Compositions and methods related to antibodies to staphylococcal protein a
a staphylococcal protein and antibody technology, applied in the field of immunology, microbiology, pathology, can solve the problem that the fda approved staphylococcal disease vaccine is currently unavailable, and achieve the effect of reducing activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0256]Monoclonal Antibodies to Staphylococcus Aureus Protein A
[0257]SpAKKAA-mAbs Protect Mice Against Staphylococcal Disease.
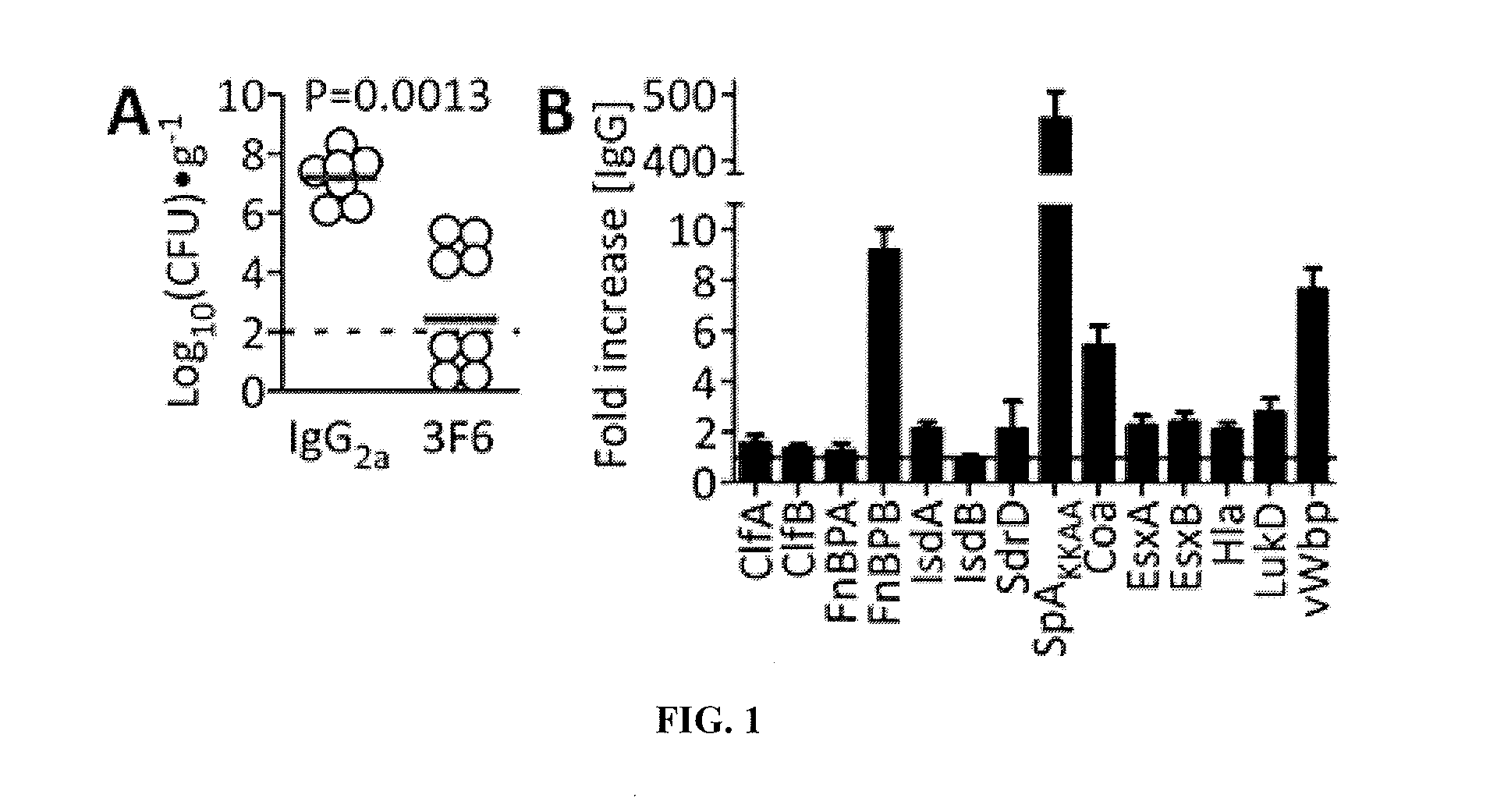
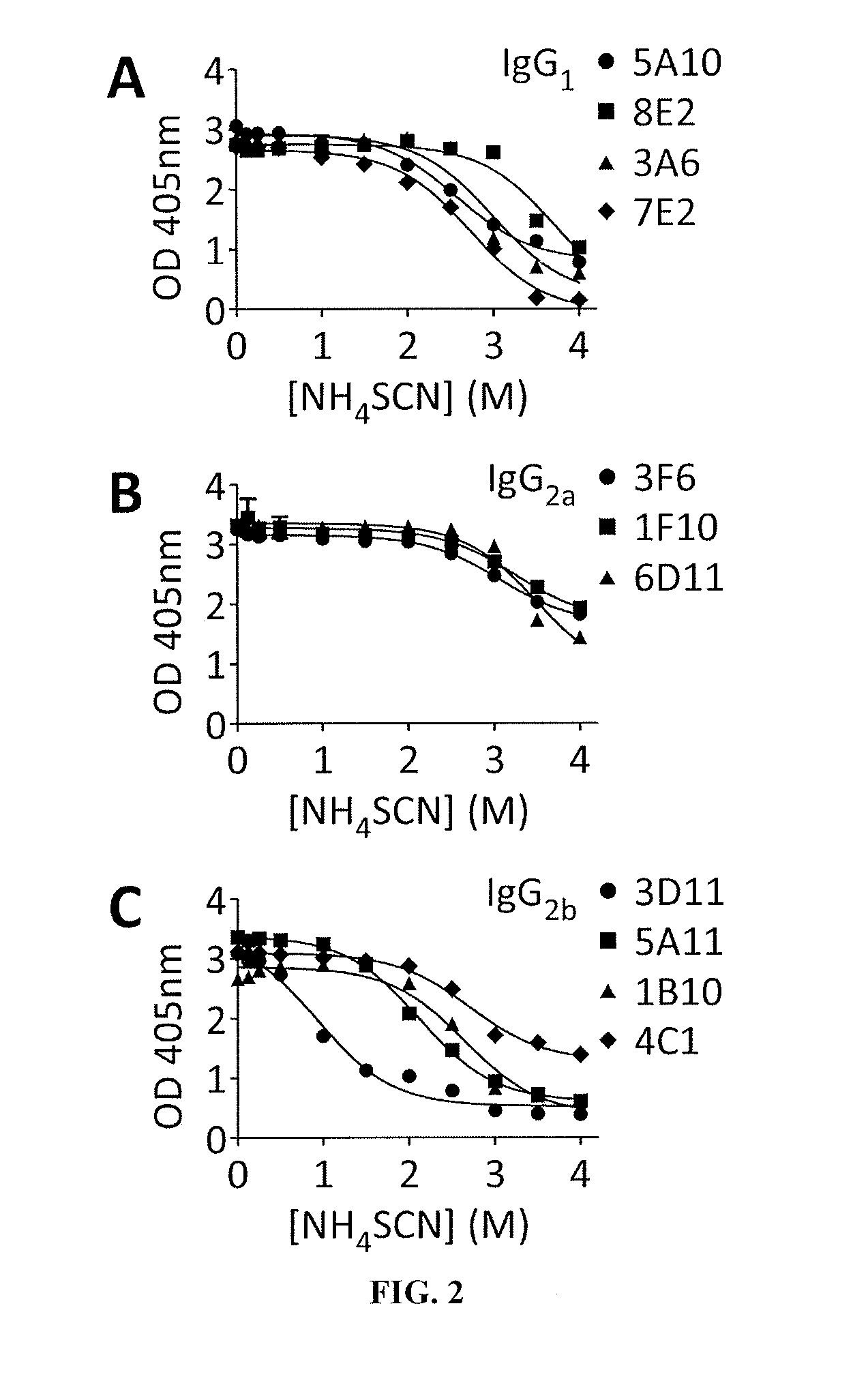
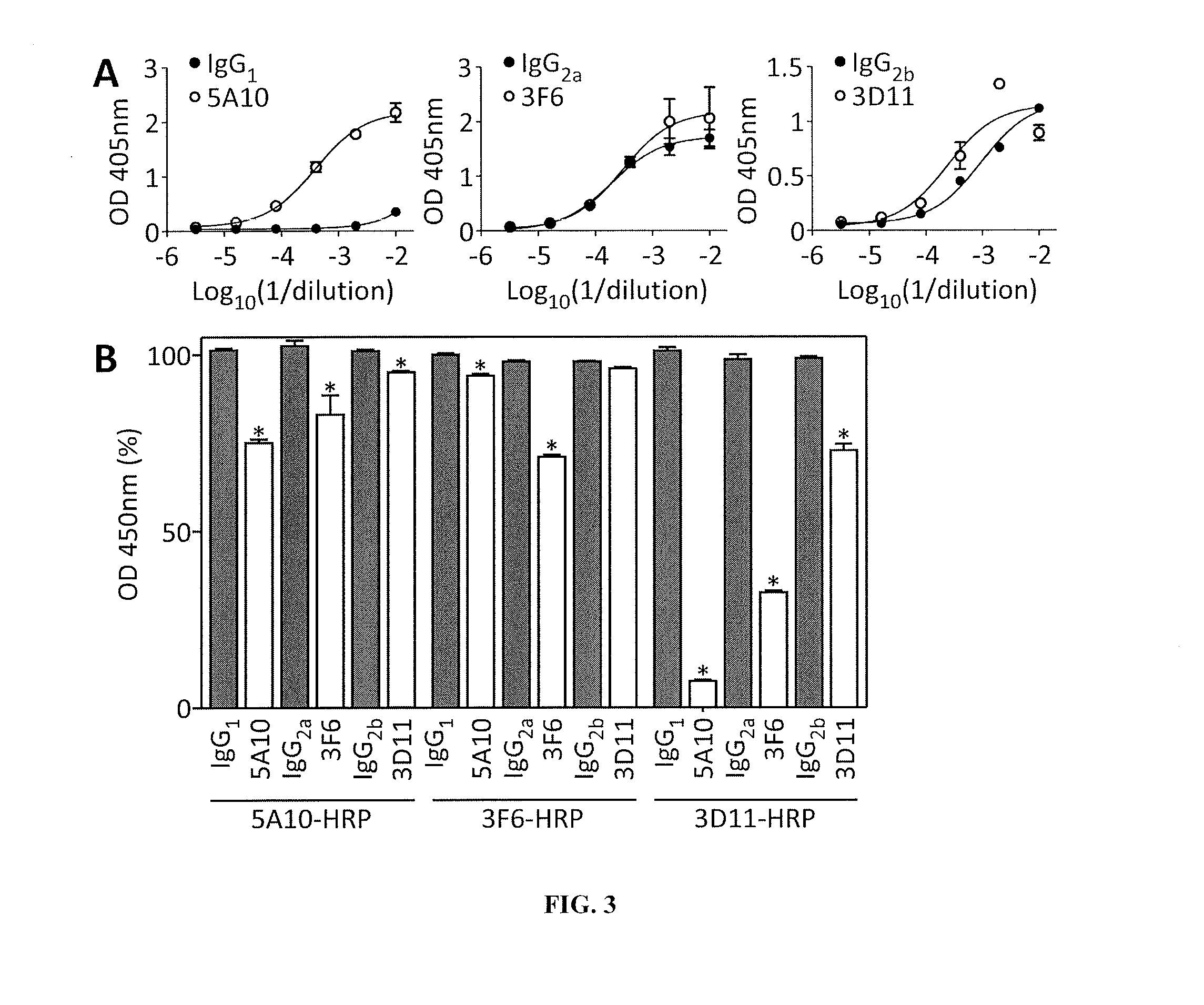
[0258]BALB / c mice were immunized with purified SpAKKAA using a prime-booster regimen and antigen specific IgG responses were quantified by ELISA. Animals were euthanized and their splenocytes fused with myeloma cells. The resulting hybridomas were screened for the production of antigen-specific