Machine for removing the sharp edge in plates in general and in particular in glass plates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
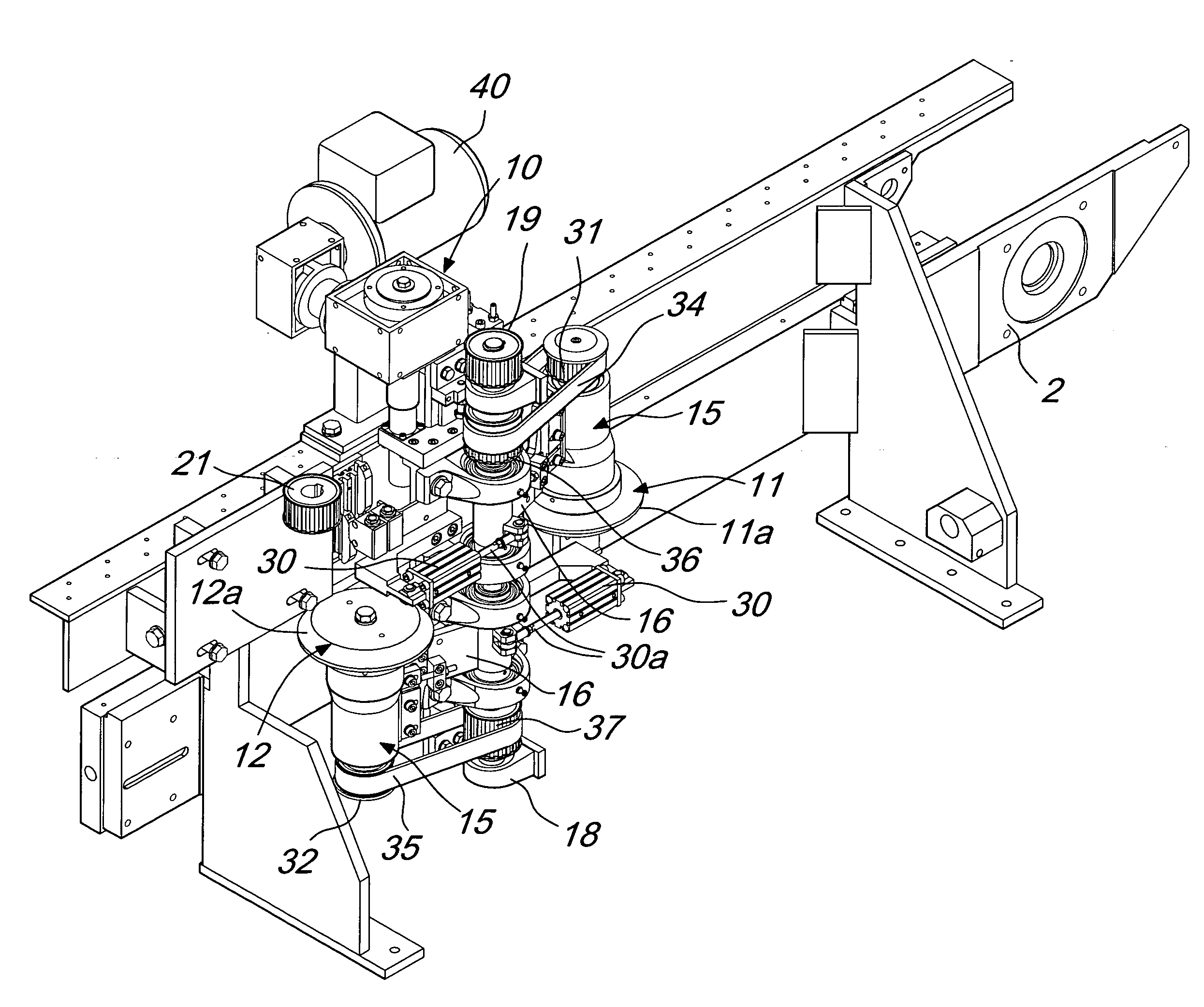
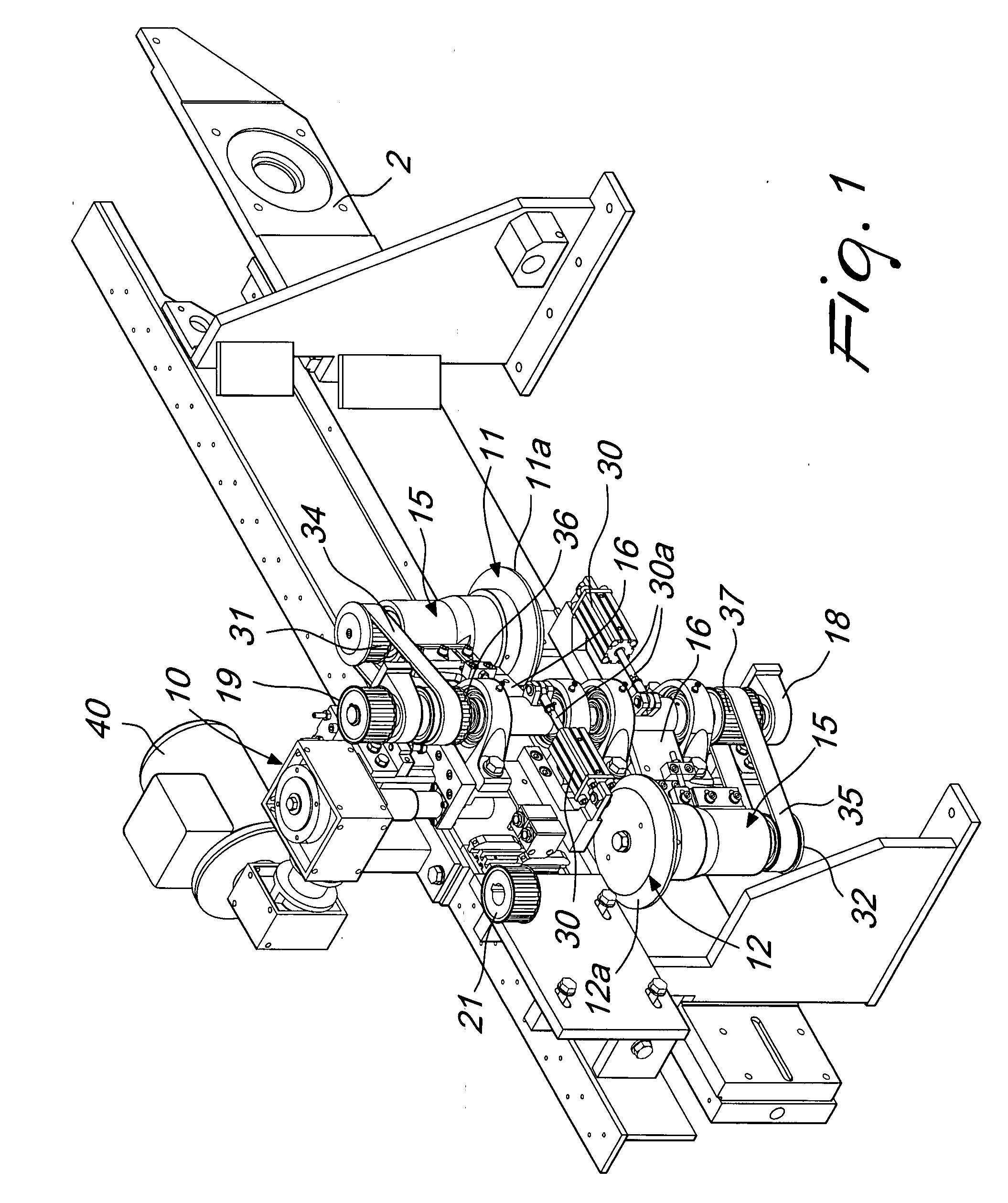
[0028]With reference to the figures, the machine for removing the sharp edge in plates in general and in glass plates in particular, generally designated by the reference numeral 1, comprises a frame 2 for the support and advancement of a plate 3 which is rested for example on a belt 4 which unwinds continuously.
[0029]At least one and preferably a plurality of arrissing stations, generally designated by the reference numeral 10, are typically provided at the edges of the plate.
[0030]Arrissing stations are usually provided on both of the advancement sides of the plate, which has a rectangular shape, and moreover the line provides for two machines with an interposed 90° transfer system, so that all the four edges of the plate are machined.
