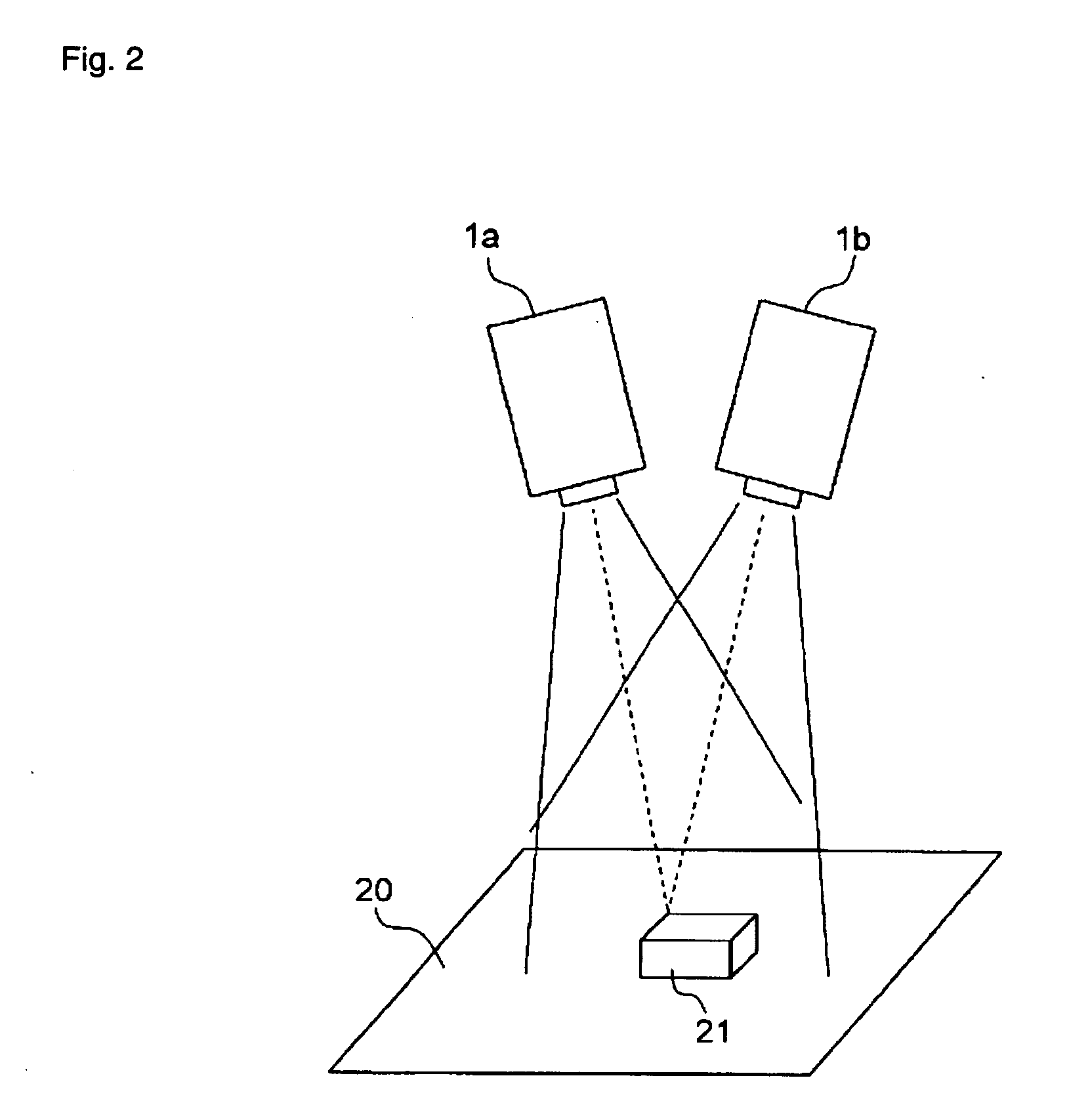
[0068] It is assumed that the image capturing apparatuses 1a and 1b and the reference plane 20 have the positional relations as shown in FIG. 10. In the diagram, a point C1 is the optical center of the first image 51, and a point C2 is the optical center of the second image 52. A point P1 is the meeting point of the optical axis L1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com