Small separation apparatus
a separation apparatus and small technology, applied in the direction of solid separation, electrolysis components, material analysis by electric/magnetic means, etc., can solve the problems of inability to separate very small samples, inability to satisfactorily use electrotrophoresis for separating very small samples, and other methods are time-consuming, so as to achieve the effect of effective and efficient separation of selected products from small sample volumes and fast separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
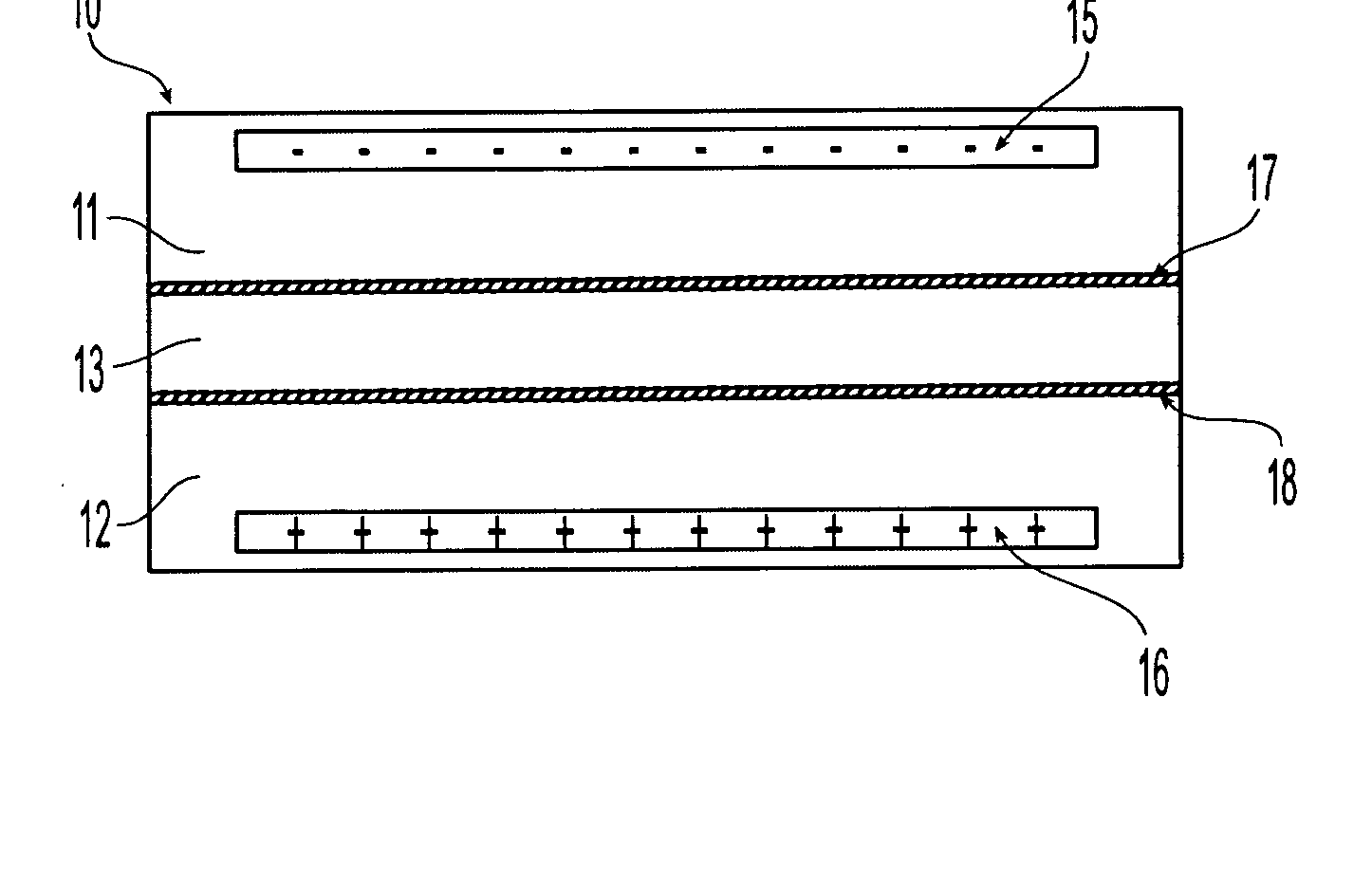
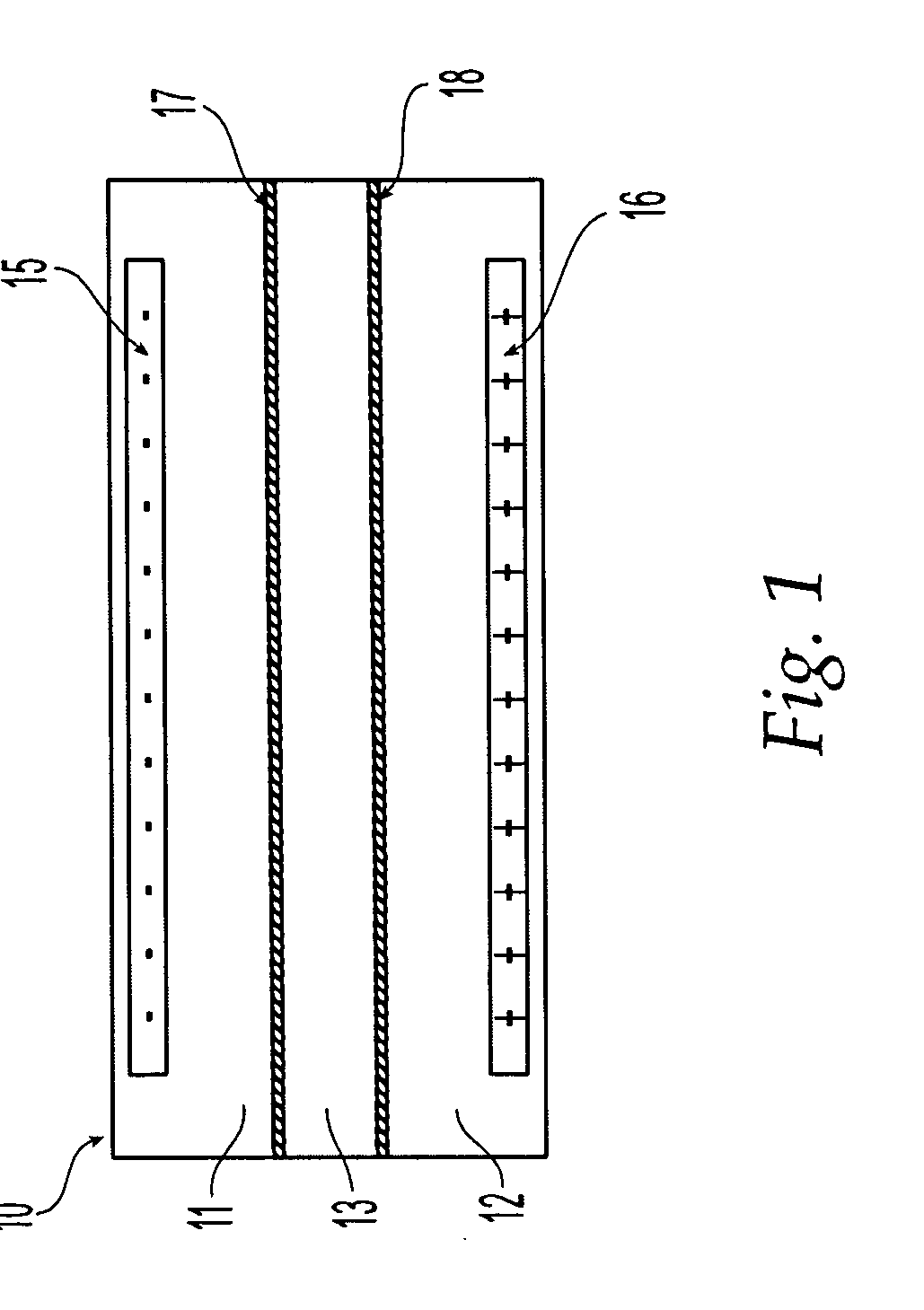
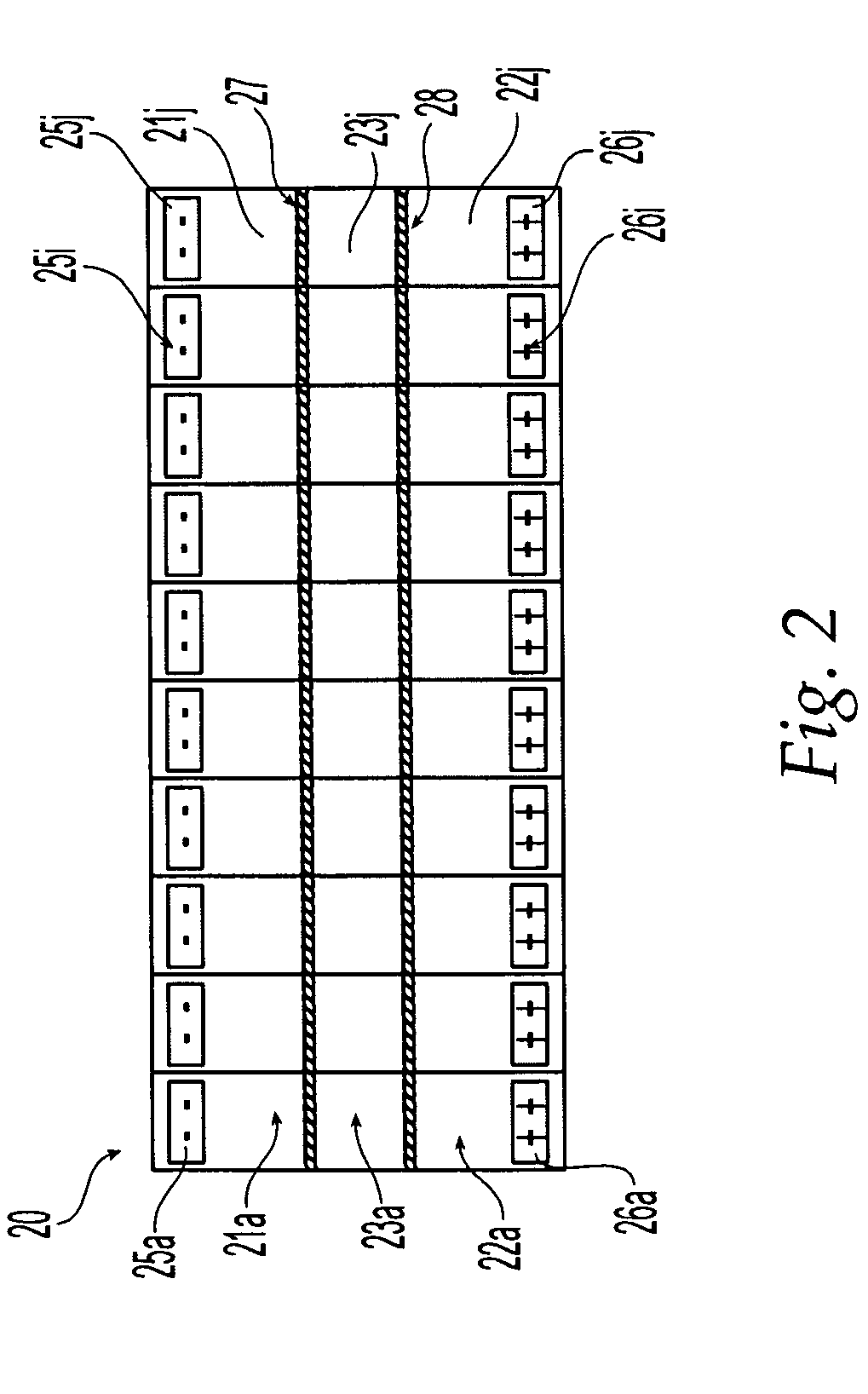
[0041] Before describing the preferred embodiments in detail, the principal of operation of the apparatus will first be described. An electric field applied to charged molecules including macromolecules such as proteins in solution will cause the molecules to move to one of the electrodes. If the compound has a positive charge, it will move to the negative electrode (cathode). Conversely, a negatively-charged compound will move to the positive electrode (anode).
[0042] In the apparatus of the present invention for separating compounds, an electrophoretic separation membrane is placed in an electric field and compounds are selectively transported between the sample and the separation chambers. The particular separation membrane used will vary for different applications and generally has a relatively large, but well defined, pore size. The sample and separation chambers are isolated from the electrodes by two restriction membranes. Depending on the type of restriction membranes used, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com