Patents
Literature
33 results about "Interstitial volume" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The volume of extracellular fluid in a young adult male of 70 kg (154 lbs) is 20% of body weight – about fourteen litres. Eleven litres is interstitial fluid and the remaining three litres is plasma.
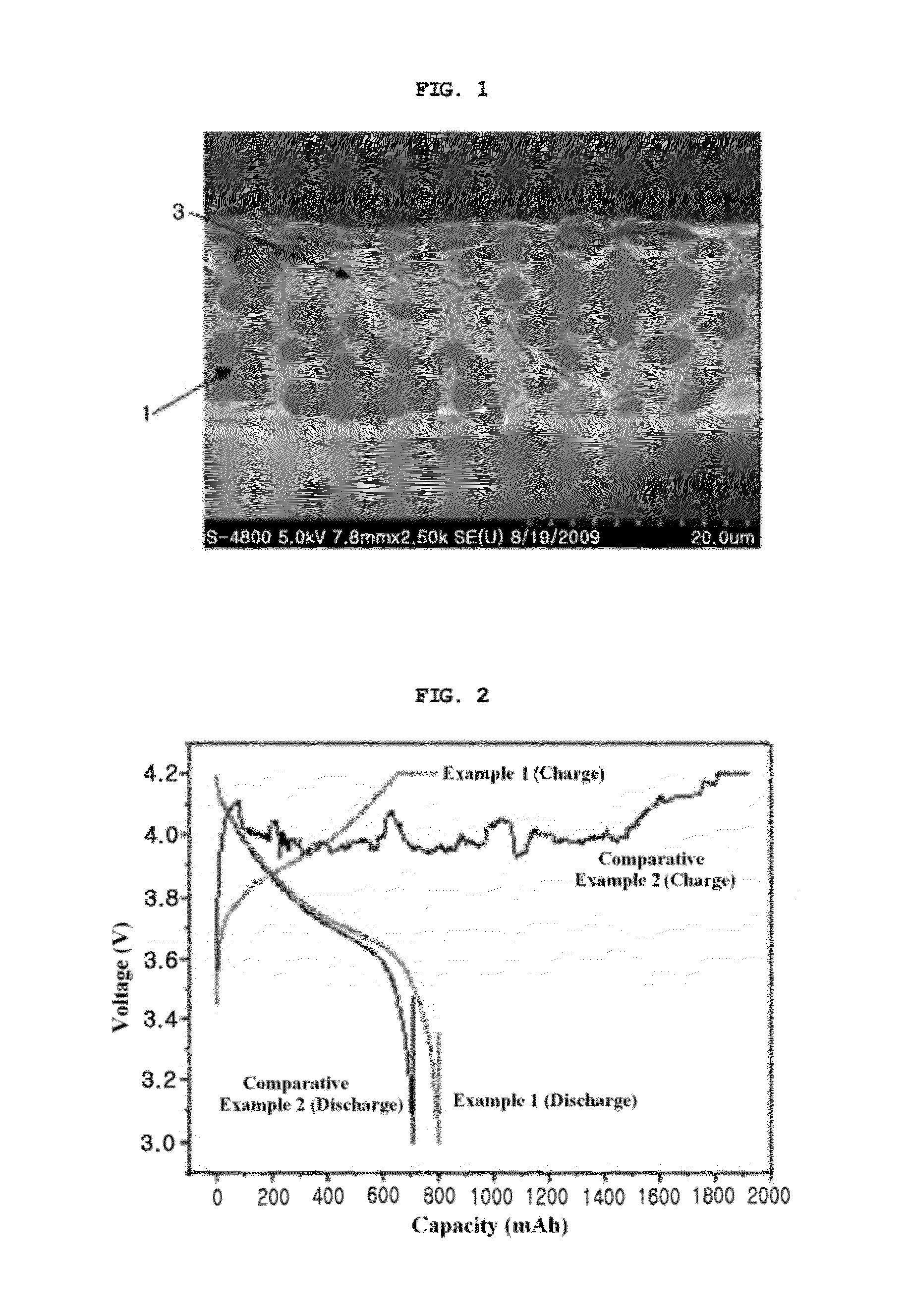
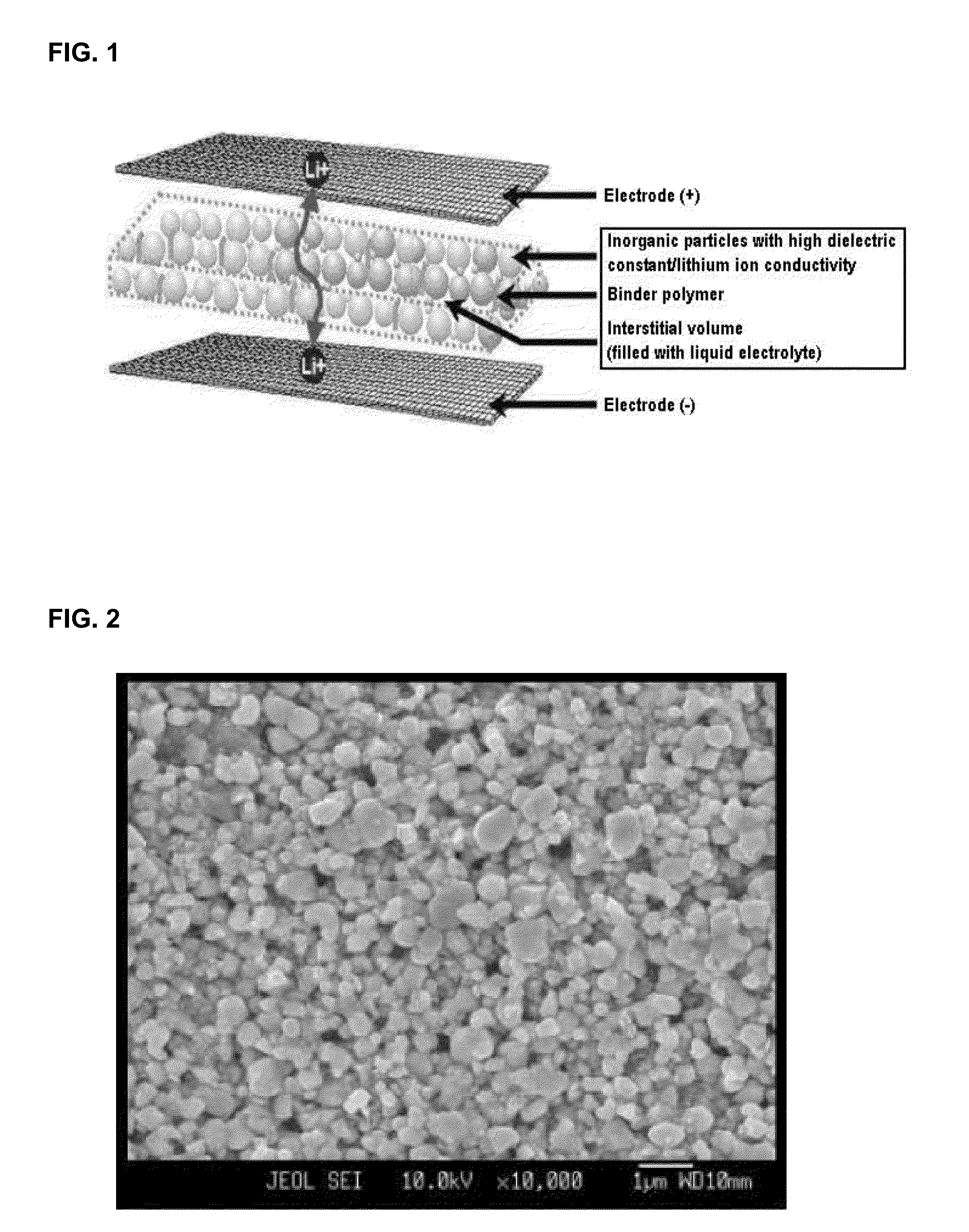
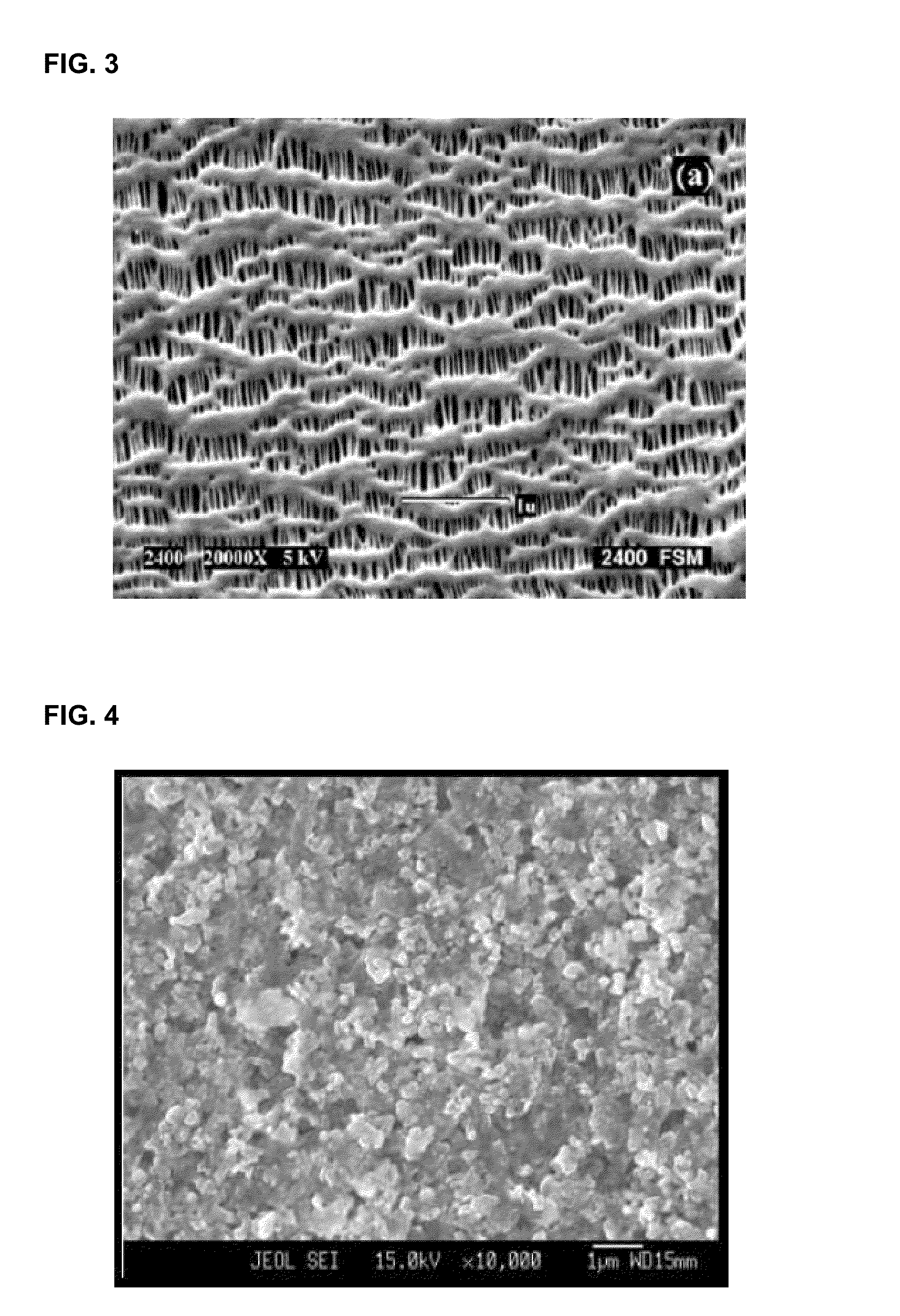
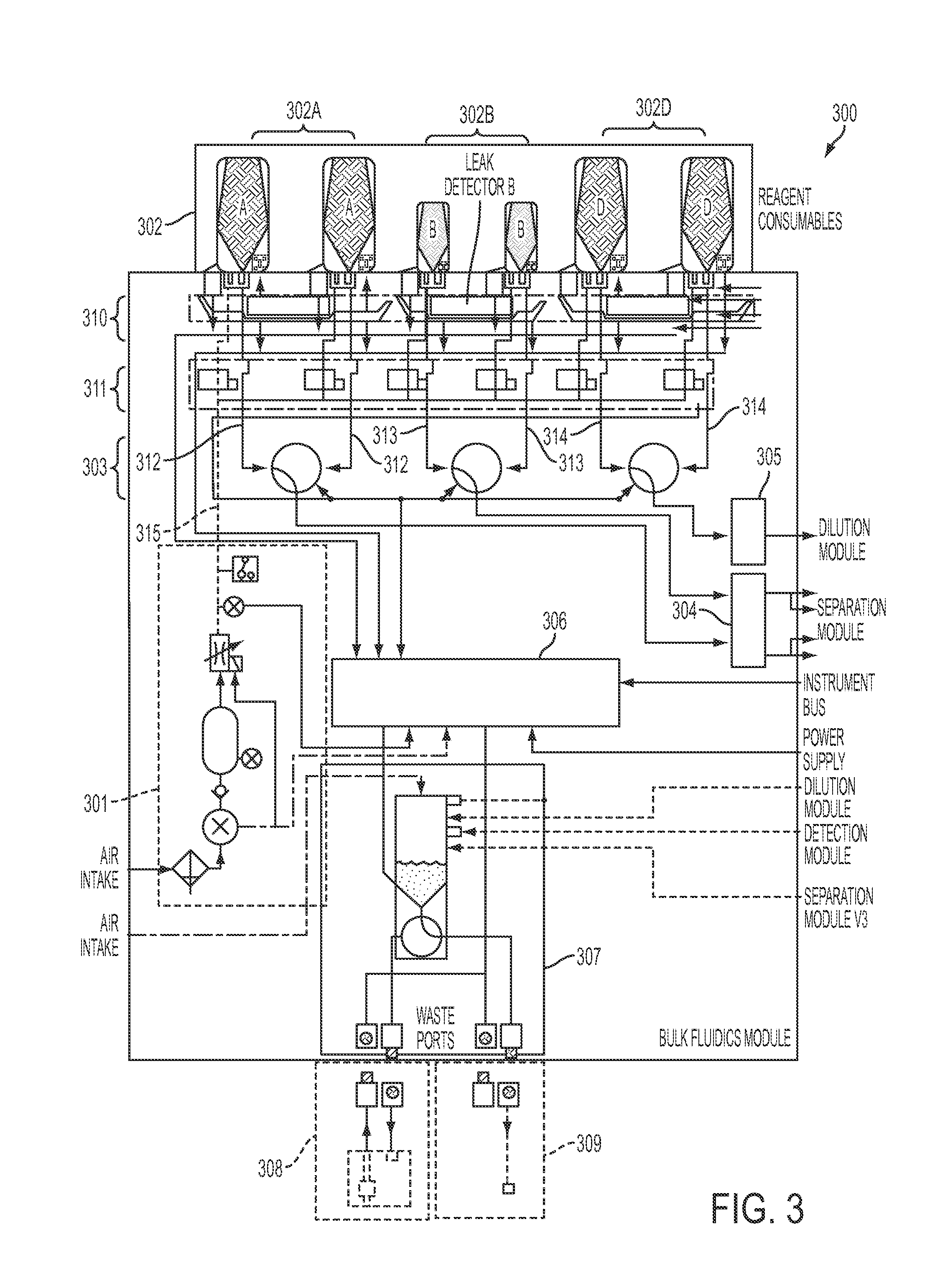
Separator including porous coating layer, method for manufacturing the separator and electrochemical device including the separator
ActiveUS20120015228A1Avoid it happening againInhibit the electrochemical reaction processFinal product manufacturePretreated surfacesPorous coatingInorganic particle
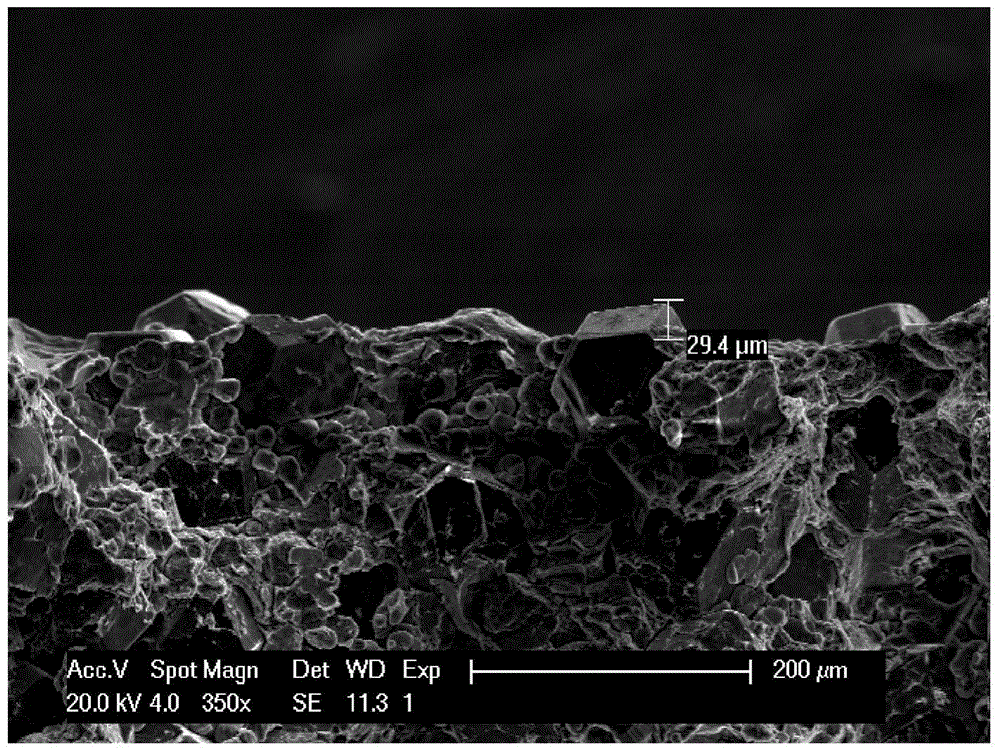
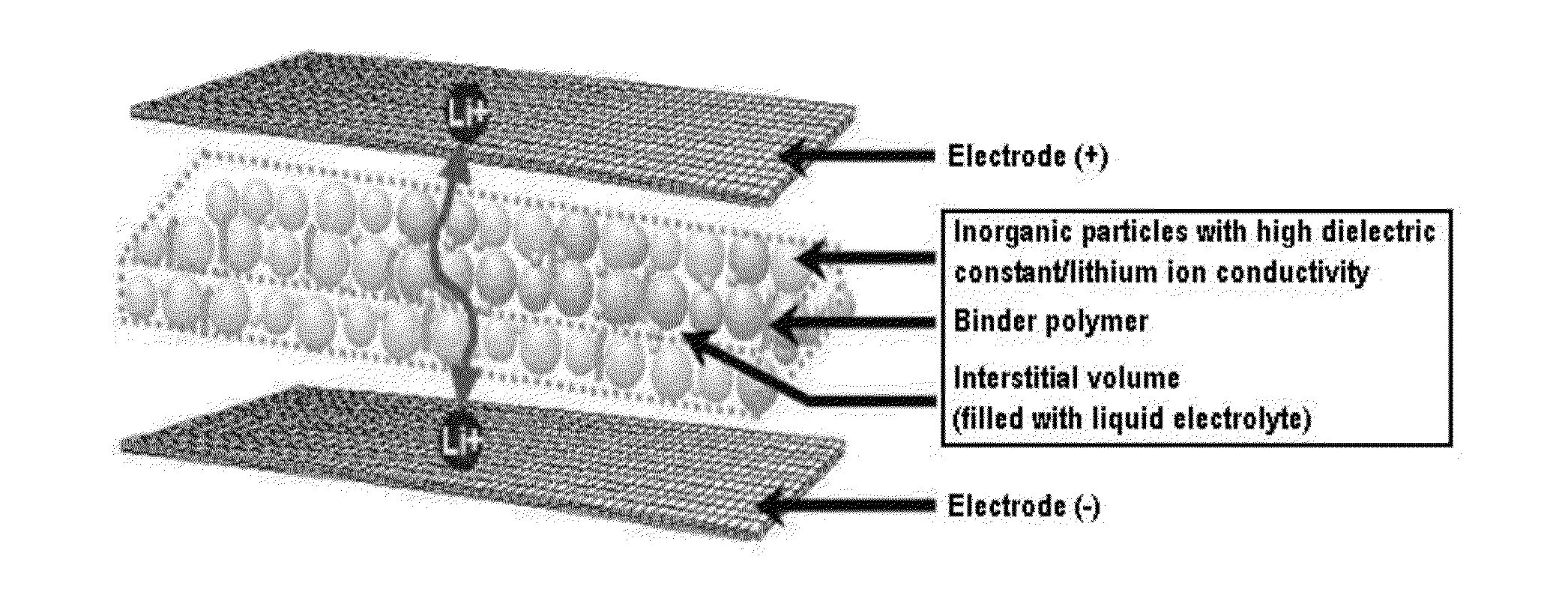
A separator includes a non-woven fabric substrate having pores, fine thermoplastic powder located inside the pores of the non-woven fabric substrate, and a porous coating layer disposed on at least one surface of the non-woven fabric substrate. The fine thermoplastic powder has an average diameter smaller than that of the pores and a melting point lower than the melting or decomposition point of the non-woven fabric substrate. The porous coating layer includes a mixture of inorganic particles and a binder polymer whose melting point is higher than the melting or decomposition point of the fine thermoplastic powder. In the porous coating layer, the inorganic particles are fixedly connected to each other by the binder polymer and the pores are formed by interstitial volumes between the inorganic particles. Previous filling of the large pores of the non-woven fabric substrate with the fine thermoplastic powder makes the porous coating layer uniform.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD +1
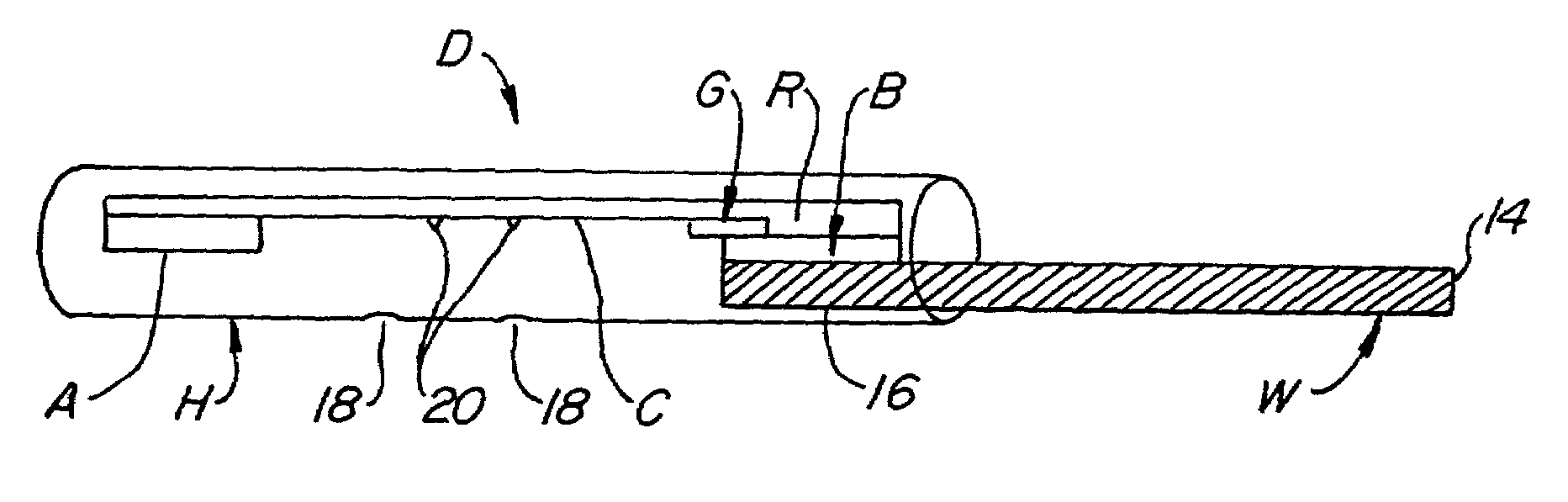
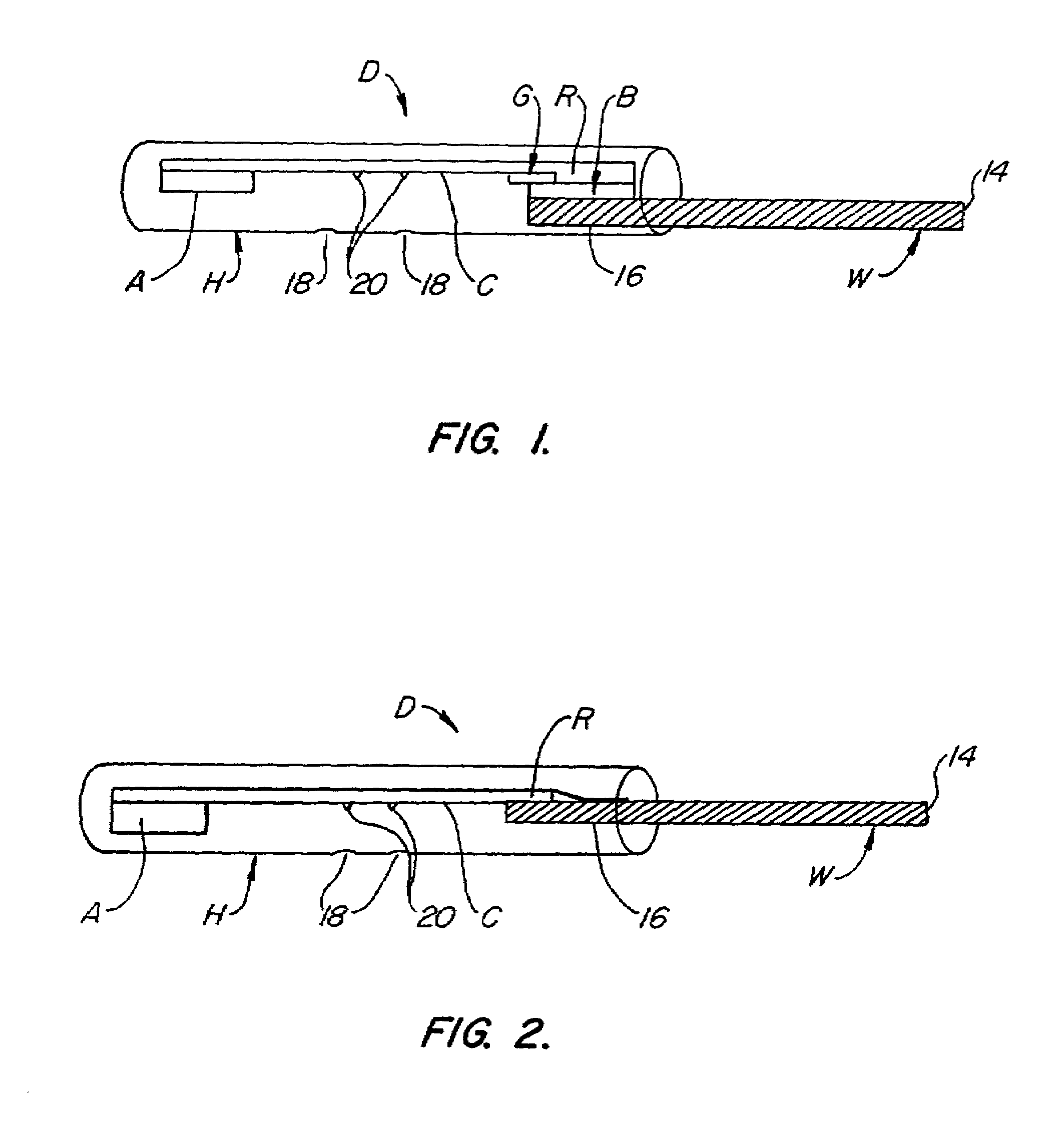
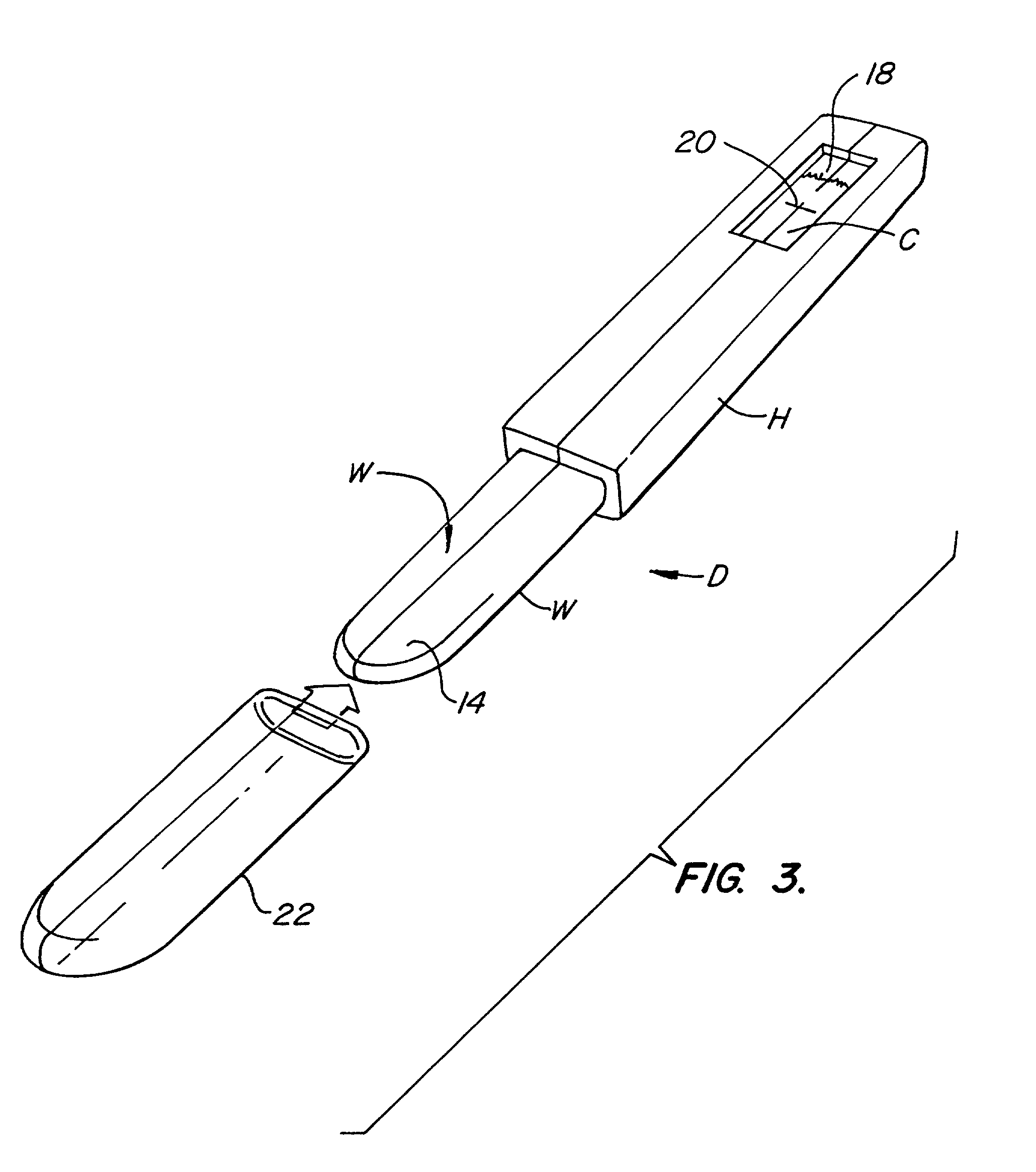
Device for collection and assay of oral fluids
InactiveUS7192555B2Low volumeRisk minimizationIon-exchange process apparatusAnalysis using chemical indicatorsParticulatesInterstitial volume
A device for collecting and transporting aqueous fluid from the oral cavity to a lateral chromatographic strip for test is disclosed. The lateral chromatographic strip is placed within and extend along a cavity defined in a housing. At least one inspection site to the lateral chromatographic strip is provided to enable inspection of selected sites on the lateral chromatographic strip for test results. A porous wick material protrudes from the housing to a collection site exterior of the housing at one end and communicates to the lateral chromatographic strip at the other end. The porous wick material has particulate construction, the particles adsorbing aqueous oral fluid to transport the fluid from the mouth to the lateral chromatographic strip without substantial absorption. The particles of the porous wick material are bound together to define a continuous interstitial volume for the flow of oral fluid to be transported and are treated to be hydrophilic to the adsorbed oral fluids. The porous wick material readily releases oral fluid to the lateral chromatographic strip. Prevention of reverse flow to the oral cavity from the lateral chromatographic strip naturally occurs due to the circuitous flow path of the porous wick material. A bite plate is coupled to the housing and insertable between the teeth of the patient to position the porous wick in the oral cavity for collecting the oral fluid. The bite plate is typically held in place by the occlusal force of the teeth, preferably the molars and / or the bicuspids, to position the porous wick in the buccal space. By observing the lateral chromatographic strip while the test device is in the mouth immediate test results are obtained.
Owner:ORASURE TECHNOLOGIES
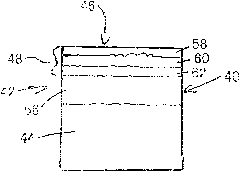
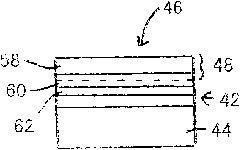
Cutting Element
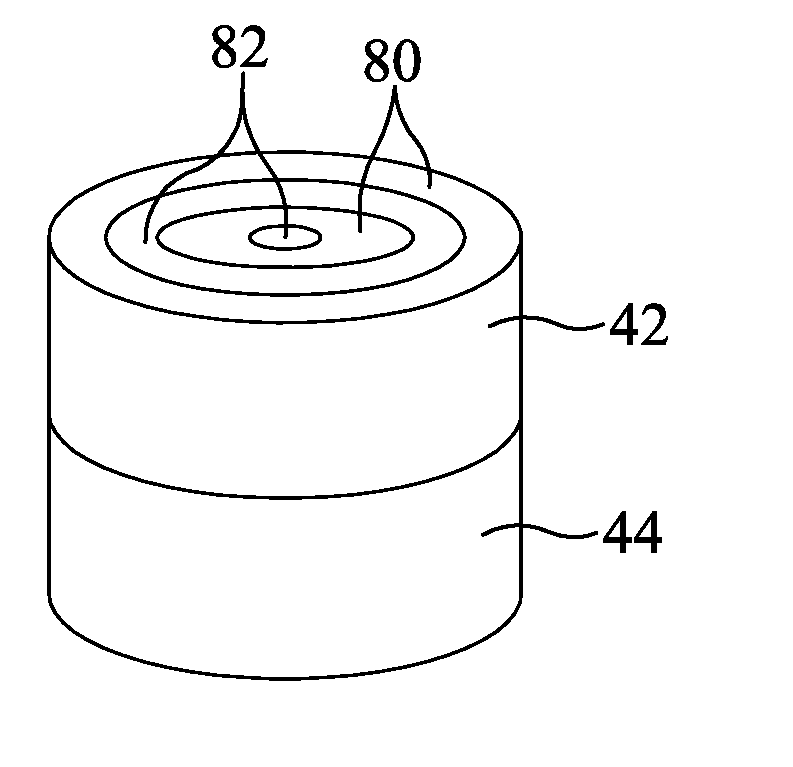
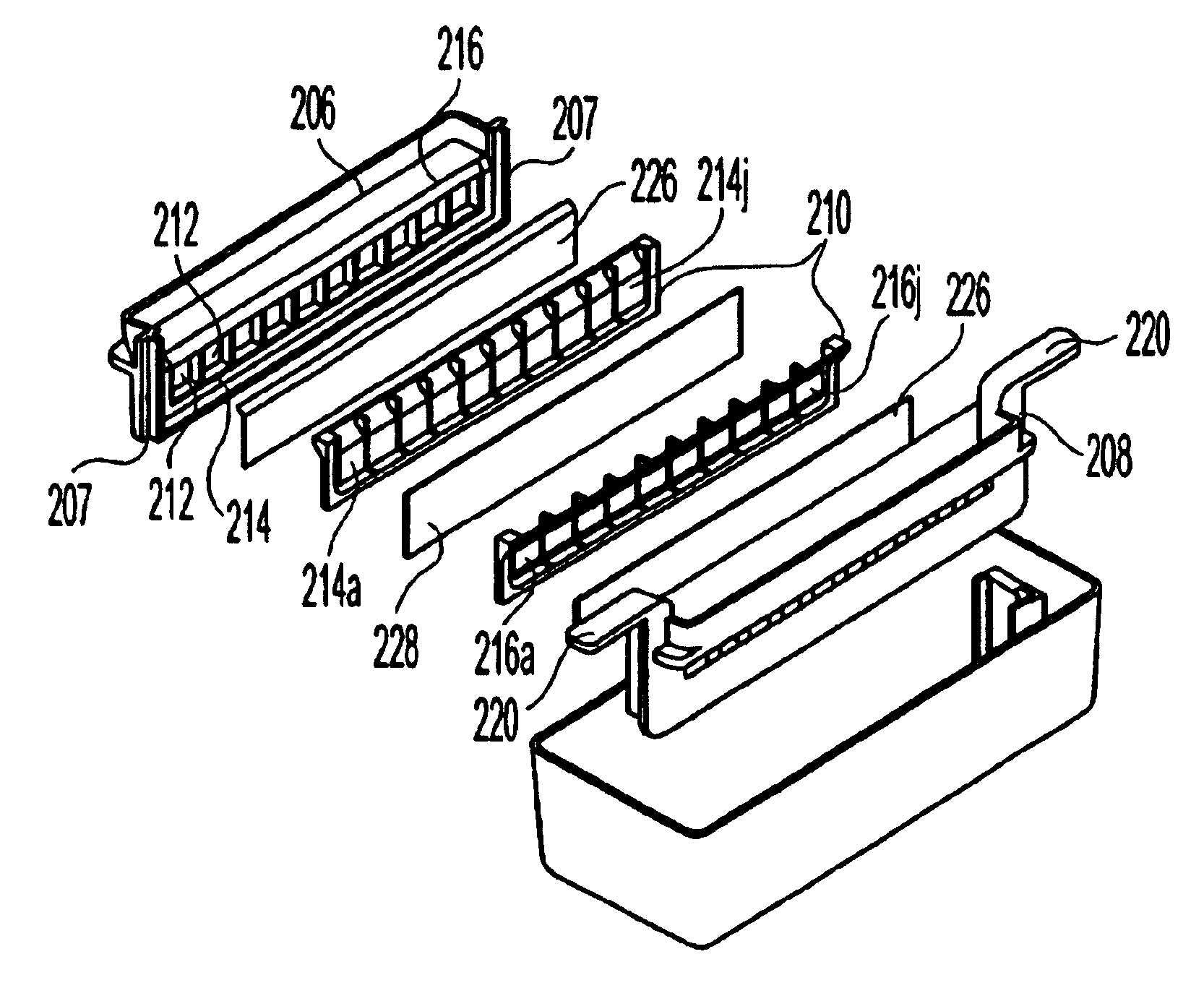
A cutting element comprises a multilayer polycrystalline diamond element 42 bonded to a substrate 44 of a less hard material, the polycrystalline diamond element 42 defining a matrix of interstitial volumes, the interstitial volumes of a first region of the diamond layer 42 adjacent a working surface 46 thereof being substantially free of a catalysing material, the interstitial volumes of a second region of the diamond layer 42 remote from the working surface 46 containing catalysing material.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
Lithium secondary battery
InactiveUS20130209861A1Improve securityIncrease space volumeCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersSecondary cellsPorous substrateLithium
Disclosed is an organic / inorganic composite porous film, having: (a) inorganic particles; and (b) a binder polymer coating layer formed partially or totally on surfaces of the inorganic particles, wherein the inorganic particles are interconnected among themselves and are fixed by the binder polymer, and interstitial volumes among the inorganic particles form a micropore structure. Further disclosed is a porous film having: (a) a porous substrate having pores; and (b) a coating layer formed on at least one region selected from the group consisting of a surface of the substrate and a part of the pores present in the substrate, wherein the coating layer comprises styrene-butadiene rubber. Also disclosed is an electrochemical device containing the organic / inorganic composite porous film, a method of manufacturing the film.
Owner:TORAY BATTERY SEPARATOR FILM
Device for collection and assay of oral fluids
InactiveUS20090170072A1Low volumeRisk minimizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticulatesInterstitial volume
A device for collecting and transporting aqueous fluid from the oral cavity to a lateral chromatographic strip for test is disclosed. The lateral chromatographic strip is placed within and extend along a cavity defined in a housing. At least one inspection site to the lateral chromatographic strip is provided to enable inspection of selected sites on the lateral chromatographic strip for test results. A porous wick material protrudes from the housing to a collection site exterior of the housing at one end and communicates to the lateral chromatographic strip at the other end. The porous wick material has particulate construction, the particles adsorbing aqueous oral fluid to transport the fluid from the mouth to the lateral chromatographic strip without substantial absorption. The particles of the porous wick material are bound together to define a continuous interstitial volume for the flow of oral fluid to be transported and are treated to be hydrophilic to the adsorbed oral fluids. The porous wick material readily releases oral fluid to the lateral chromatographic strip. Prevention of reverse flow to the oral cavity from the lateral chromatographic strip naturally occurs due to the circuitous flow path of the porous wick material. A bite plate is coupled to the housing and insertable between the teeth of the patient to position the porous wick in the oral cavity for collecting the oral fluid. The bite plate is typically held in place by the occlusal force of the teeth, preferably the molars and / or the bicuspids, to position the porous wick in the buccal space. By observing the lateral chromatographic strip while the test device is in the mouth immediate test results are obtained.
