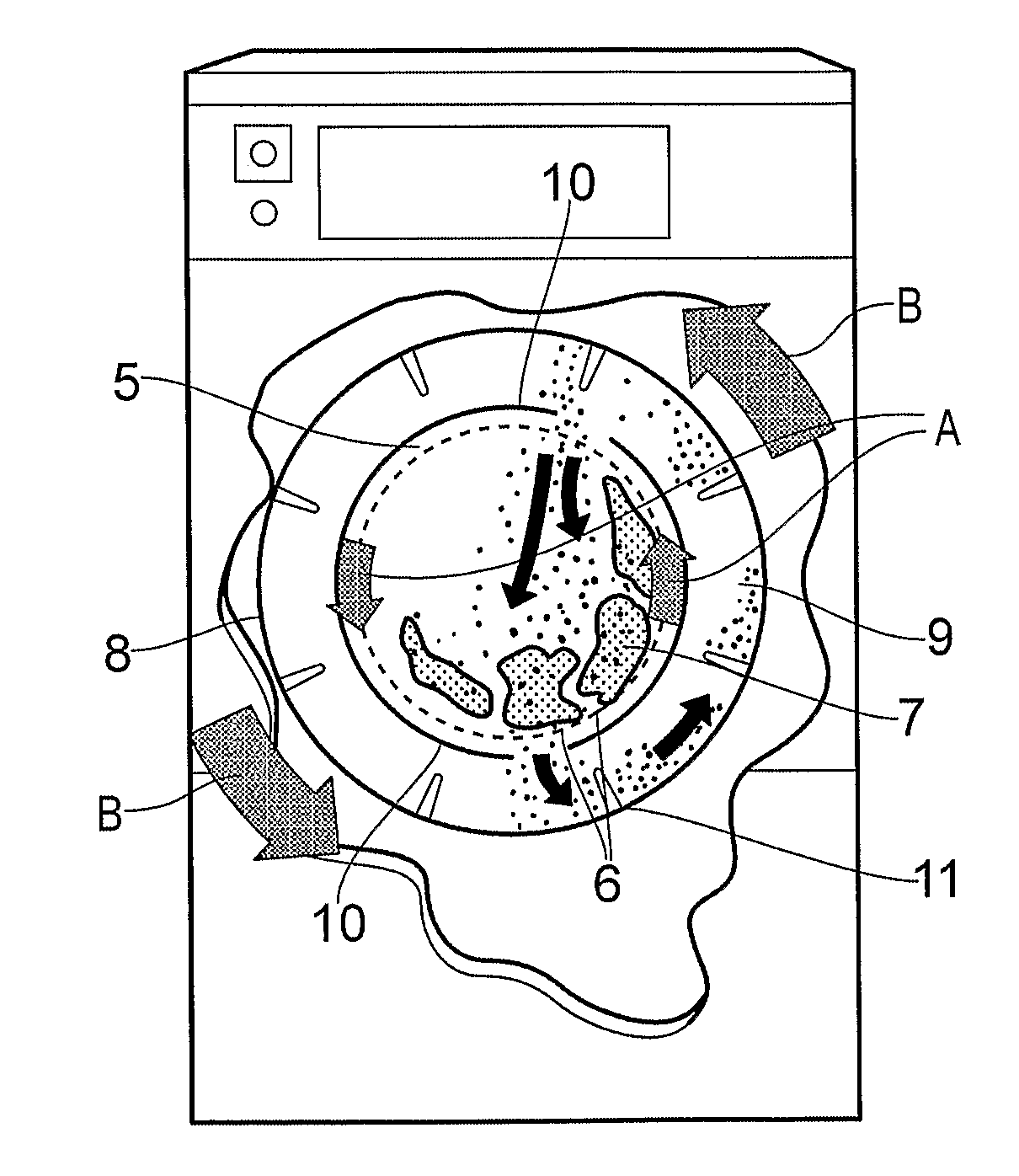
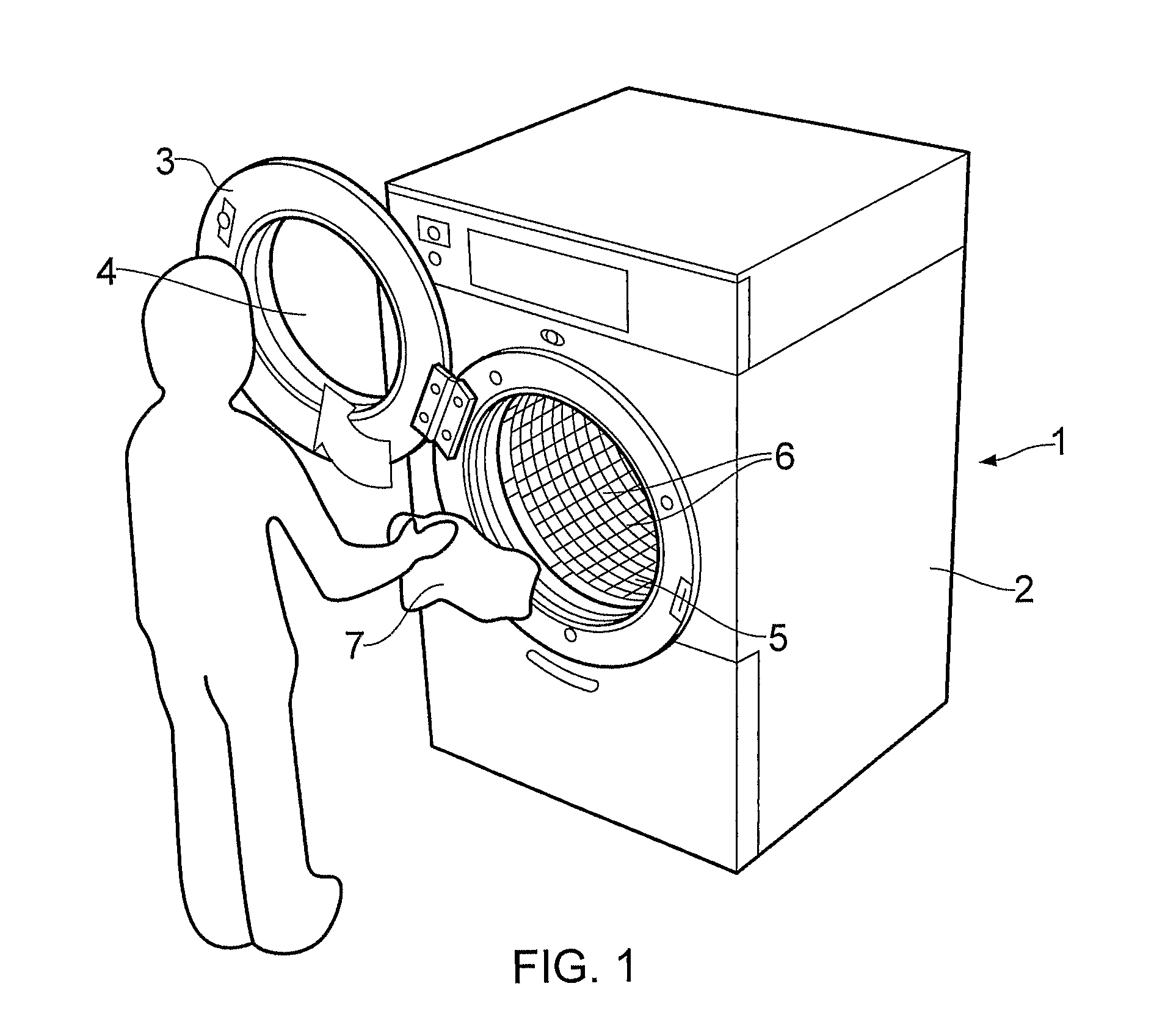
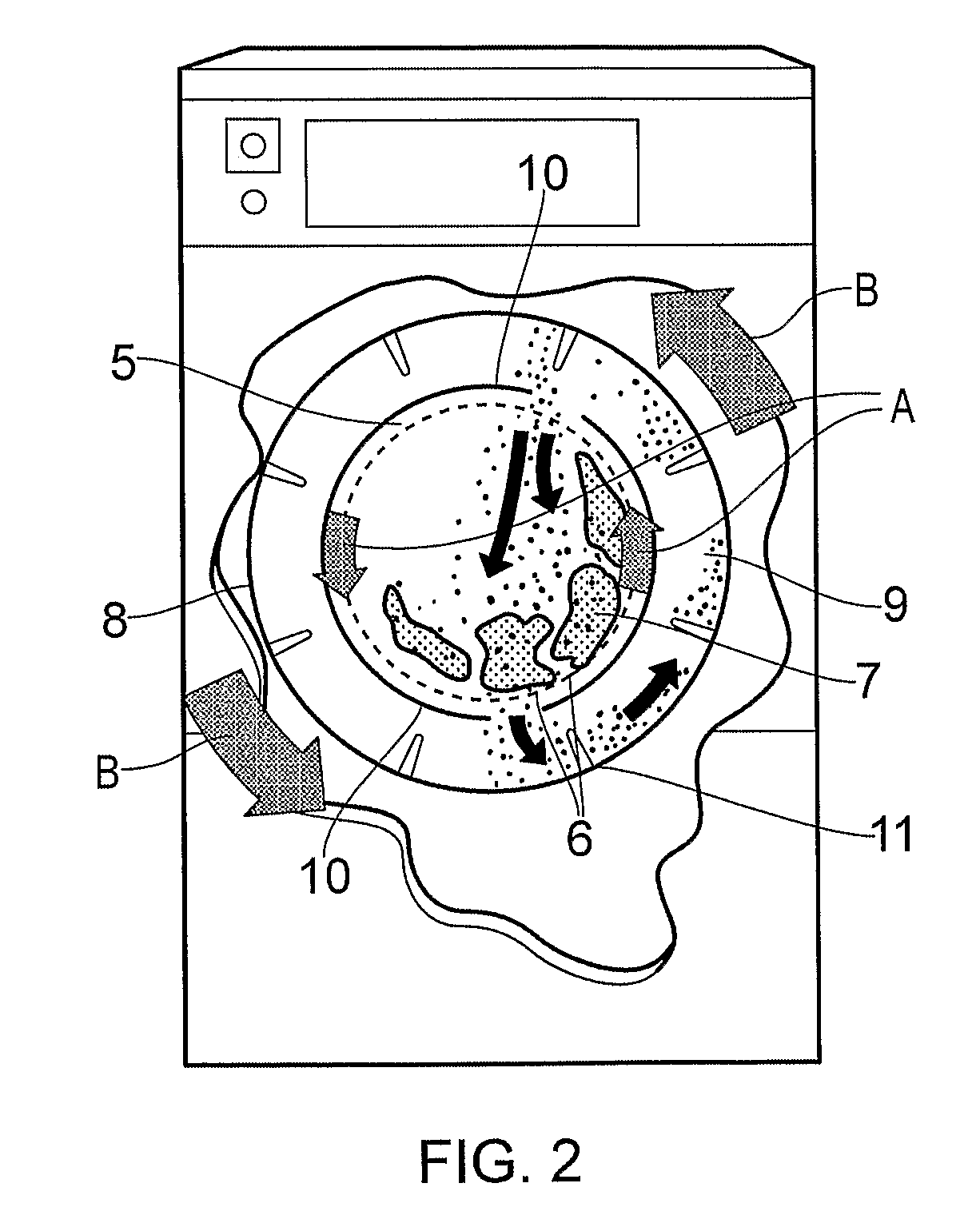
Cleaning Apparatus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0073]The polymer particles comprised cylindrical nylon chips comprising Nylon 6,6 polymer having a molecular weight in the region of 15000-16000 Daltons, with average dimensions of 4 mm in length and 2-3 mm in diameter, and an average particle weight of 30-40 mg.
[0074]The fabric to be cleaned comprised soiled and stained Nylon 6,6 fibres, and the wetted dyed fabric was loaded into an apparatus according to the invention containing 75 g (air dry mass) of polymer particles. The temperature was raised to 40° C. and maintained at 40° C. for 10 minutes, then increased to 70° C. at a rate of 2° C. per minute, and then maintained at 70° C. for 20 minutes to complete the wash cycle, after which time the cycle for removal of the nylon chips was operated for 5 minutes before the fabric was removed from the apparatus, rinsed and dried. Complete removal of the soiling and staining was achieved and the fabric was found to be free of residual nylon chips.
