Hydrometallurgical process using resin-neutralized-solution of a heap leaching effluent
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
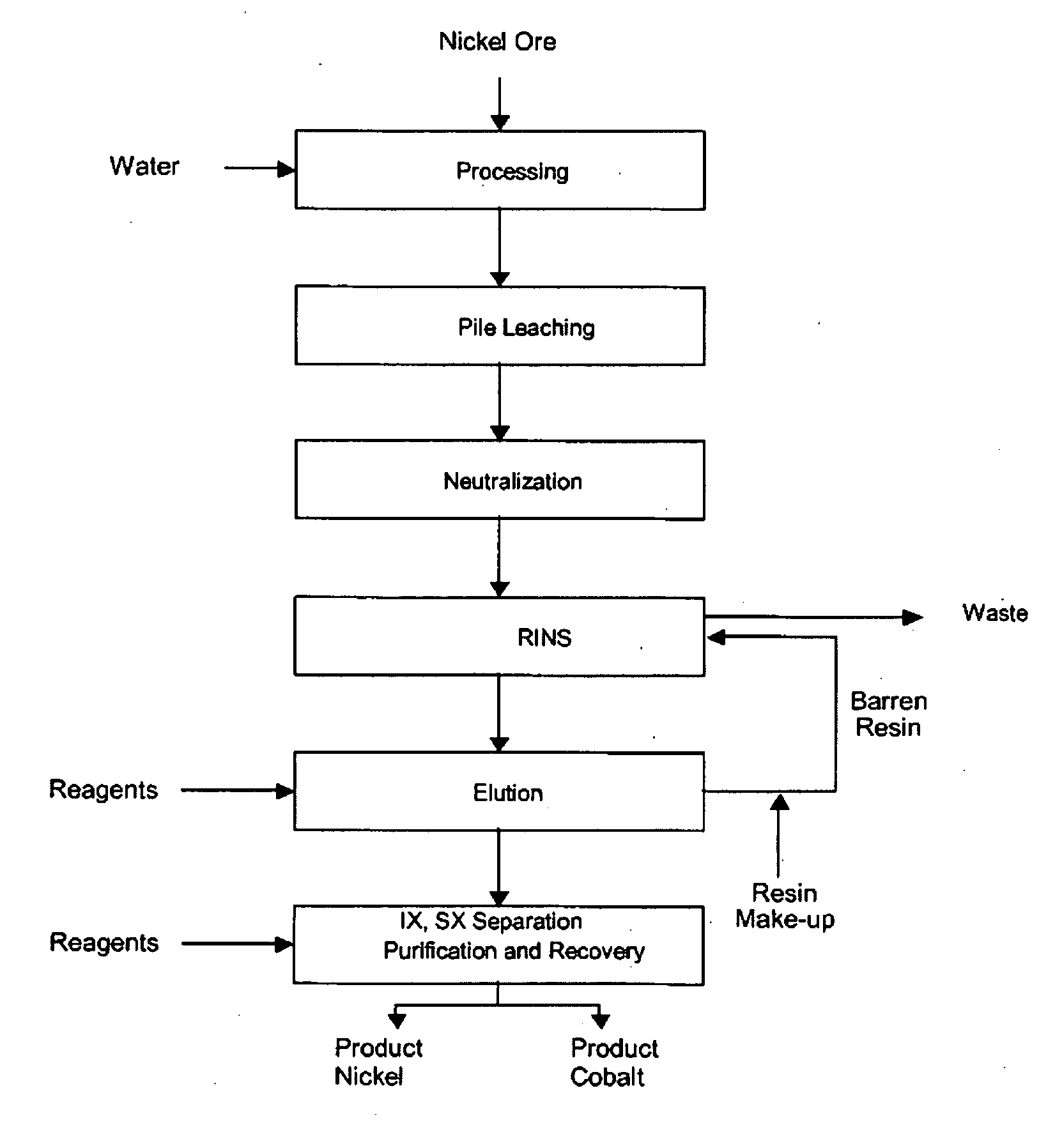
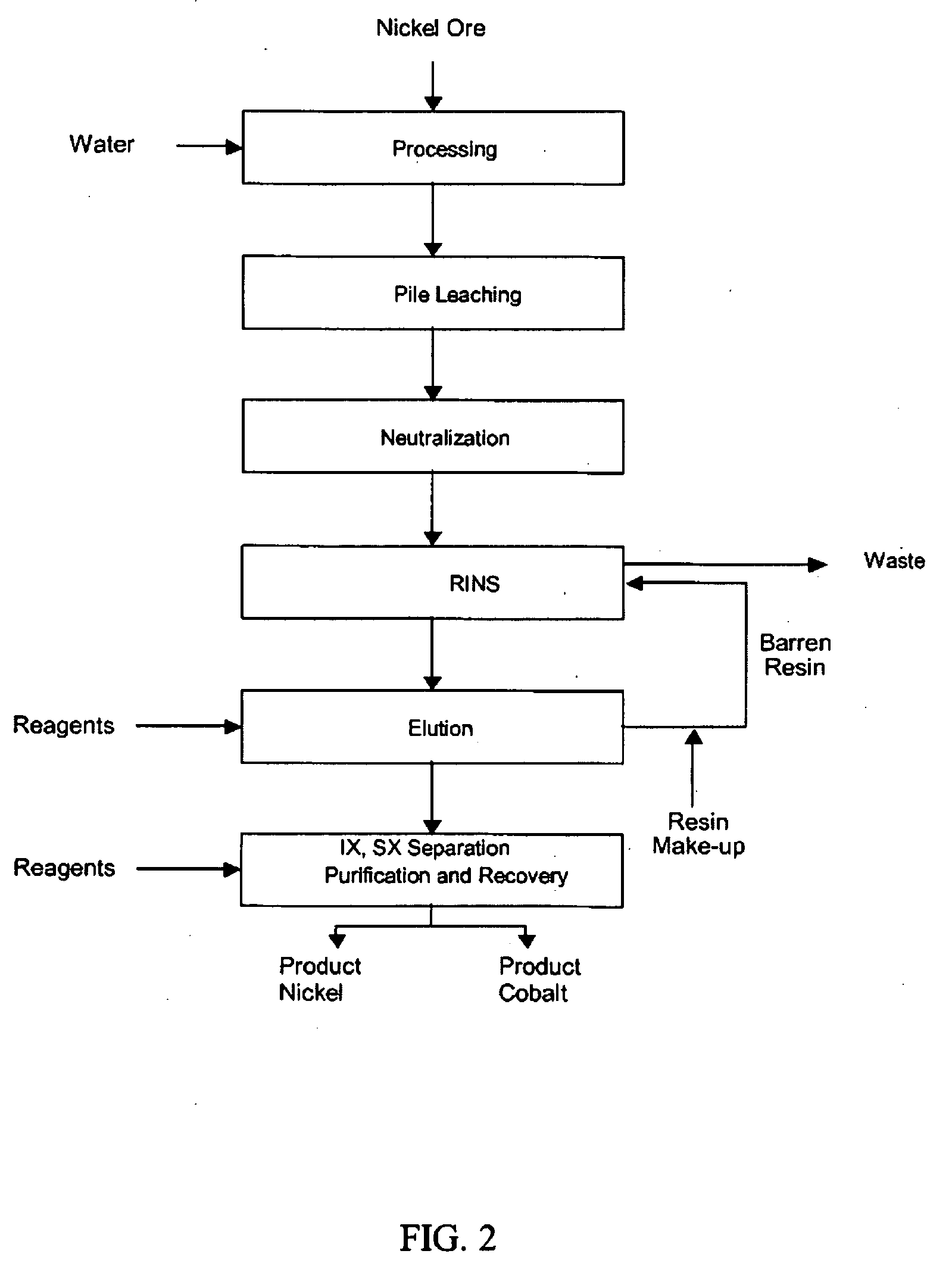
[0062]The present invention refers to a hydro-metallurgical process using resin-in-neutralized-solution of a heap leaching effluent. It provides the following advantages:
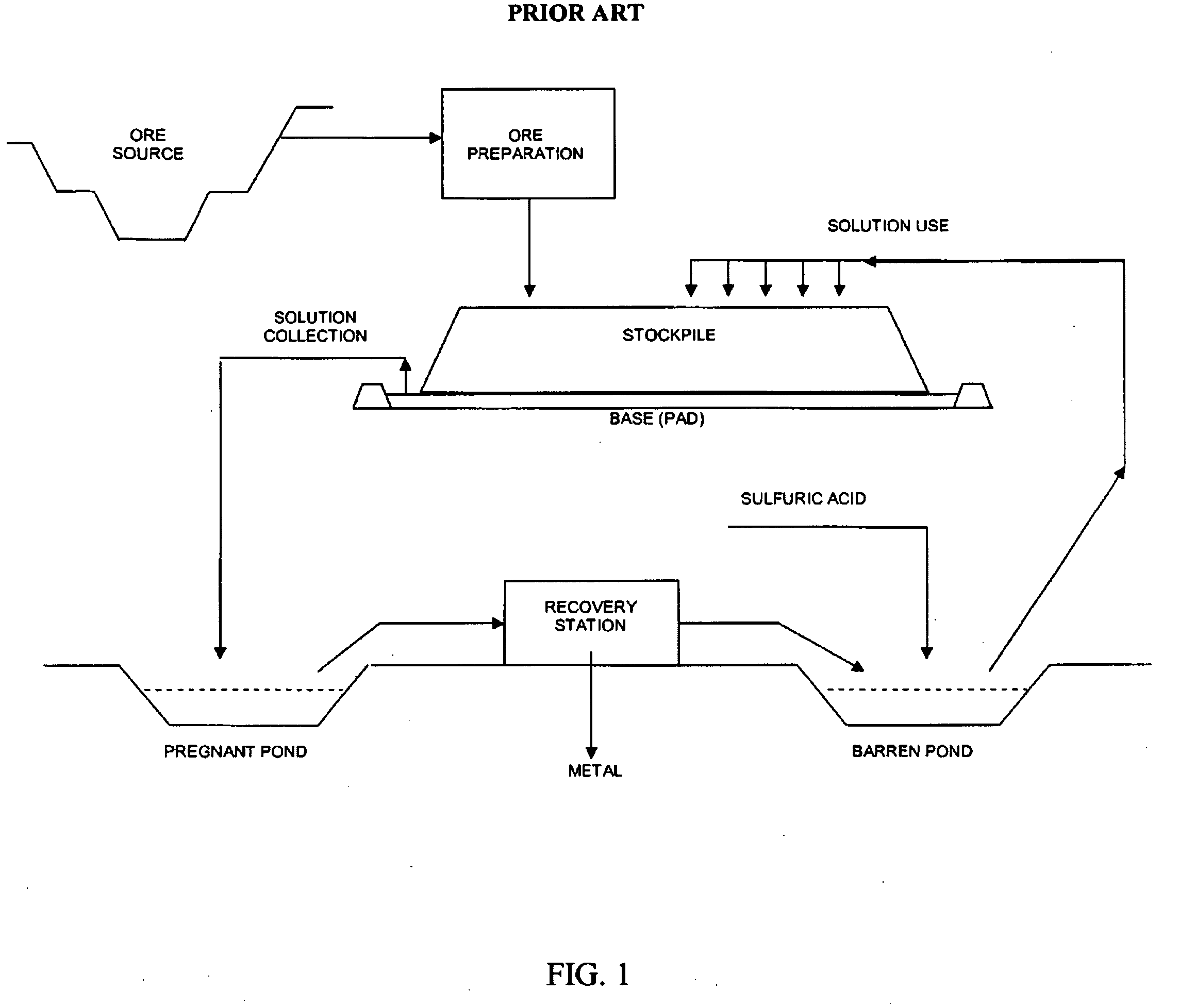
[0063]Ore leaching is preferably acid, with an option to use sulfuric or hydrochloric acid. The pregnant leaching solution (“PLS”) coming from the pile should have free acidity preferably between 02 and 200 grams per litre. One such technology is heap leaching. Downsides are less nickel recovery efficiency and higher operating cost (due to greater acid consumption). However, lower investment cost makes it a highly attractive technical alternative. Leaching yields an impurity-bearing solution and highly concentrated with metals of interest. However, neutralization is necessary to adjust this solution's pH, complying with RINS operational standards. That demands neutralizing excessive leaching effluent acid, in addition to precipitating iron and some impurities. Temperature in this stage should be in the 70° C.−95° C....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com