Liquid crystal display device
a display device and liquid crystal technology, applied in semiconductor devices, instruments, optics, etc., can solve the problem of providing superior display characteristics, and achieve the effect of superior display characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0081] A liquid crystal display device according to Example 1 of the embodiment of the invention will be described. FIG. 14 schematically shows the configuration of the liquid crystal display device according to the embodiment. As shown in FIG. 14, the liquid crystal display device has the TFT substrate 2, the counter substrate 4, and the liquid crystal layer 6 (not shown in FIG. 14) which is sealed between the two substrates 2 and 4.
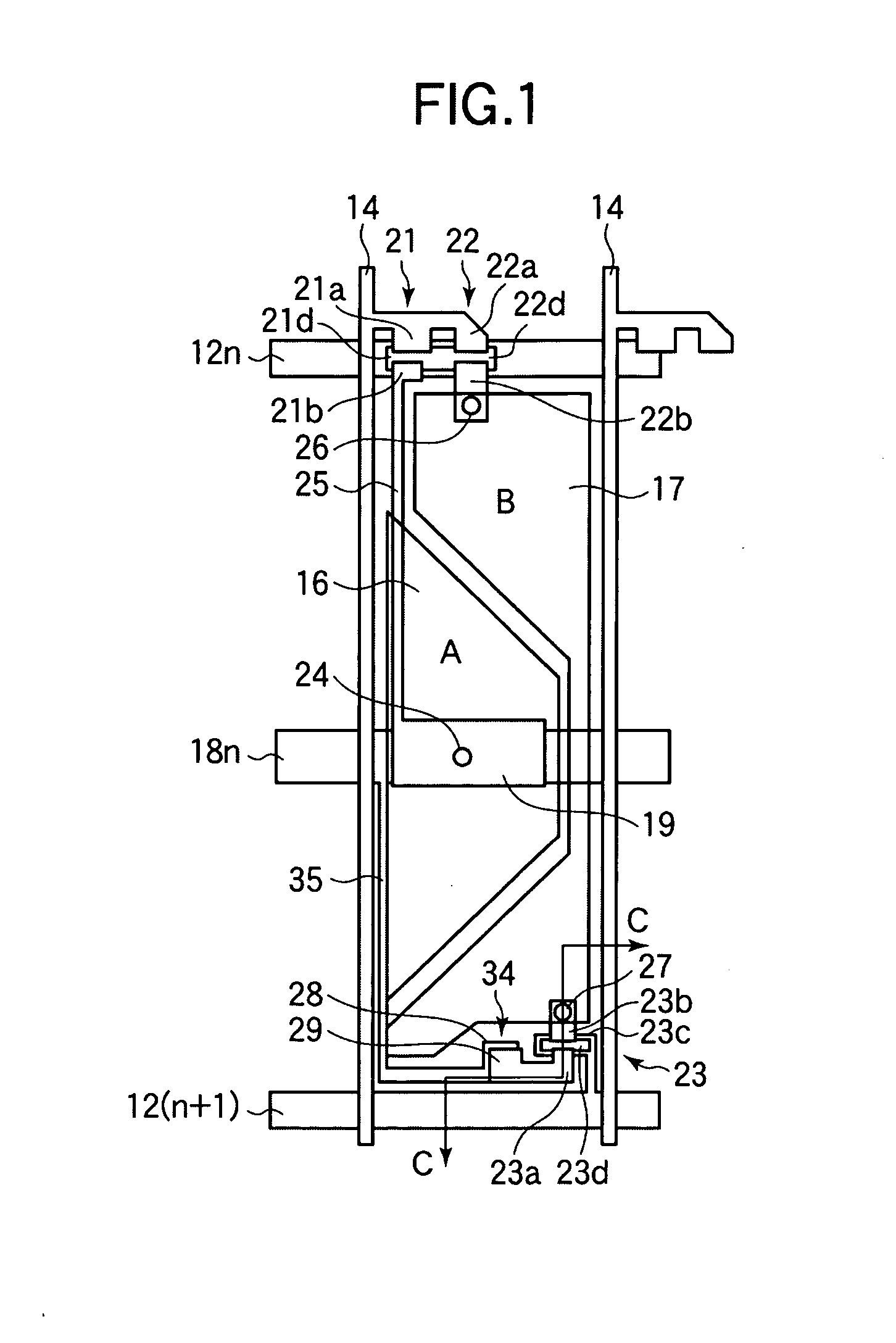
[0082] A gate bus line driving circuit 80 incorporating a driver IC for driving the plural gate bus lines and a drain bus line driving circuit 82 incorporating a driver IC for driving the plural drain bus lines are connected to the TFT substrate 2. The driving circuits 80 and 82 output scanning signals and data signals to prescribed gate bus lines and drain bus lines on the basis of prescribed signals that are output from a control circuit 84. A polarizing plate 87 is disposed on that surface of the TFT substrate 2 which is opposite to its TFT elements...