mAbs. Initially, protein A-specific mAbs were screened using the functional assays as well as the murine infection model (Table 1). After the initial screen, we selected three mAbs (5A10, 3F6, and 3D11) for further characterization as these antibodies displayed the best immune protection in each isotype group (Table 1). BALB / c Mice were immunized with affinity purified mAbs (5 mg·kg−1 body weight) and challenged by injecting 1×107 CFU S. aureus Newman, a methicillin-sensitive clinical isolate (MSSA) (Baba et al., 2007), into the periorbital venous sinus of the right eye...
example 2
Materials and Methods
[0299]Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions.
[0300]S. aureus strains Newman and MW2 were grown in tryptic soy broth (TSB) at 37° C. Escherichia coli strains DH5a and BL21 (DE3) were grown in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth with 100 μg·ml-1 ampicillin at 37° C.
[0301]Monoclonal Antibodies.
[0302]Mouse monoclonal antibodies were generated by the conventional method (Köhler, G., and C. Milstein. 1975). Briefly, BALB / c mice (8 week old, female, Jackson Laboratory) were immunized by intraperitoneal injection with 100 μg purified SpAKKAA emulsified 1:1 with Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA, DIFCO). On days 21 and 42, mice were boosted by intraperitoneal injection with 100 μg of the same antigen emulsified 1:1 with Incomplete Freund's Adjuvant (IFA, DIFCO). On days 31 and 52, mice were bled and serum samples screened by ELISA for specific antibodies. Seventy-nine days following initial immunization, mice that demonstrated strong antigen-immunoreactivity by ELISA were boosted wi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dimensionless property | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dimensionless property | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com