Owner:ORASURE TECHNOLOGIES
Device for collection and assay of oral fluids
InactiveUS20070116597A1Low volumeRisk minimizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticulatesAssay
A device for collecting and transporting aqueous fluid from the oral cavity to a lateral chromatographic strip for test is disclosed. The lateral chromatographic strip is placed within and extend along a cavity defined in a housing. At least one inspection site to the lateral chromatographic strip is provided to enable inspection of selected sites on the lateral chromatographic strip for test results. A porous wick material protrudes from the housing to a collection site exterior of the housing at one end and communicates to the lateral chromatographic strip at the other end. The porous wick material has particulate construction, the particles adsorbing aqueous oral fluid to transport the fluid from the mouth to the lateral chromatographic strip without substantial absorption. The particles of the porous wick material are bound together to define a continuous interstitial volume for the flow of oral fluid to be transported and are treated to be hydrophilic to the adsorbed oral fluids. The porous wick material readily releases oral fluid to the lateral chromatographic strip. Prevention of reverse flow to the oral cavity from the lateral chromatographic strip naturally occurs due to the circuitous flow path of the porous wick material. A bite plate is coupled to the housing and insertable between the teeth of the patient to position the porous wick in the oral cavity for collecting the oral fluid. The bite plate is typically held in place by the occlusal force of the teeth, preferably the molars and / or the bicuspids, to position the porous wick in the buccal space. By observing the lateral chromatographic strip while the test device is in the mouth immediate test results are obtained.
Owner:ORASURE TECHNOLOGIES
Composition for improving efficiency of drug delivery
InactiveUS20090208422A1Enhancing infusionMinimizing backflowOrganic active ingredientsBiocideInfusion catheterInterstitial volume
Owner:TEL HASHOMER MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & SERVICES +1
Hydrogen storage with graphite anion intercalation compounds
InactiveUS20080175780A1Increase the volume ratioIncrease distanceMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenMultiwalled carbonAnion intercalation
The disclosure relates to a material for reversibly storing and releasing hydrogen comprising graphite or a graphitic structure, for example, comprising an ordered graphite structure of carbon and nitrogen atoms wherein the interlayer and / or interstitial volume is occupied with at least one intercalated anionic species. While any suitable anionic species can be employed, examples of suitable species are at least one of: F− (fluoride), (C≡C)2− (diacetylide), and (N═C═N)2−. Desirable anionic species typically have a relatively high charge to volume ratio. The disclosure also relates to a material for reversibly storing and releasing hydrogen comprising ordered graphitic structures comprising at least one member selected from the group of graphite, single walled carbon nanotubes, multiwalled carbon nanotubes, graphite nanofibers, carbon nanohorns, and boron nitride. The carbon materials may incorporate substitutional nitrogen atoms in the graphite lattice at a level ranging from about 1 to about 40 atomic percent.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Method for restoring power cables
A method for extending the useful life of an in-service electrical cable section having a stranded conductor surrounded by a conductor shield encased in a polymeric insulation jacket and having an interstitial void volume in the region of the conductor, the cable section having an average conductor temperature T. The method comprising (i) continuously introducing a non-condensing exclusion fluid into the interstitial volume, the exclusion fluid comprising at least one non-condensing exclusion component having a solubility in the insulation polymer at least 100 times the corresponding solubility of water, each solubility being determined at temperature T; and (ii) injecting a condensing dielectric enhancement fluid into the interstitial void volume, wherein the dielectric enhancement fluid has a virtual flow rate within the interstitial void volume of less than about 0.1 liter per hour.
Owner:NOVINIUM LLC
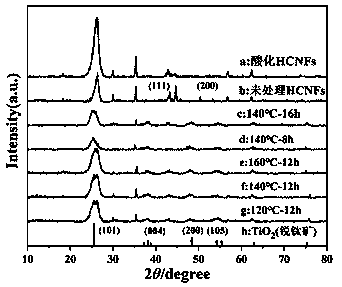
A helical carbon nanofiber/TiO2 composite material and application thereof
The invention discloses a helical carbon nanofiber / TiO2 composite material and application thereof, wherein the helical nanometer carbon fiber is modified by a liquid phase oxidation method to activate the helical nanometer carbon fiber, and then the helical nanometer carbon fiber loaded titanium dioxide composite electrode material is obtained by a hydrothermal method. The activated helical carbon nanofibers remove impurities such as amorphous carbon on the surface of the helical carbon nanofibers. The interstitial volume and specific surface area of the composites are increased, and the surface active groups are also increased, which enhance the loading capacity and adhesion of TiO2. The dispersion of the composites is better, the aggregation is less, and the original helical structure of HCNFs is not destroyed, which facilitated the storage and transfer of electrons. The helical carbon nanofiber / TiO2 composite material prepared by the invention has large specific surface area, goodspecific capacity, cycle performance and safety performance, and has good application prospect in the field of supercapacitor materials. The helical carbon nanofiber / TiO2 composite material has good specific capacity, cycle performance and safety performance, and has good application prospect in the field of supercapacitor materials.
