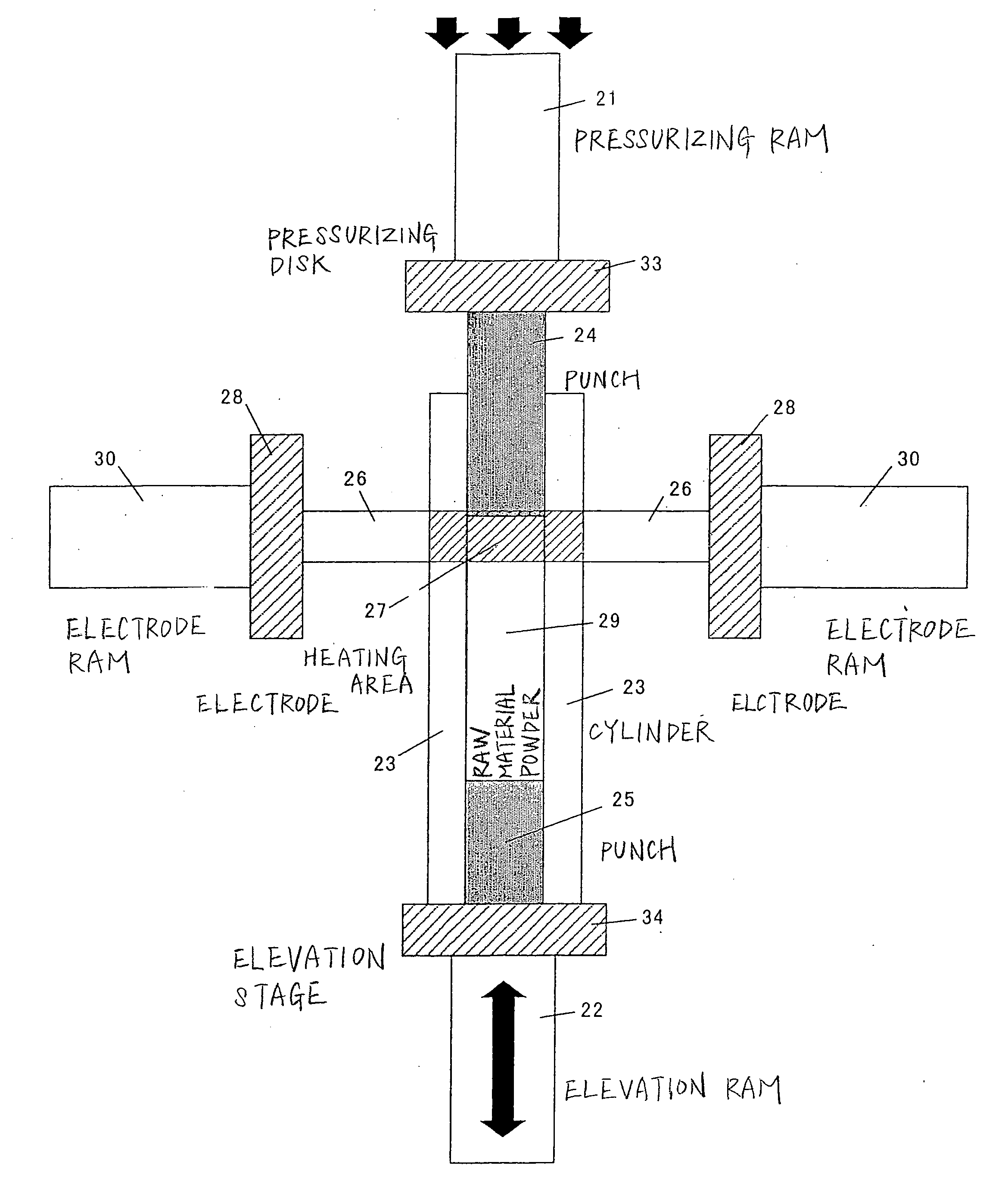
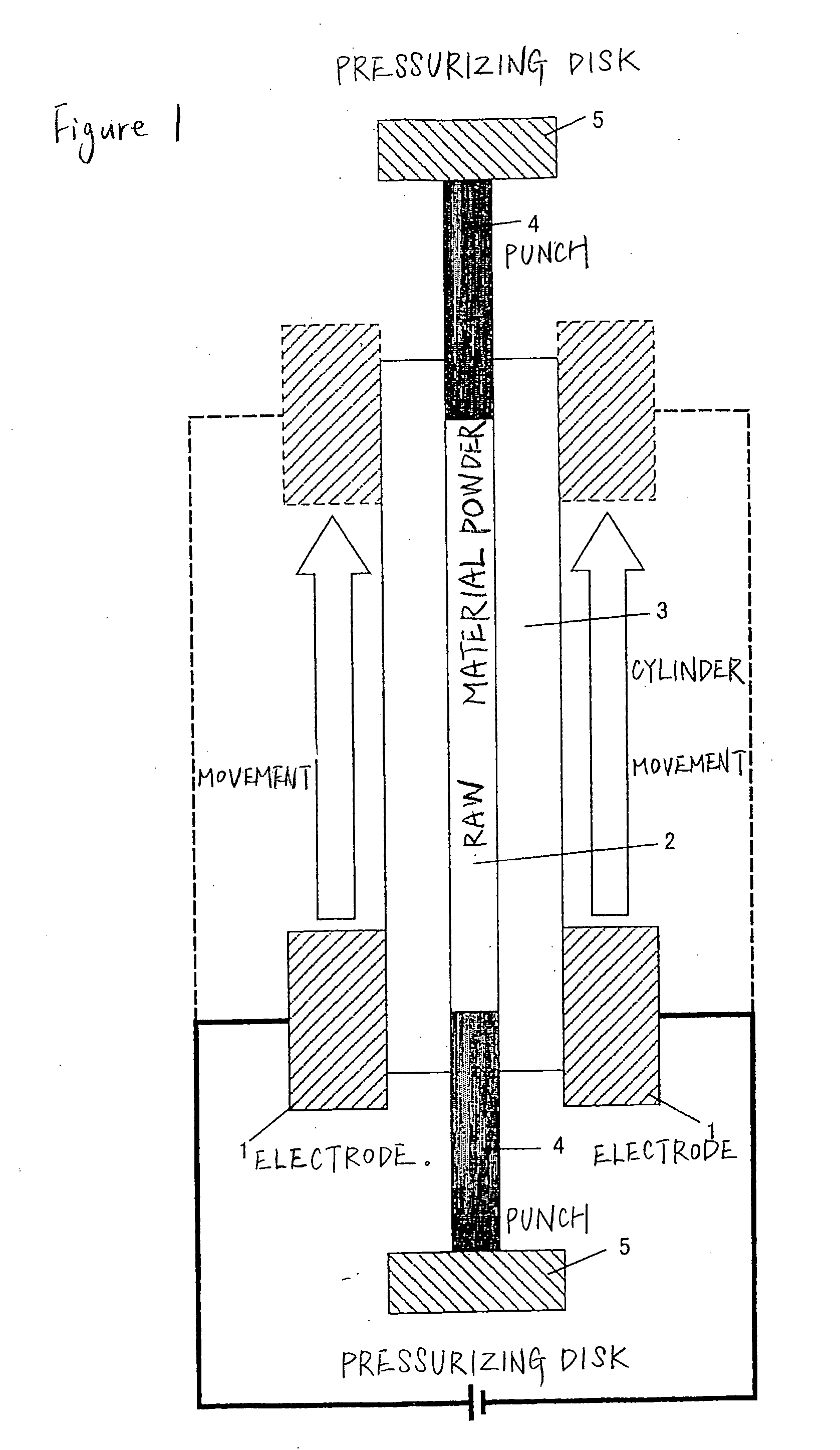
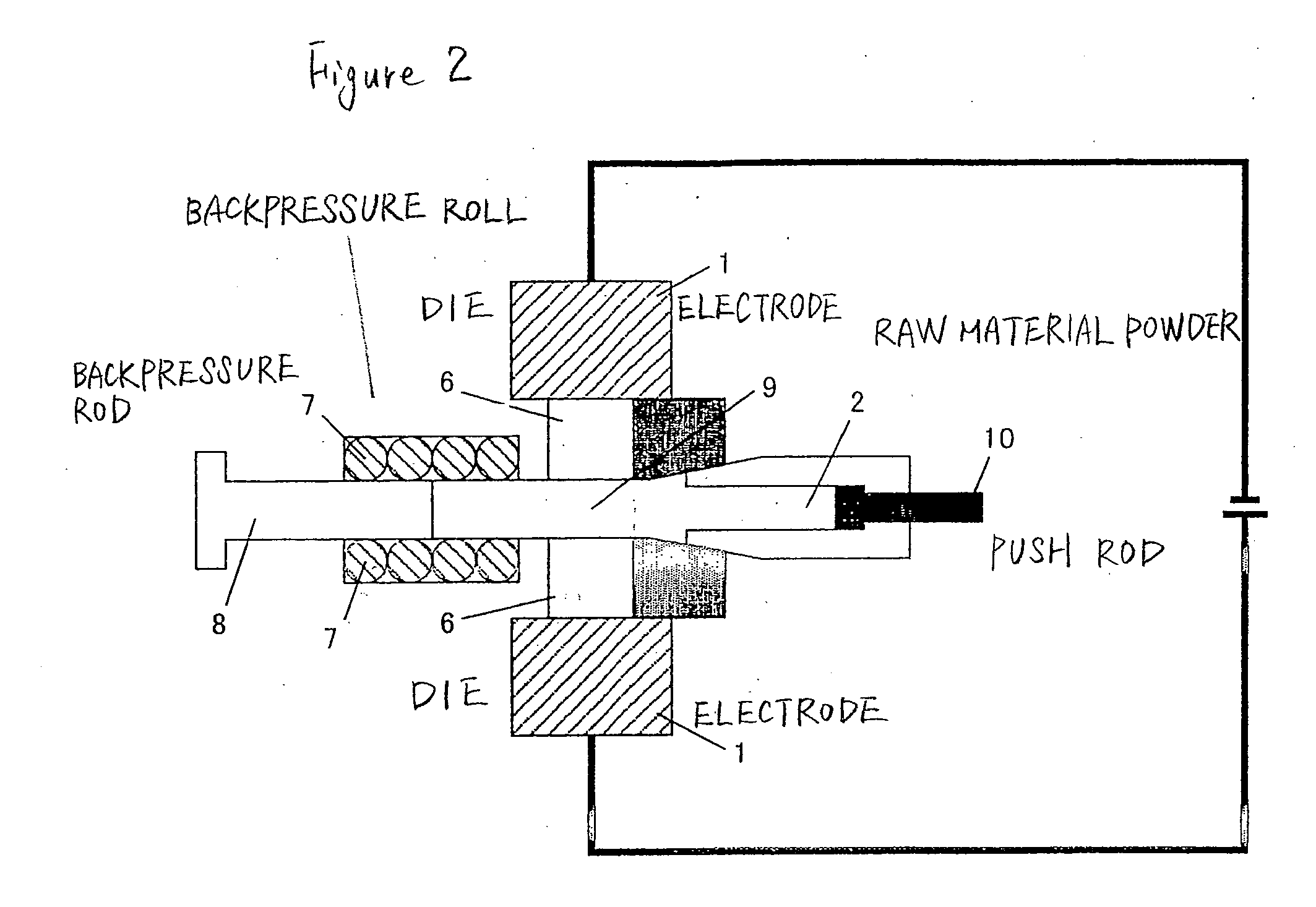
Sintering method and device
a sintering method and a technology for a material are applied in the field of sintering methods and devices, which can solve the problems of inability to obtain a sintered body, change in heating value, and difficulty in sintering the overall material at an even temperature, and achieve the effect of superior sintering ability and uniform quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0059] As shown in FIG. 4, a graphite electrode connection terminal assembly 11 having a thickness of t=10.0 mm was mounted to a mold filled with aluminum as the raw material powder, and the temperature distribution in relation to the distance from the connection terminal assembly 11 upon energization thereof was measured.
[0060] Results of the temperature distribution measured in Example 1 are shown in FIG. 5. It is evident that the temperature becomes lower as the distance from the electrode connection terminal assembly 11 becomes longer. From these results, it is clear that the present invention is able to heat only an arbitrary, limited area up to the sintering temperature.
