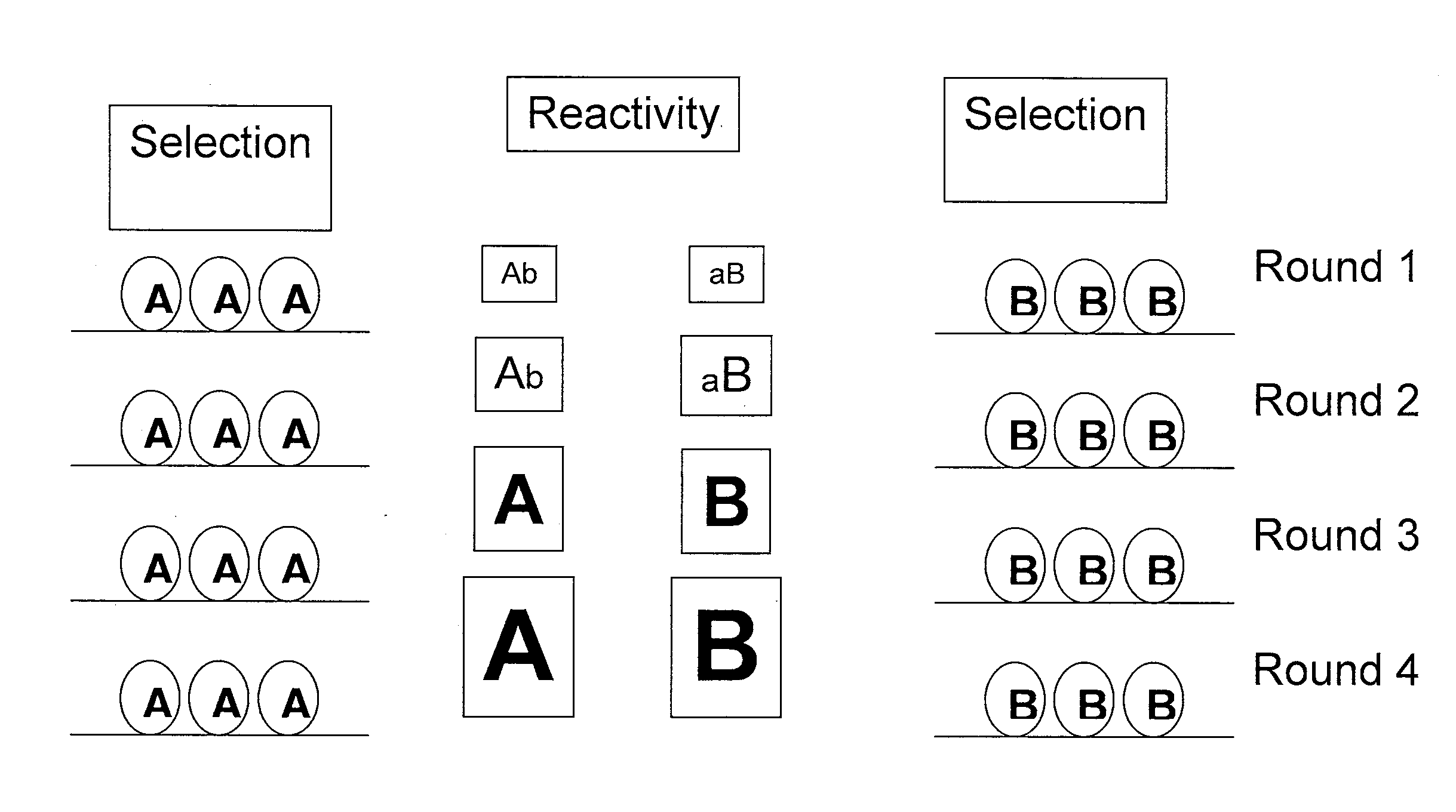
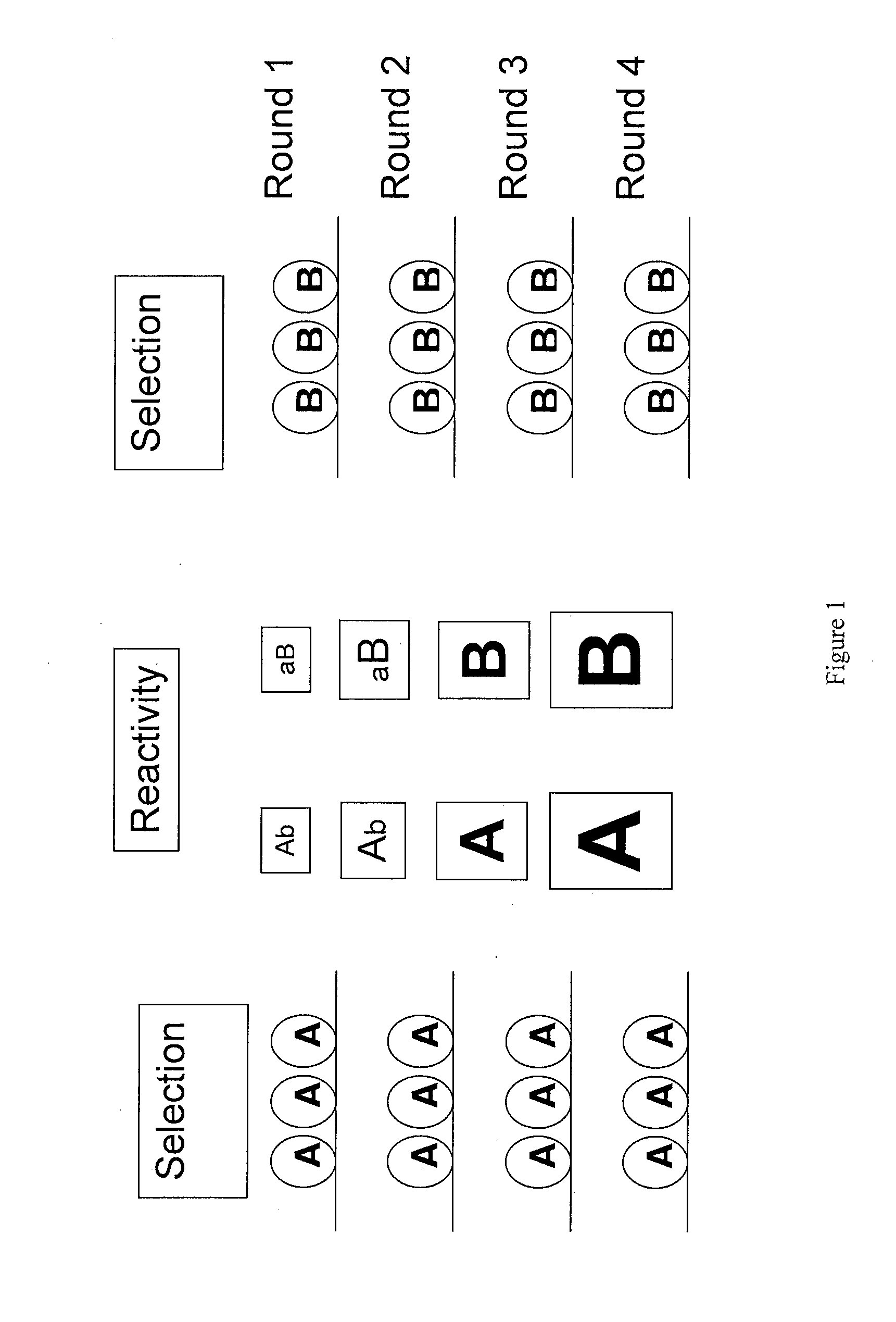
Neutralizing antibodies to influenza viruses
a technology of neutralizing antibodies and influenza viruses, applied in the field of neutralizing antibodies to influenza viruses, can solve problems such as molecules not being able to react with hemagglutination, and achieve the effect of not inhibiting hemagglutination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Antibody Libraries from Survivors of Prior Bird Flu Outbreaks and Preparation of Neutralizing Antibodies
[0252]The widespread incidence of H5N1 influenza viruses in bird populations poses risks to human health. Even though the virus has not yet adapted for facile transmission between humans, it can cause severe disease and often death. Here we report the generation of combinatorial antibody libraries from the bone marrow of five survivors of the recent H5N1 avian influenza outbreak in Turkey. To date, these libraries have yielded >300 unique antibodies against H5N1 viral antigens. Amongst these antibodies, we have identified several broadly reactive neutralizing antibodies that could be used for passive immunization against H5N1 virus or as guides for vaccine design. The large number of antibodies obtained from these survivors provides a detailed immunochemical analysis of individual human solutions to virus neutralization in the setting of an actual virulent influenza outbreak. Rema...
example 2
Generating Universal Influenza Vaccines