example 2
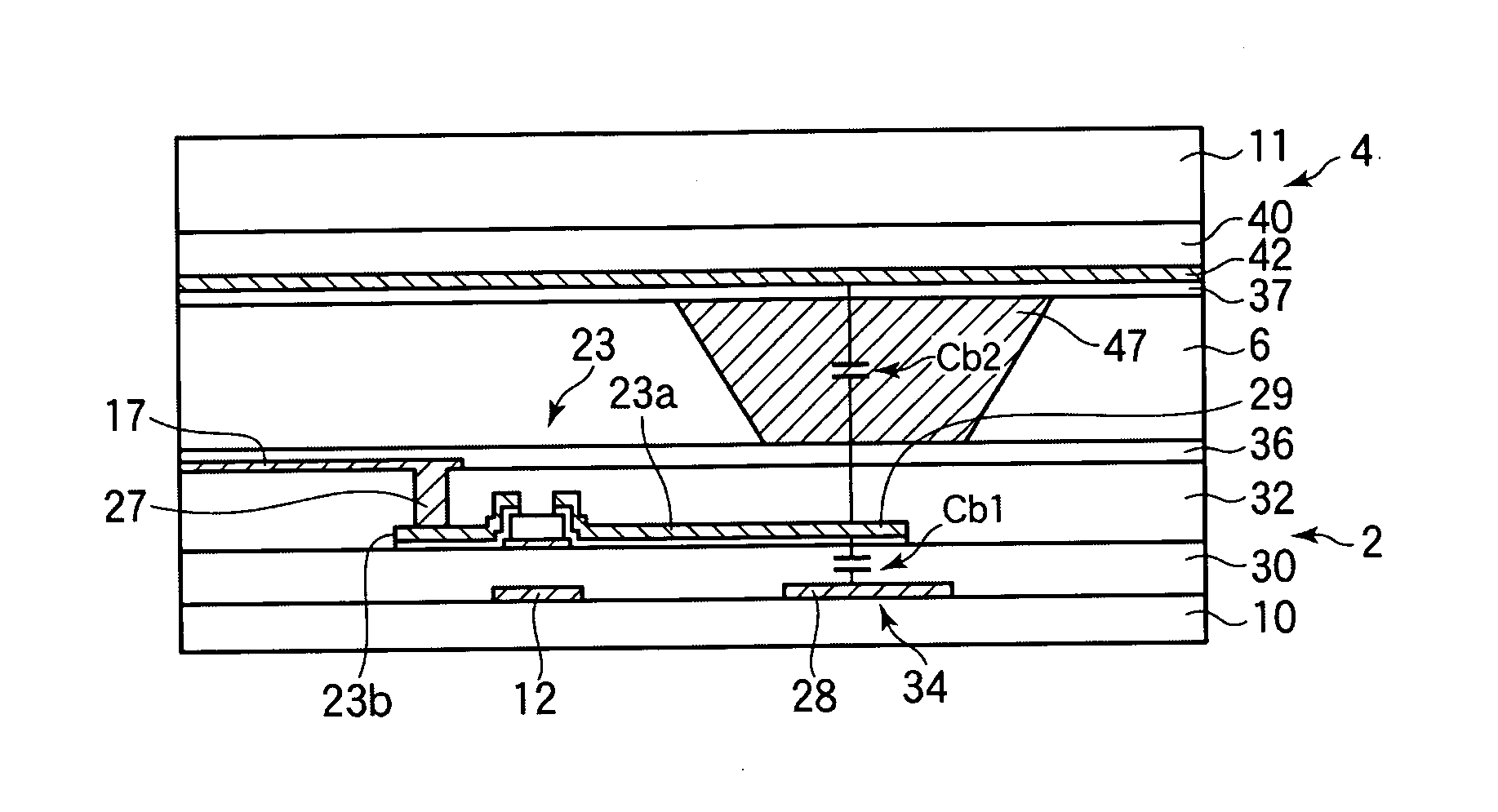
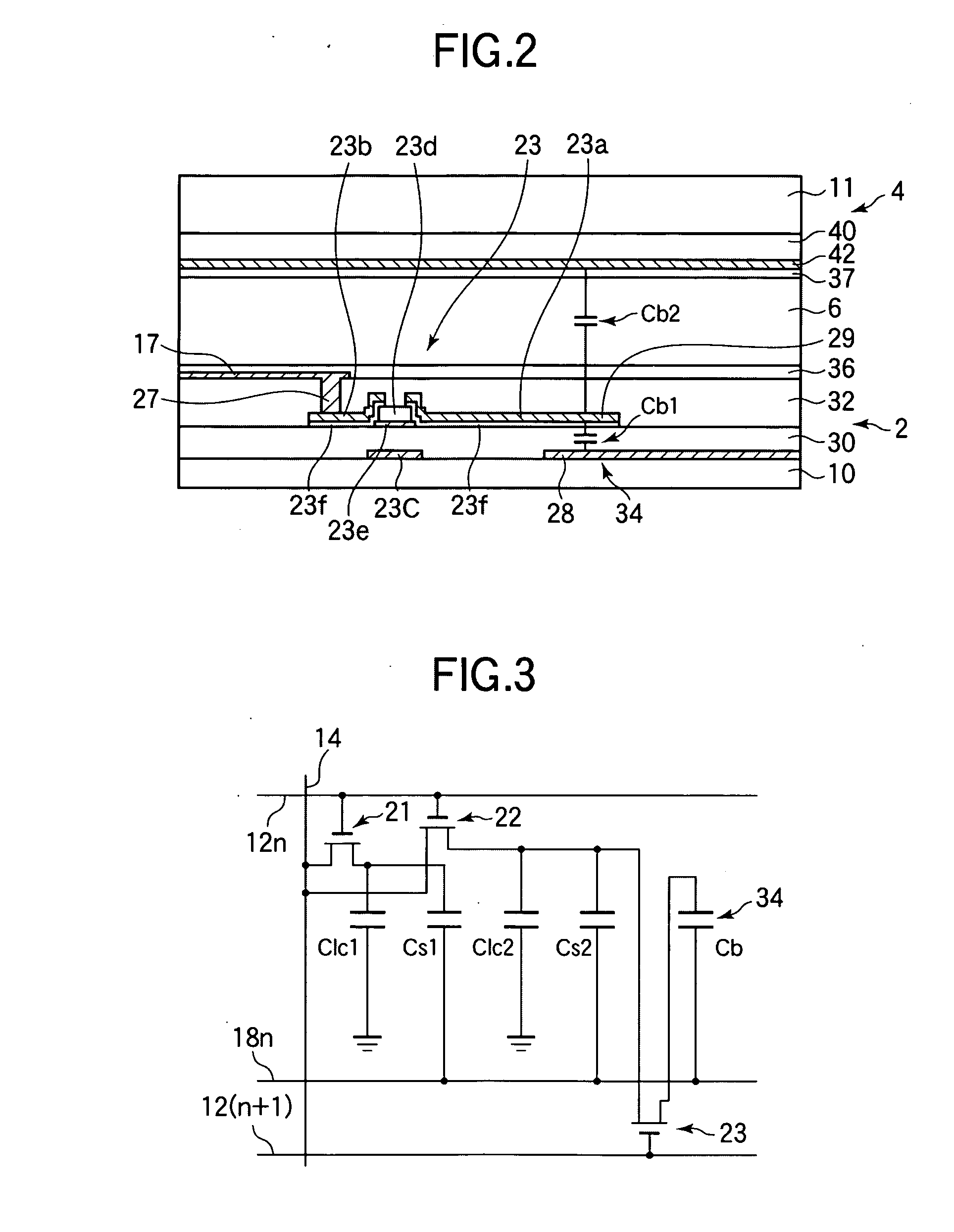
[0087] A liquid crystal display device according to Example 2 of the embodiment will be described. In Example 2, as already shown in FIG. 9, the column-shaped spacer 47 is disposed in the region of formation of the buffer capacitance portion 34. The permittivity e of a liquid crystal varies depending on the alignment state and the voltage application state and hence is a factor of variation of the buffer capacitance Cb (Cb2). In contrast, in Example 2, the capacitance Cb2 is stable because that part of the liquid crystal which is located in the buffer capacitance portion 34 is removed by the column-shaped spacer 47. Incidentally, the buffer capacitance electrodes 28 and 29 of the buffer capacitance portion 34 are usually made of an opaque metal. Therefore, the region of formation of the buffer capacitance portion 34 does not contribute to display and hence is a factor of reduction of the aperture ratio. Example 2 provides an additional advantage that the degree of reduction of the a...
example 3
[0090] In Example 3, according to the fourth principle shown in FIGS. 11A and 11B, the buffer capacitor Cb is formed by the buffer capacitance electrode 61 which is formed in the same layer as the pixel electrodes 16 and 17 and is electrically connected to the connection electrode 35 and the storage capacitance bus line 18 via the contact hole 54, the buffer capacitance electrode 29 which coextends with part of the buffer capacitance electrode 61 and extends from the drain electrode 23a of the TFT 23, and that part of the protective film 32 which is interposed between them. Since the thickness of the protective film 32 can be changed more easily than that of the insulating film 30, in Example 3 the thicknesses of the insulating film 30 and the protective film 32 were set at 350 nm and 150 nm, respectively. With these settings, a buffer capacitance Cb which was 2.3 (350 / 150) times larger than in the case where the insulating film 30 was used as a dielectric layer was obtained in the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| voltages | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| polar angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com