System for preventing gear hopout in a tooth clutch in a vehicle transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
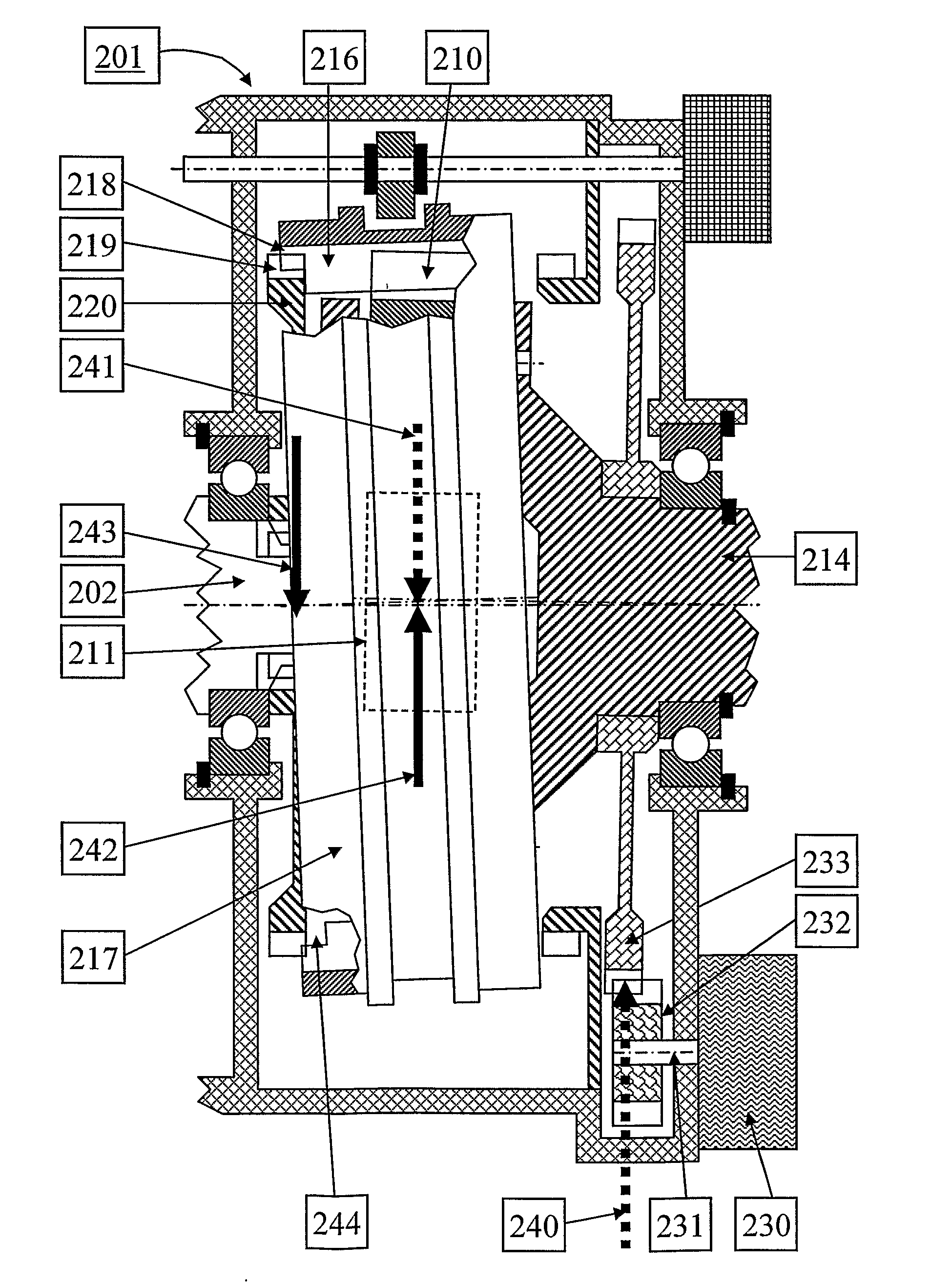
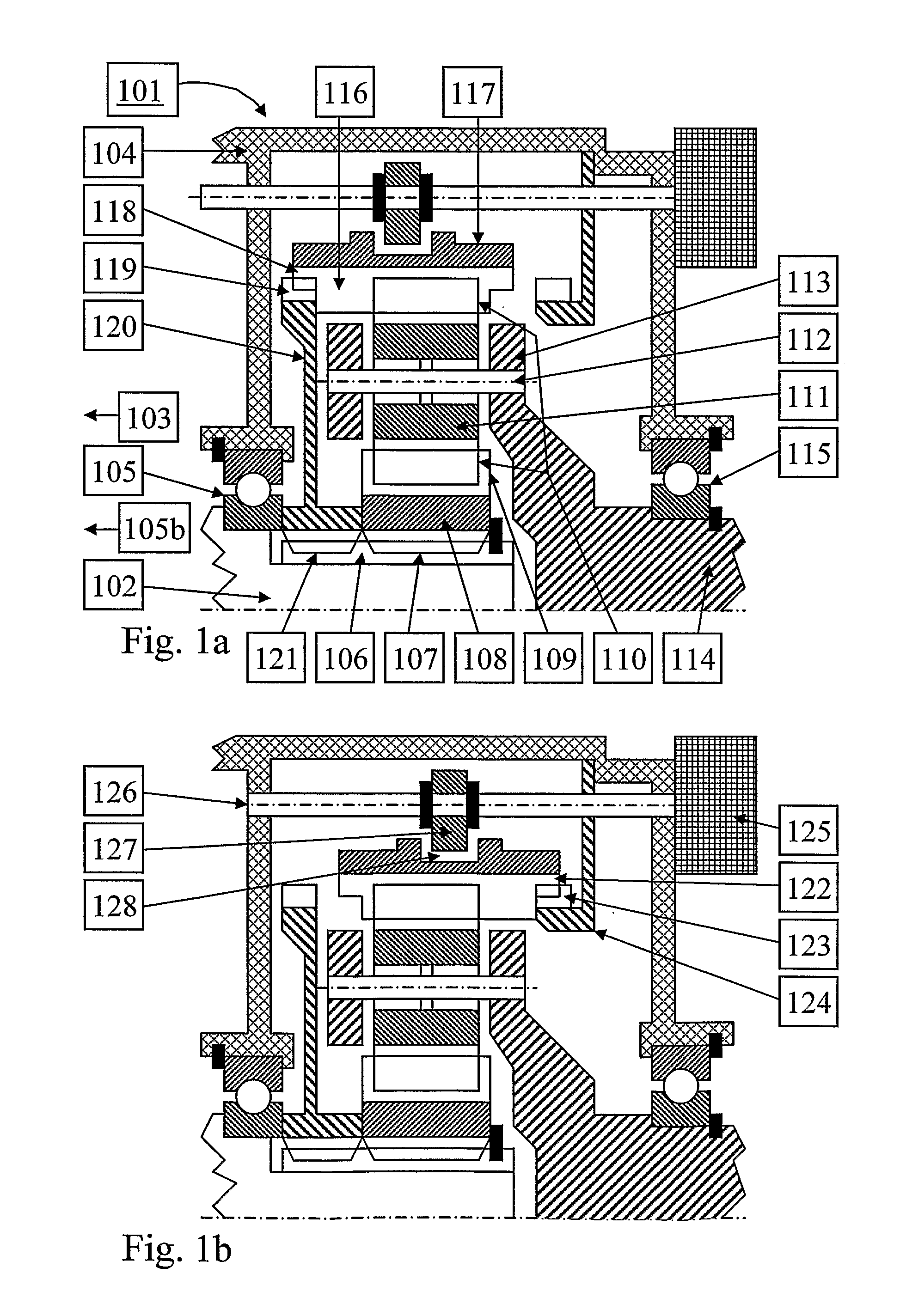
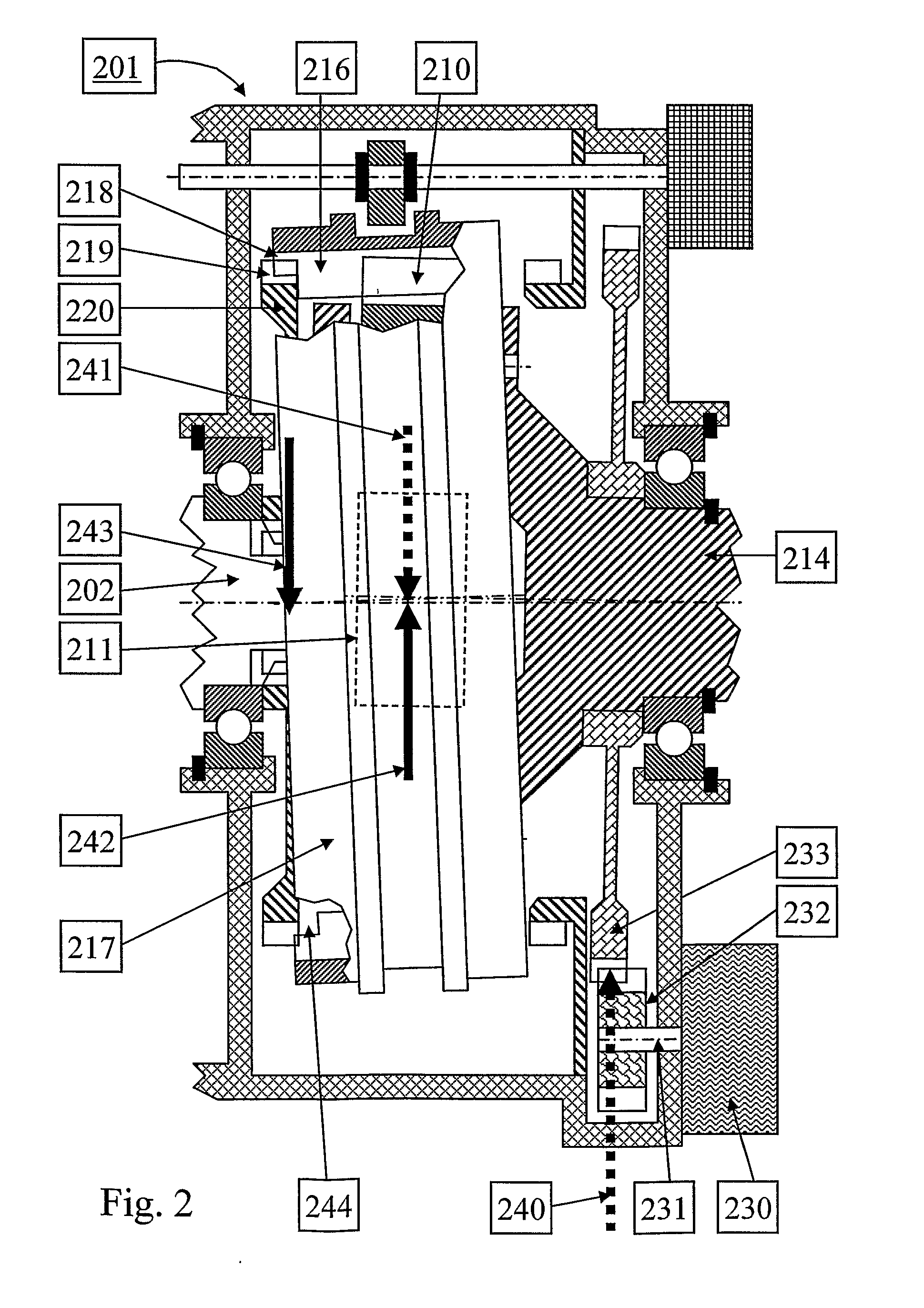
[0037]When studying FIG. 3 and FIG. 4 it can be noted that the misalignment of the engaging sleeve 351 will lead to a varying degree of engagement along the periphery with the clutch teeth of the second gearwheel 354. The lowest degree of engagement is where the axial gap 365 is largest. During rotation, this varying degree of engagement will require a relative motion between the clutch and spline teeth in contact of the engaging sleeve 351, input shaft 352 and second gearwheel 354. In order to prevent gear hopout, it is vital that this relative motion takes place. Thereby, friction will occur between the teeth in contact. In FIG. 4, the friction component of the sleeve clutch force 363 is referred to as 363f. Similarly, the friction component of the sleeve spline force 364 is referred to as 364f. In order to enable the relative motion between the contacting teeth, substantially the parallel component 363p of the sleeve clutch force 363 must be larger than the sum of the friction fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com