Low-loss cryostat configuration
a cryostat and low-loss technology, applied in the field of cryostat configuration, can solve the problems of reducing the interval between helium refills, achieving the effect of superconducting short-circuited operation, and producing high magnetic field in short-circuited
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
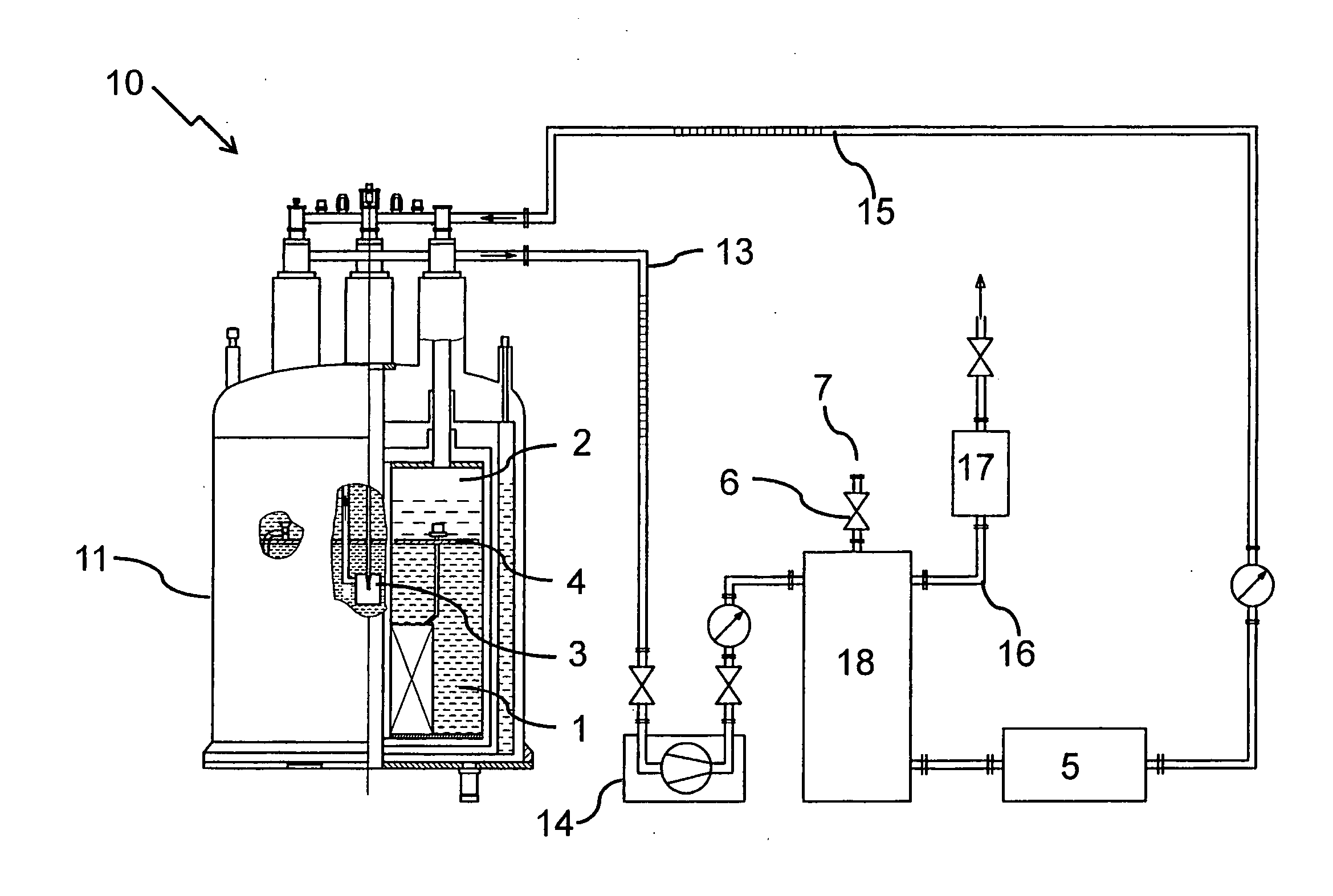
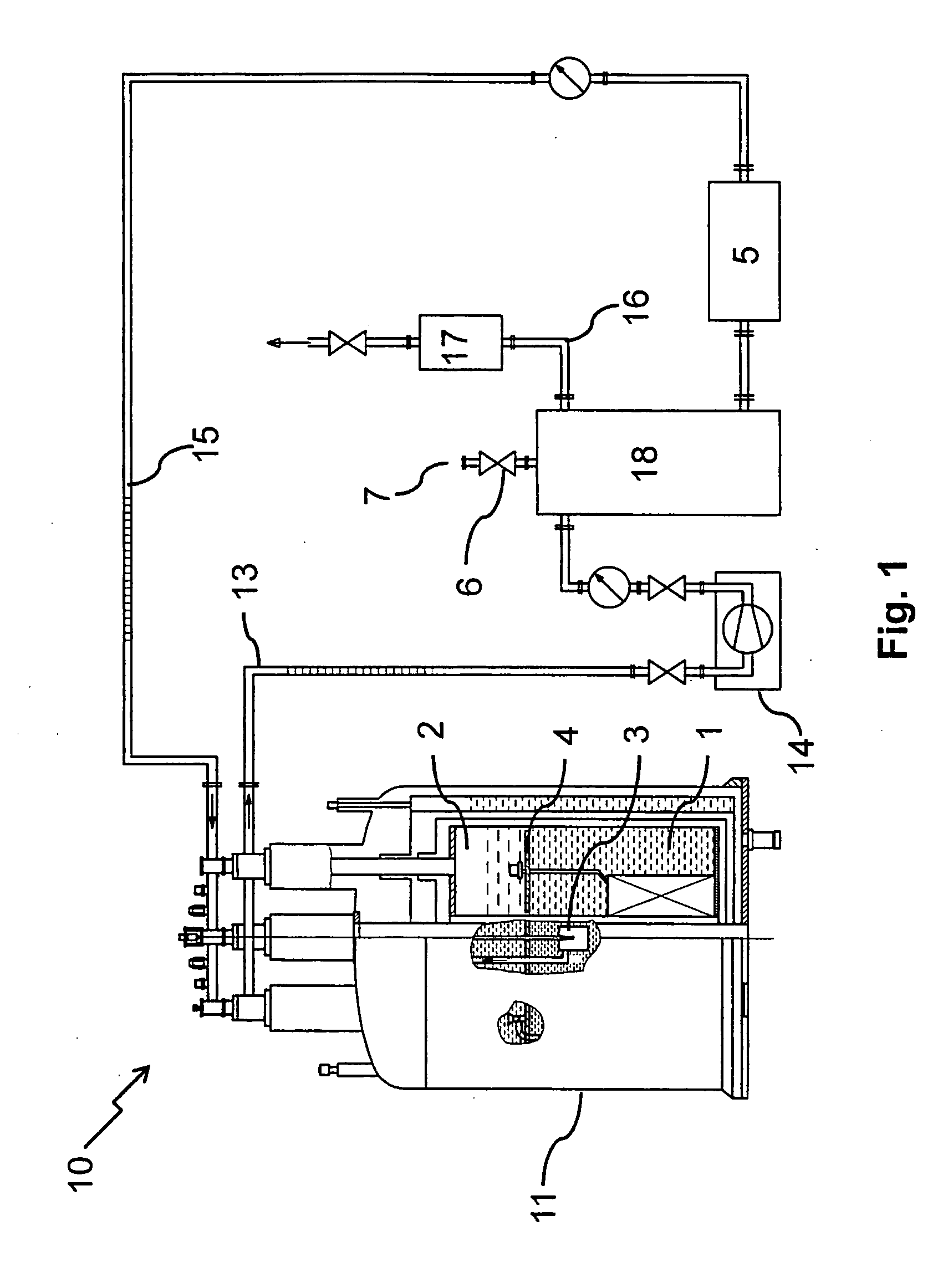
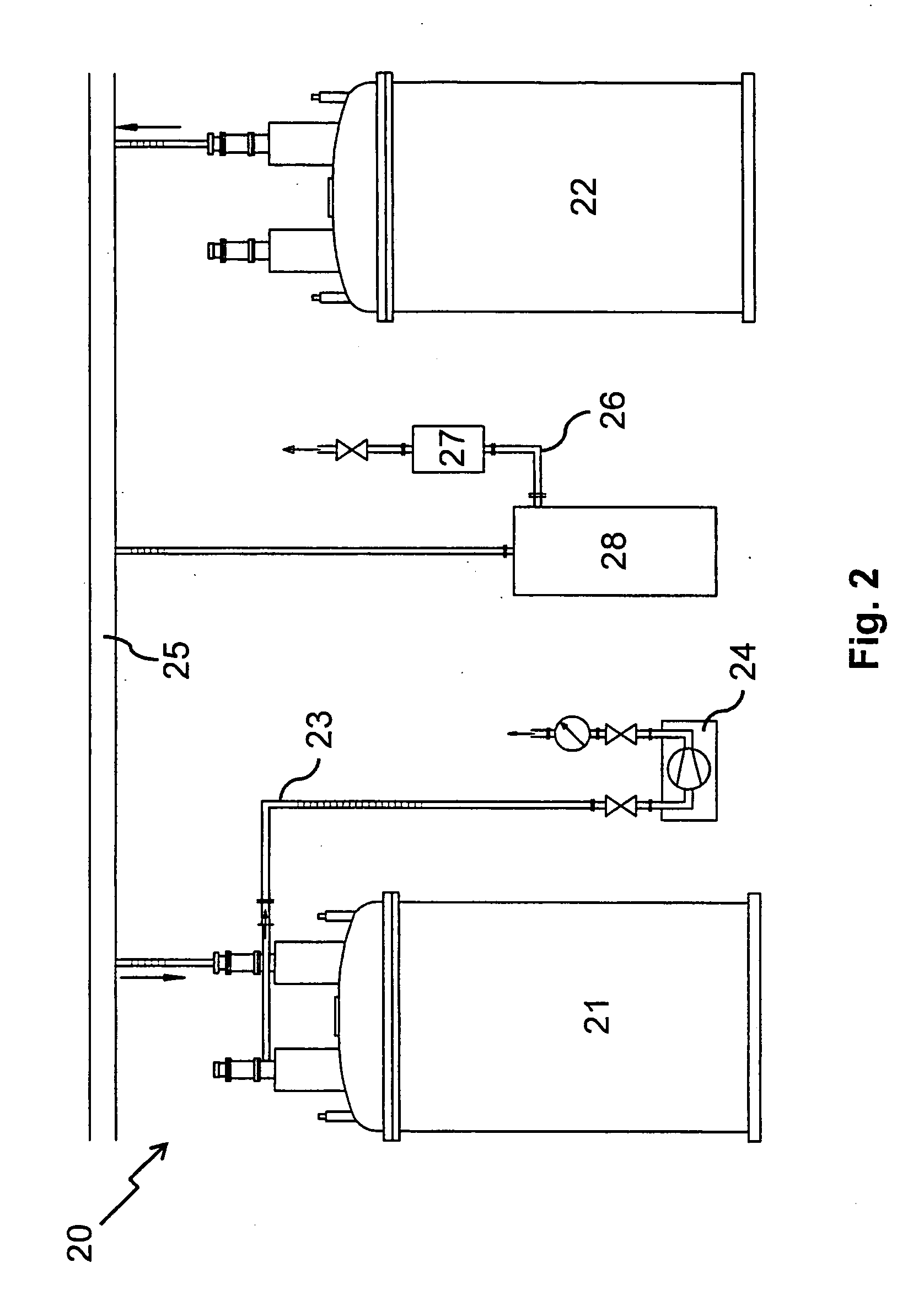
[0048]FIG. 1 shows an embodiment of an inventive cryostat configuration 10 with one cryostat 11 with supercooled helium. The cryostat 11 consists of a first chamber 1 with supercooled helium (temperature 2 with liquid helium (temperature approx. 4.2 K), that are separated by a thermally insulating barrier 4. In the first chamber 1, a Joule-Thomson valve 3 is disposed through which the helium can expand from the further chamber 2 into the pump-off pipe 13, thus supercooling the first chamber 1. The helium is pumped off from the pump-off pipe 13 by a pump 14 and led to a cryogen pipe 15. In the embodiment depicted, the latter comprises a buffer vessel 18 to provide to the helium an additional volume that can serve as a pressure reserve and / or backflow reserve. A relief valve 6 with a bursting disk 7 prevents an excessive pressure in the cryogen pipe 15 if the pressure regulating device 17 of the branch-off device 16 fails or if the pressure cannot be kept constant for any other reason...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com