Semiconductor memory device with low standby current
a memory device and low standby current technology, applied in the field of semiconductor memory devices, can solve the problem that the standby current has not been sufficiently reduced in the conventional sram
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
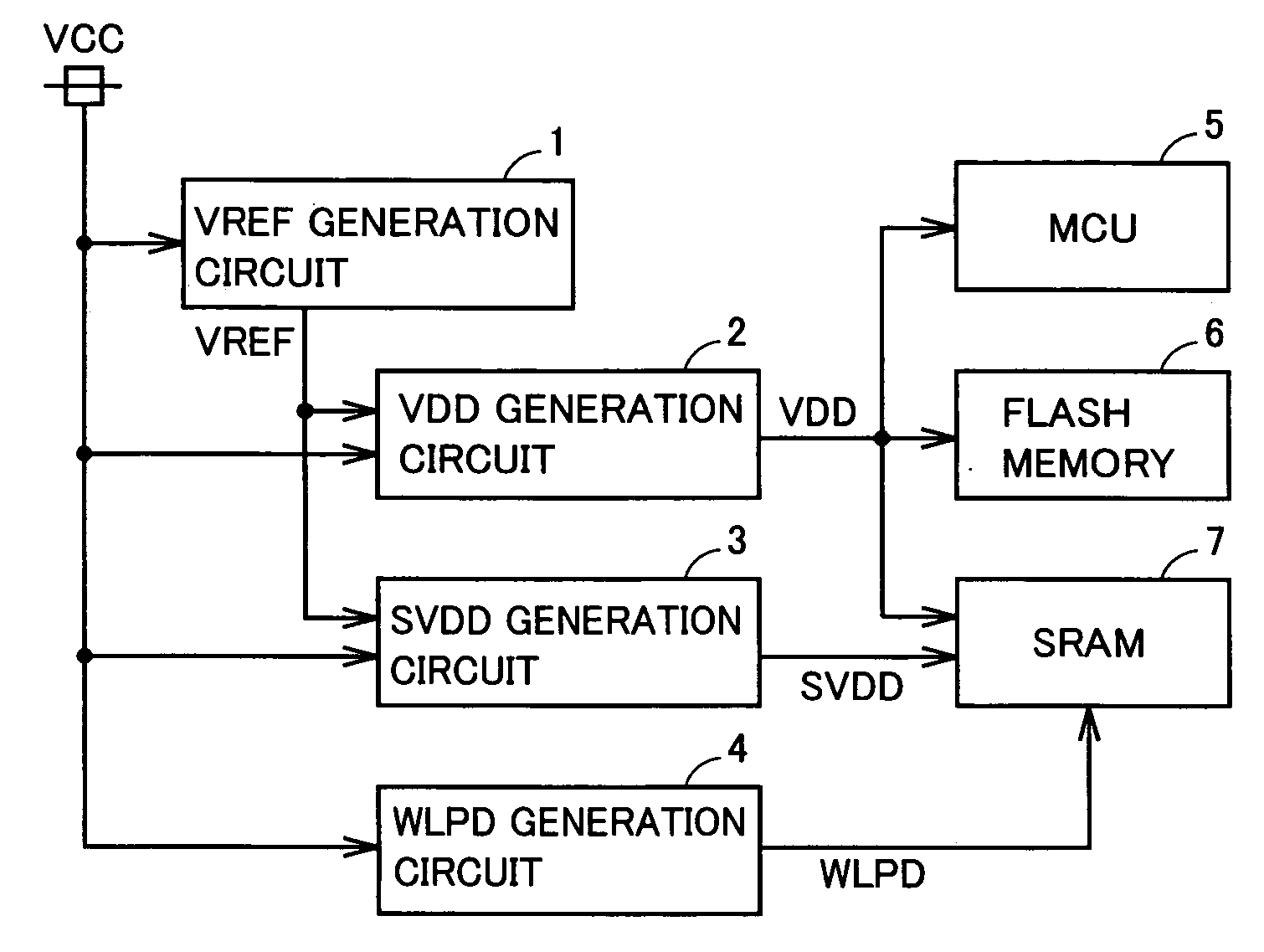
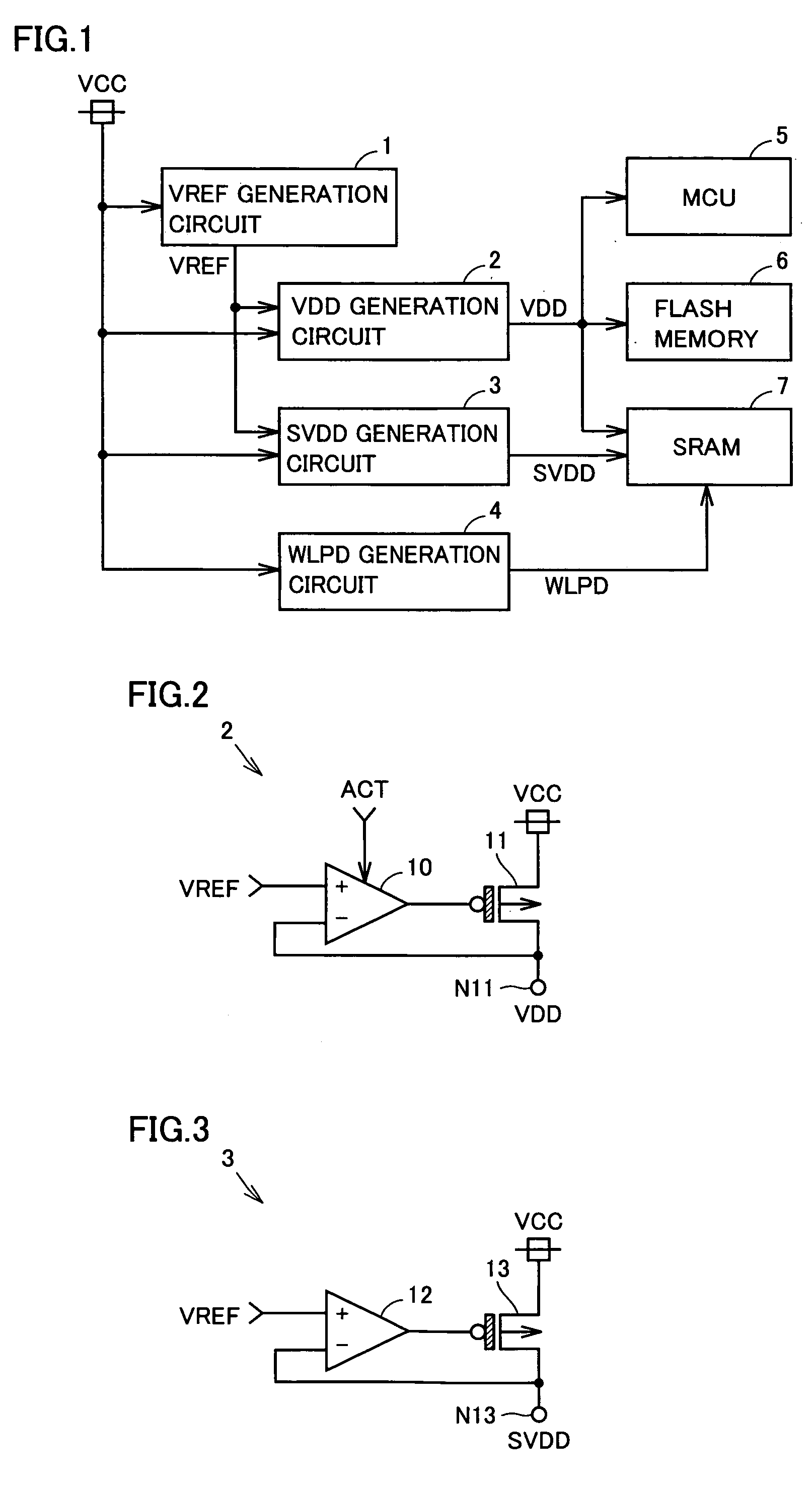
[0063]FIG. 9 is a circuit block diagram that shows a substantial part of an SRAM according to a second embodiment of the present invention, in comparison with FIG. 6. With reference to FIG. 9, the SRAM differs from the SRAM in the first embodiment in that transistors 50-56 are replaced with transistors 70-76, respectively, and that internal power supply voltage VDD for a peripheral circuit is applied to each back gate of transistors 70-72, 75, 76. An absolute value of a threshold voltage of all the transistors 31-36, 50-56, 61-65 in FIG. 6 is 0.3 V, while an absolute value of a threshold voltage of transistors 70-76 is set to 0.5 V.
