Apparatus and method for defect inspection
a technology of defect inspection and apparatus, applied in the field of defect inspection apparatus and method, can solve the problems of limiting the enhancement of resolving power, unable to improve the spatial frequency itself for the resolution limit, and the defect to be inspected is becoming more and more microscopic. , to achieve the effect of high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
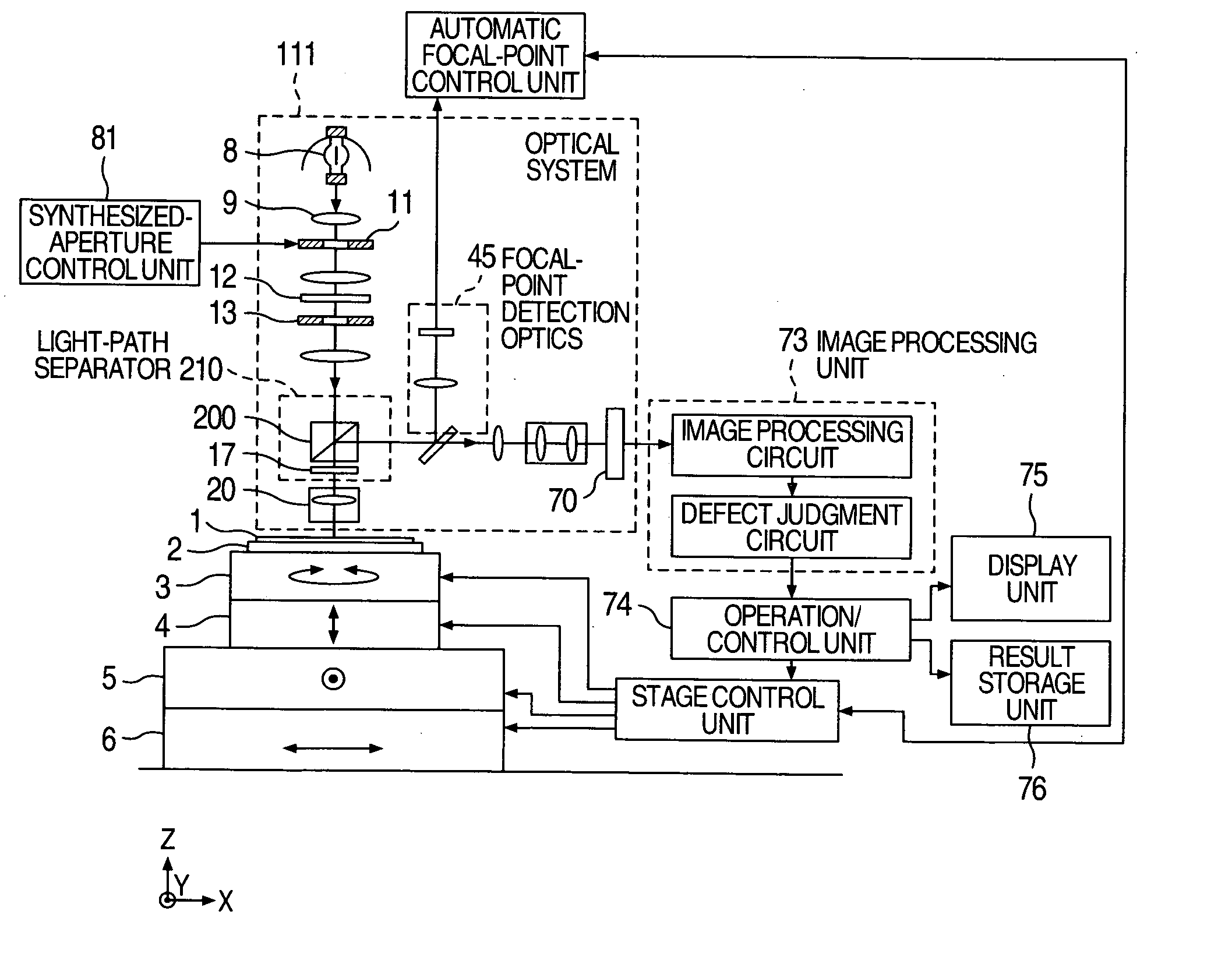
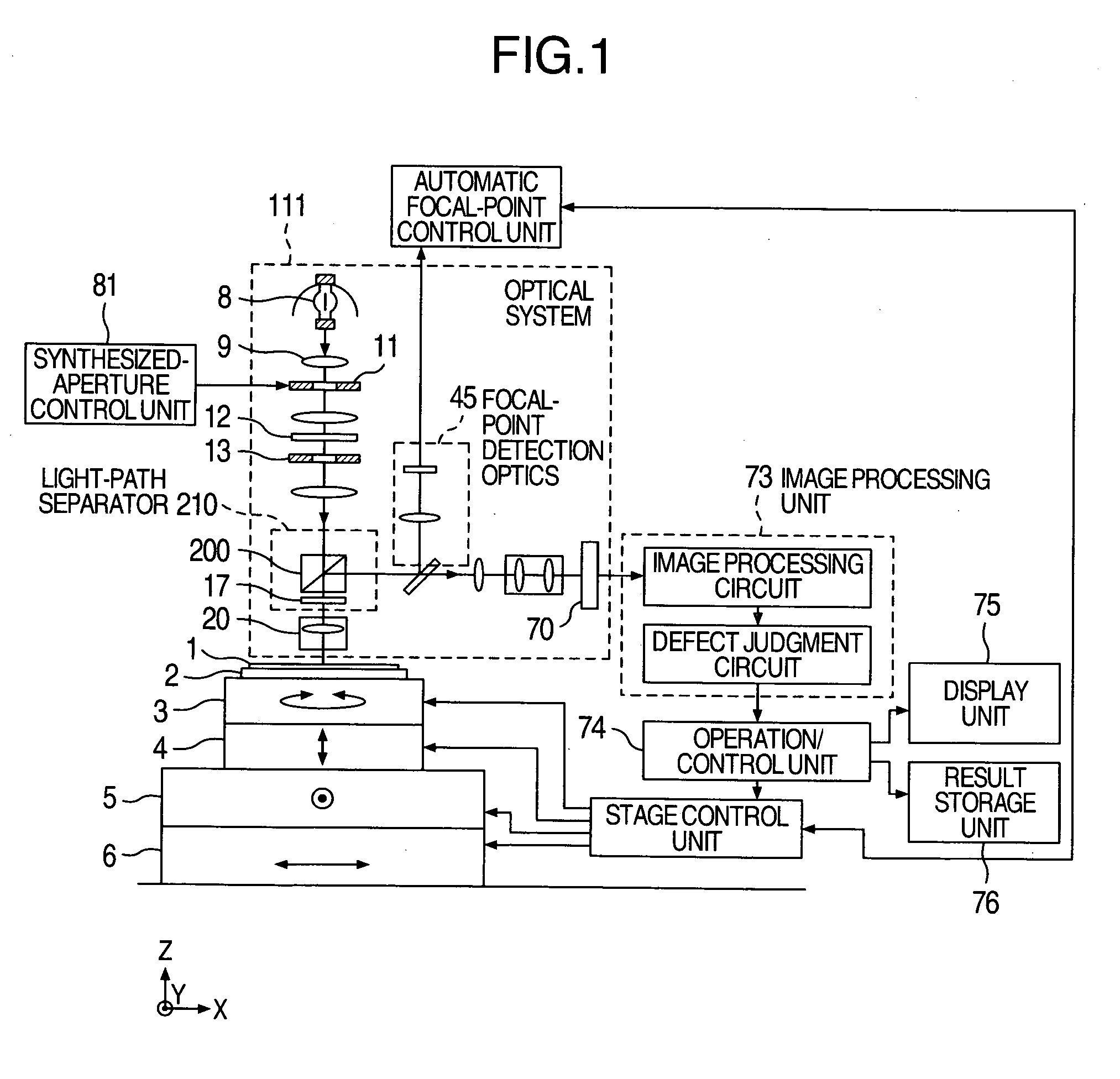
[0029]FIG. 1 illustrates an embodiment of the optical defect inspection apparatus using a microscopic-defect detection method according to the present invention. A semiconductor wafer 1, which is an inspection-target object, adheres to a wafer chuck 2 through vacuum absorption. This wafer chuck 2 is mounted on a O stage 3, a Z stage 4, a Y stage 5, and an X stage 6. An optics 111 located above the semiconductor wafer 1 photographs an optical image of the semiconductor wafer 1 in order to perform defect inspection of patterns formed on the semiconductor wafer 1. The optics 111 mainly includes an illumination optics, an image-formation optics for creating and imaging the image of the semiconductor wafer 1, and a focal-point detection optics 45. A light-source 8 located in the illumination optics is an incoherent light-source, which is, e.g., a xenon lamp.
