Composition and method for preparation of organic electronic devices
a technology of electronic devices and organic materials, applied in the direction of sustainable manufacturing/processing, non-metal conductors, final product manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of difficult production of multi-layer devices based on the technology as mentioned above, drawbacks regarding the performance of films formed, and difficult to achieve high-level film forming, performance, lifetime and efficiency of oe devices can be improved, and the effect of high film forming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0216]The substrate (2 cm2 glass plates coated with PEDOT) was activated by heating for 10 minutes at 180° C. and used directly.
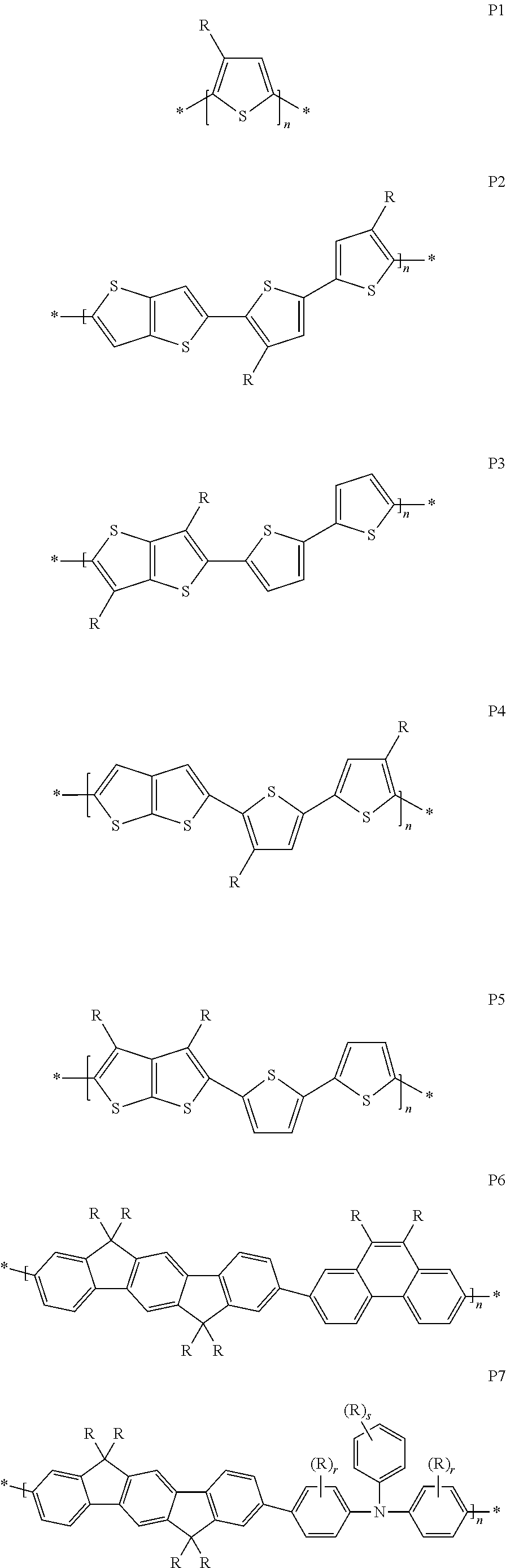
[0217]An OLED polymer ink was formulated by dissolving 0.5% by weight OLED polymer comprising structural units of the following formulae
in a weight ratio of 9% to 11% to 41% to 24% to 5% to 8% to 2% in pentamethylbenzene and gave a viscosity of 3.8 cp at 60° C.
[0218]The ink was printed with the Dimatix DMP 2800 printer (print head heated to 60° C. plus heated glove) onto the substrate. 6 mm squares were printed with a drop spacing of 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 and 40 μm. Drop formation in the ink jet process was good as determined by visualization using a microscope illuminated by a strobe which effectively freezes the droplets in flight.
[0219]After printing the ink on the substrate, further leveling was achieved by heating and cooling the film before removal of the solvent (53° C. for about 20 seconds).
[0220]Thereafter, the solvent was removed on a hot plat...
examples 2 to 4
[0222]Example 1 was repeated. However, 1% OLED polymer as mentioned in Example 1 was dissolved in 2-methylnaphthalene, pentamethylbenzene and 1,5-dimethylnaphthalene by heating the solvent to 80° C., respectively.
[0223]The compositions were processed as described in Example 1. However, the temperature of the leveling step was about 2-5° C. above the melting point of the solvent for approximately 20 seconds and the solvent removal was performed at 100° C.
[0224]Excellent OLED films were formed as observed via a fluorescence method (using a Nikon Eclipse E400 microscope).
example 5
[0225]Example 1 was repeated. However, 1% OLED polymer as mentioned in Example 1 was dissolved in 1,2,4,5-tetramethylbenzene by heating the solvent to 85° C.
[0226]The composition was processed as described in Example 1. However, the temperature of the leveling step was about 88° C. and the solvent removal was performed at 100° C.
[0227]An excellent OLED film was formed as observed via a fluorescence method (using a Nikon Eclipse E400 microscope).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com