Owner:ZIGONG DONGXIN CARBON CO LTD
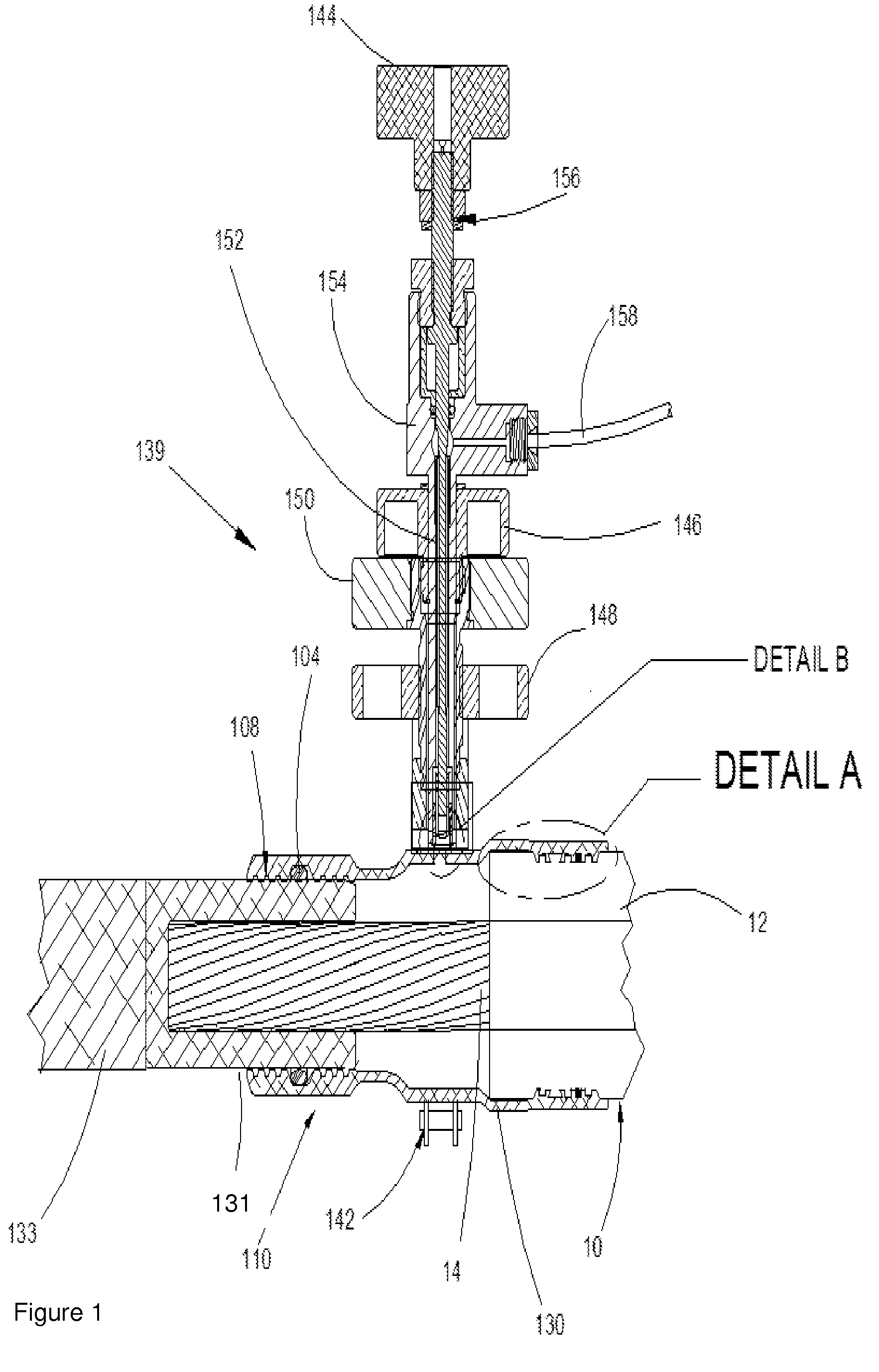
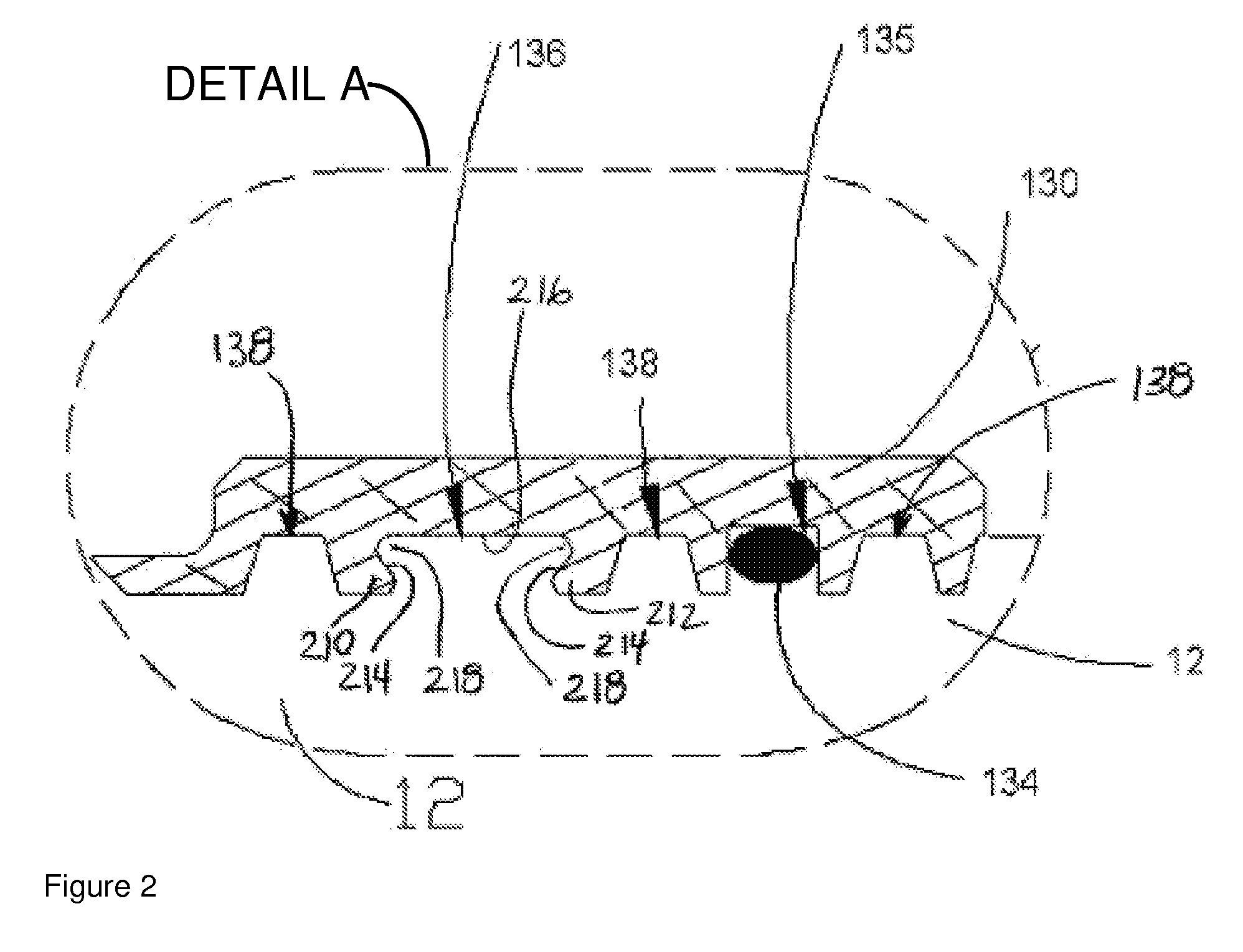
Alternate fuel storage system and method
ActiveUS8256401B2Non-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesAlternative fuelsInterstitial volume
A fuel tank for storing an alternate fuel and providing the fuel to an internal combustion engine includes: an inner shell with an internal cavity designed to store fuel; an outer shell configured and positioned relative to the inner shell such that an interstitial volume is created between the inner and outer shells; and a heating unit positioned in the interstitial volume. In some embodiments, the interstitial volume is filled with air; in other embodiments, the interstitial volume is filled with a thermally insulative material.
Owner:GILBARCO
Collection device for assay of oral fluids
InactiveUS20100239458A1Low volumeRisk minimizationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsComponent separationParticulatesInterstitial volume
An apparatus and process for transporting aqueous fluid from the oral cavity to a lateral chromatographic strip for test is disclosed. A lateral chromatographic strip is placed within a cavity defined in a housing. The lateral chromatography strip extends within the cavity and is disposed along the housing to an inspection site. At least one inspection site to the lateral chromate phic strip is provided to enable inspection of selected sites on the lateral chromatographic strip for test results. A porous wick material protrudes from the housing to a collection site exterior of the housing at one end and communicates to the lateral chromatographic strip at the other end. This porous wick material has particulate construction, the particles adsorbing aqueous oral fluid to transport the fluid from the mouth to the lateral chromatographic strip without substantial absorption. The particles of the porous wick material are bound together to define a continuous interstitial volume for the flow of oral fluid to be transported and are treated to be hydrophilic to the adsorbed oral fluids. The porous wick material readily releases oral fluid to the lateral chromatographic strip. Prevention of reverse flow to the oral cavity from the lateral chromatographic strip naturally occurs due to the circuitous flow path of the porous wick material. By observing the lateral chromatographic strip while the entire test device is in the mouth immediate test results are obtained.
Owner:ORASURE TECHNOLOGIES
Small separation apparatus
InactiveUS6969453B2Easy to separateSample is very smallSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectric fieldInterstitial volume
An electrophoresis apparatus for processing compounds in small sample volumes comprising a cathode in a static cathode buffer zone or compartment, an anode in a static anode buffer zone or compartment. The cathode disposed relative to the anode so as to be adapted to generate an electric field in an electric field area therebetween upon application of a voltage potential between the cathode and anode. A removable cartridge disposed in the electric field area between the anode and the cathode. The cartridge containing a first non-isoelectric separation barrier and also a second non-isoelectric separation barrier disposed between a selected one of the cathode buffer zone and the anode buffer zone and the first barrier so as to define a first chamber having an interstitial volume of less than 5 ml therebetween.
Owner:NUSEP
Cysteamine in the treatment of fibrotic disease
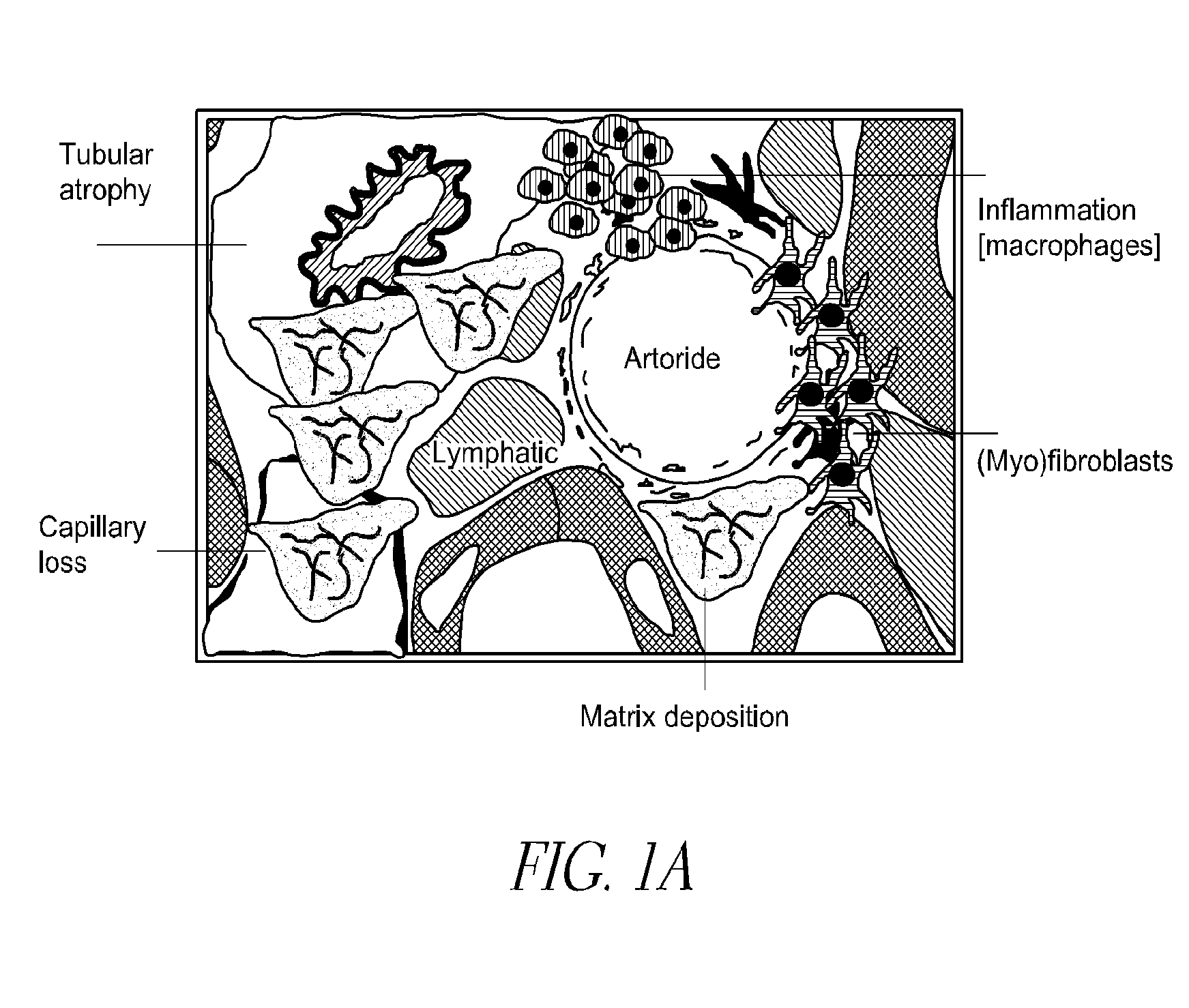
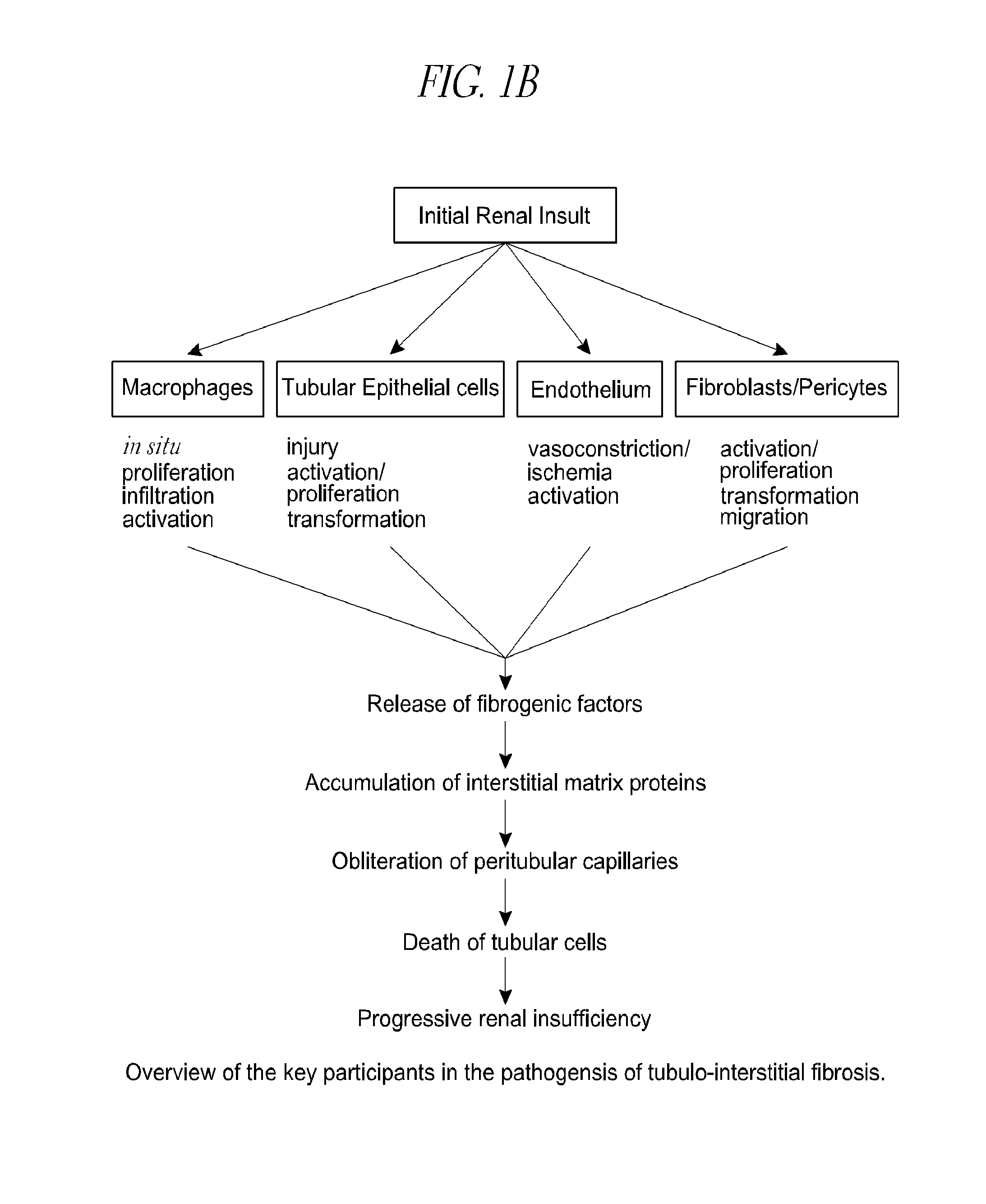
Fibrotic diseases are characterized by the replacement of healthy tissue with scar tissue and extracellular matrix in response to tissue damage. Here we describe the reduction of extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, interstitial fibroblasts, interstitial volume, expression of Collagen I mRNA and protein, expression of profibrotic cytokines and macrophage infiltration by Cysteamine treatment.
