Wave Amplitude Attenuation and Wear Prevention Methods for Non-Wood-Timber Railroad Ties
a non-wood-timber, wave-amplitude attenuation technology, applied in the direction of rail fasteners, railway track construction, ways, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the longevity of the wood tie, increasing the cost of feed stock scarcity, and not being proven effective, so as to reduce the wave amplitude and frequency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
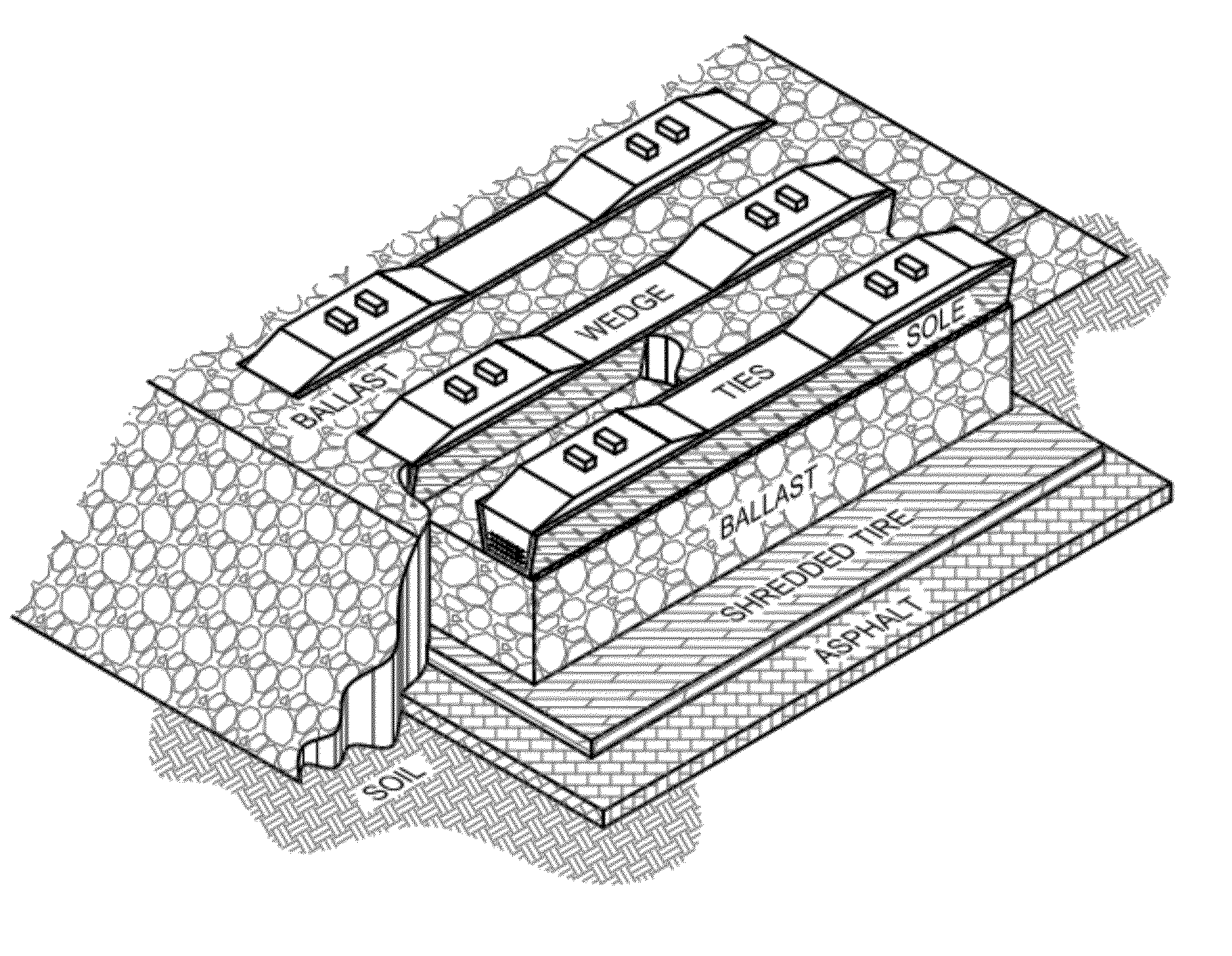
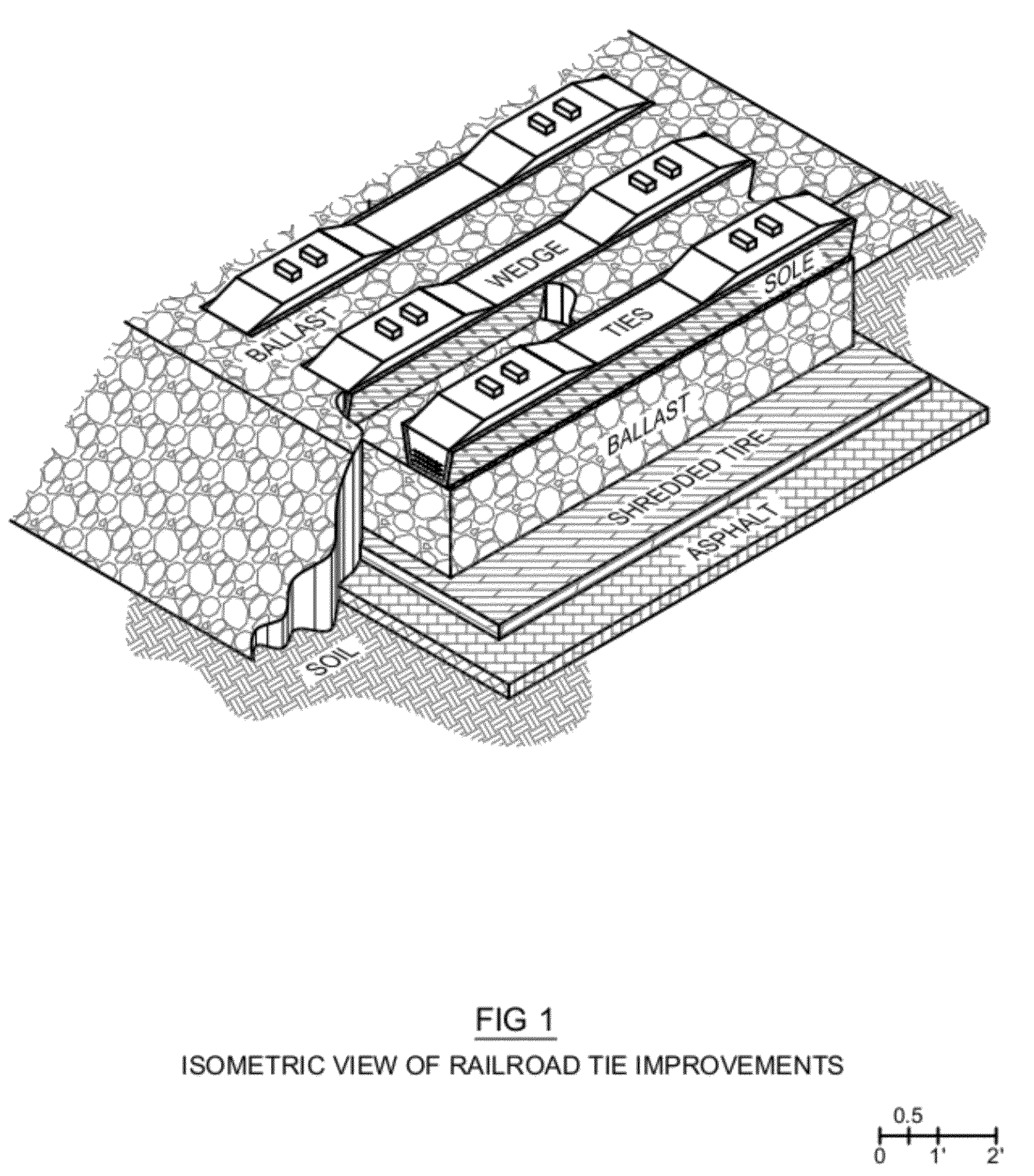