[0031]The drawing illustrates a single arrissing station, but of course, as mentioned earlier, the stations are typically four in number.
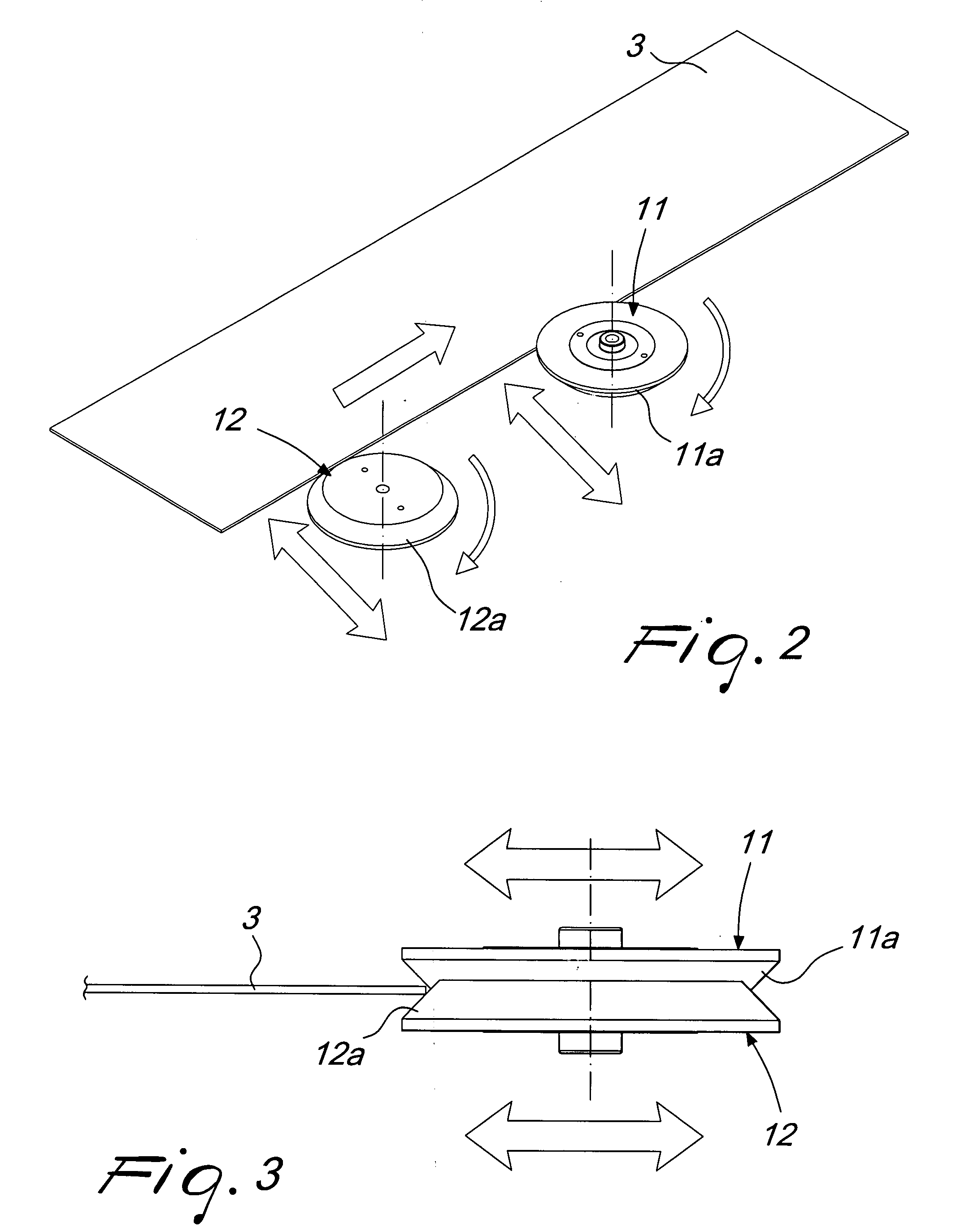
[0032]Each arrissing station 10 comprises an upper tangential grinding wheel 11 and a lower tangential grinding w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com