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL (DBA SEATTLE CHILDRENS RES INST)
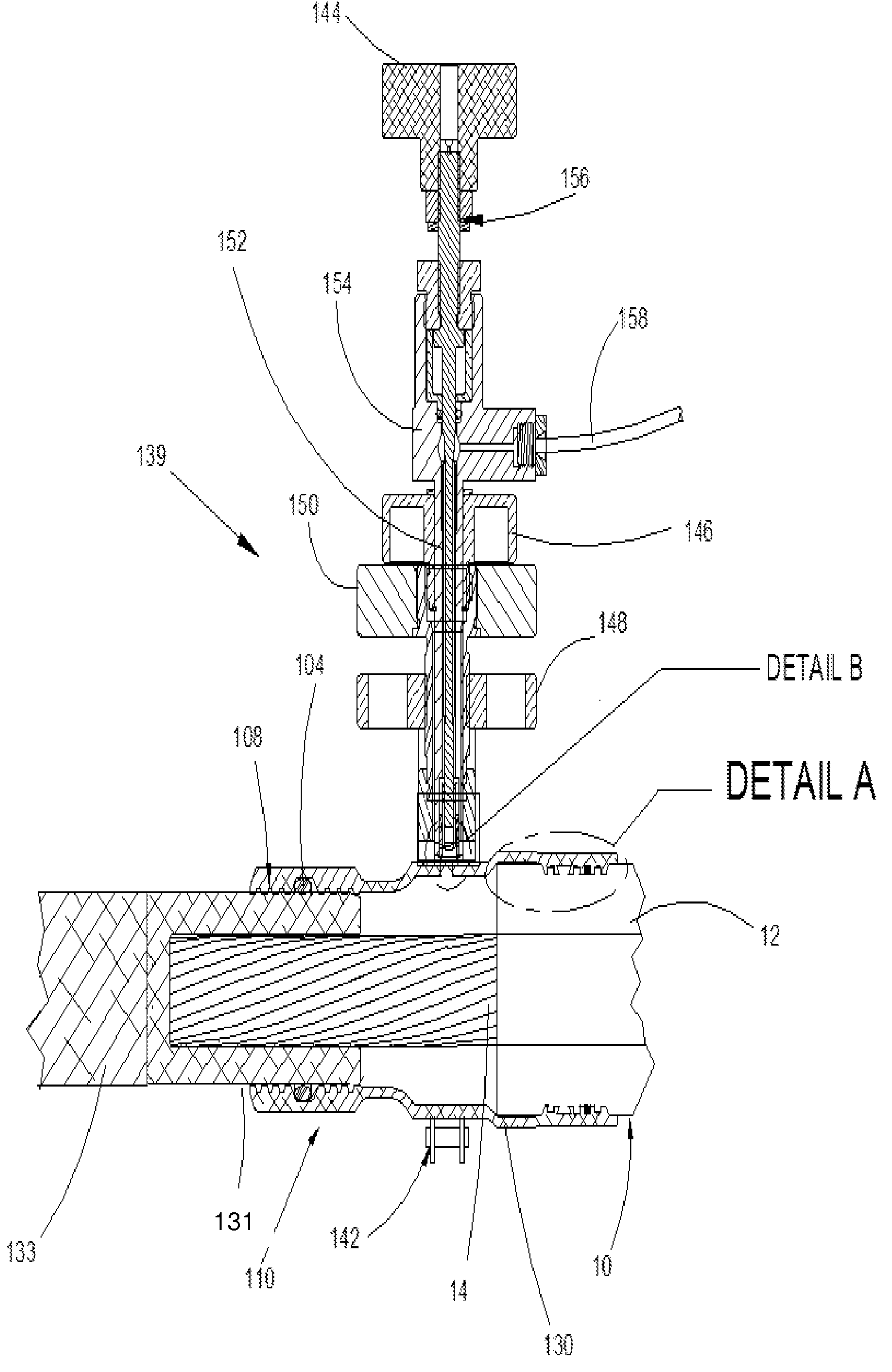
Bottle pressurization delivery system
ActiveUS20140261868A1Well formedAvoid aspirationComponent separationLiquid transferring devicesInterstitial volumePositive pressure
A container assembly for use with a high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) instrument is disclosed, in which the container assembly, when coupled to a source of pressurized gas, provides fluid medium to the HPLC instrument at positive pressure. The container assembly has an external exterior container shell, an internal fluid container for holding fluid medium, an interstitial volume between the external exterior container shell and the internal fluid container, a port for fluidly connecting the volume to a pressurized gas source, and a port for fluidly connecting the internal fluid container to the HPLC instrument. As a pressurized gas in the interstitial volume increases, fluid medium flows out of the port connected to the internal fluid bag and container assembly at a positive pressure. A system incorporating the container assembly, and method of use of the same, are also disclosed.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
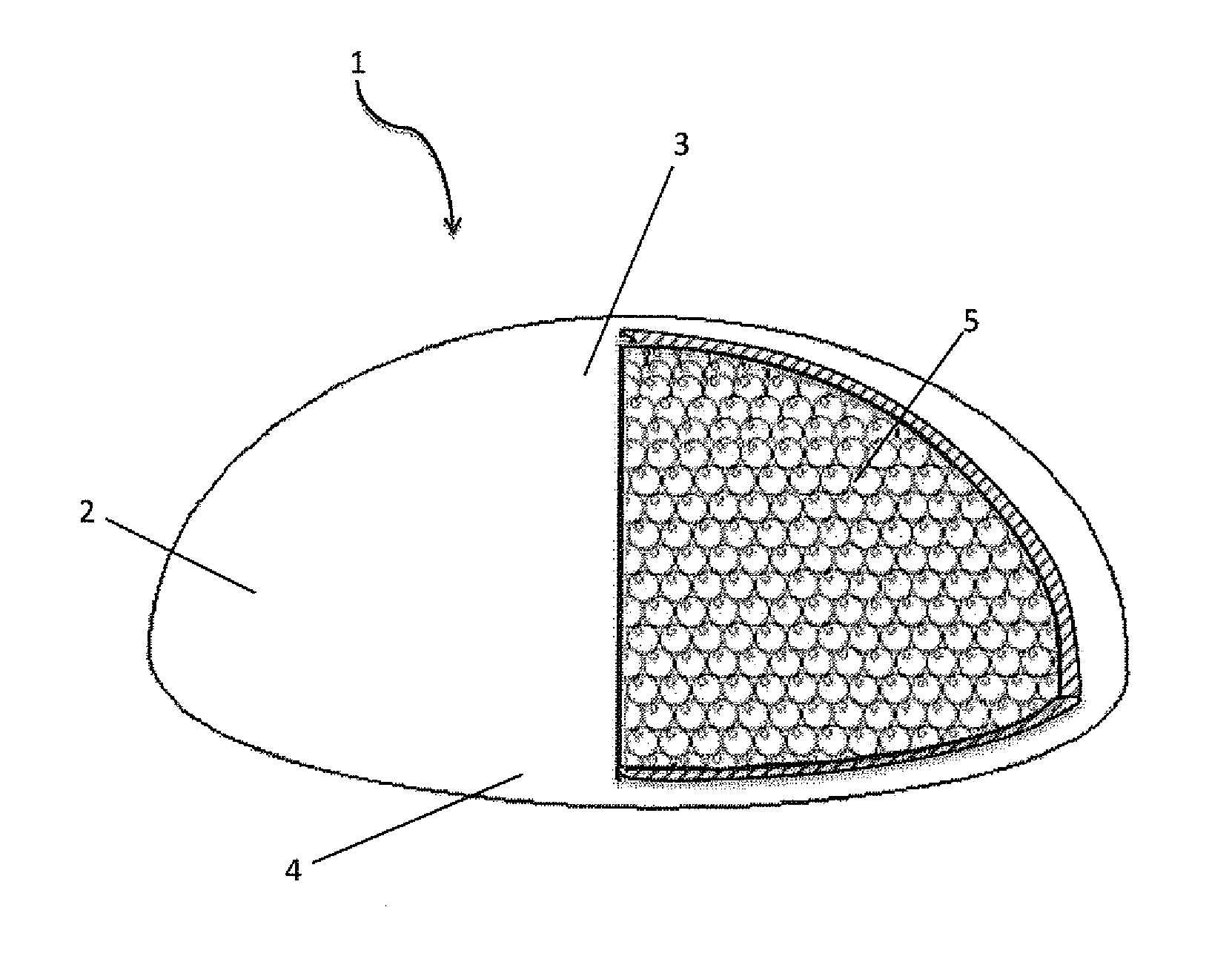
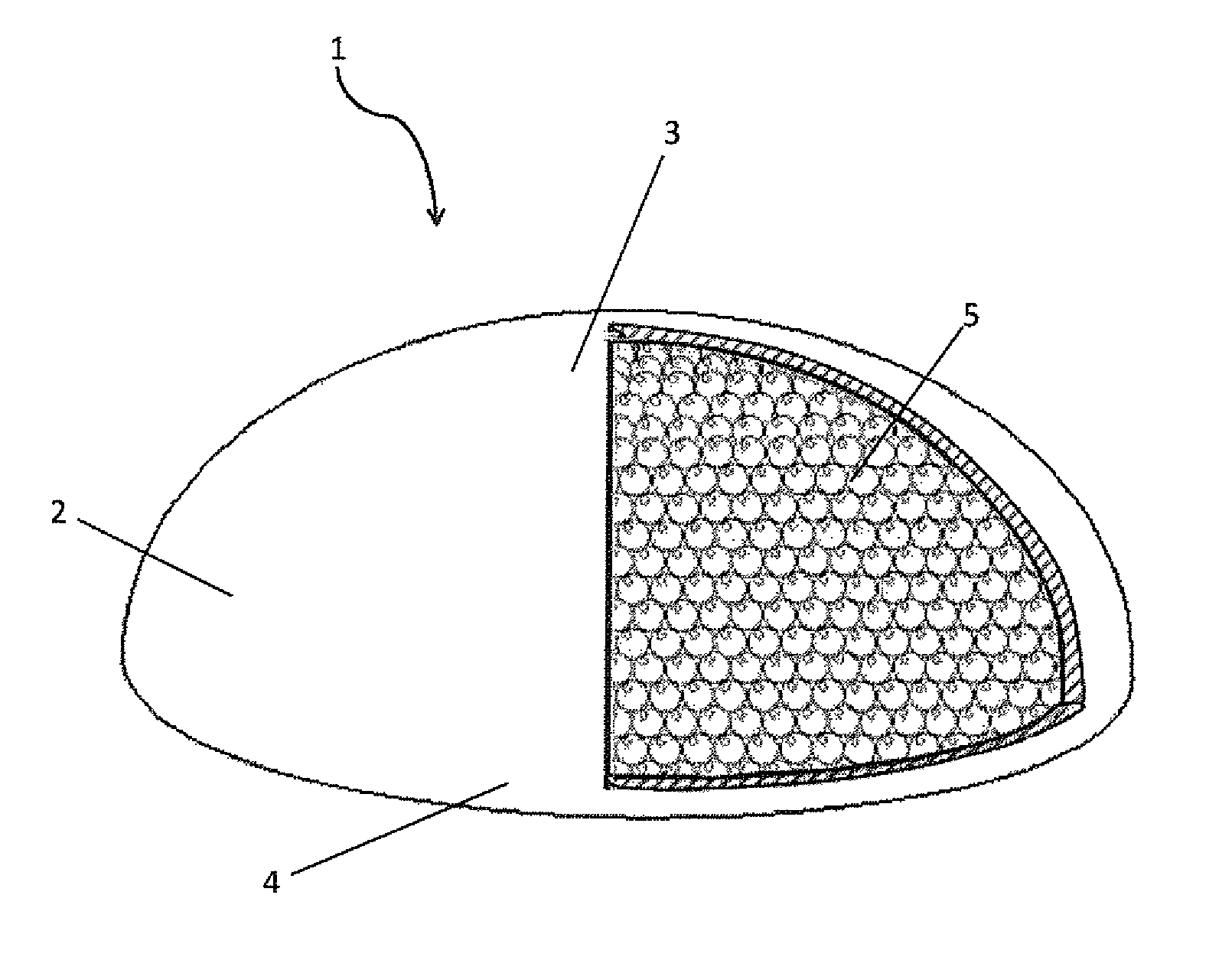
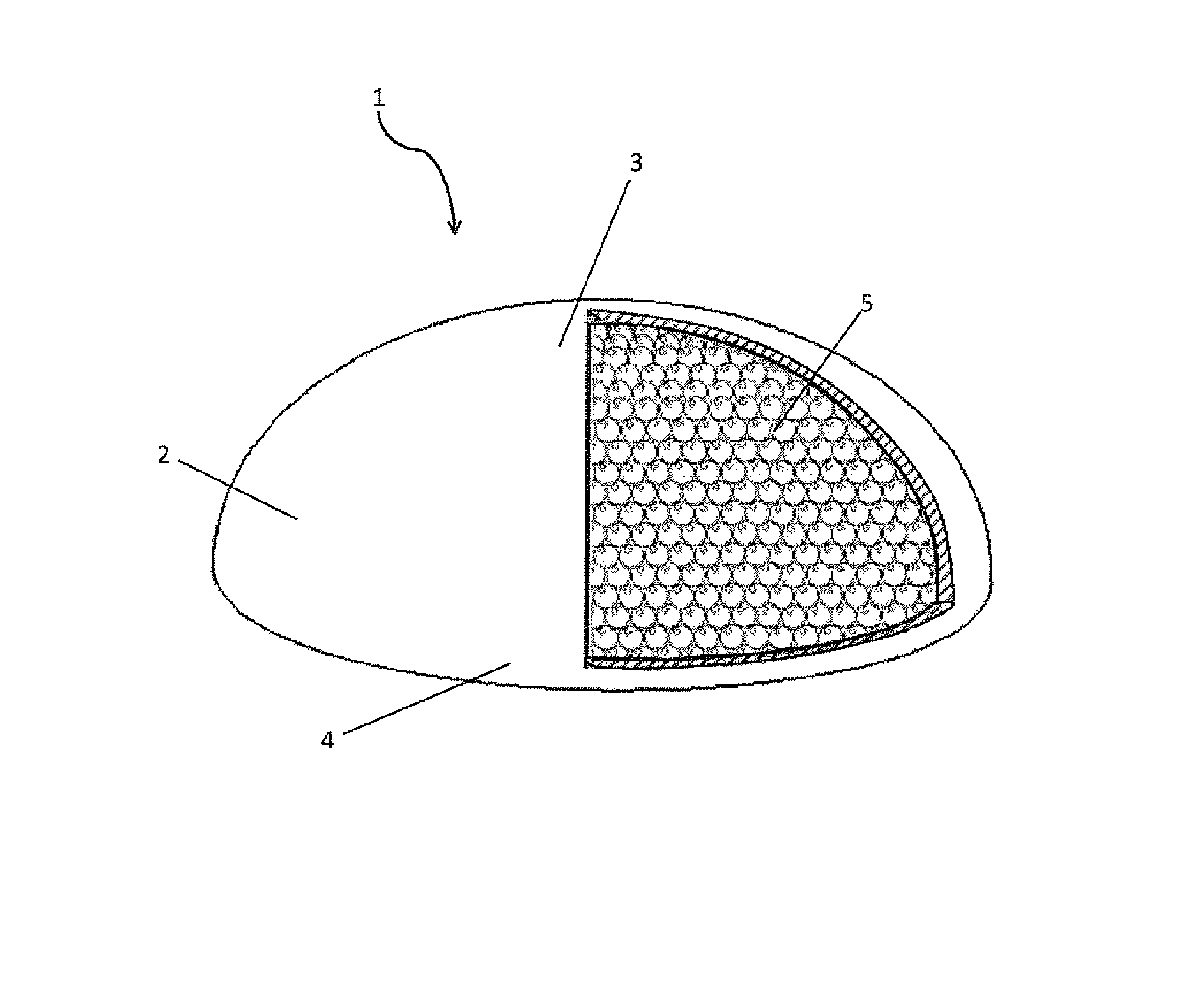
Mammary prosthesis filled with expanded polymer microspheres
InactiveUS20130150962A1Easy to disassembleNatural feelingMammary implantsMammary prosthesisAnterior surface
A mammary prosthesis built from a sack of elastic material or biocompatible material having a sealed interior cavity with the sack having an anterior surface forming a dome and a posterior surface forming a base, with a sealed and seamless interior cavity filled with microspheres of foamed or expanded polymers or a combination of both. The sack may also be permeable to establish equilibrium between body fluids and interstitial volume of the microspheres.
Owner:SANABRIA SCHARF FREDDY +1
Method for restoring power cables
ActiveUS20090133799A1Extended service lifeLiquid organic insulatorsLayered productsSolubilityElectrical conductor
A method for extending the useful life of an in-service electrical cable section having a stranded conductor surrounded by a conductor shield encased in a polymeric insulation jacket and having an interstitial void volume in the region of the conductor, the cable section having an average conductor temperature T. The method comprising (i) continuously introducing a non-condensing exclusion fluid into the interstitial volume, the exclusion fluid comprising at least one non-condensing exclusion component having a solubility in the insulation polymer at least 100 times the corresponding solubility of water, each solubility being determined at temperature T; and (ii) injecting a condensing dielectric enhancement fluid into the interstitial void volume, wherein the dielectric enhancement fluid has a virtual flow rate within the interstitial void volume of less than about 0.1 liter per hour.