[0064]In the second embodiment, the threshold voltage of transistors 70-76 is set at a high level, and hence even if internal power supply voltage VDD is set to 0 V during standby, leakage current IL is small.
third embodiment
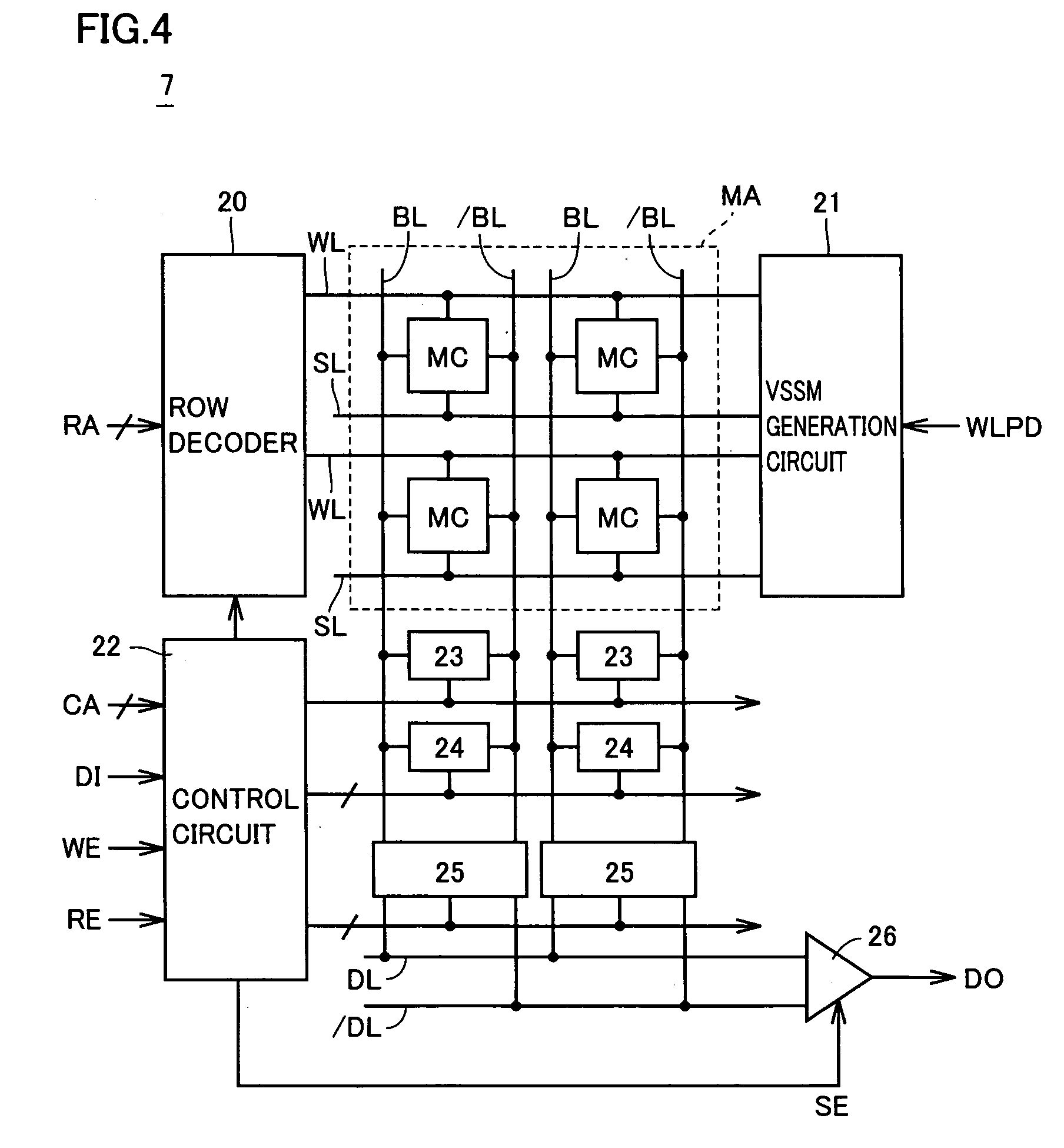
[0065]FIG. 10 is a circuit block diagram that shows a substantial part of an SRAM according to a third embodiment of the present invention, in comparison with FIG. 6. With reference to FIG. 10, the SRAM differs from the SRAM in the first embodiment in that internal power supply voltage VDD is applied to each back gate of P-channel MOS transistors 50-52, 55, 56, and that pull-up circuits (PU) 80-83 are added. Pull-up circuits 80-82 are connected to gates of P-channel MOS transistors 50-52, respectively, and pull-up circuit 83 is connected to gates of P-channel MOS transistors 55, 56. Each of pull-up circuits 80-83 pulls up the gate of the corresponding P-channel MOS transistor to an “H” level (internal power supply voltage SVDD) during standby, and fixes the corresponding P-channel MOS transistor to a non-conduction state.
[0066]As shown in FIG. 11, pull-up circuit 80 includes P-channel MOS transistors 84, 85 and an N-channel MOS transistor 86. P-channel MOS transistor 84 has a source...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com