Thermal stud or plate for building wall
a technology of thermal insulation plate and building wall, which is applied in the direction of walls, towers, constructions, etc., can solve the problems of warping after installation, increasing the cost of wood-frame buildings, and being susceptible to termites and insect damage, so as to achieve the effect of increasing the thermal insulation valu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
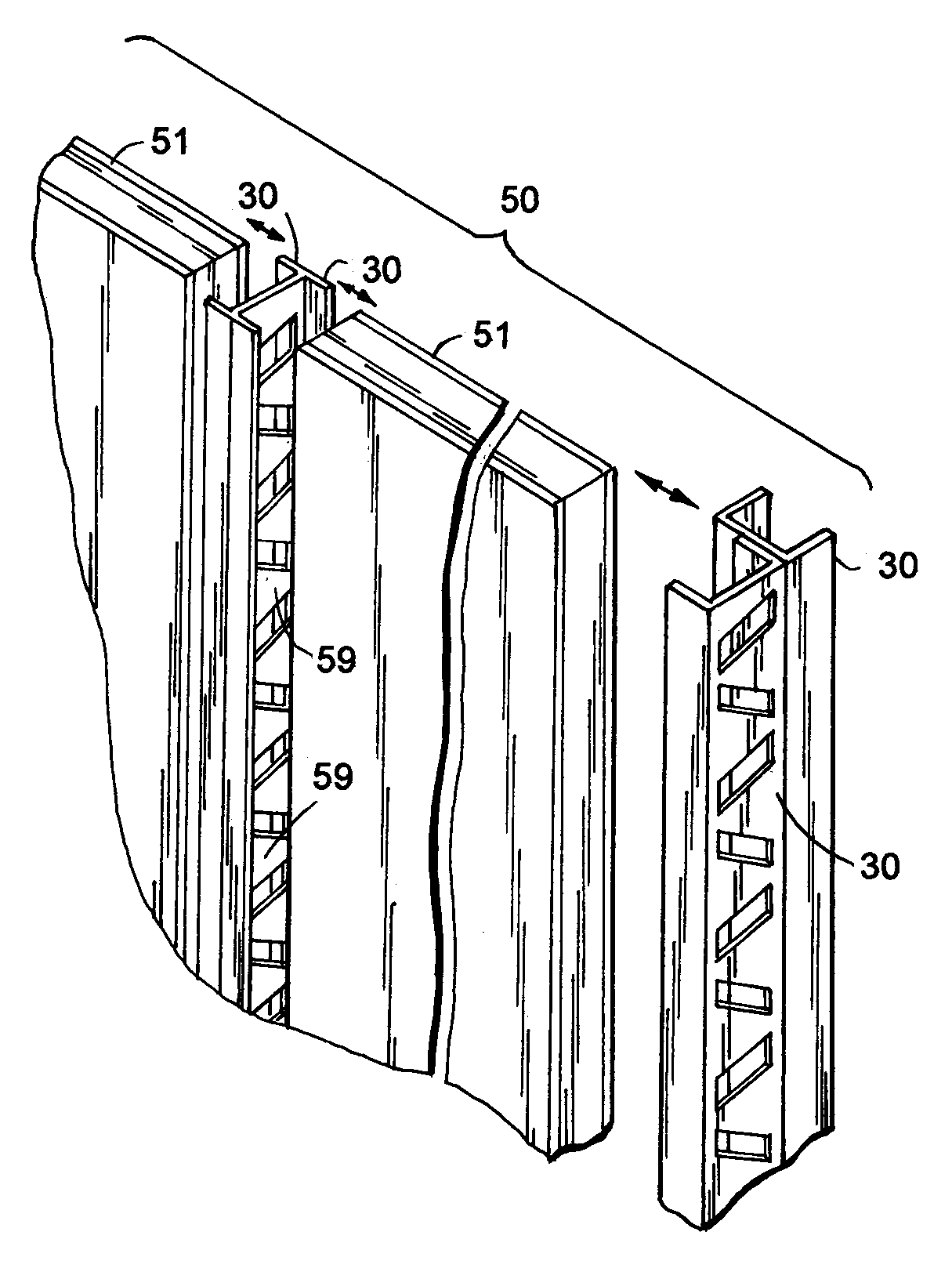
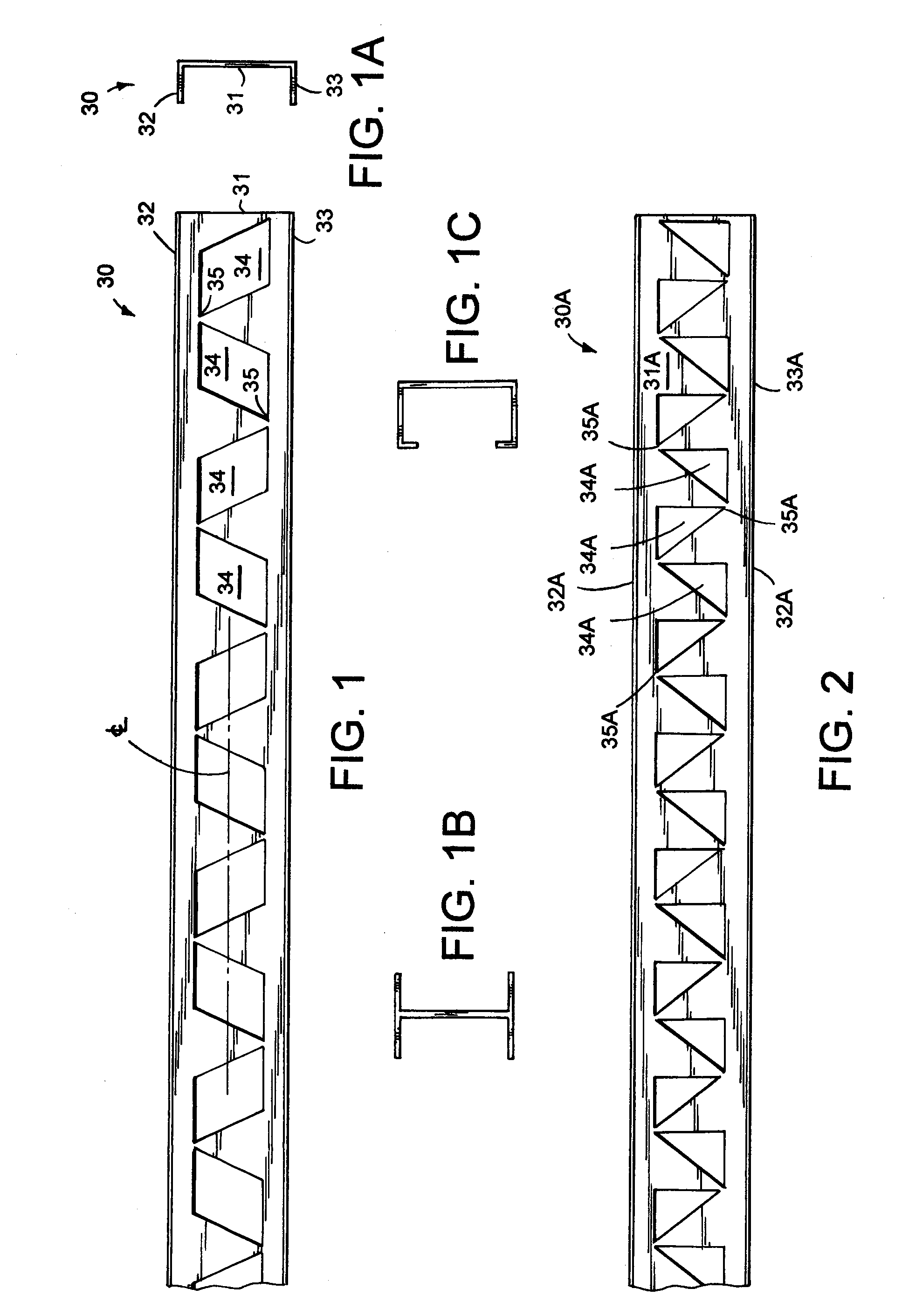