Owner:NOVINIUM LLC
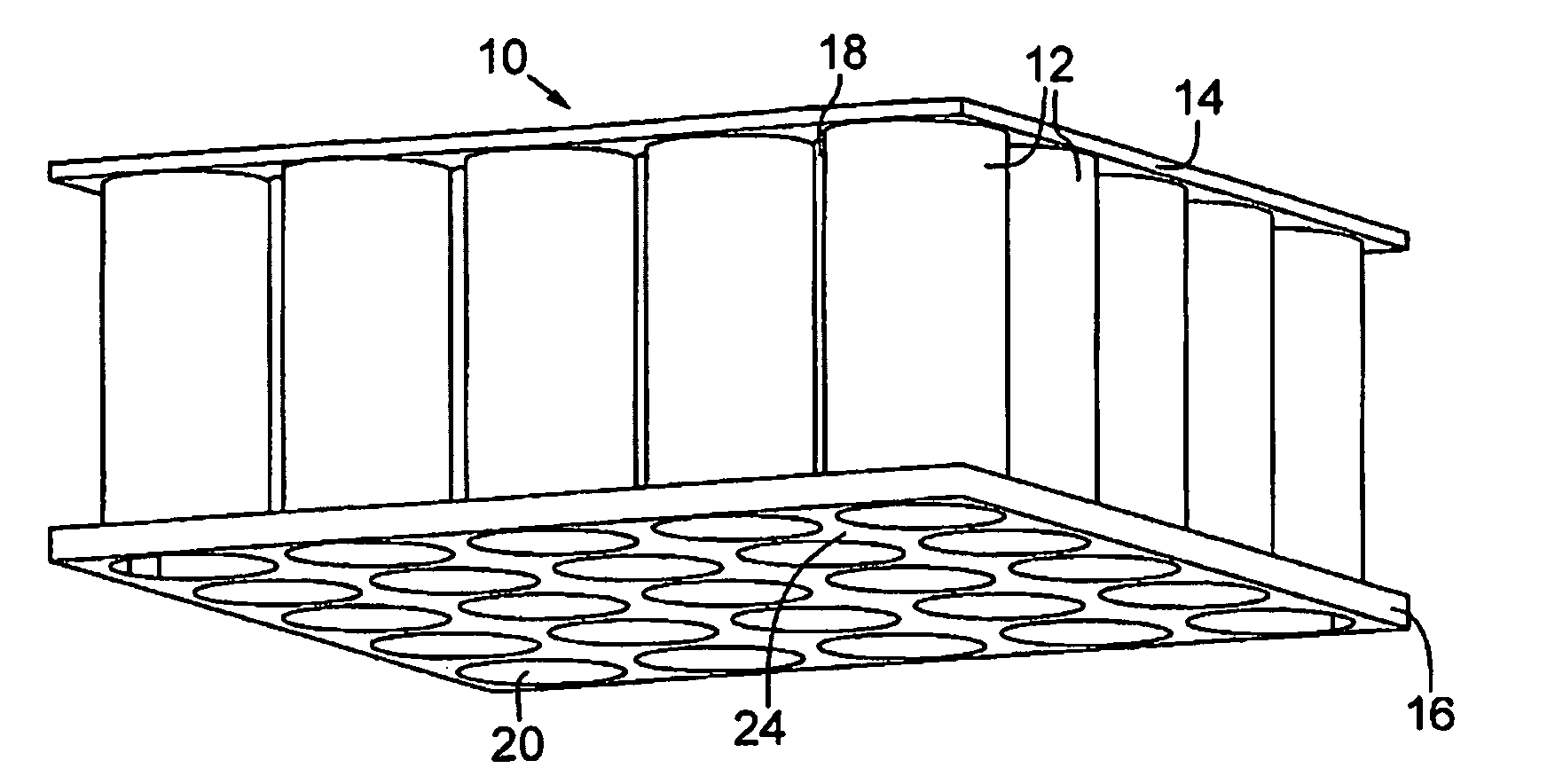
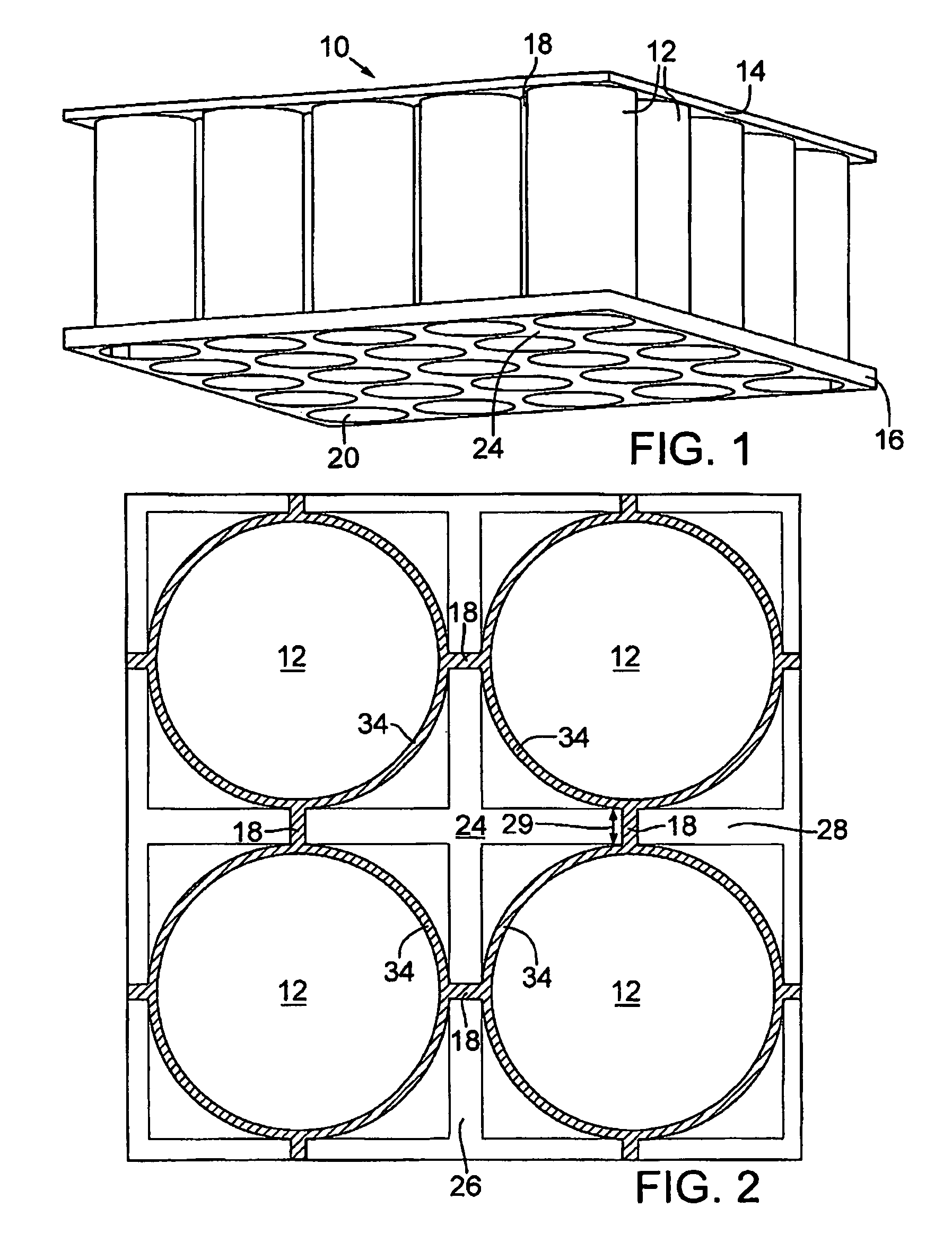
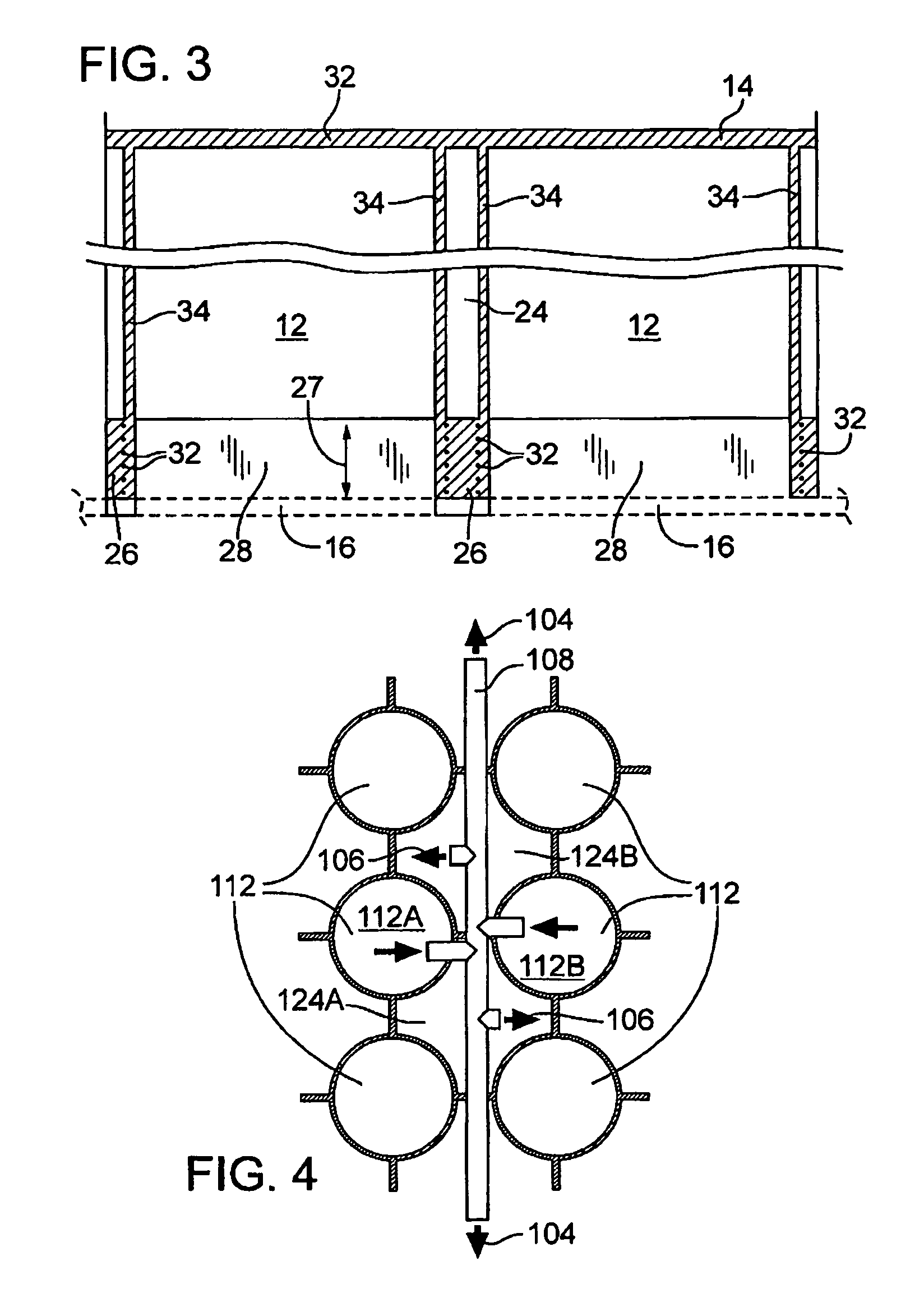
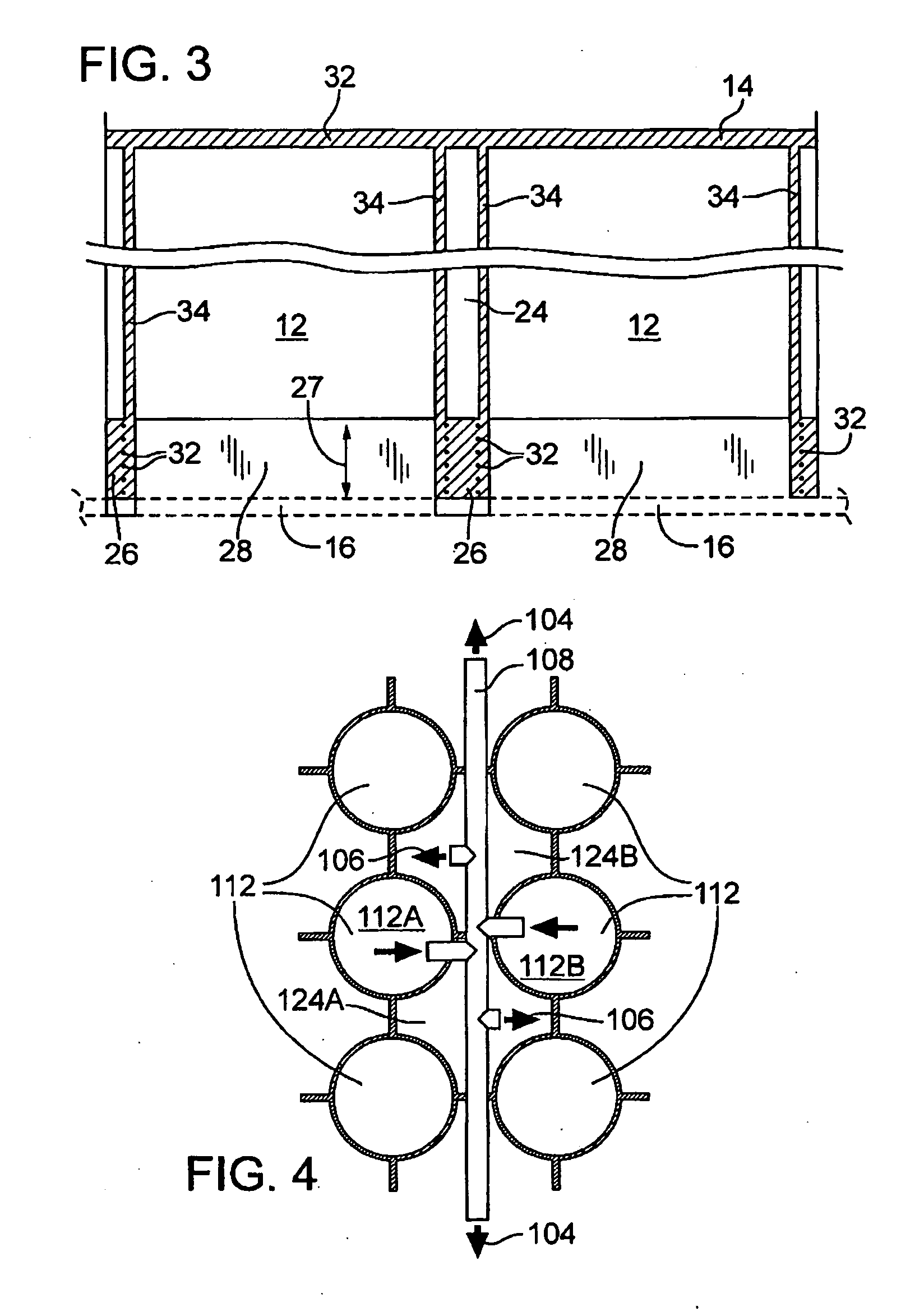
Floating platform method and apparatus
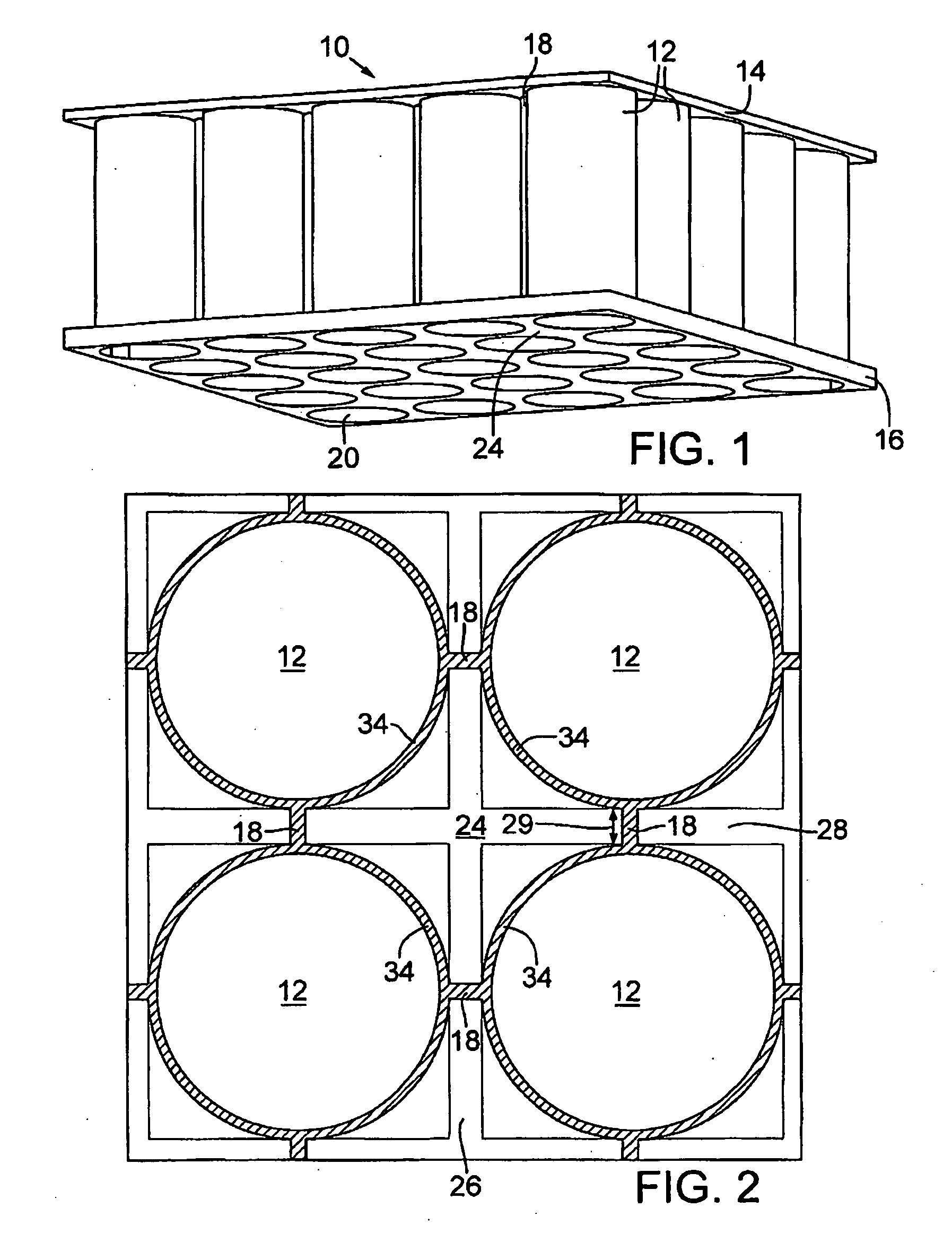
ActiveUS7823525B2Vessel movement reduction by wave dampingFloating buildingsInterstitial volumeEngineering
A floating platform is provided. The floating platform includes a top surface (14), a plurality of buoyancy members (12) interconnected to the top surface and extending downwardly into a body of water, a bottom plate (16) and a plurality of interstitial volumes (24) that are sealed at a bottom end by the bottom plate to prevent the flow of water into the interstitial volume.
Owner:FLOAT
Cutting element
A cutting element comprises a multilayer polycrystalline diamond element 42 bonded to a substrate 44 of a less hard material, the polycrystalline diamond element 42 defining a matrix of interstitial volumes, the interstitial volumes of a first region of the diamond layer 42 adjacent a working surface 46 thereof being substantially free of a catalysing material, the interstitial volumes of a second region of the diamond layer 42 remote from the working surface 46 containing catalysing material.
Owner:REEDHYCALOG UK
Small separation apparatus
InactiveUS20060037860A1Valid choiceSmall loadSludge treatmentElectrostatic separationElectrophoresisInterstitial volume
An apparatus for processing compounds in small volumes by electrophoresis, the apparatus comprising: (a) a cathode in a static cathode buffer zone or compartment; (b) an anode in a static anode buffer zone or compartment, the anode disposed relative to the cathode so as to be adapted to generate an electric field in an electric field area therebetween upon application of a voltage potential between the cathode and anode; (c) a first separation barrier disposed in the electric field area; (d) a second separation barrier disposed between a selected one of the cathode buffer zone and the anode buffer zone and the first barrier so as to define a first interstitial volume or chamber therebetween; wherein in use, electrophoretic buffer is disposed in the cathode buffer zone and the anode buffer zone, a sample constituent is provided to the first interstitial volume; wherein upon application of the voltage potential, a selected separation product is removed from the sample constituent through a selected one of the first and second separation barriers, and provided to a selected one of the cathode buffer and anode buffer zones; and wherein there is substantially no circulation of buffer or sample constituent in the buffer zones or the first interstitial volume.
