Bonding of elastomeric substrate under stretched conditions
a technology of elastomeric substrate and stretched conditions, which is applied in the direction of packaging, labelling, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of limited ability to form strong ultrasonic bonds using conventional processes, and achieve the effects of efficient bonding of high loft substrates, economical manufacture and use, and suitable bonding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
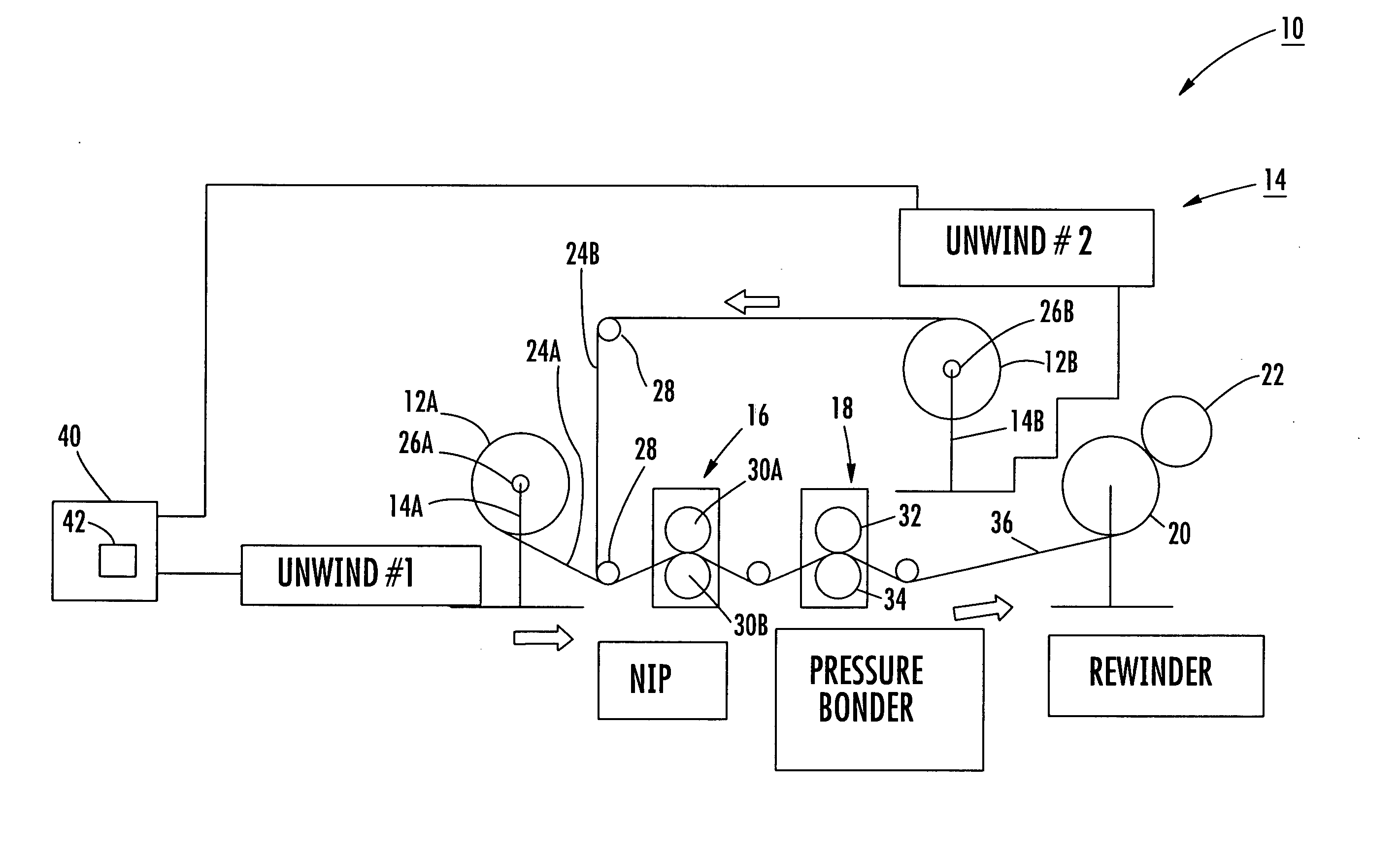
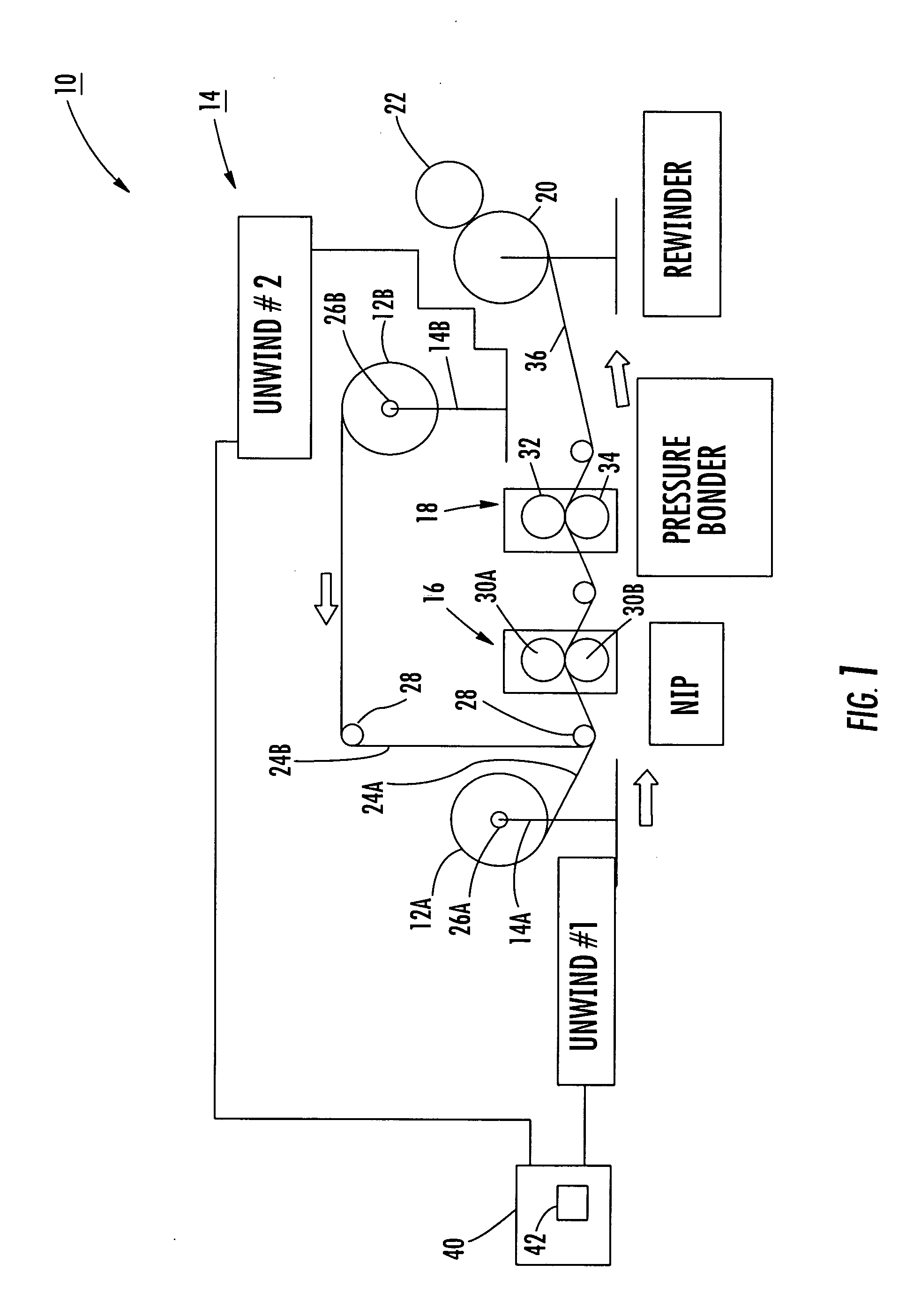
