Apparatus and method for regulation of fluid flow from a straw
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
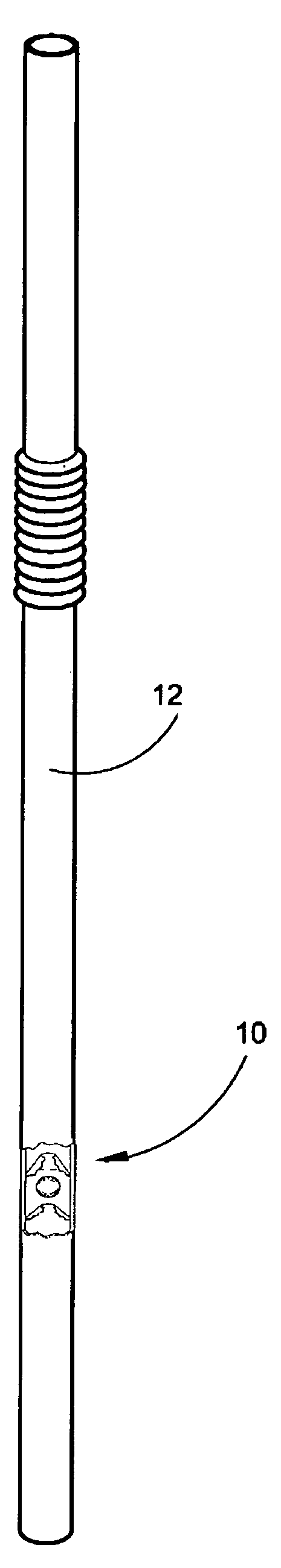
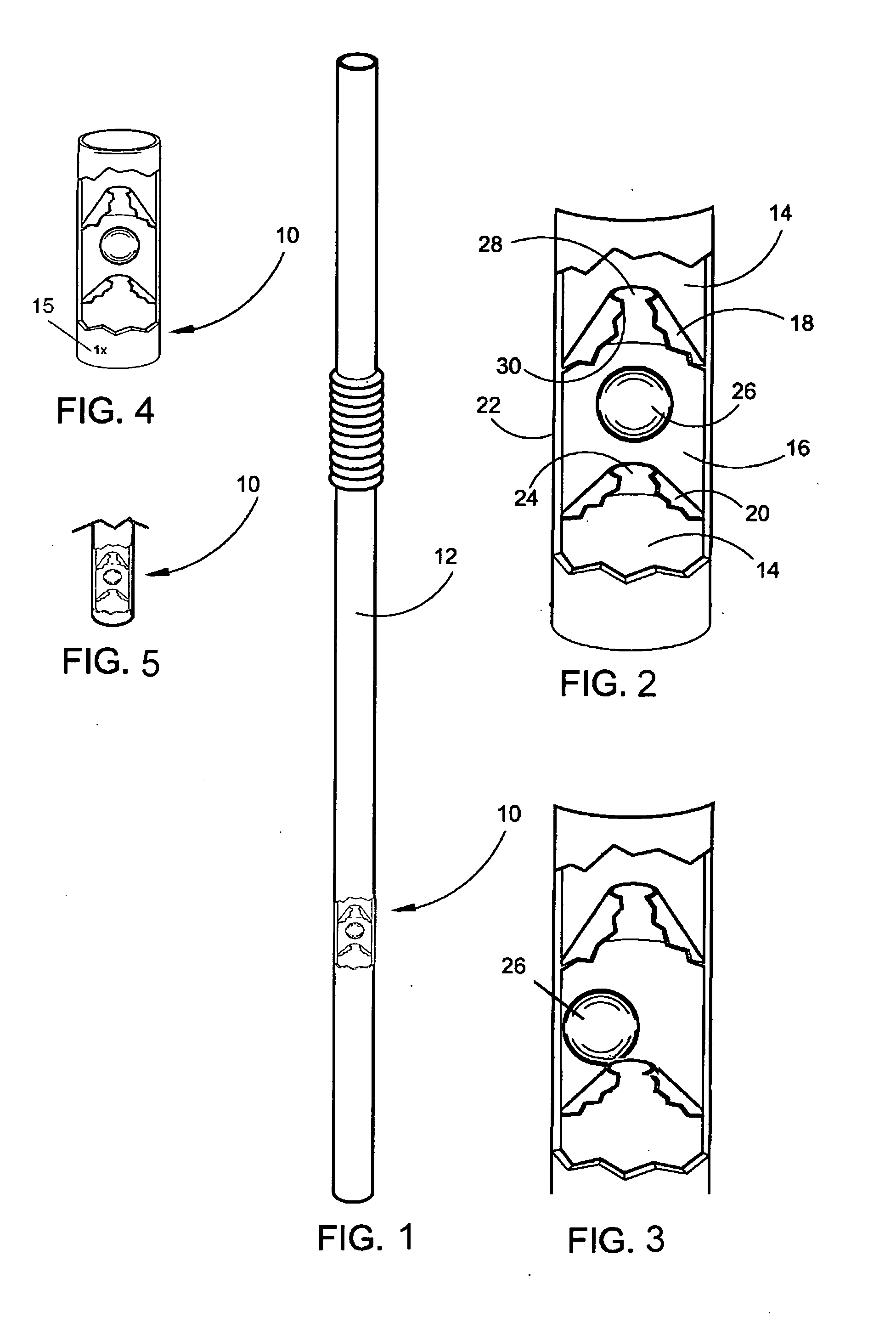
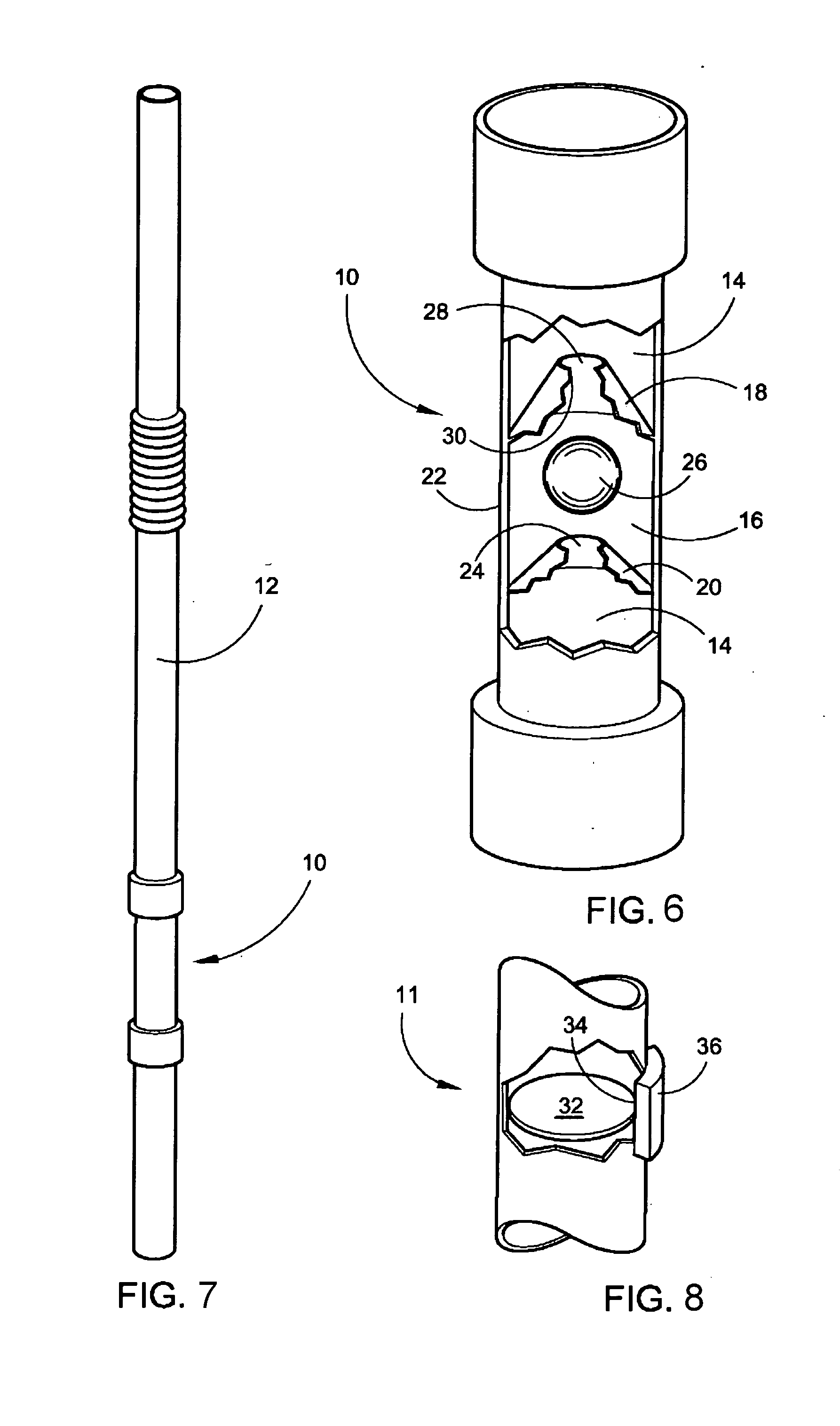
[0038]Referring now to the drawings, FIGS. 1-7 disclose modes of the device herein described and disclosed for regulating fluid velocity and volume when exiting a straw to a user's mouth.
[0039]In one preferred mode of the device 10 depicted in FIG. 1, with the device 10 disposed in a straw 12 during extrusion of the straw 12, an inexpensive and disposable means to regulate fluid velocity and maximum volume exiting a straw 12 is depicted. Because it is inexpensive to manufacture and install within the straw 12 during extrusion, the device 10 and straw 12 may be disposed once used and replaced to mitigate hygiene and sterility problems that occur with permanent devices for this purpose that collect food and germs thereon.
[0040]The straw 12 in all modes in which the device 10 is employed, has an axial passage 14 communicating therethrough in a conventional fashion from a lower end of the straw to the distal end, which would be engaged by the user's mouth. The device provides a restrict...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com