Owner:GRADIPORE
Composition for improving efficiency of drug delivery
InactiveUS8391959B2Enhancing infusionMinimizing backflowBiocideOrganic active ingredientsInfusion catheterInterstitial volume
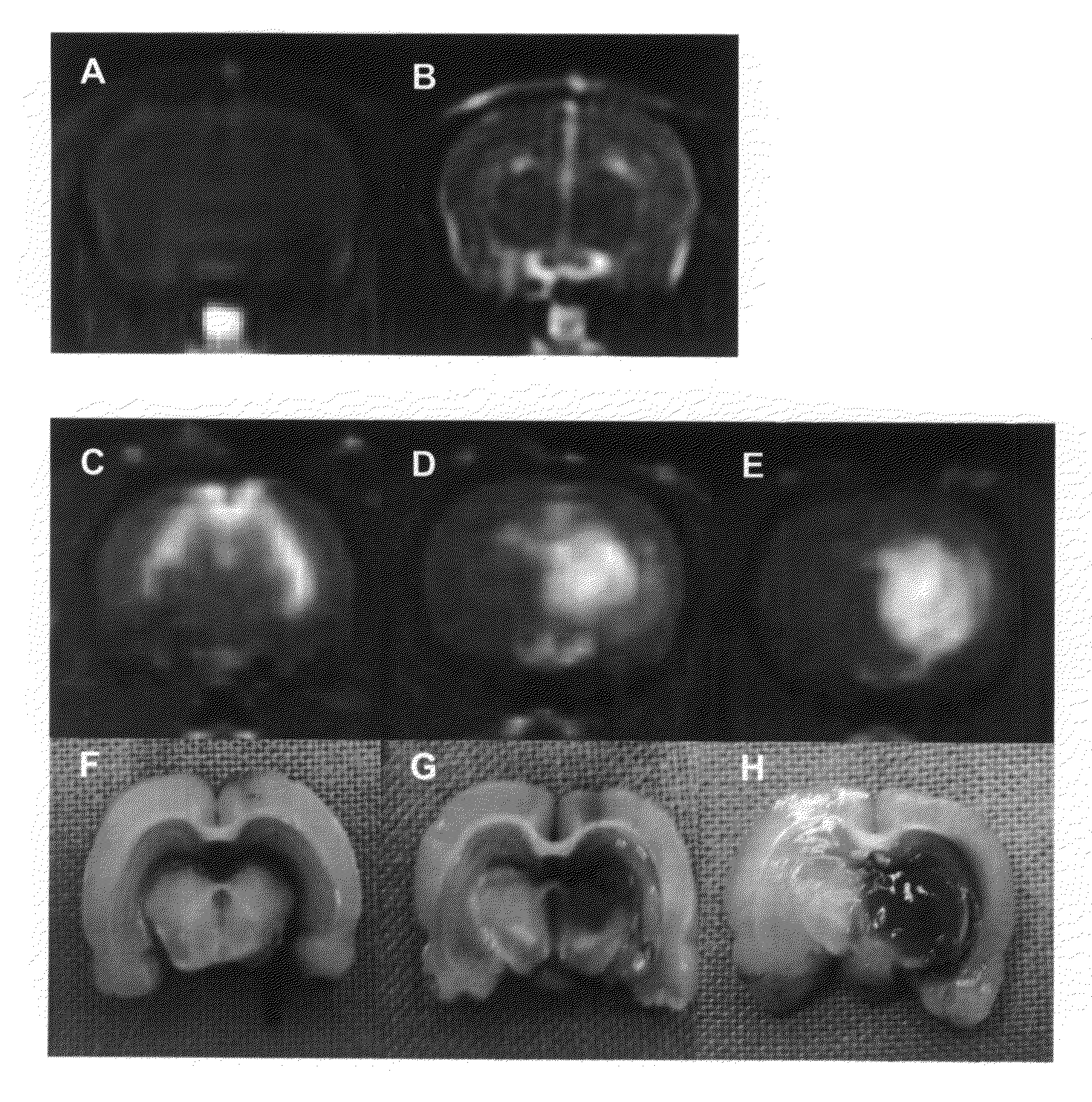
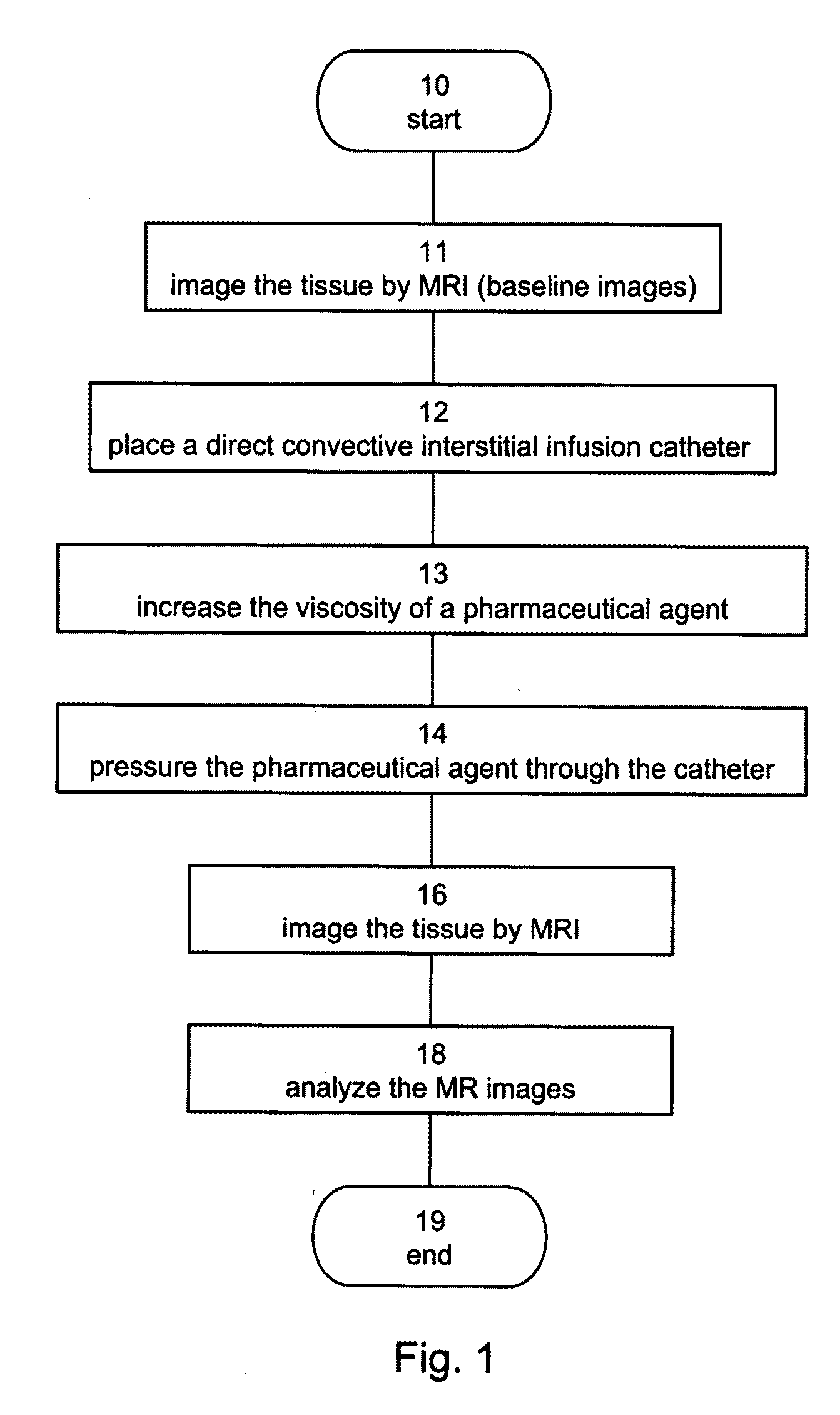
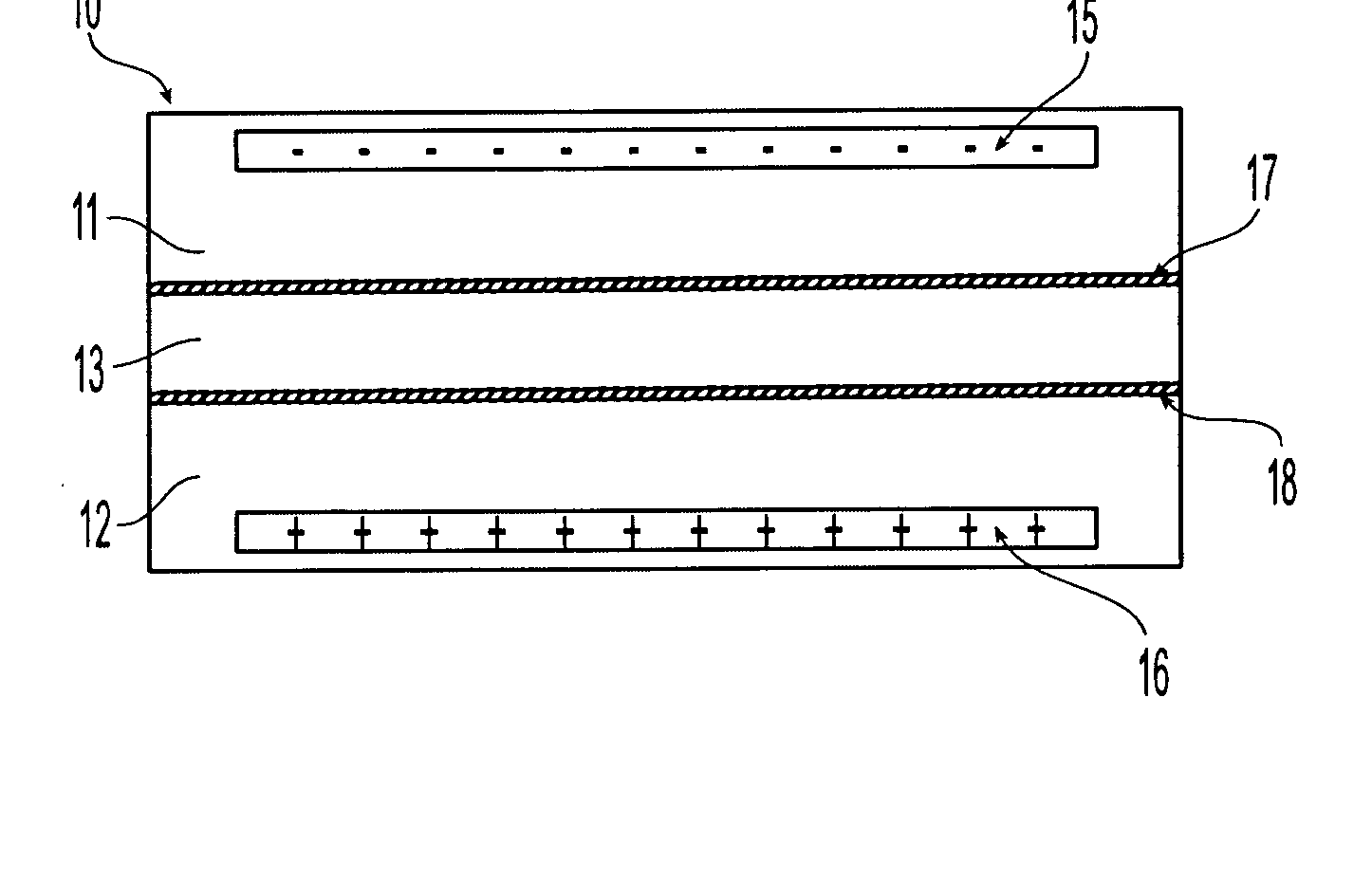
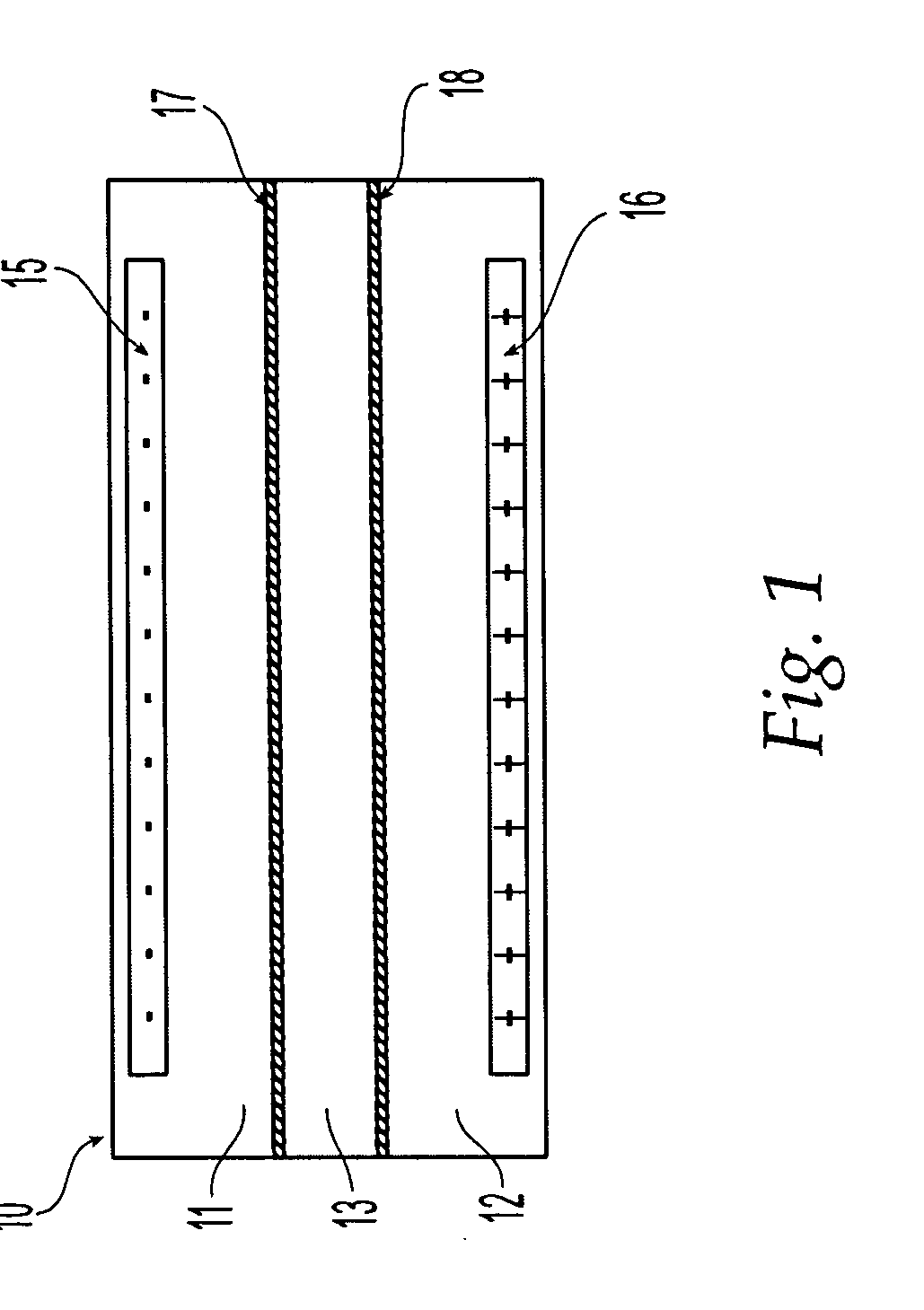
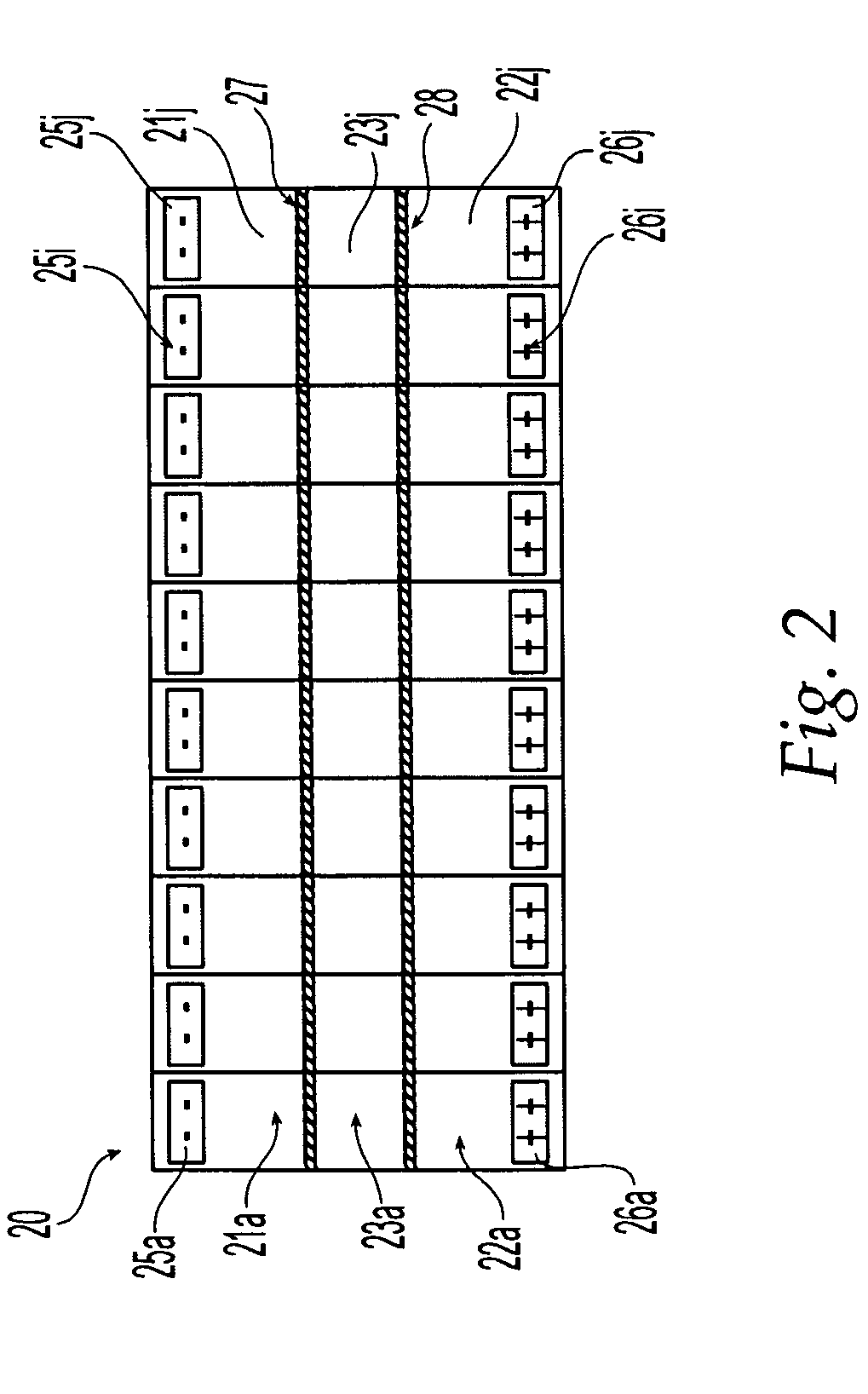
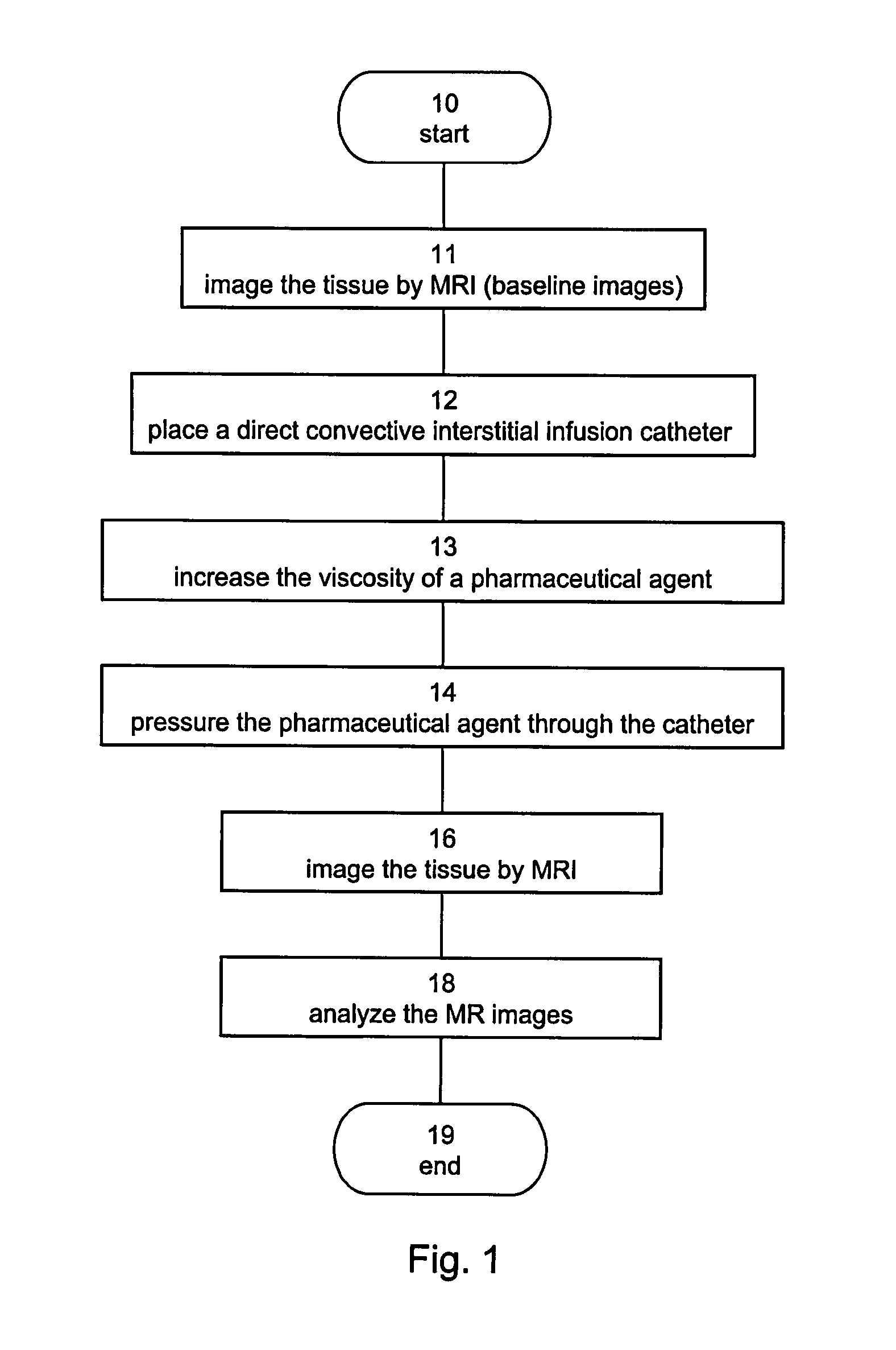
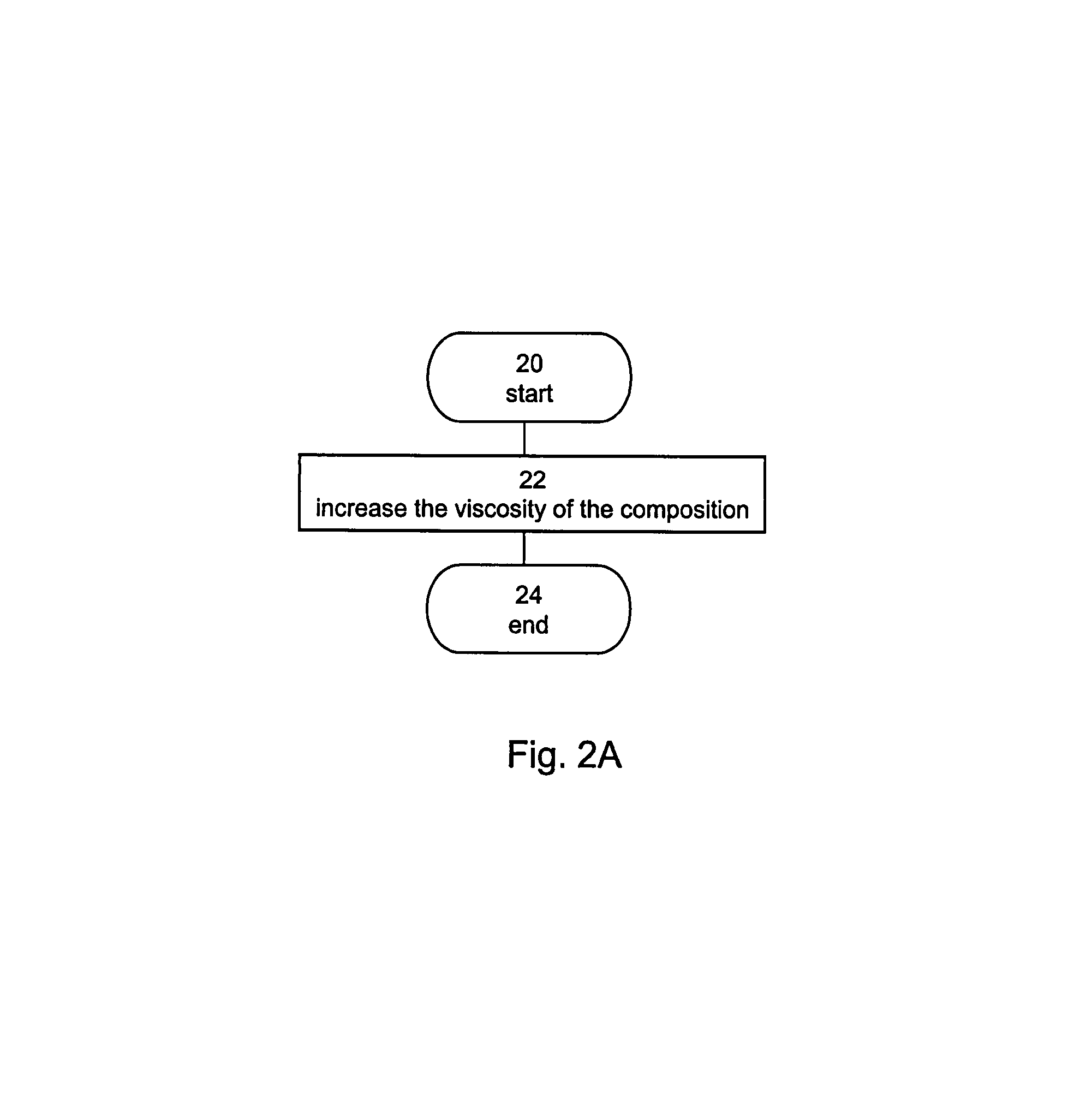
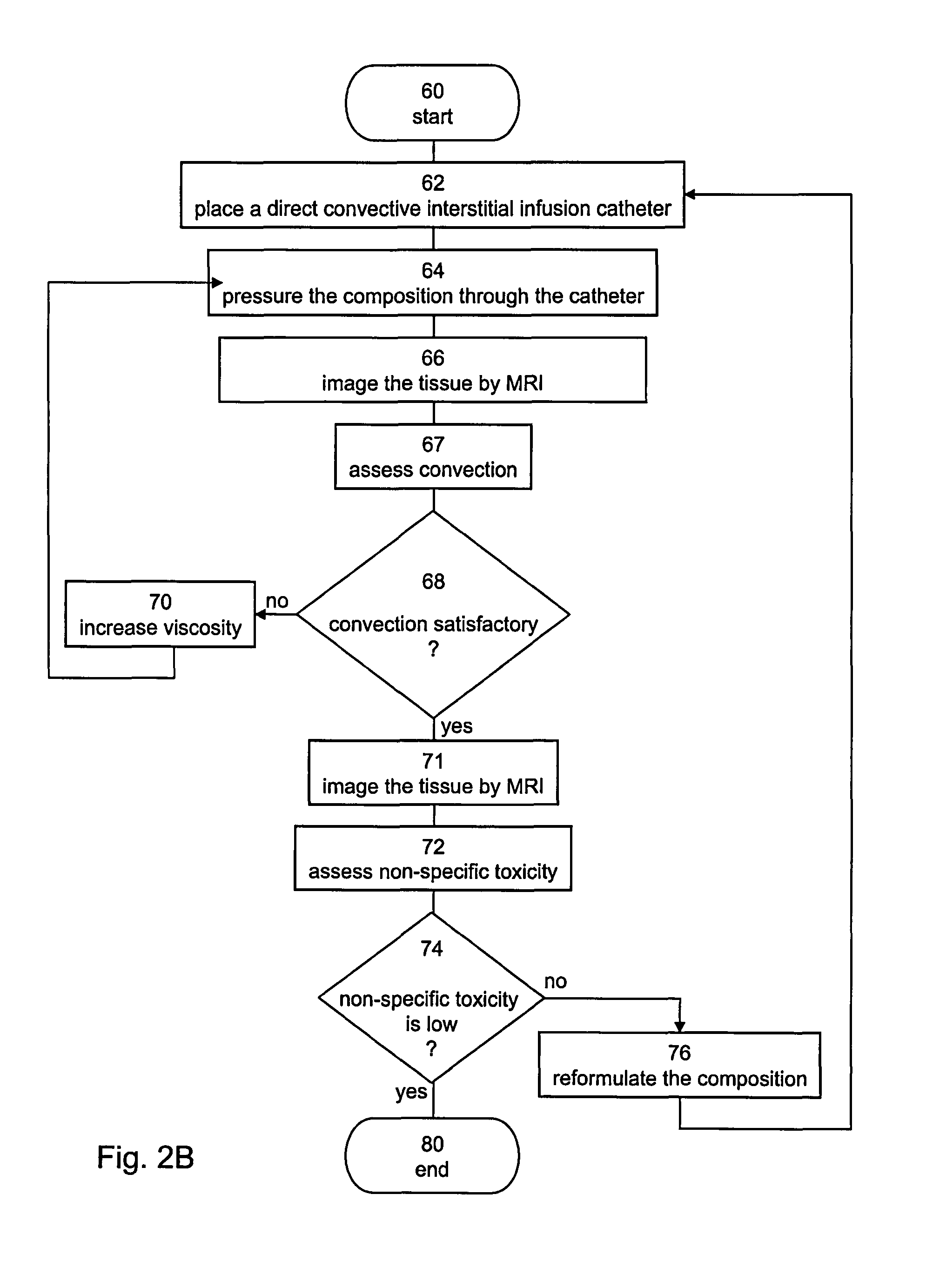
Method and composition suitable for administering by direct convective interstitial infusion are disclosed. The method comprises: placing at least one direct convective interstitial infusion catheter in contact with the tissue, and pressuring the composition through the catheter. The composition is in a liquefied form having a viscosity above a predetermined value. The predetermined value is selected so as to improve infusion of the compositions into interstitial volumes of the tissue, while minimizing backflow of the compositions along an outer wall of the catheter or leakage into low resistance paths. It is demonstrated that high viscosity results in higher treatment efficiency.
Owner:TEL HASHOMER MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & SERVICES LTD +1
Floating platform method and apparatus
ActiveUS20090173269A1Vessel movement reduction by wave dampingFloating buildingsFloating platformInterstitial volume
A floating platform is provided. The floating platform includes a top surface (14), a plurality of buoyancy members (12) interconnected to the top surface and extending downwardly into a body of water, a bottom plate (16) and a plurality of interstitial volumes (24) that are sealed at a bottom end by the bottom plate to prevent the flow of water into the interstitial volume.
Owner:FLOAT
Lithium secondary battery containing cathode materials having high energy density and organic/inorganic composite porous membrane
ActiveUS20130187082A1Increase energy densityExcellent capacity characteristicsPositive electrodesLi-accumulatorsPolyolefinHigh energy
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
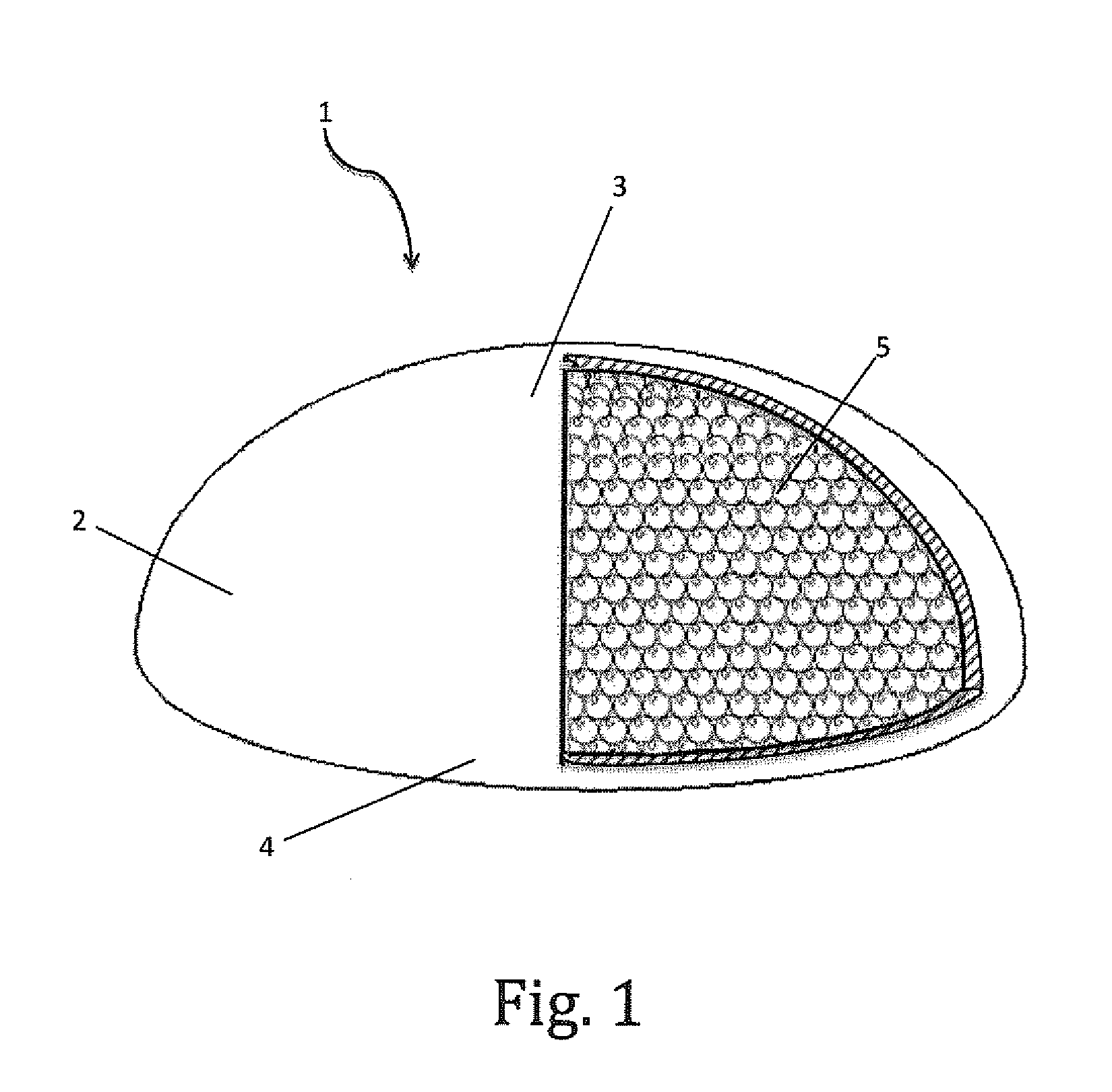
Mammary prosthesis filled with expanded polymer microspheres
A mammary prosthesis built from a sack of elastic material or biocompatible material having a sealed interior cavity with the sack having an anterior surface forming a dome and a posterior surface forming a base, with a sealed and seamless interior cavity filled with microspheres of foamed or expanded polymers or a combination of both. The sack may also be permeable to establish equilibrium between body fluids and interstitial volume of the microspheres.
