Headgear
a headgear and headband technology, applied in the field of headgear, can solve the problems of eye injury, lack of protection, and high cost of glasses, and achieve the effects of low-tech, low cost and convenient mass production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
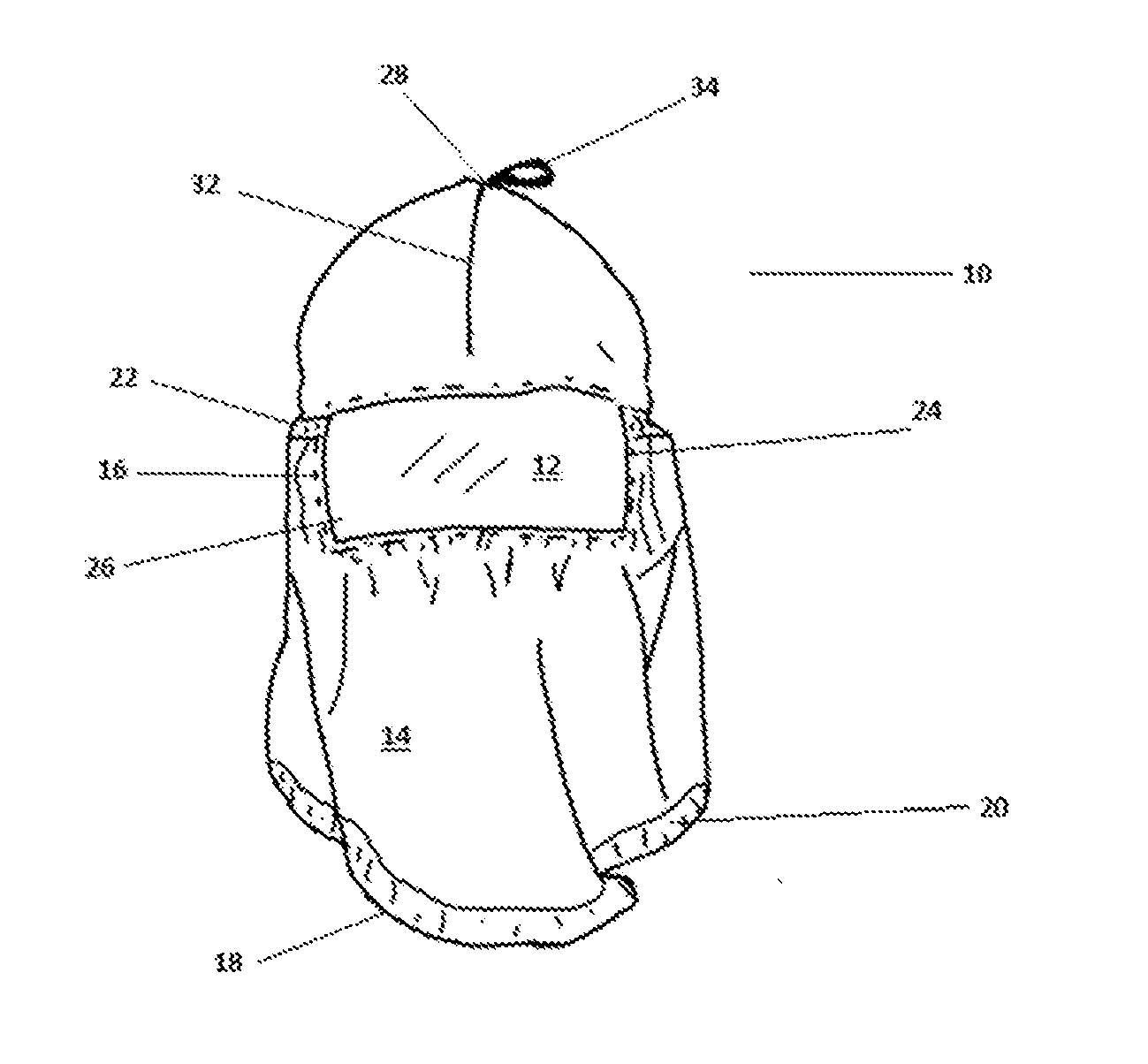
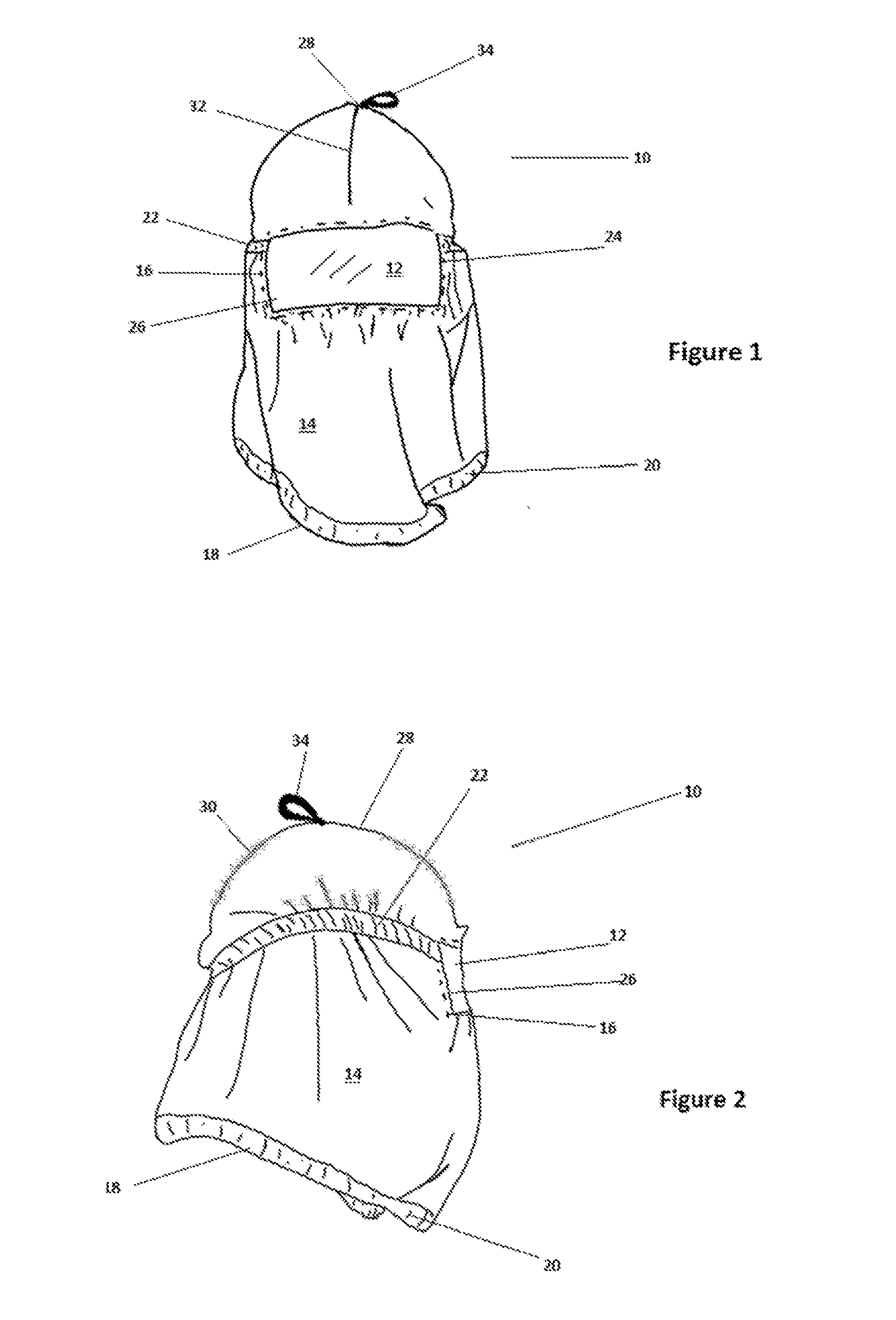
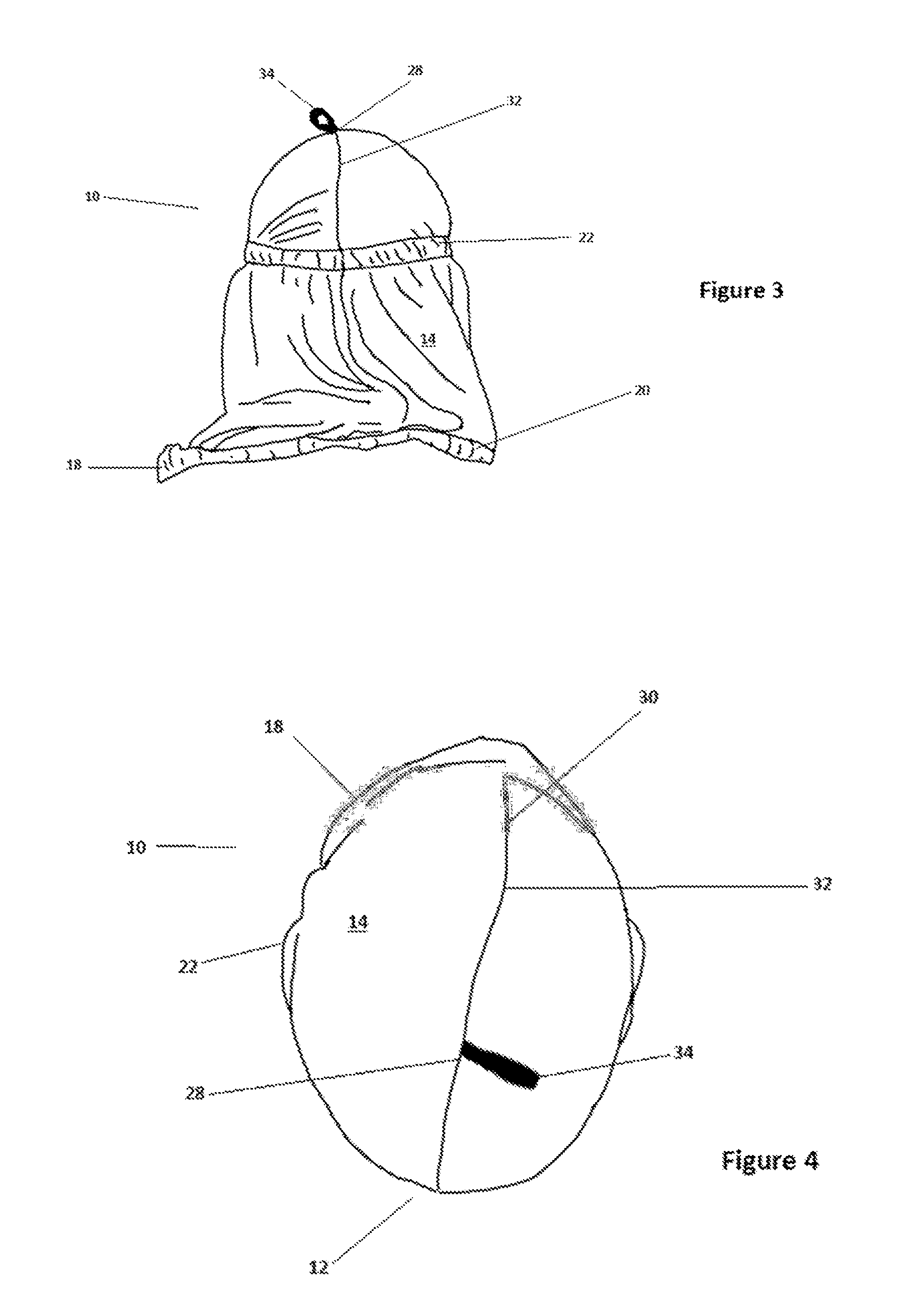
[0053]Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, an item of protective headgear, according to a preferred embodiment of this invention, is generally denoted by the number 10. It has a transparent membrane of clear polyvinyl-chloride (PVC) 12 surrounded by a fabric wall, defined by a second membrane 14. The wall is adapted to the form of a hood and comprises a single panel of cloth. Membrane 12 is sewn into a correspondingly shaped and sized aperture in the wall as shown by seam 16 (denoted by a broken line), which surrounds it Seam 32 extends over the apex 28 of the headgear and down the rear side at 30, to provide closure for wall 14 to form a hood. In other embodiments, the hood structure may be fabricated from two or more panels of flexible material.
[0054]An eye 34 of a looped strip of textile tape material is attached at the apical region to facilitate hanging of the hood on a suitable peg or nail when not in use In further embodiments, the attachment means for attaching transparent membrane 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com