Method And Apparatus For Register Renaming Using Multiple Physical Register Files And Avoiding Associative Search
a physical register and register renaming technology, applied in the field of method and register renaming, can solve the problems of affecting processor performance, ambiguity of all memory references at compile time, and high cost of counter-based physical register solutions, so as to avoid associative searching
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
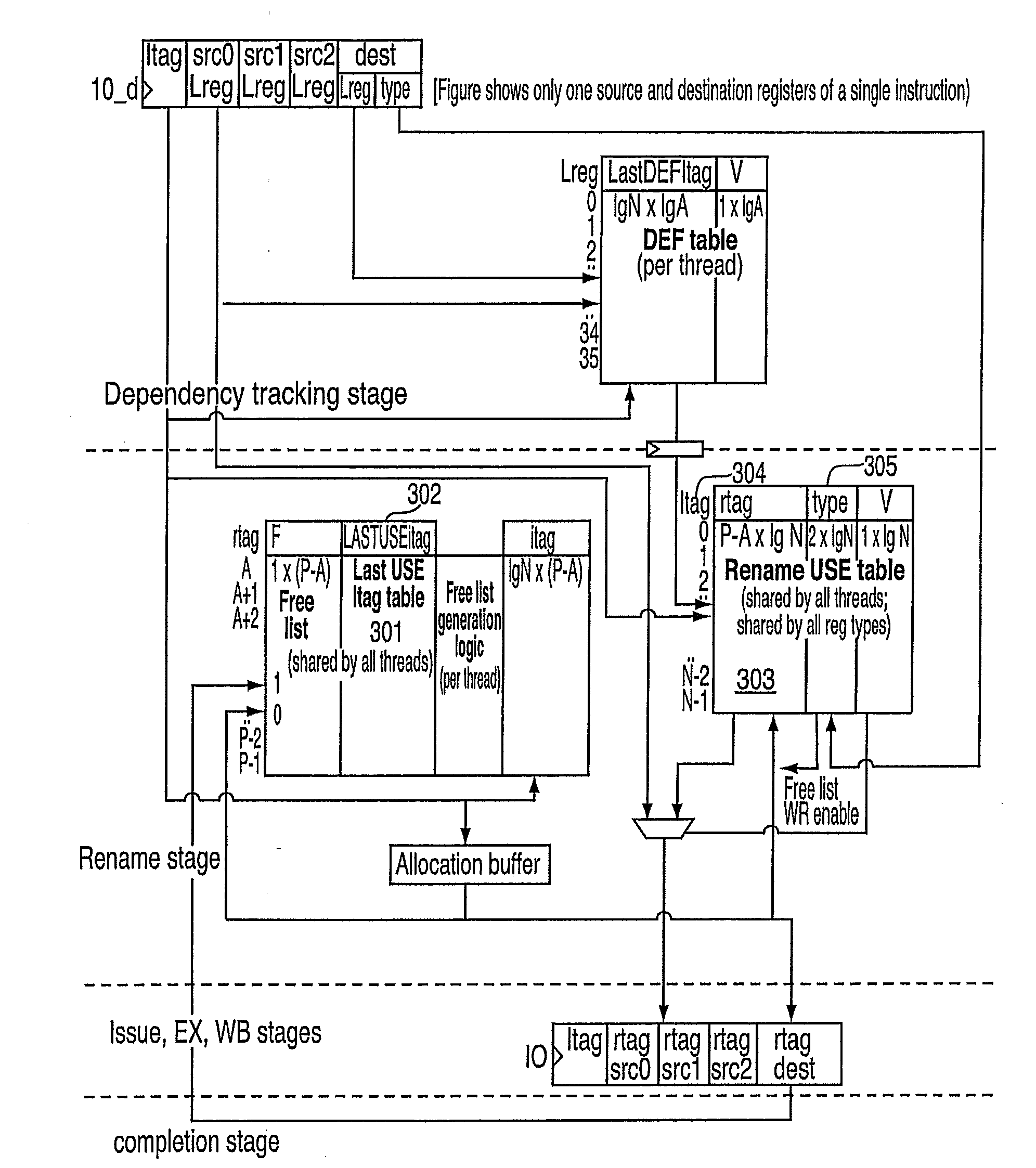
[0024]One aspect of the exemplary embodiments is a method for renaming registers. Another aspect of the exemplary embodiments is a method for reducing the complexity and size of register renaming hardware by using a shared mapping table indexed by instruction tags to store logical-to-physical register mapping for different types of logical registers (such as general-purpose or integer registers (GPRs), floating-point registers (FPRs), vector registers (VRs), etc.) used by multiple threads and avoiding associative searching.