example 2
[0075]The fabric to be cleaned comprised a soiled cloth of mercerised cotton stained with coffee in an aqueous transport medium. This pre-soiled fabric sample was placed in an apparatus according to the invention containing 75 g (air dry mass) of polymer particles comprising cylindrical chips of Nylon 6,6 polymer, with average dimensions of 4 mm in length and 4 mm in diameter. The pre-soiled fabric sample was wetted with tap water before commencement of cleaning to give a substrate to water ratio of 1:1. The apparatus was operated on the cleaning cycle for 30 minutes to a maximum of 70° C. with a cooling stage at the end of the cycle, then the cycle for removal of the nylon chips was operated for 5 minutes. Once this was complete, the cleaned fabric was removed from the apparatus and dried flat. The degree of staining of the cloth was very significantly reduced following the cleaning process.
example 3
[0076]The fabric to be cleaned comprised a soiled cloth of mercerised cotton stained with city street dirt in an aqueous transport medium. This pre soiled fabric sample was placed in an apparatus according to the invention with 75 g (air dry mass) of polymer particles comprising cylindrical chips of Nylon 6,6 polymer, with average dimensions of 4 mm in length and 4 mm in diameter. The pre-soiled fabric sample was wetted with tap water before commencement of cleaning to give a substrate to water ratio of 1:2. The apparatus was operated on the cleaning cycle for 30 minutes to a maximum of 70° C. with a cooling stage at the end of the cycle, then the cycle for removal of the nylon chips was operated for 5 minutes. Once this was complete, the cleaned fabric was removed from the apparatus and dried flat. A significant reduction in numbers of dirt particles was observed after the cleaning process had taken place.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com