[0321]The goal of vaccine design against heterogeneous pathogens is to identify and design effective and broadly protective antigens. In the case of influenza, considerable historical efforts have gone into the empirical testing of conserved linear sequences and regions with little success. A plausible reason for these failures is a lack of knowledge that focused responses against antigenic test articles are actual bona fide productive sites for neutralization of an antigen on the pathogen in the setting of an actual infection. For influenza one would be expect to find these bona fide solutions within the repertoires of survivors of an influenza infection. In our case we have demonstrated that several related antibodies amongst a large collection of antibodies, derived from an H5N1 influenza survivor, (see Table 4 above) are capable of broadly neutralizing several subtypes of Influenza. These antibodies neutralize influenza through a novel mech...
example 3
Increasing the Potency and Spectrum of Cross Subtype Neutralizing Antibodies
[0340]As mentioned previously, the group of cross subtype neutralizing antibodies that are partially represented by Ab-1, 2, & 3 contain very distinct and seemingly requisite heavy chain mutations within CDR2 and framework 3 (FR3), yet remarkably little to no diversity within CDR3. Considering the shear number of clones that were identified with these hallmark sequences, all of which were restricted to a 1-e, or 1-e like frameworks, leads one to suspect that this broad spectrum activity is principally driven by the this specific heavy chain framework and the CDR2 and Framework 3 (FR3) mutations. Recently, two groups have confirmed this at a structural level by analyzing co-crystals of hemagglutinin and other broad spectrum antibodies that utilize the 1-e like, 1-69 germline framework (Kashyap et al. supra; Throsby et al., PLoS ONE 3(12): e3942). In each instance the predominant binding was driven by CDR2 and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com