Method for Producing Patterned Structures by Printing a Surfactant Resist on a Substrate for Electrodeposition
a technology of surfactant resist and substrate, applied in the field of lithography, can solve the problems of inability to use in conjunction with sputter deposition or evaporation, inability to deposit material from the vapor phase, and inability to produce patterned structures. the effect of high energy, low cost and considerable cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Electrodeposition of Conductive Material
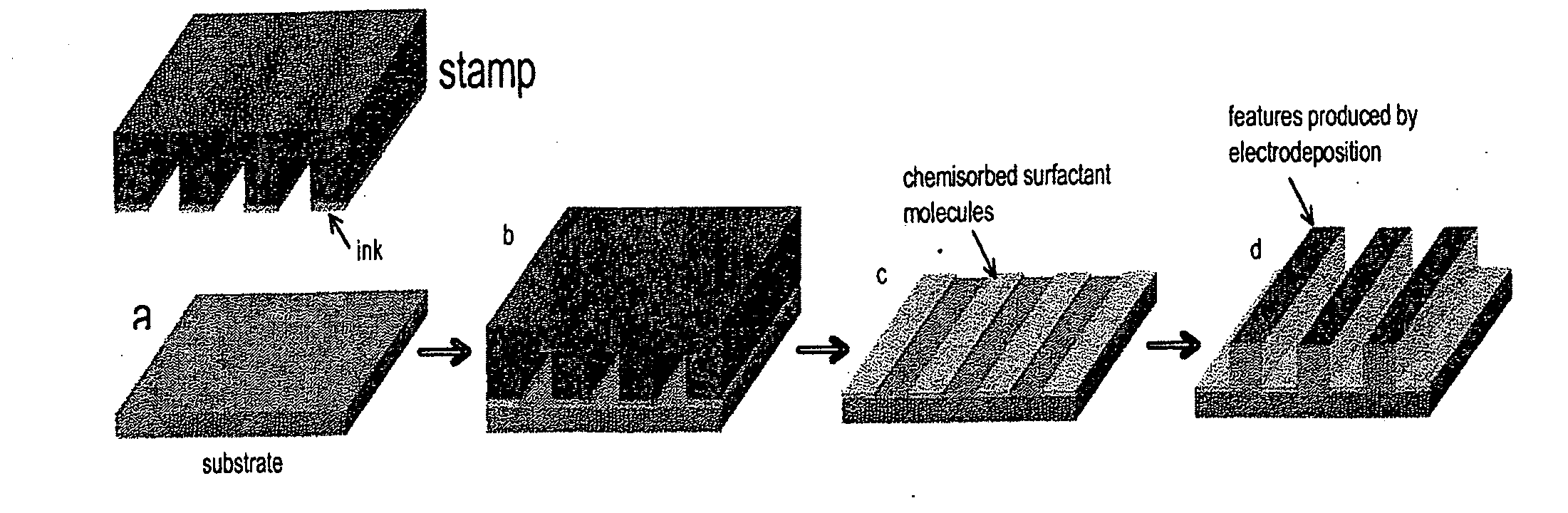
[0030]In a preferred embodiment, a molecule with a sulfhydryl group at one end is used as the surfactant molecule. A stamp is used to transfer a pattern of the surfactant molecule to a gold or silver substrate. The patterned surfactant may be used to direct deposition of a material to the surfactant-free regions. The material is deposited at a potential positive to the reduction potential for the chemisorbed surfactant molecule, that is, at a potential positive to the potential where the surfactant molecule is desorbed from the substrate. In certain embodiments of the present invention, the deposited material is not applied to the regions where the substrate is covered with the surfactant molecule. The conditions under which deposition only occurs in the surfactant-free regions of the substrate and where the material is deposited with no lateral growth to heights greater than the height of the surfactant layer are dependent on the molecular st...
