Forming display color image
a color image and display technology, applied in the field of color images, can solve the problems of loss of overall display efficiency, not all of the light of undesired polarization is recycled, and not all of the recycled light exits, so as to enhance the color gamut of the display, greatly increase the display brightness, and enhance the viewing brightness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] In order to facilitate reading of the specification, the following terms are defined. Optic axis herein refers to the direction in which propagating light does not see birefringence. Polarizer and analyzer herein refer to elements that polarize electromagnetic waves. However, the one closer to the source of the light will be called a polarizer although the one closer to the viewer will be called an analyzer. Polarizing elements herein refers to both the polarizer and analyzer. Azimuthal angle φ and tilt angle θ are herein used to specify the direction of an optic axis. For the transmission axes of the polarizer and the analyzer, only the azimuthal angle φ is used, as their tilt angle θ is zero.
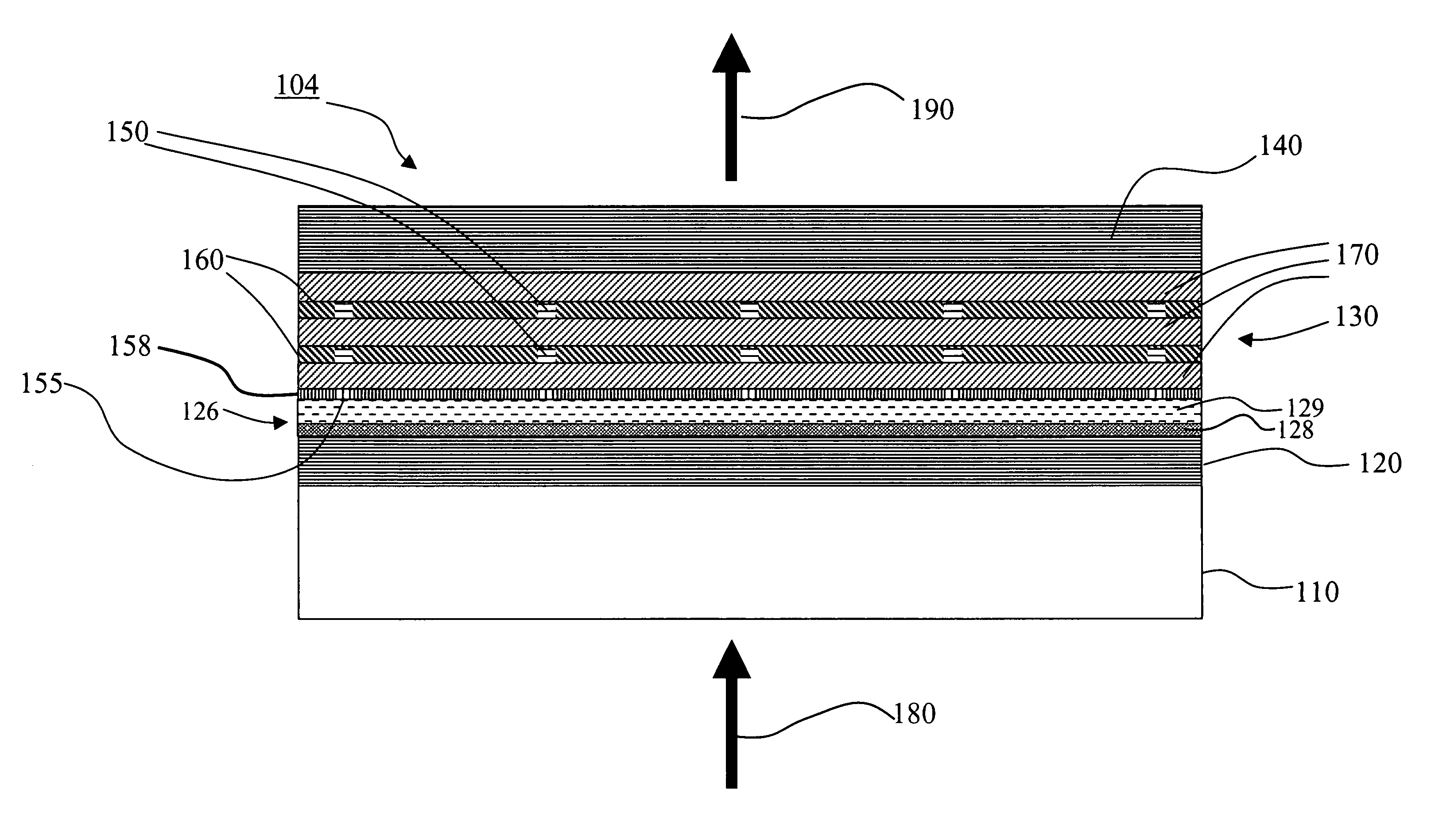
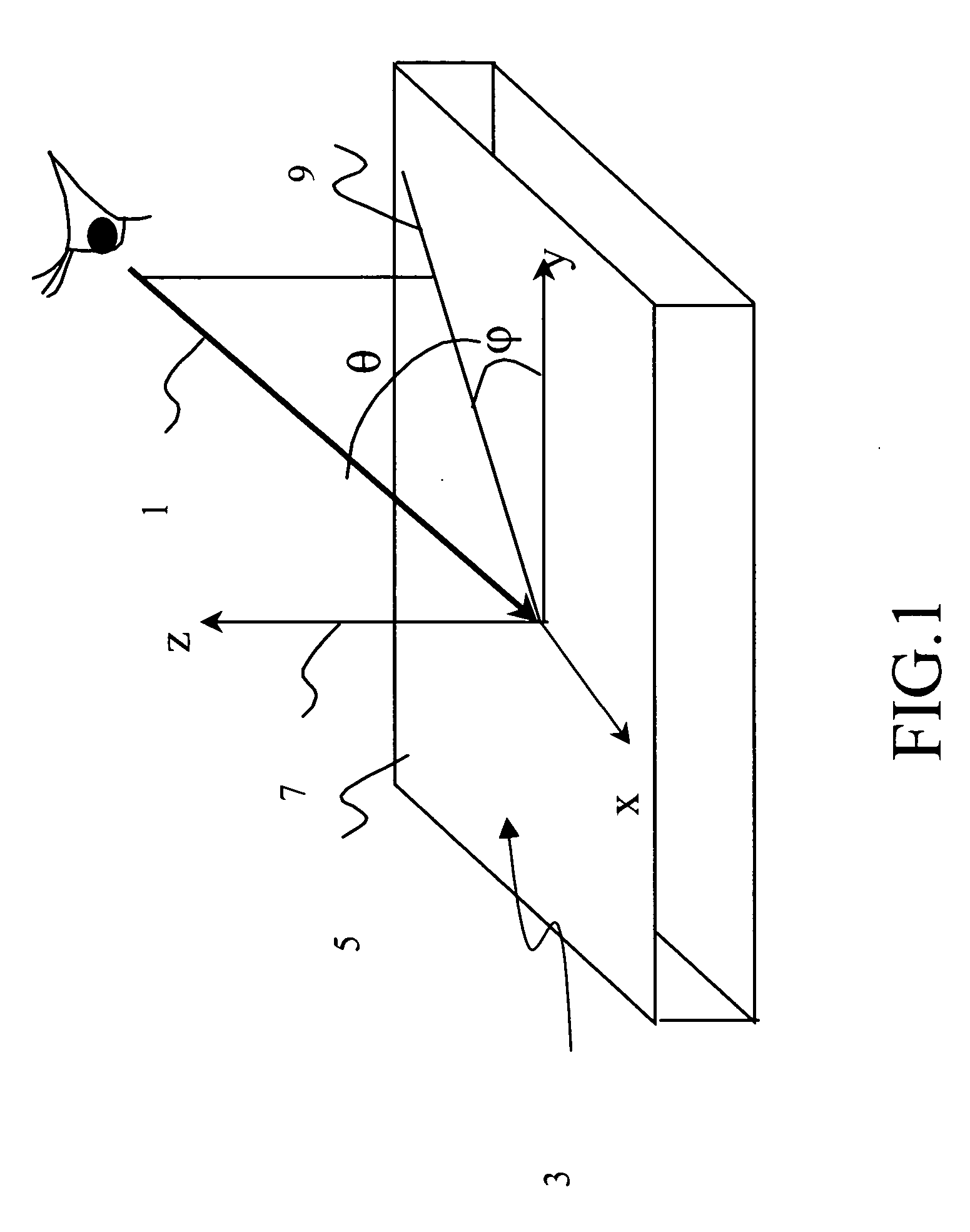
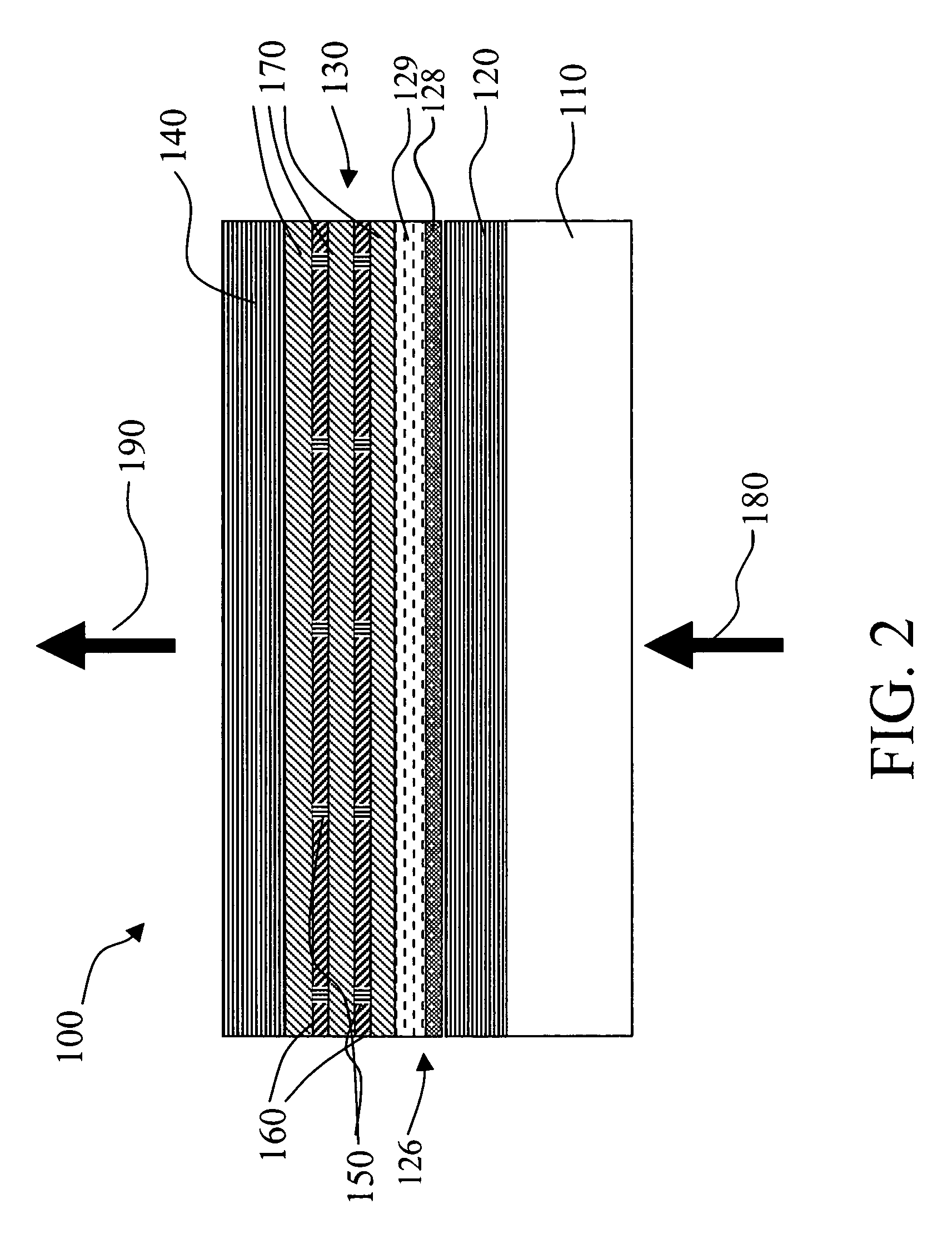
[0038]FIG. 1 shows the definition of the azimuthal angle φ and tilt angle θ to specify the direction of the optic axis 1 with respect to the x-y-z coordinate system 3. The x-y plane is parallel to the display surface 5, and the z-axis is parallel to the display normal direction 7. The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com