Method and apparatus for determining interstitial volume
A volume and gap technology, applied in the field of diagnostic tools for the treatment of diseases, can solve problems such as difficult dry weight of patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0122] Example 1: Method for generating a calibration curve
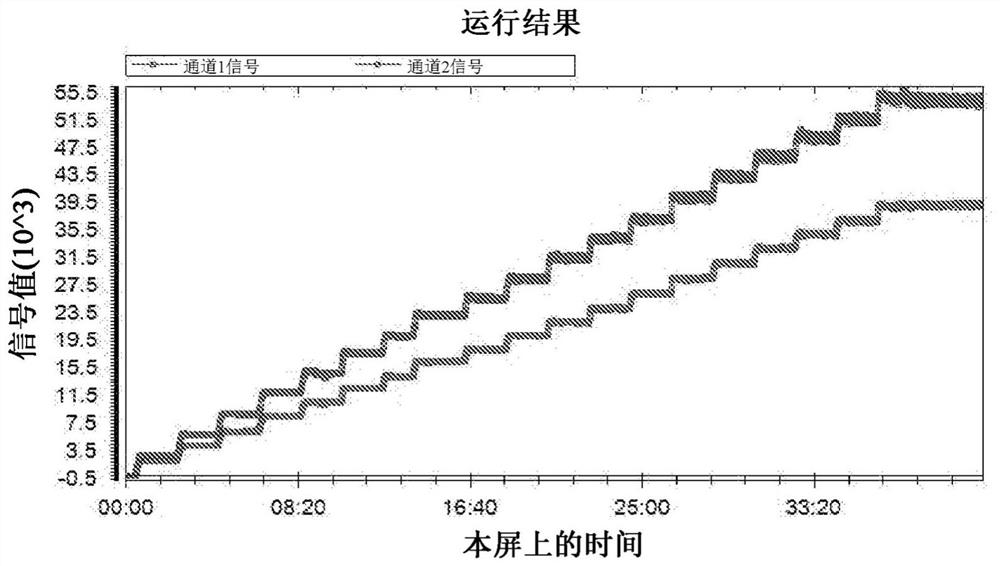
[0123] 1. Run a stepwise dose blood test set on a whole blood sample containing two fluorescent markers, each with its different emission wavelength. An example of the result is in figure 1 , where the upper curve represents the first emission signal from the first fluorescent marker or label recorded in channel 1 as the channel 1 signal and the second emission signal from the second fluorescent marker or label recorded in channel 2. The transmit signal is represented as a channel 2 signal. As previously discussed, the step-dose blood test set can also be generated using one static marker with two fluorescent labels, each with its different emission wavelength. Hereinafter, each fluorescent marker or each fluorescent label may be referred to as a "fluorescent component".
[0124] 2. Calculate the average signal level of the "flat" or stable fraction of each dose step for each fluorescent component.
[0125] 3. B...
example 2
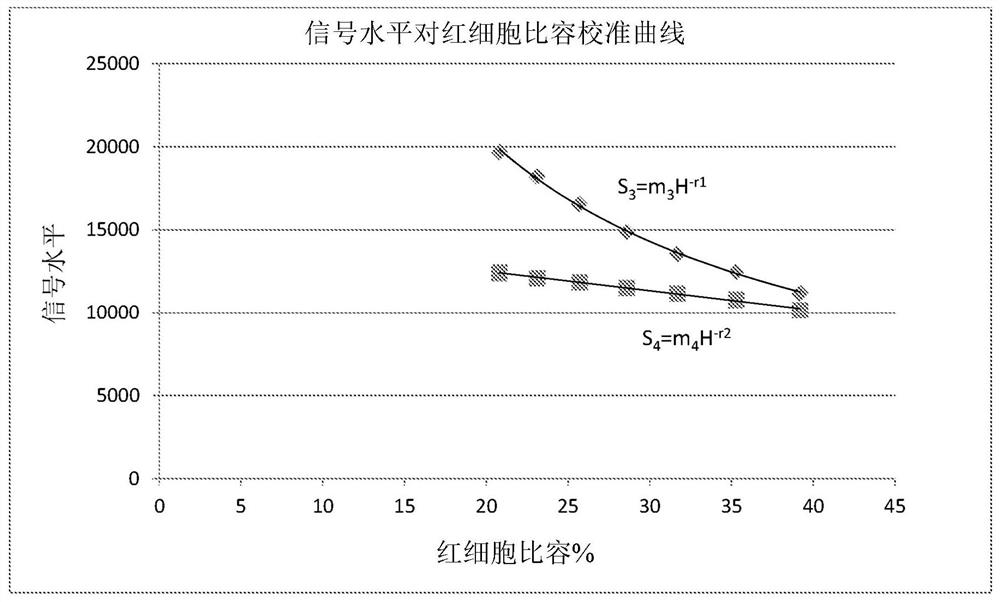
[0131] Example 2: Method for generating a species-specific hematocrit (HCT) calibration curve
[0132] 1. Run a blood test with the single-dose method. Using the known blood volume (V t ) and known blood HCT (H calib ), calculate the volume of saline required for the test (V S ).