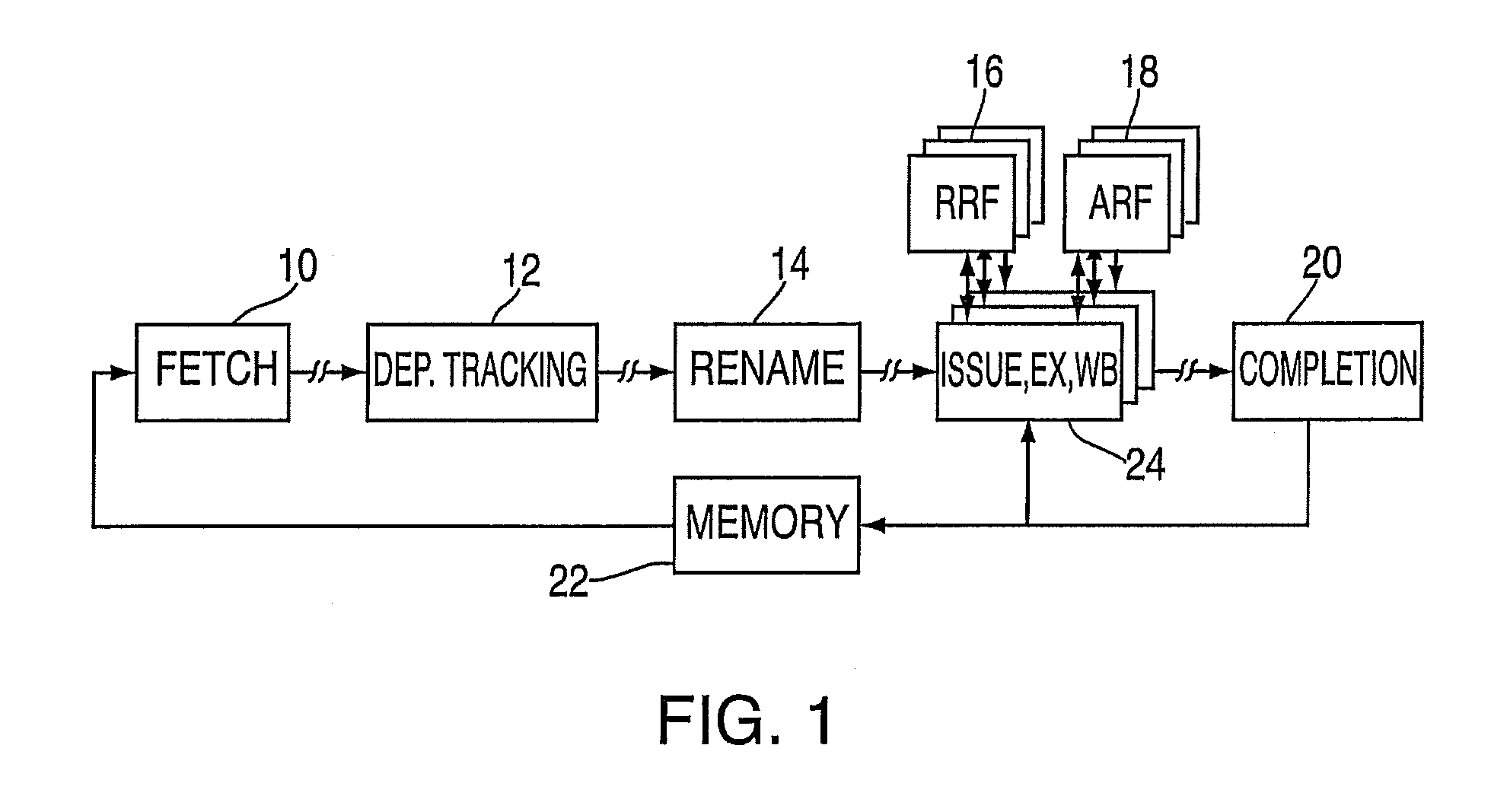
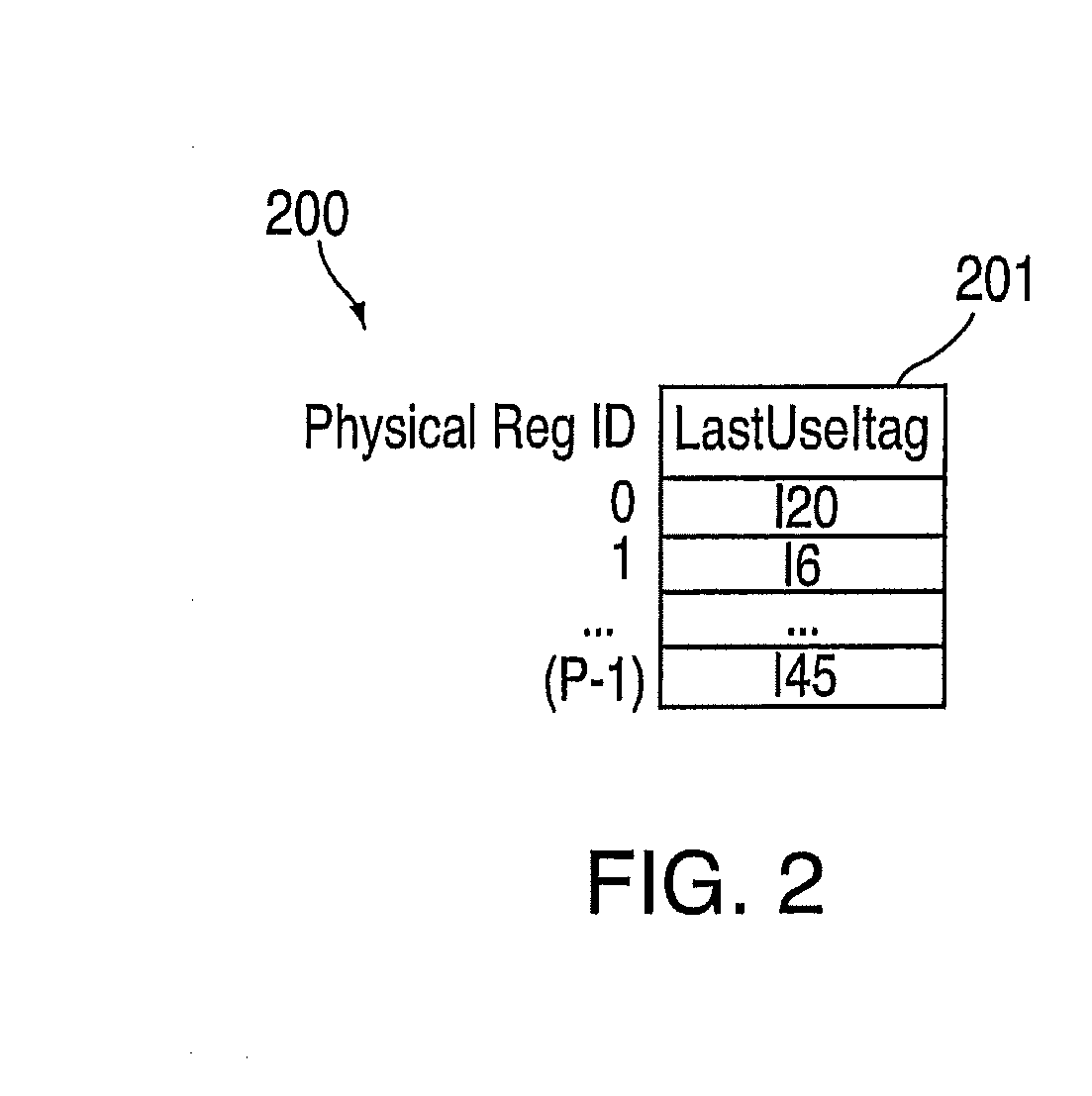
[0025]The exemplary embodiments provide for a technique for implementing an area and power efficient renaming scheme for a digital data processor using multiple physical register files. The exemplary embodiments further provide for an improved pipeline processor design which exploits simple hardware structures for register renaming to execute instructions at a higher rate than known pipeline processors by enabling higher clock frequency processor designs. In addit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com