Rotor of brushless direct-current motor
a brushless direct-current, motor technology, applied in the direction of dynamo-electric machines, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuit shape/form/construction, etc., can solve the problem of unavoidable transfer of electromagnetic vibration noise of rotating magnetic field, resonance noise, cogging torque vibration due to interaction with armature core,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030]Reference will now be made in detail to the embodiments, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings, wherein like reference numerals refer to the like elements throughout. The embodiments are described below by referring to the figures.
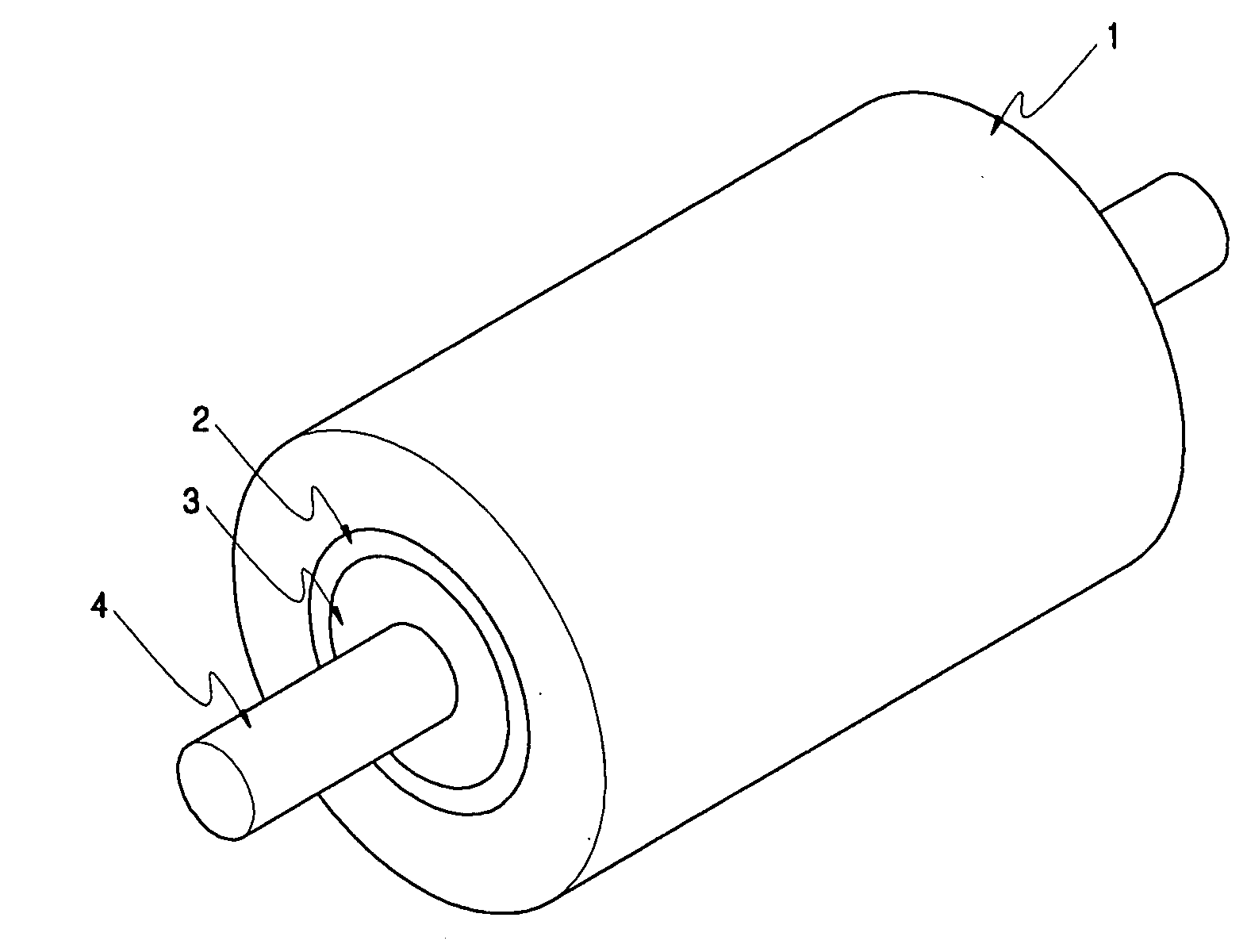
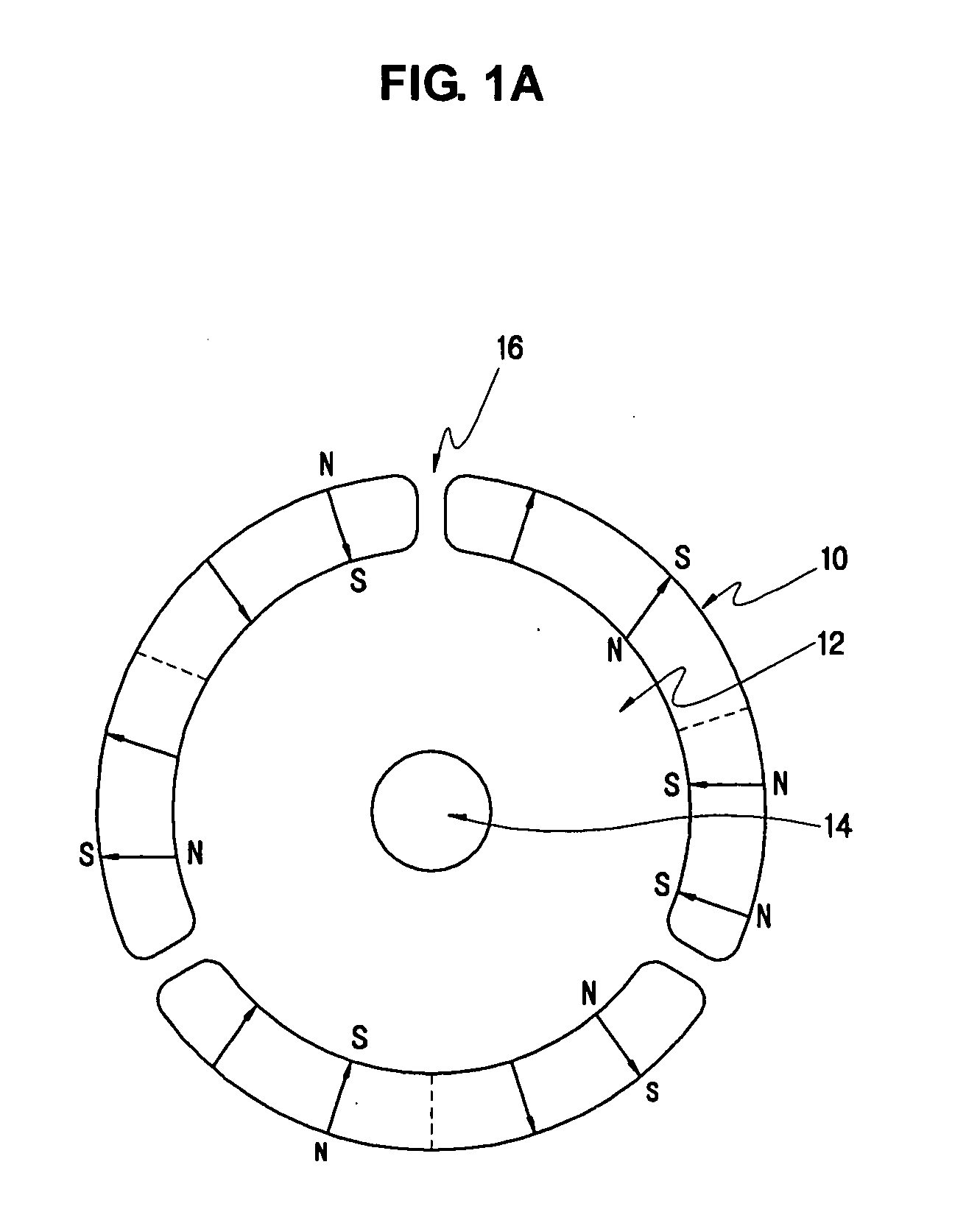
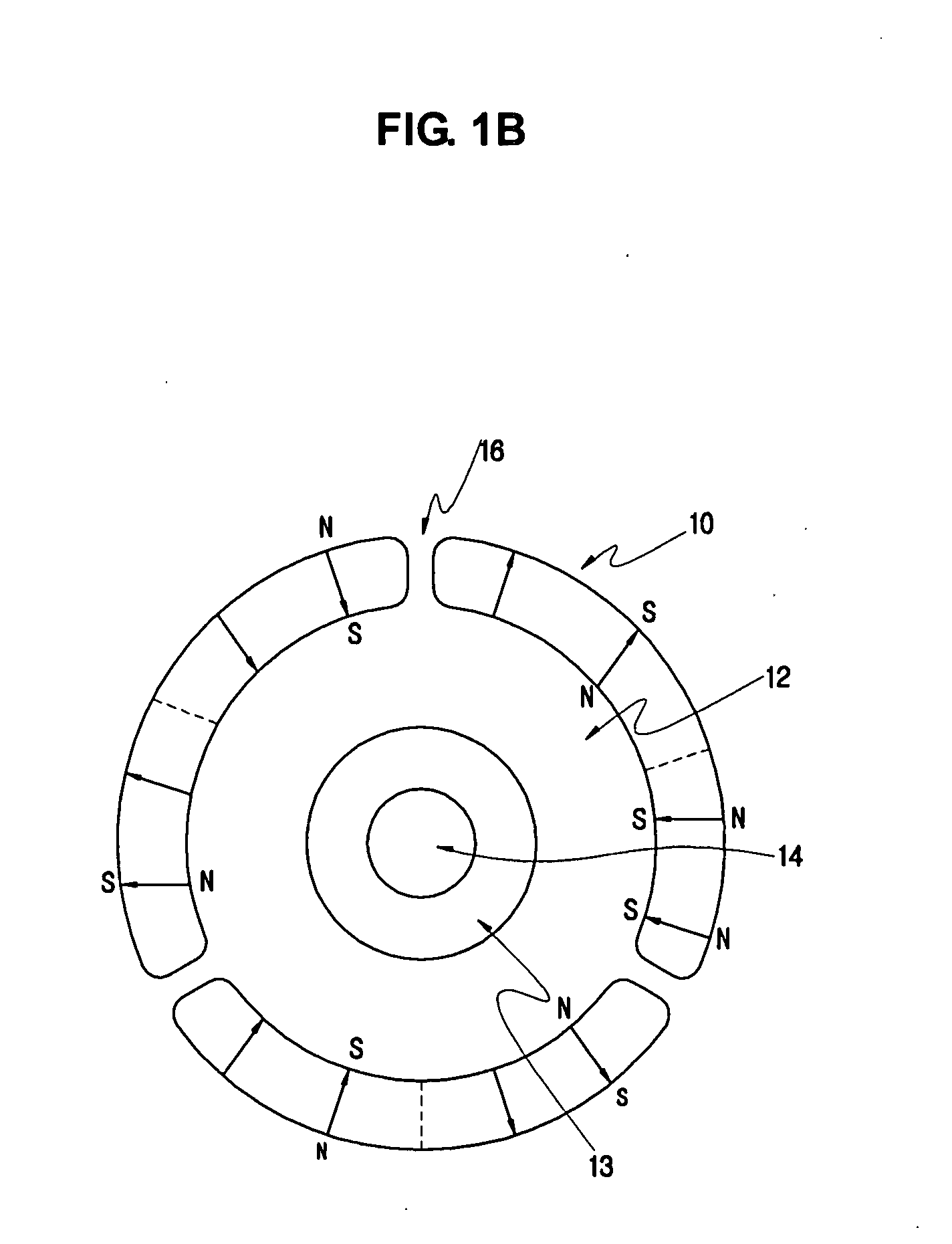
[0031]FIG. 3 illustrates the structure of a rotor of a BLDC motor. As illustrated in FIG. 3, the rotor includes a cylindrical permanent magnet 1 and a cylindrical high-strength core portion 2 made of aluminum having a very low thermal expansion coefficient, alloy, or high-strength engineering plastic, which is adhered to the inner circumferential portion of the permanent magnet 1.
[0032]It is preferable that in an embodiment the thickness of the high-strength core portion 2 can be 40-100% of that of the permanent magnet 1.
[0033]In the rotor of an embodiment, the cylindrical high-strength core portion 2 is inserted and adhered to an inner circumferential portion of the polar anisotropic permanent magnet 1, a sound-absorbing res...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com