[0133] V t –V t h calib =V S (4)
[0134] 2. Blood and saline are administered in equal amounts from the same VFI vial.
[0135] 3. Remove a predetermined volume of blood from the test set and discard. The same volume of dosing saline as the previously removed blood was injected back into the test set. This swap will maintain the concentration of each component as well as the total volume of the test set, but change the ratio of distribution volume to HCT. Repeat this step multiple times to generate multiple data points at which the volume of distribution and HCT ratio vary.
[0136] 4. Allow each new point to stabilize before generating a new point. A new HCT is calculated at each sta...
example 3
[0150] Example 3: Methods for determining various biometric indicators
[0151] When running the test on a subject, the "batch" of the VFI must be known, since the signal calibration and HCT calibration curves used for interpretation must be based on the same "batch" of VFI given to the subject.
[0152] 1. From Figure 5 The test data sample extraction T 0 The raw ratio at (R T0 ) and average stable component 2 (FD003) signal level (S avg ). Figure 5 The lower curve in the figure represents the channel 1 signal, while the upper curve represents the channel 2 signal.
[0153] 2. Use T 0 The raw ratio at (R T0 ), the subject's apparent HCT was calculated from the ratio versus HCT calibration curve.
[0154] R T0 =KH -q (10)
[0155] H=H app (11)
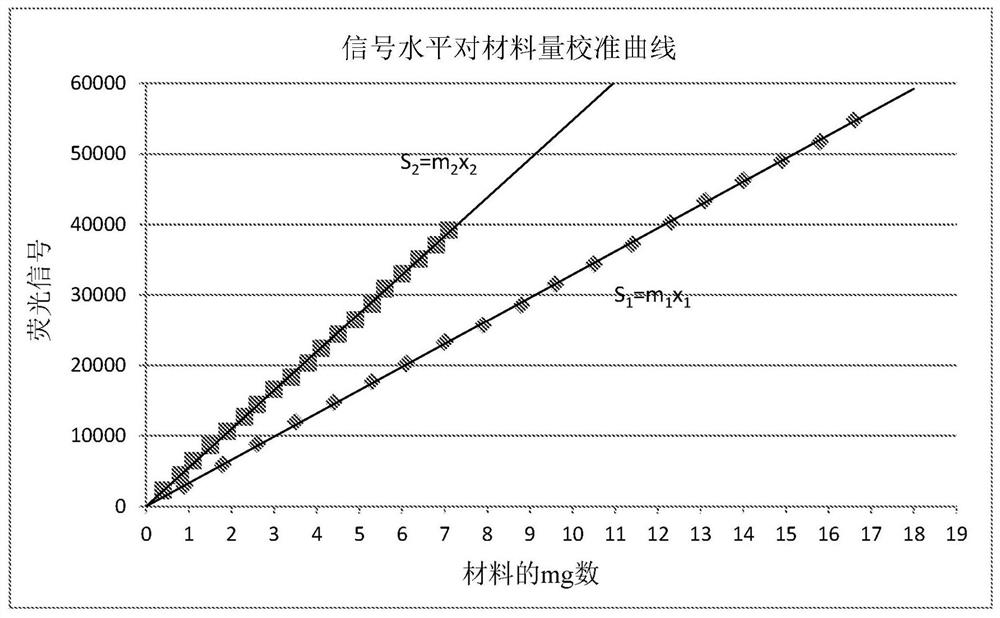
[0156] 3. Using the calculated apparent HCT and signal level versus material amount calibration curve; calculate the correction amount C and apply it to the mean signal level components.
[0157] According to Equation ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com