example 2
Sequential Stamping
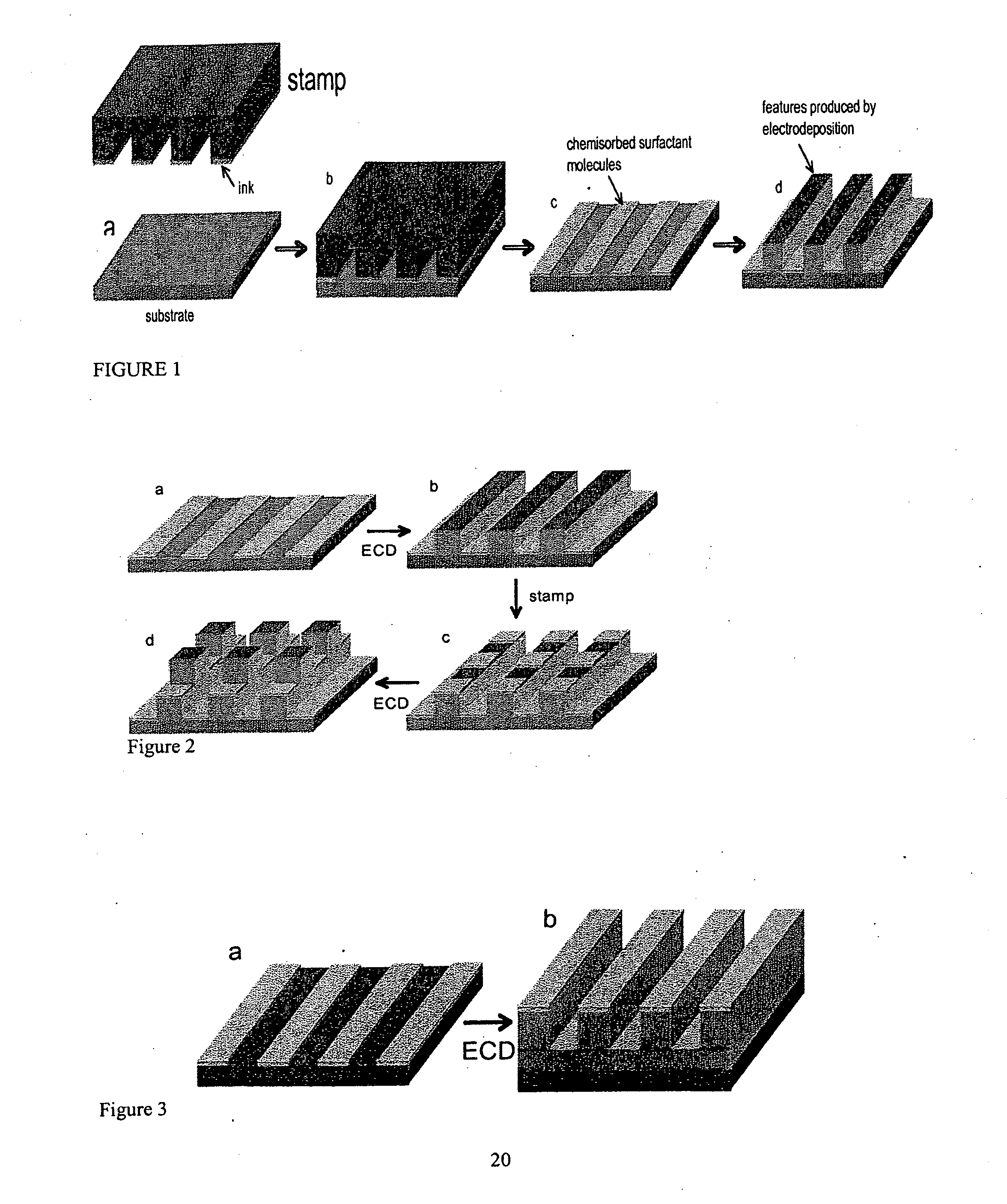
[0031]As shown in FIG. 2a, a substrate 230 is stamped with a surfactant material 220, using a stamp coated or inked with surfactant molecules, thereby transferring surfactant molecules that chemisorb onto the substrate 230 in regions where the stamp contacts the surface of the substrate 230. A conductive material 240 is deposited by electrodeposition onto the substrate to create features that grow vertically from the substrate with lateral dimensions defined by the pattern, as shown in FIG. 2b. Thereafter, the deposited material 240 obtained via the initial electrodeposition is stamped with a second layer of surfactant 250 that chemisorbs to that material.