[0061] Even when the cross section shape (electrical resistance) in the sintering subject material changes, so as long as the heating area is made smaller, the absolute value of the difference of the heating value at the respective positions pursuant to the change in shape will be small. Therefore, if the thi...
example 2
[0063] As shown in FIG. 6, 3.82 g of aluminum having an average grain size of 20 μm was filled in a graphite cylinder mold having an outer diameter of φ30 mm, inner diameter of φ15 mm, and length of L=160 mm, and this is pressed from the top and bottom with a graphite punch having a length of 80 mm.
[0064] A graphite electrode connection terminal assembly (perforated square plate) 11 having a φ30 mm hole in the center and in which the length of one side thereof is 70 mm and the thickness is t=10.0 to 13.2 mm was fitted so as to be attached to the side wall of the cylinder. FIG. 7 shows the cross section of the heating portion in which the thermocouple 12 exists.
[0065] Here, the material of the electrode connection terminal assembly (perforated square plate) 11 used is the same as the material of the cylinder. As a result, the current will flow to the cylinder, and the raw material powder will be heated with energization when the electrical resistance of the raw material powder in t...
example 3
[0074] As shown in FIG. 10, in accordance with the sintering method depicted in Example 2, 9.54 g of aluminum was filled, and a graphite terminal assembly was successively moved from position 1 to position 3 while sintering was effected to the respective positions via current heating.
[0075] Upon examining the density of the aluminum sintered product obtained in Example 3, the relative density showed a value of 99% or more. If the distance to be moved is made longer, the manufacture of an even longer product is possible. Thus, it is evident that a rod-shaped sintered product superior in density can be manufactured with this method.
[0076] Next, as an example of sintering a material having an uneven cross section while setting the heating area, when considering sintering a stepped component as illustrated in FIG. 11, this case shows the sintering of a stepped sintered product formed from a portion having a large diameter and a portion having a small diameter. Foremost, when sintering...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com