Owner:SANABRIA SCHARF FREDDY +1
Apparatus and method for separation of molecules and movement of fluids
InactiveCN1482939ADispersed particle separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansInterstitial volumeElectrophoresis
An electrophoresis apparatus comprising: (a) a first electrode in a first electrode zone; (b) a second electrode in a second electrode zone, the first electrode disposed relative to the second electrode so as to be adapted to generate an electric field in an electric field area therebetween upon application of an electric potential between the first and second electrodes; (c) a first membrane disposed in the electric field area; (d) a second membrane disposed between the first electrode zone and the first membrane so as to define a first interstitial volume therebetween; wherein the first interstitial volume is separated from the first and second electrode zones by the first and second membranes, and wherein at least one membrane being a barrier capable of controlling substantial bulk movement of liquid under the influence of an electric field; (e) means adapted to communicate liquid to the first electrode zone and the second electrode zone; and (f) means adapted to communicate a sample constituent to the first interstitial volume; wherein, upon application of the electric potential, liquid is caused to move from the sample constituent through at least one membrane to an adjacent electrode zone and at least one membrane prevents substantial bulk movement of liquid into the sample.
Owner:GRADIPORE
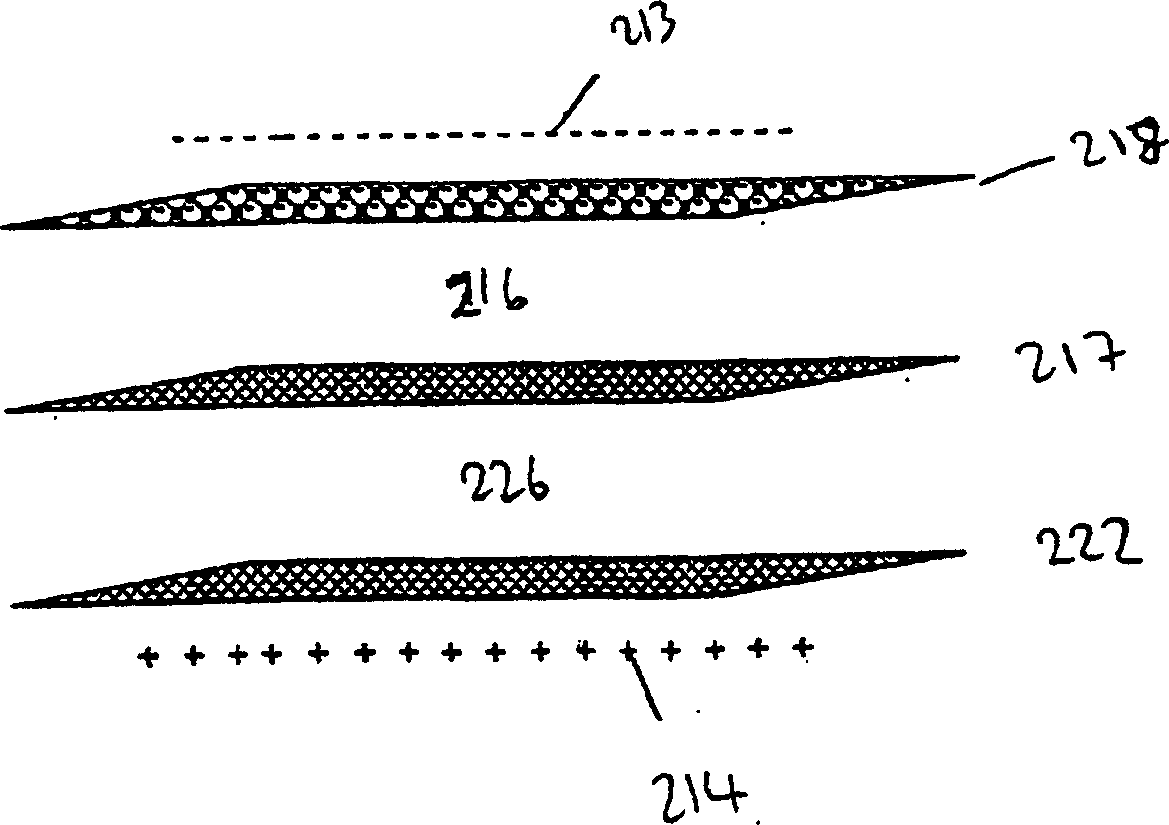
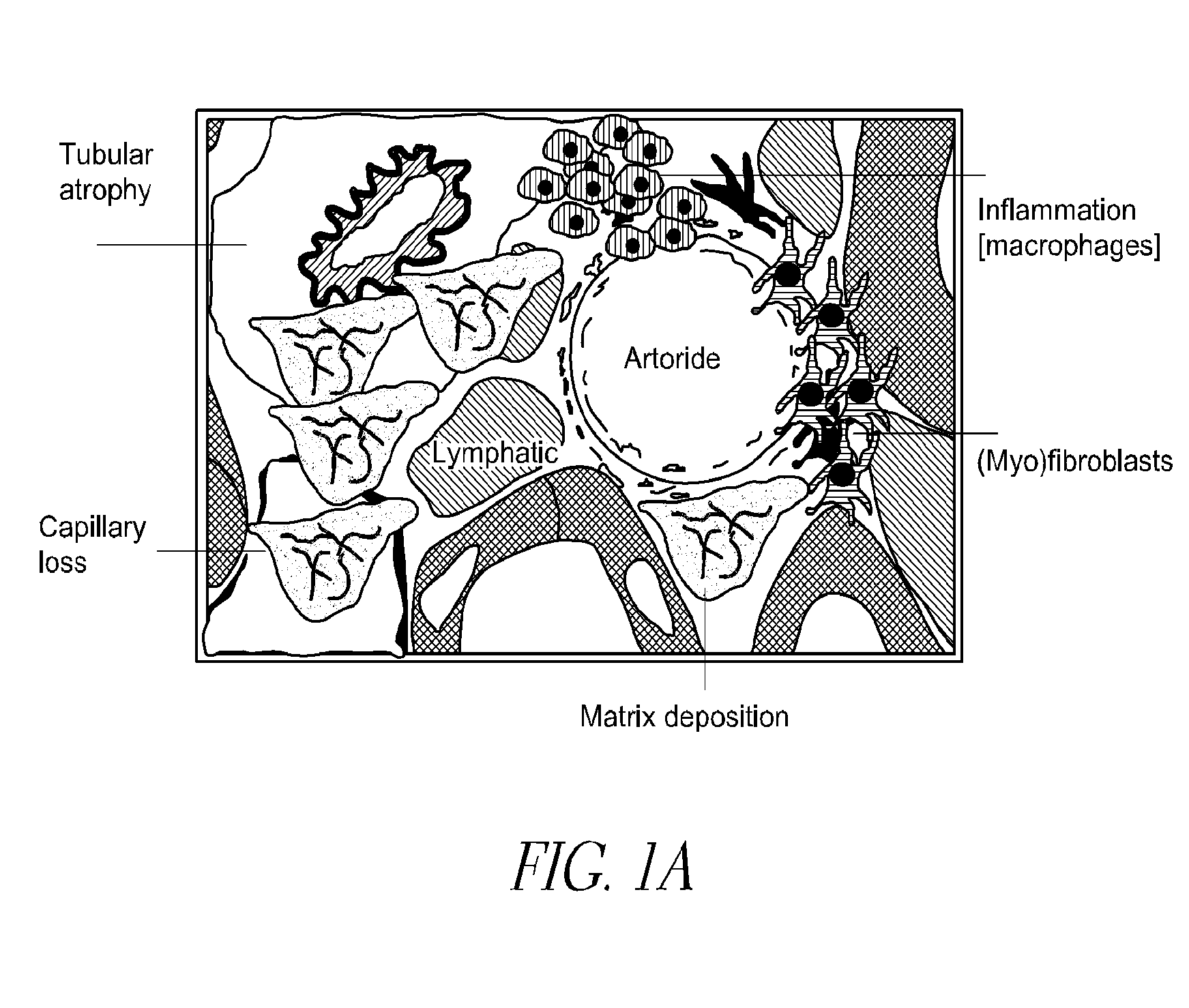
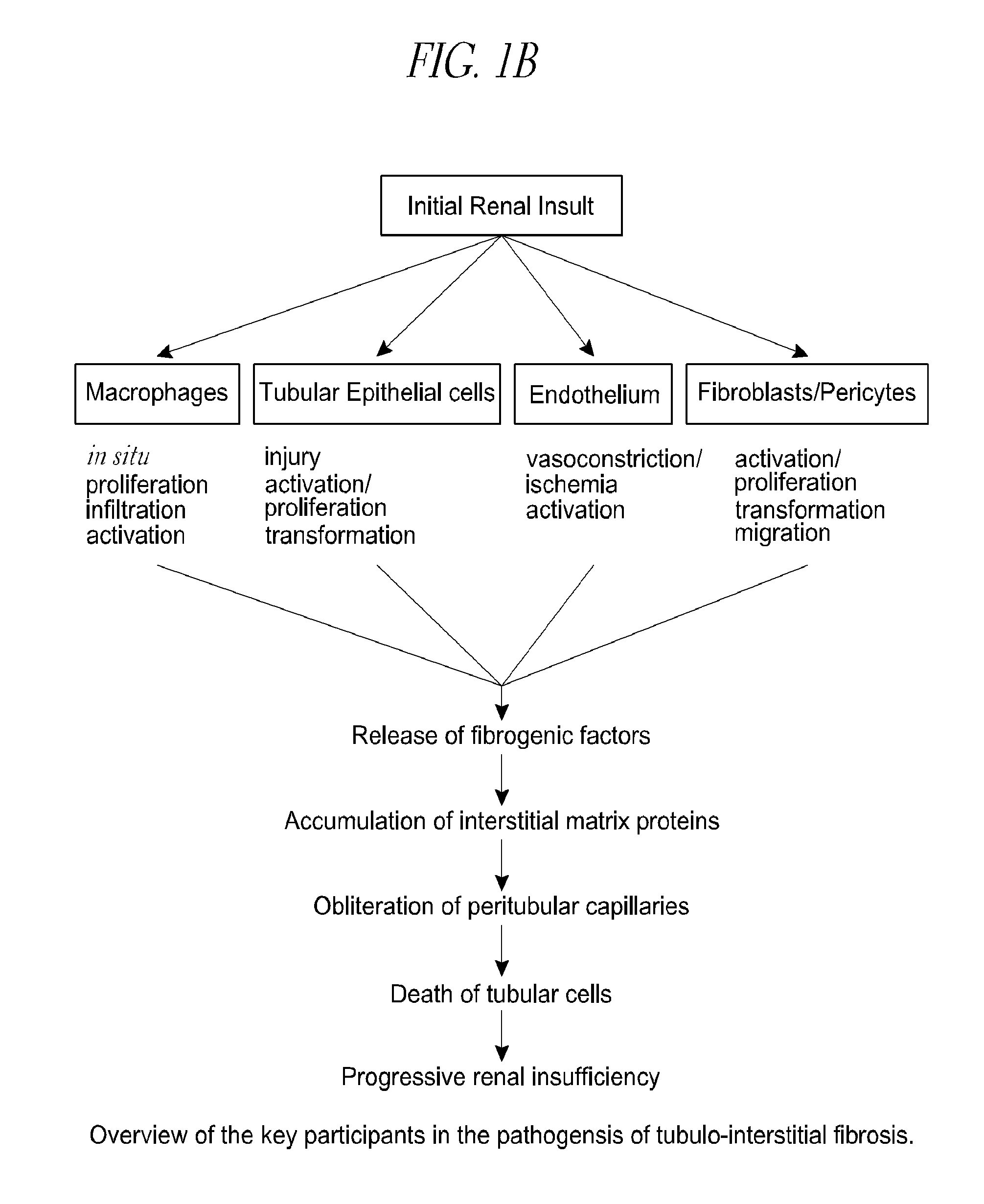
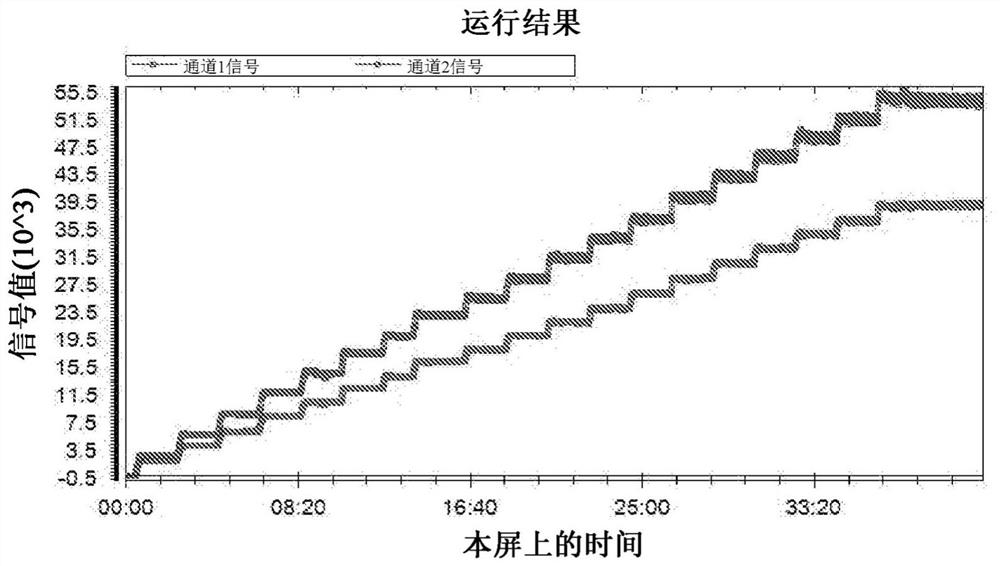
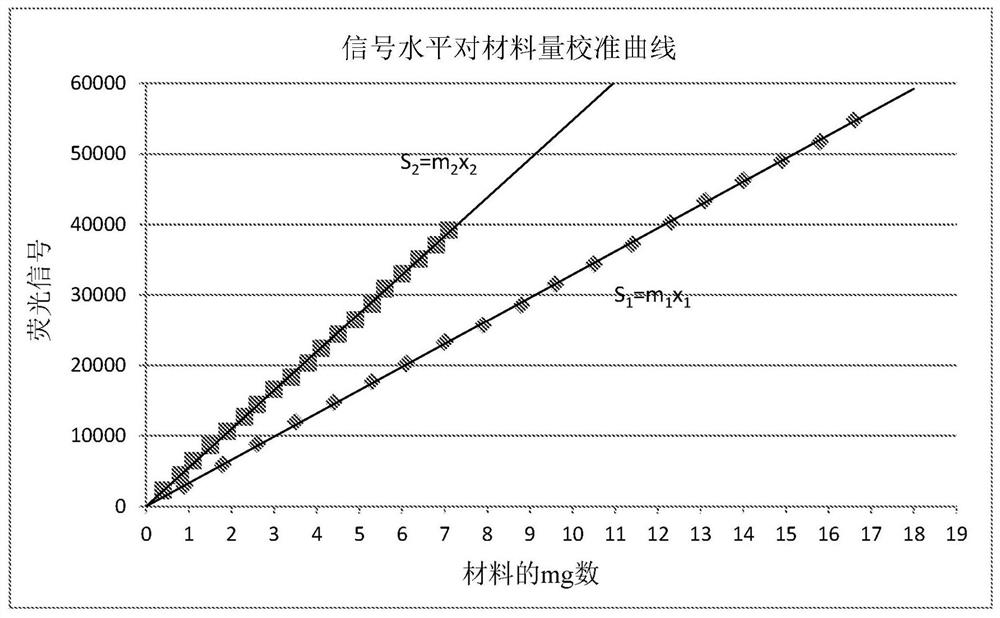
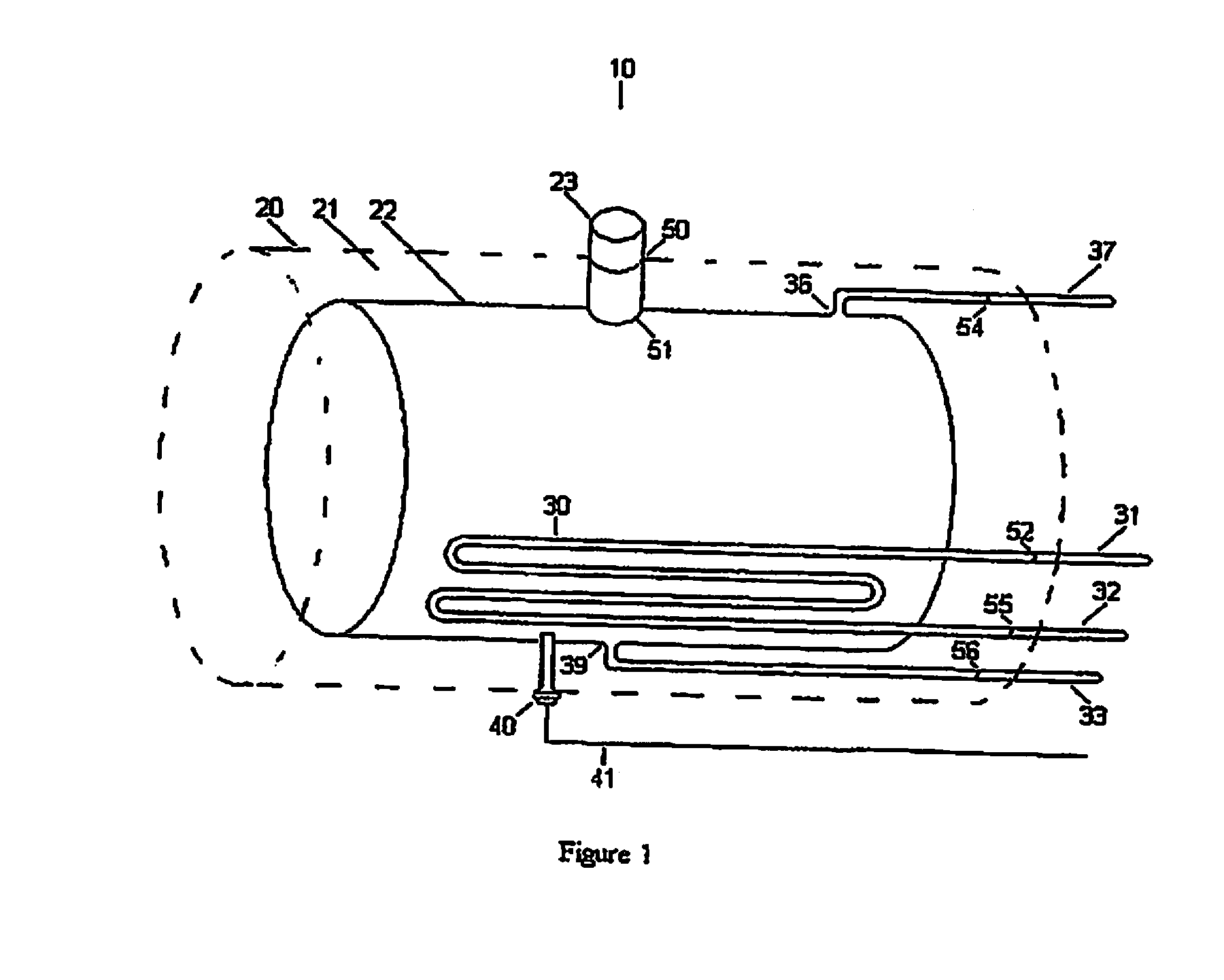
Method and apparatus for determining interstitial volume
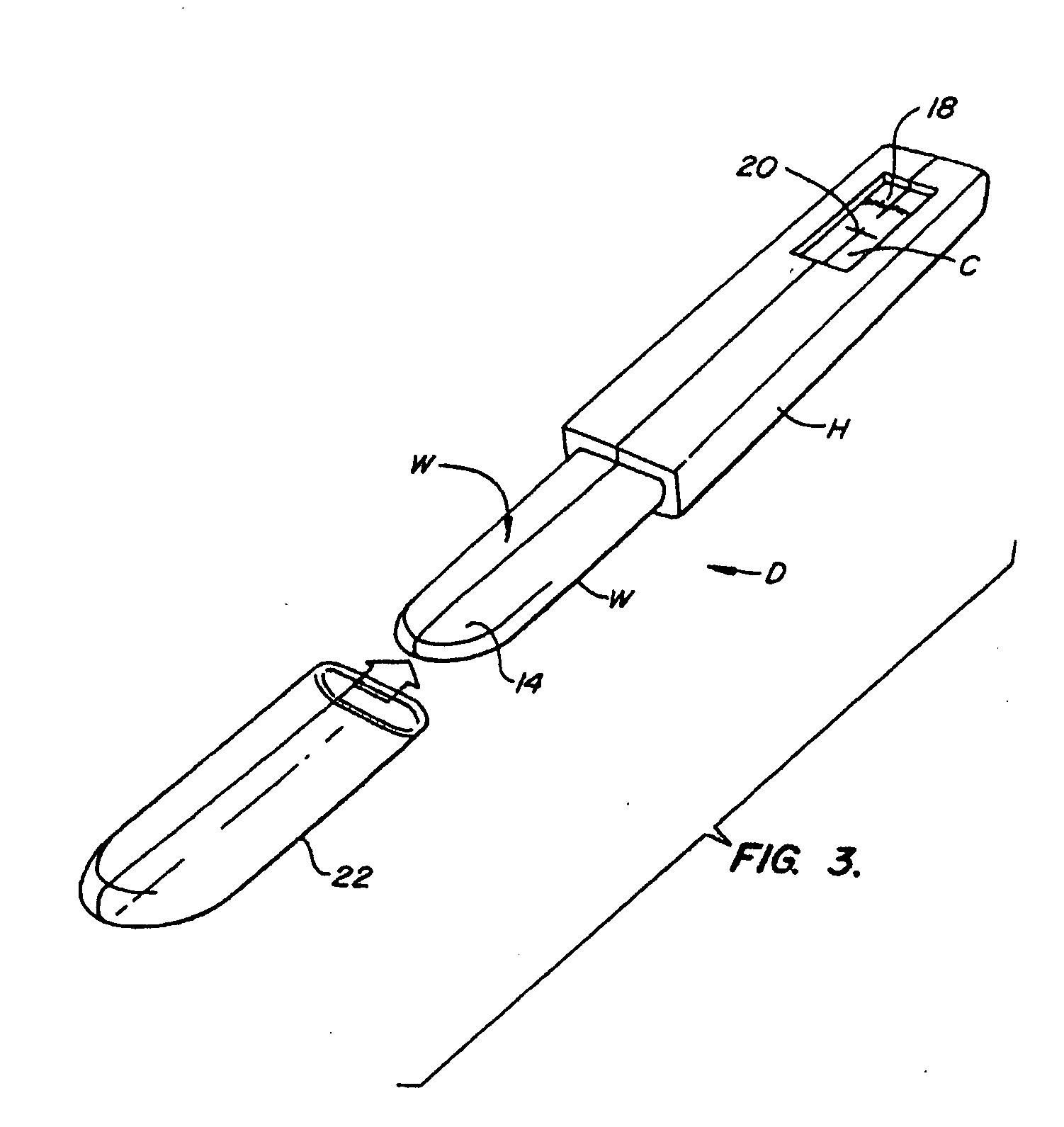
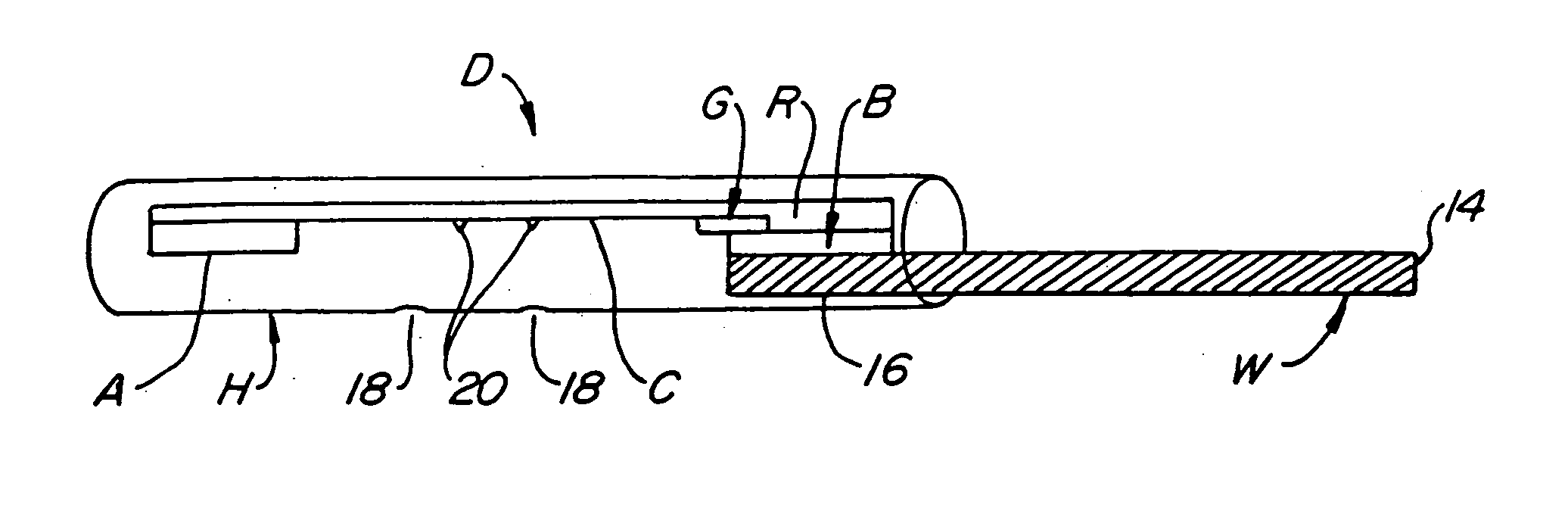
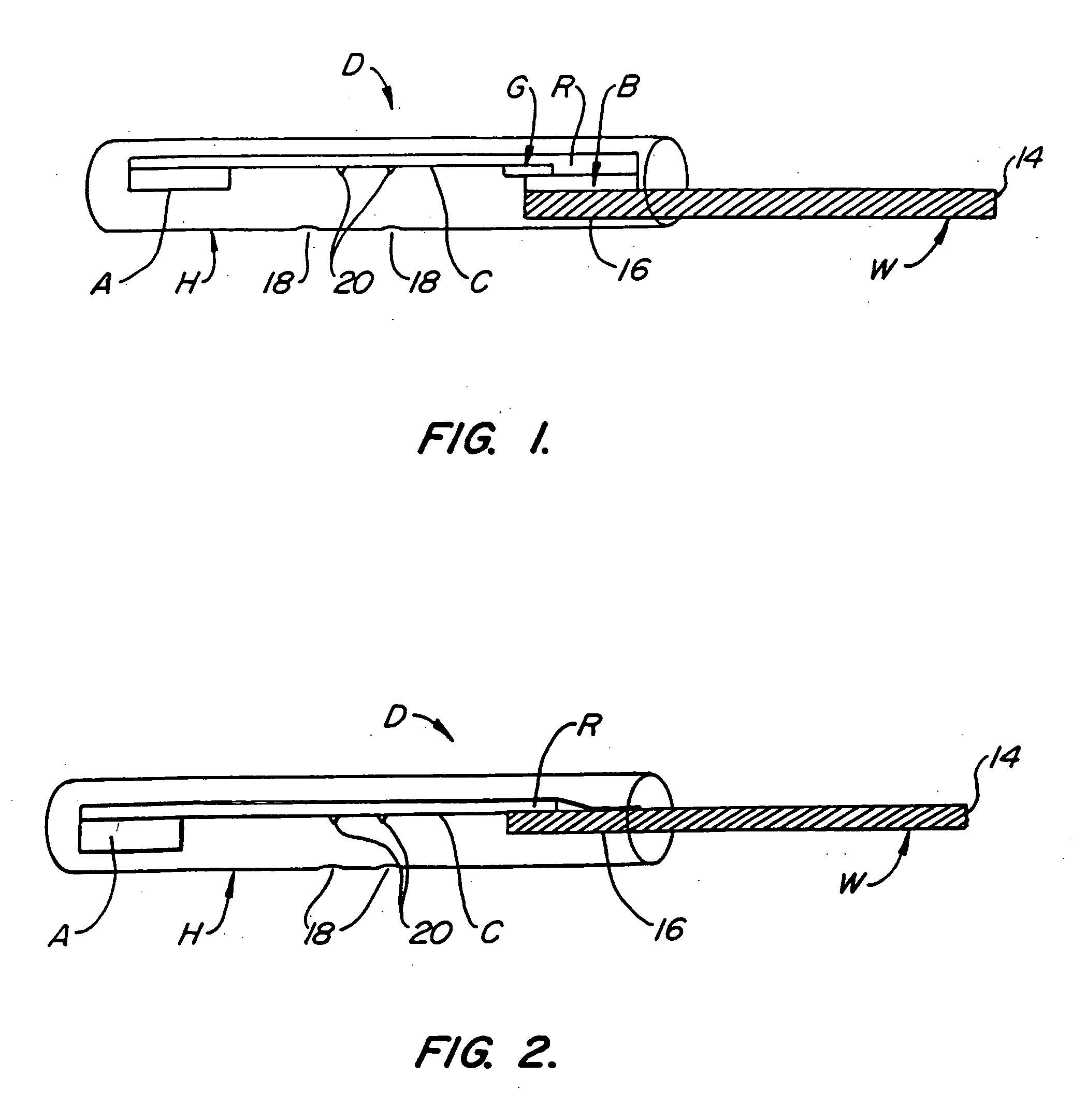
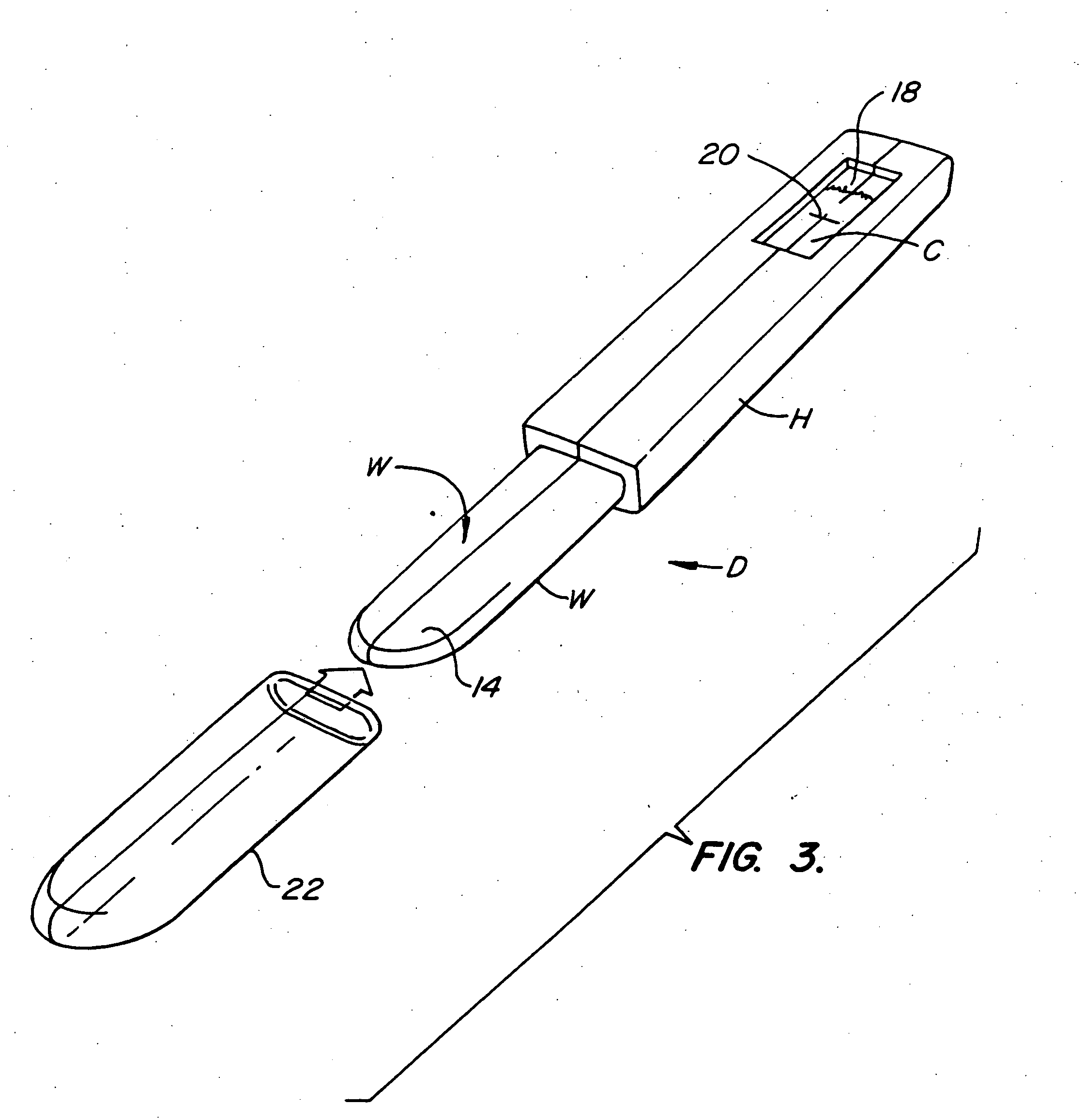
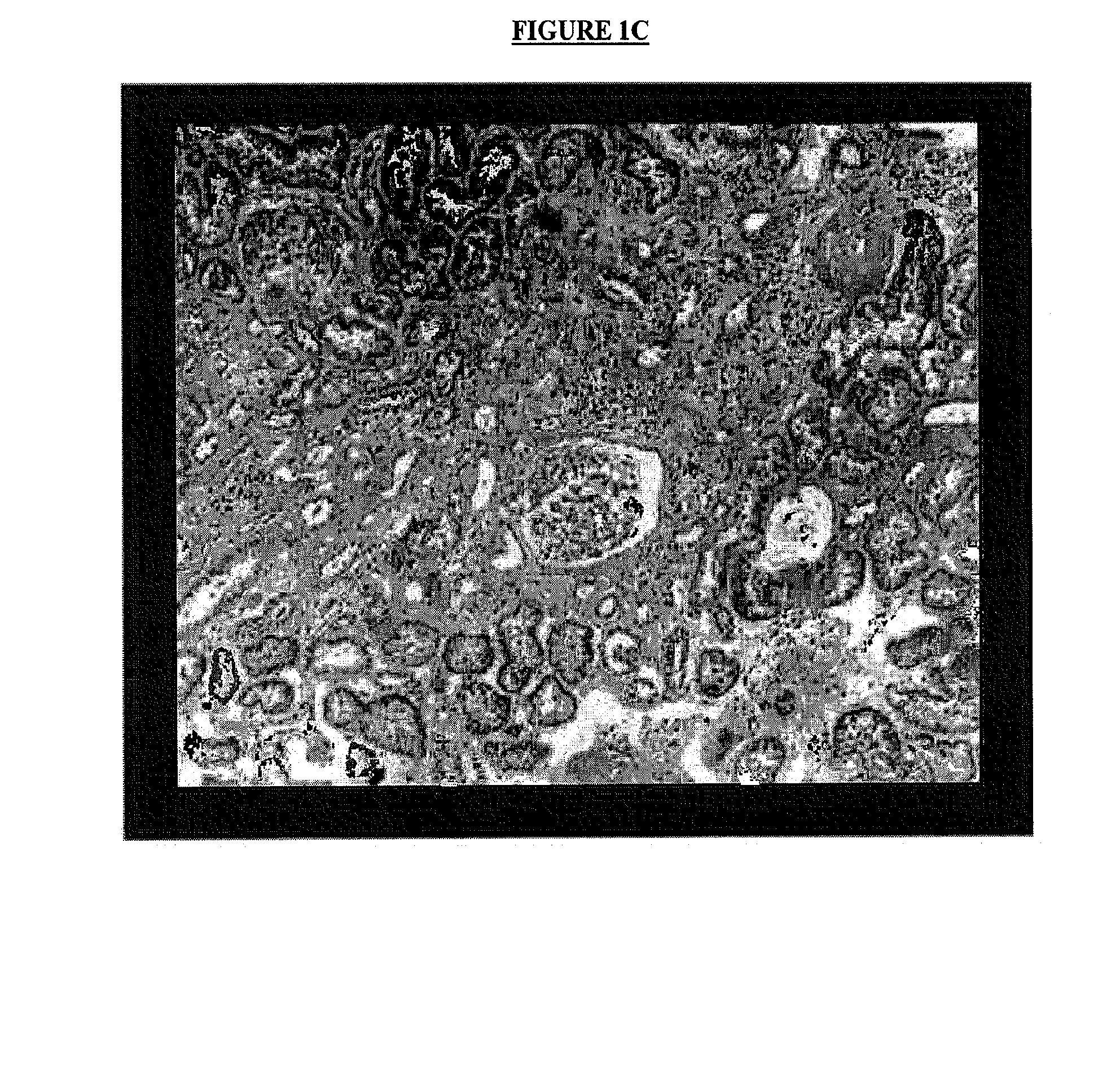
InactiveUS20200174018A1Medical automated diagnosisDianostics using fluorescence emissionRenal glomerulusBlood specimen
A method and system for selecting a treatment for a subject based on a value for the interstitial space volume of the subject utilizes plurality of sample data values representing concentrations of small and large markers in plurality of blood samples over time. The sample concentrations are utilized to predict a hypothetical peak concentration of the small marker prior to the dissipation of the markers during the test period. This hypothetical peak concentration and other sample values are utilized with either a bi-exponential or tri-exponential decay curve fitting algorithm to define a decay curve, the curve characteristics of which are then utilized to calculate values for glomerular filtration rate, a leakage rate of the small marker into interstitial space, and finally a value for the interstitial volume. The determined value for the interstitial volume can then be compared with number thresholds and decisions made for recommended therapy for the subject, if desired.
Owner:PHARMACOPHOTONICS INC
Cysteamine in the treatment of fibrotic disease
ActiveUS9468612B2Preventing interstitial fibrosisSkeletal disorderUrinary disorderCysteamineCollagen i
Fibrotic diseases are characterized by the replacement of healthy tissue with scar tissue and extracellular matrix in response to tissue damage. Here we describe the reduction of extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, interstitial fibroblasts, interstitial volume, expression of Collagen I mRNA and protein, expression of profibrotic cytokines and macrophage infiltration by Cysteamine treatment.