[0032]The stamp orientation and pattern are selected to place the surfactant molecules in a pattern of interest on top of the layer of deposited material 240. On removing the stamp (FIG. 2c) the surfactant molecule is transferred to and chemisorbs only in regions where the stamp is in contact with top of the feat...
example 3
Preferential Deposition in the Regions where a Surfactant Molecule is Chemisorbed to the Surface
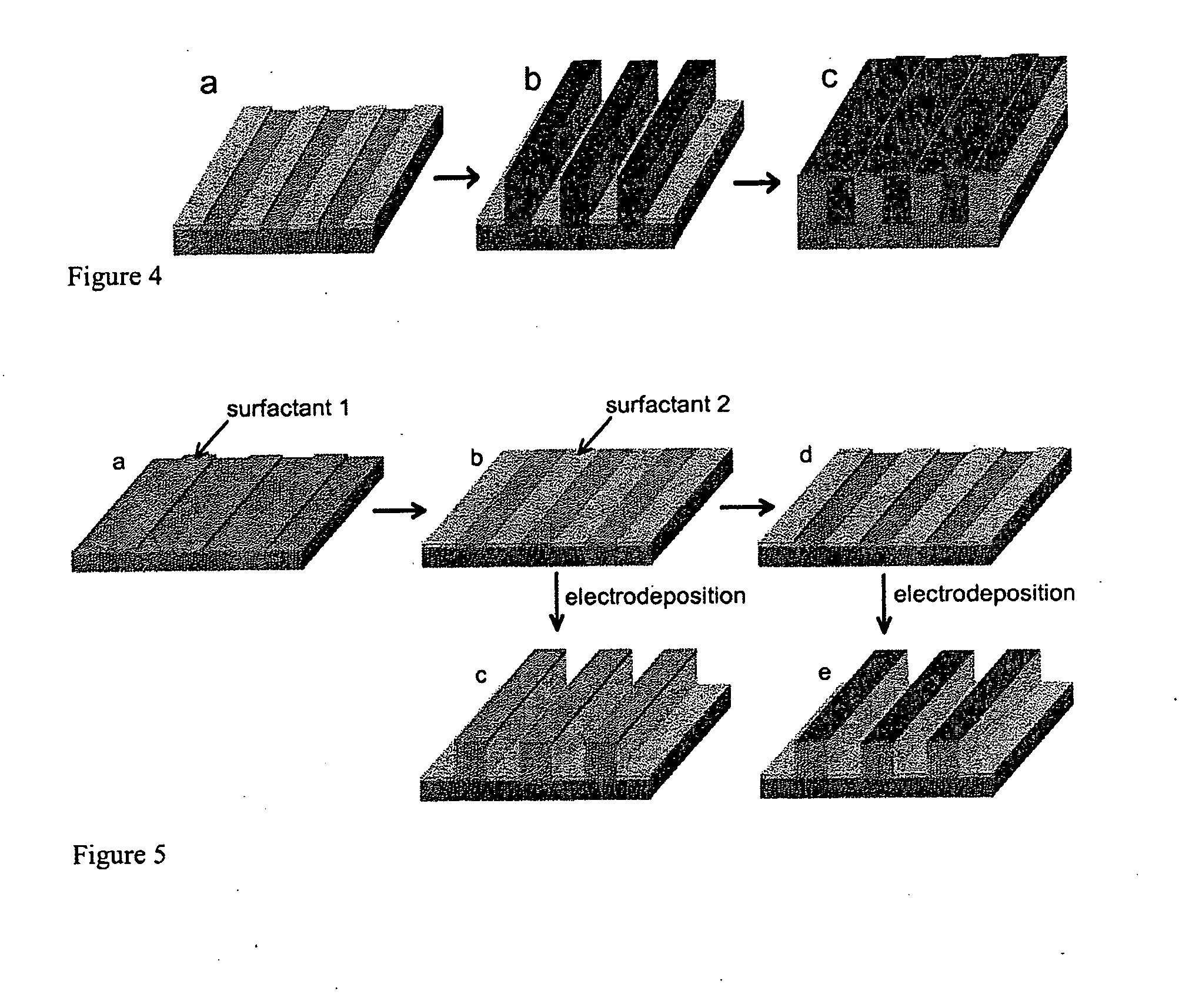
[0034]According to the embodiment depicted in FIG. 3, a substrate 330 is stamped with a surfactant material 320, using, for example, a stamp coated or inked with surfactant molecules, thereby causing the surfactant molecules 320 to chemisorb onto the substrate 330 in regions where the stamp made contact with the surface of the substrate 330, as shown in FIG. 3a. Next, a conductive material 340 is deposited by electrodeposition onto the substrate, as shown in FIG. 3b. In this embodiment, the material of interest is deposited on both the regions of the surface covered with surfactant molecules and on the regions that are not covered with surfactant molecules. The rate of deposition in the regions covered by the surfactant molecules is faster or higher than the rate of deposition in the surfactant-free regions. As shown in FIG. 3b, this preferential deposition results in the deposited featur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductor | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Deposition rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com