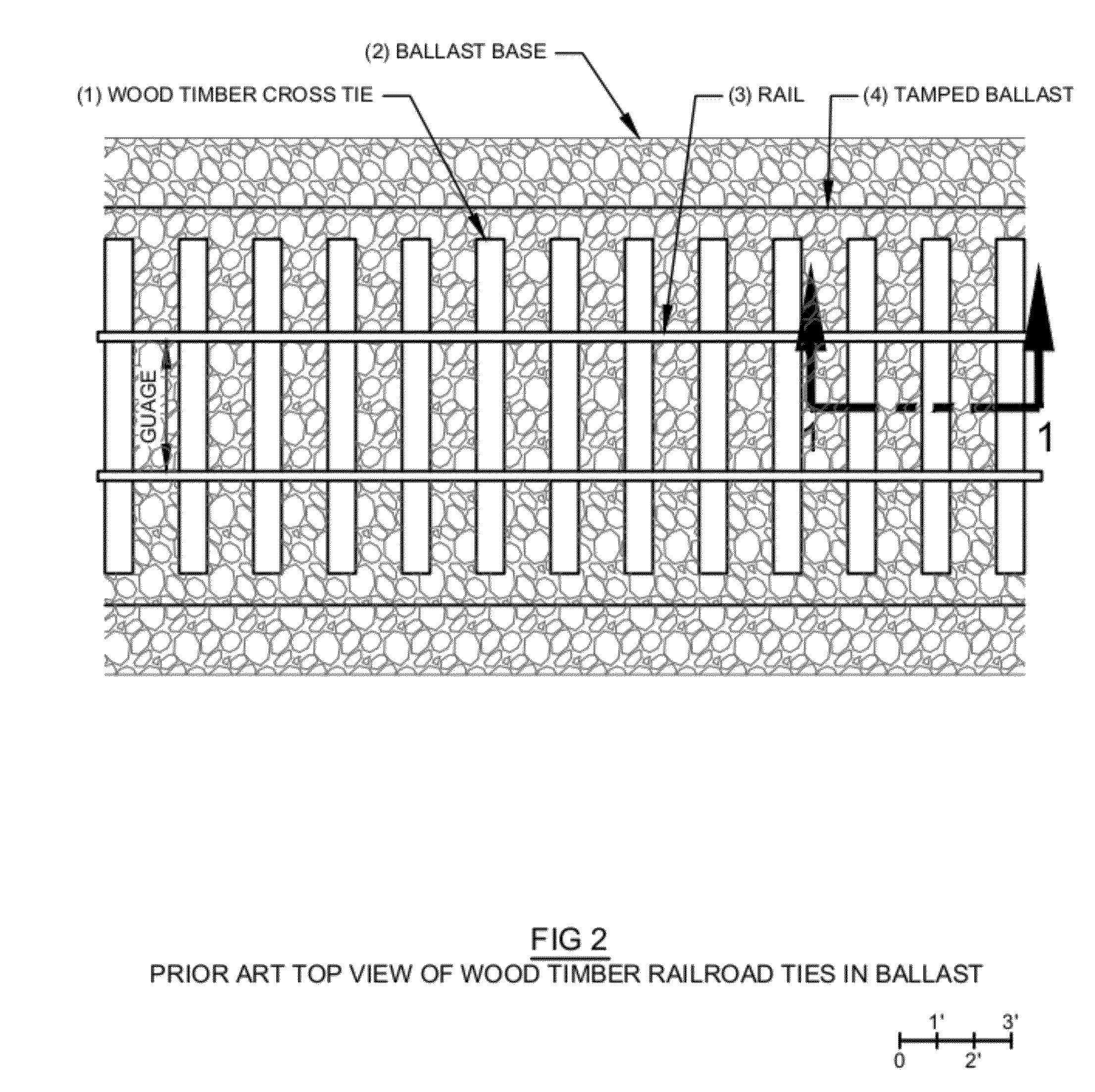
[0067]FIGS. 11, 12 and 22 a geotextile 15 or similar products placed over the soil to distribute forces over larger areas increases railway stability and reduces tie 1,6 pumping.[0068]FIGS. 11, 12, and 22 reclaimed asphalt 14 creates a hardpan where naturally occurring hardpan 5 fails to form under the railway. Asphalt removed from automobile roadways is inexpensive and compacts well to create a hard superficies. Examples of other similar uses are rural driveways and parking lots made of reclaimed asphalt 14 rather than gravel. In a similar manner reclaimed asphalt 14 creates a hardpan for the railway. Reclaimed asphalt may be utilized in both wood timber 1 and NWT railroad tie 6 applications. Reclaimed asphalt 14 applied atop geotextile 15 further increases the hardpan effectiveness, increases railway stability and reduces tie 1,6 pumping.[0069]FIGS. 11, 12, and 22 applied atop the hardpan 5,14 a thin layer of shredded automobile tires pieces 17 attenuate pressure waves created by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com