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL (DBA SEATTLE CHILDRENS RES INST)
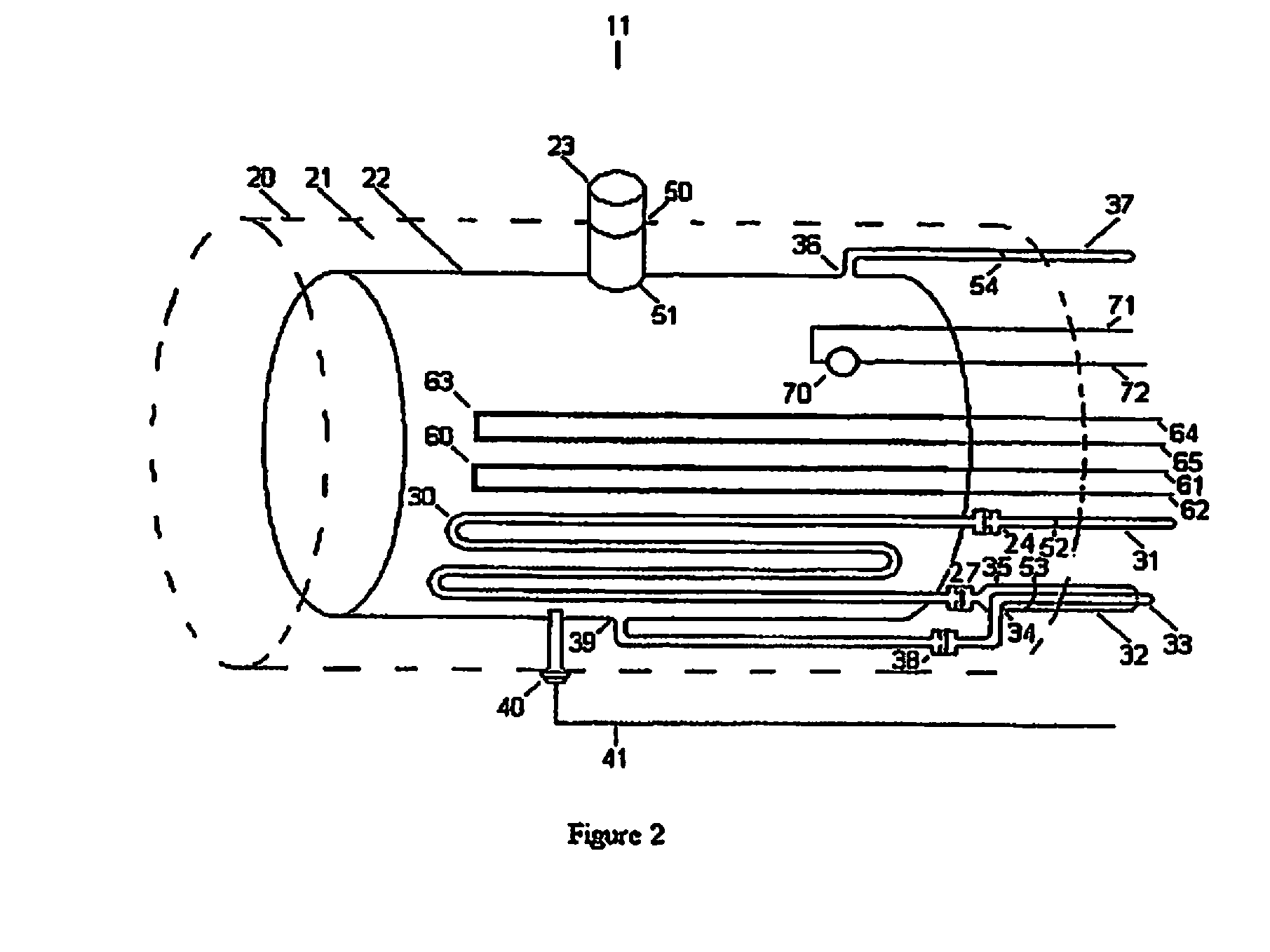
Method and apparatus for determining interstitial volume
PendingCN113164107AMedical automated diagnosisDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionRenal glomerulusBlood specimen
A method and system for selecting a treatment for a subject based on a value for the interstitial space volume of the subject utilizes plurality of sample data values representing concentrations of small and large markers in plurality of blood samples over time. The sample concentrations are utilized to predict a hypothetical peak concentration of the small marker prior to the dissipation of the markers during the test period. This hypothetical peak concentration and other sample values are utilized with either a bi-exponential or tri-exponential decay curve fitting algorithm to define a decay curve, the curve characteristics of which are then utilized to calculate values for glomerular filtration rate, a leakage rate of the small marker into interstitial space, and finally a value for the interstitial volume. The determined value for the interstitial volume can then be compared with number thresholds and decisions made for recommended therapy for the subject, if desired.
Owner:PHARMACOPHOTONICS INC
Preparation method of ultrahigh thermal conductivity, surface machinable diamond‑al composites
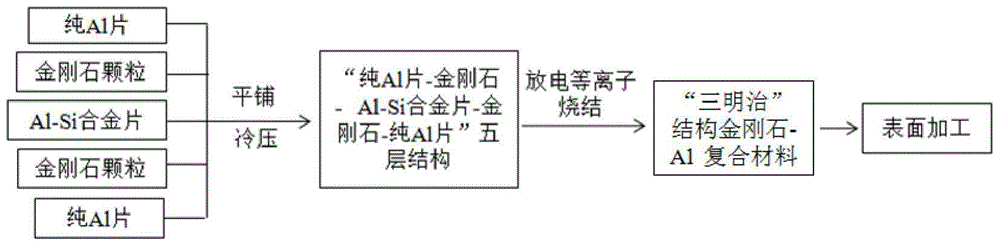
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing an ultrahigh-heat-conductive diamond-Al composite material with the surface capable of being machined. The method includes the specific steps that a second pure Al sheet, diamond particles, an Al-Si alloy sheet, diamond particles and a first pure Al sheet are sequentially placed in a graphite die from bottom to top, a stacking system is subjected to cold-pressing and then put in a discharging plasma sintering furnace (SPS) to be heated and pressurized, the Al-Si alloy sheet is melted and seeps into gaps among the diamond particles, and the diamond-Al composite material of a sandwich structure is obtained. The surface aluminum layer of the composite material is ground and mechanically polished or electrolytically polished, so that a flat and smooth surface is obtained. The surface is free of a coating; the interstitial volume of Al-Si alloy is slightly larger than that of the diamond particles; and the thickness of each pure Al sheet ranges from 2 mm to 3 mm. The method has the beneficial effects that the advantages of SPS and the fusion infiltration process are combined, the diamond-Al composite material with the ultrahigh heat conductance and with the surface capable of being machined can be efficiently manufactured, and the requirements for surface flatness and roughness of an electronic packaging material are met.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Alternate fuel storage system and method
ActiveUS20130025574A1Internal combustion piston enginesThermal treatment of fuelInterstitial volumeFuel tank
A fuel tank for storing an alternate fuel and providing the fuel to an internal combustion engine includes: an inner shell with an internal cavity designed to store fuel; an outer shell configured and positioned relative to the inner shell such that an interstitial volume is created between the inner and outer shells; and a heating unit positioned in the interstitial volume. In some embodiments, the interstitial volume is filled with air; in other embodiments, the interstitial volume is filled with a thermally insulative material.
Owner:GILBARCO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com