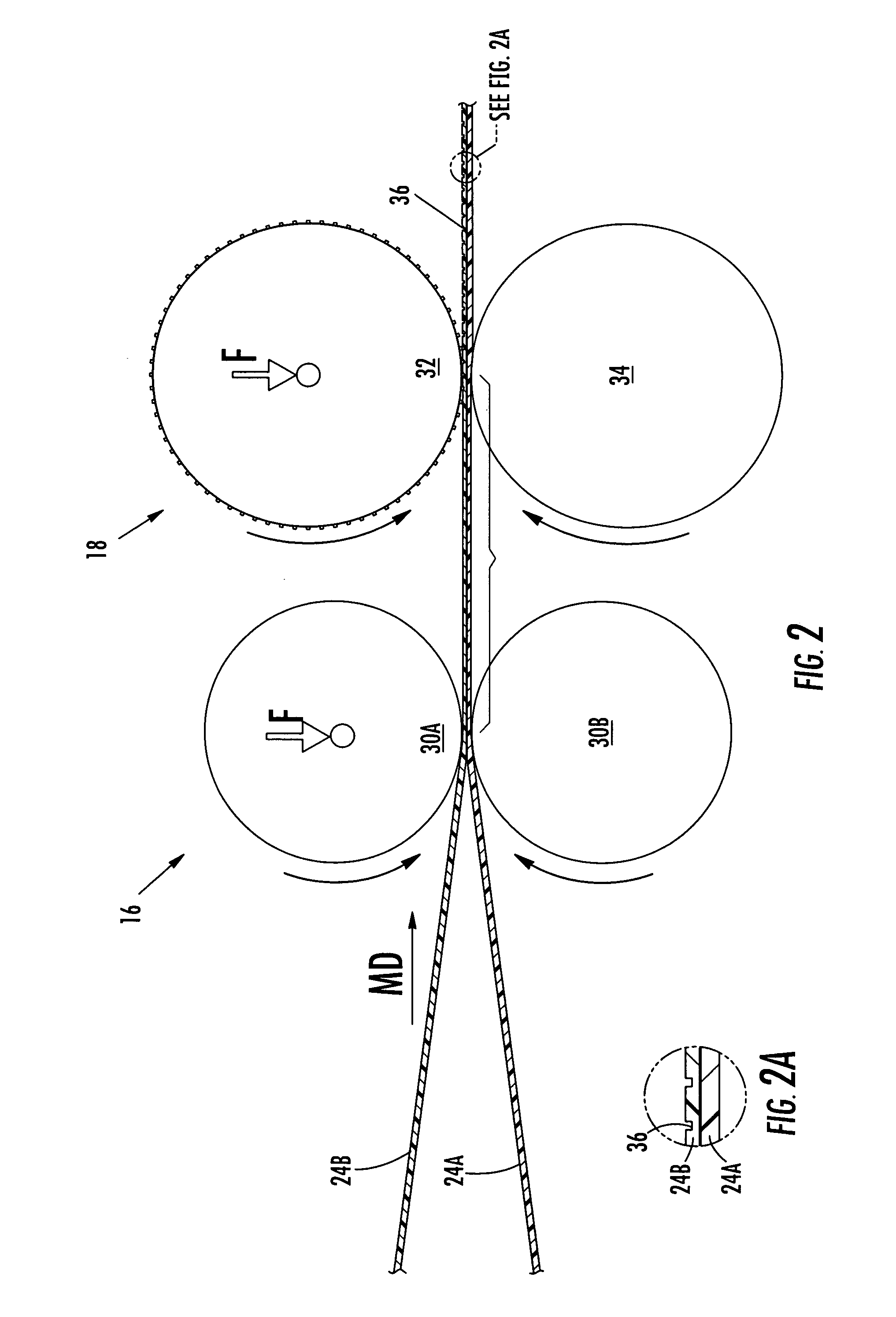
[0069] The following example was performed in order to determine the effect of stretching webs of material, such as webs 24A, 24B discussed herein, prior to bonding using a bonder such as the bonder 18 as shown in FIG. 1. At least one of the webs of material 24A, 24B was unwound into the nip 16, specifically between the rolls 30A, 30B and stretched prior to the pressure bonder 18 and the rewinder 20. The pressure bonder 18 and the rewinder 20 were processing at a line speed approximately twice that of the unwind system 14 and the nip 16. Stated another way, the pressure bonder 18 and the rewinder 20 took away the material 24A, 24B at a speed twice that of the nip 16 prior to the pressure bonder 18, which ensured that the material 24A, 24B was in a stretched state at the bonder 18. Thirty samples were produced and tested. As shown in the following charts, various product speeds per minute—assuming a product pitch of 29 inches based on the trial pressure bonder—were employed for this ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com