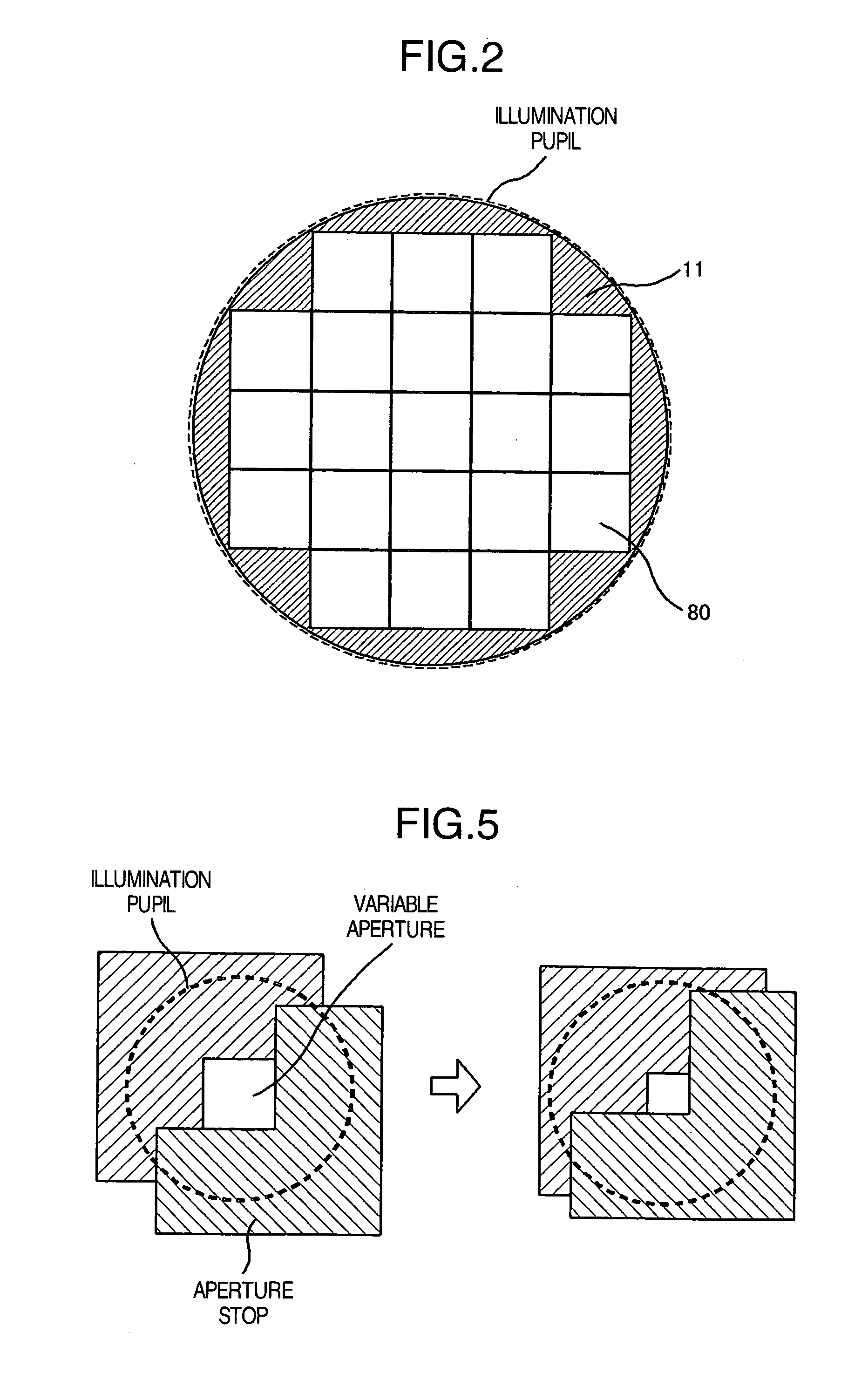
[0030] Light emitted from the light-source 8 passes through an aperture portion of an aperture stop 11 located on an illumination p...
embodiment 2
[0046] Next, FIG. 6 illustrates another embodiment of the optical defect inspection apparatus using the microscopic-defect detection method according to the present invention. Except the configurations of the light-source and the illumination optics, the other configurations are in common with the first embodiment illustrated in FIG. 1. Accordingly, the explanation about the other configurations will be omitted. In the present embodiment, the light-source 8 located in the illumination optics is a laser light-source.
[0047] Light emitted from the light-source 8 is shaped by a beam shaper 85 in its beam cross-section configuration. Even after the shaping, cross-section area of the laser beam is smaller than the illumination pupil. This laser beam performs incidence into a light-flux fluctuation system 86. Based on an instruction from a deflection control unit 87, the light-flux fluctuation system 86 is capable of deflecting the laser beam so that the laser beam will pass through an ar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| defect inspection | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com