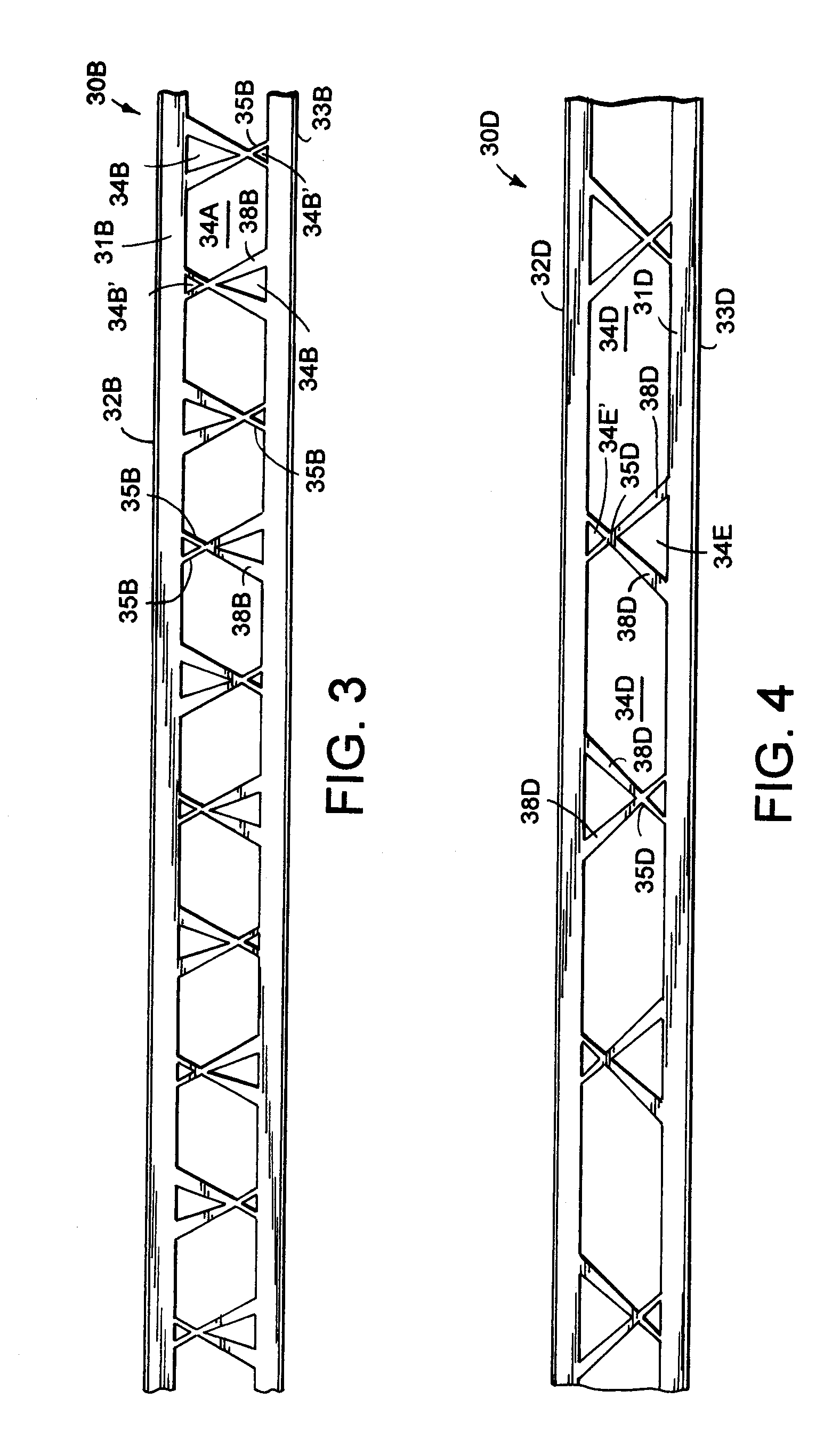
[0021]The present metal thermal structural component for buildings (also called a “beam” or “stud” or “plate” herein) includes apertures (i.e. cut-outs) in its center web configured to minimize thermal transfer laterally across the stud while still maximizing a strength of the center web and of the stud. It is contemplated that the discussion regarding one illustrated product, such as studs 30-30D (FIG. 1), applies equally to other products, such as plates 60, 60A, 61, 61A (FIGS. 6-7). The thermal structural components are preferably made of metal, such as steel or aluminum, and are preferably galvanized or coated for corrosion resistance. They have a center web with geometrically-shaped apertures spaced longitudinally along its centerline CL, the apertures being shaped to define alternatingly-positioned narrow necks of material therebetween near flange-adjacent ends of the center web. The narrow necks minimize thermal conductivity between the spaced flanges, but adjacent ones of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com